What causes the appearance of green stool in a newborn?
With the arrival of a child in the family, parents have many concerns and reasons for concern: even the color of the baby’s stool does not always meet expectations and raises many questions. for a child to have green stool or is there still cause for concern? Let's figure it out together.
Why then can the stool be green?
A common cause is certain foods that are fed to the baby, such as leafy greens. Sometimes it can also be associated with diarrhea or bacterial infections.
The reasons for green stool in children can be different - it depends on various factors, including the age of the child.
Nutrition
The main reason why a baby's stool turns green is nutrition. Products containing chlorophyll are found in all green plants and can turn your stool green. Artificial food coloring gives the same effect.
Foods that cause your baby's stool to turn green:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, lettuce, etc.)
- Candies, cakes and other sweets with artificial green coloring
- Nutritional supplements containing iron.
Diarrhea in infants
The appearance of diarrhea in a child under 1 year of age is often associated with lactose deficiency. Its deficiency can cause dysbiosis. Lactose provides about 40% of a baby's energy needs. It promotes the absorption of iron and calcium, so its deficiency has an overall detrimental effect on the development of the child. At the first manifestation of diarrhea in infants, this is the cause of the problem that should be considered. Only a doctor can help cope with it. In addition, a baby may develop diarrhea even with inflammation of organs not related to the gastrointestinal tract, for example, with ear disease.
A common cause of changes in stool color. With diarrhea, the water and electrolyte content in the intestines changes, and because stool moves through the digestive system faster than usual, this often causes it to turn green.
Some common causes of diarrhea in children:
- Norovirus
- Rotavirus
- Bacterial infections such as salmonella
- Some medications, such as antibiotics
- Caffeine
- Food poisoning.
Chronic diarrhea in a child may signal inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome, food allergies, hyperthyroidism and other disorders.
Green stool itself is normal in infants, but if it is accompanied by diarrhea, this is very dangerous for the child. Worldwide, diarrhea is the second leading cause of death in children under 5 years of age, as it can lead to a dangerous condition called dehydration.
Newborn stool: norm, how many times a day, color
What to do if your child's stool is green
As mentioned above, if there are no additional symptoms, you can either take a wait-and-see approach or try to cancel some innovations in the diet. If alarming symptoms are present, you should consult a pediatrician, who, in turn, can refer you to a gastroenterologist, allergist and immunologist.
In order to understand the cause of the child’s condition, it will be necessary to undergo tests:
- blood;
- urine;
- feces;
- anal swab.
In a conversation with doctors, it is necessary to talk in detail about the child’s reactions to food, his diseases (if any), and what new things the baby has tried recently.
In some cases, children undergo an ultrasound of the gastrointestinal tract; they are prohibited from undergoing other procedures such as colonoscopy and endoscopy.
Based on the test results, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment.
Green stool in babies
Green stool is normal in infants and children under 1 year of age.
According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP):
- Breastfed babies usually have mustard yellow stools. It can also come in various shades of green. The color of the stool may change with changes in the mother's diet.
- Babies who are fed formula have brown or yellow stools with a green tint. Sometimes the stool appears greener than usual.
Green stool is normal, especially for young children. Therefore, if the child feels well (eats, sleeps, gains weight, etc.) there is no reason to worry!
Green stool in older children
When children begin to eat complementary foods, food becomes a more common culprit for green stools. Parents should not worry about the green color of his stool if the child is healthy and there are no other reasons for concern.
You need to see a doctor if:
- The baby's stool is discolored, almost white - this may mean that there are problems with the liver, gall bladder or pancreas.
- The stool is very dark. This is normal for newborns who are just a few days old. But in older children, very dark stools can be a sign of gastrointestinal bleeding.
The child has diarrhea and has any of the following symptoms:
- Signs of dehydration
- Vomiting for longer than one day
- Temperature above 38 °C
- The child refuses to eat.
If you notice blood in your child's stool, he needs emergency medical attention!
Reasons for changes in the color of feces
The color of infant bowel movements is influenced by various reasons:
- Type of feeding;
- The diet of the parent (if the baby is breastfed);
- Composition of the mixture;
- Underdevelopment of the gastrointestinal tract of infants.
The body of an infant is not yet fully ready for the digestive process - there are not enough enzymes and beneficial bacteria.
All newborns have a dark green first stool. It is called meconium. This almost black, sticky substance is secreted by the baby the first two to three days after birth. Then the feces become lighter in color. They usually have a light brown, yellowish tint. However, it is also normal for a tiny baby to poop green. Especially if mom’s menu contains a significant amount of cucumbers, parsley, spinach, green pears or apples.
Situations when stool turns light yellow or even white are also dangerous. The table below shows photos of normal feces in a child, as well as feces that signal danger, as in the case of white feces.
A very common complaint with which patients turn to therapists, gynecologists and surgeons is abdominal pain below the navel. There are many reasons why such an uncomfortable condition may arise, so a full range of diagnostic measures is required to identify and treat the disease. Read more in the article: “stomach hurts below the navel.”
Causes of green diarrhea
There are many root causes of green diarrhea Infants green stools when they consume only “foremilk” or when feces become oxidized when exposed to air. At the same time, the number of bowel movements does not differ from the norm. In children older than one year, this may be due to nutritional factors or serious illnesses. The causes of the disease may be the following pathologies :
- Dysbacteriosis;
- Allergic reaction;
- Cow's milk protein intolerance - lactose intolerance;
- Food poisoning;
- Infectious or bacterial diseases;
- Intestinal infections: dysentery, rotavirus, salmonellosis, amoebiasis, giardiasis;
- Diseases of the digestive tract;
- Pyelonephritis in young children;
- Nervous system diseases
- Diseases of the endocrine system: Addison's disease, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, thyrotoxicosis;
- Worm infestations;
- Celiac disease;
- Cystic fibrosis;
- Liver diseases;
- Disaccharidase deficiency;
- Eating large amounts of greens, green fruits, green food dyes;
- Taking certain medications.
We can conclude that only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis, and therefore carry out treatment. In case of illness, first aid must be provided, but not self-medication .
Symptoms of diarrhea
The following clinical symptoms exist, depending on the type of diarrhea:
- Enteral diarrhea is caused by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the small intestine. It is characterized by copious discharge up to 4-6 times a day, which may contain pieces of undigested food. Accompanied by pain in the abdomen and around the navel.
- Colitic - appears when there is inflammation of the lower intestines. Manifested by frequent bowel movements up to 10-15 times a day, painful urges. The discharge is small and may contain blood and mucus.
- Gastric diarrhea occurs when the secretion of gastric enzymes is reduced, causing indigestion and rapid emptying of the stomach. The stool increases in frequency up to 4-6 times a day, has a liquid consistency, is dark in color and may contain remnants of undigested food. Sometimes it has a putrid smell. The patient is bothered by a feeling of fullness and dull arching pain in the pancreas.
- Pancreatic - occurs when the secretion of the pancreas decreases. Manifested by a moderate increase in heavy discharge. The stool has a pasty or liquid consistency and contains mucus. Characterized by an unpleasant putrid odor, pain in the upper abdomen, and flatulence.
- Diarrhea in children can present with many symptoms . The main symptom of the disease is repeated green diarrhea, which occurs more than 3 times per day in children over one year old, and more than 10 times in children under one year old. Other manifestations include: nausea, vomiting, belching, flatulence, abdominal pain, blood, mucus and food particles in the stool.
Green feces due to dysbiosis in children
Dysbacteriosis or dysbiosis is one of the most common diagnoses in children 2 months of age. In addition to changes in the color of feces, dysbiosis is accompanied by constipation/diarrhea, increased regurgitation, anxiety and sleep disturbances. One of the reasons for the development of dysbiosis in a child is treatment with antibiotics.
Dysbiosis is easy to distinguish from food poisoning. With food poisoning, the baby may suffer from vomiting and diarrhea, but the stool is rarely green and never foams.
Attention! Children under one year old with dysbacteriosis suffer from severe colic and often regurgitate. Because of this, they do not receive enough nutrition and can quickly lose weight.
Green stool due to salmonellosis in children
Salmonellosis is a dangerous infectious disease caused by salmonella, which enter the body most often from chicken eggs. With this pathology, the patient complains not only of bright, marsh-colored feces, but also of severe vomiting and diarrhea. The feces have a strong sour aroma, the process of defecation is painful, and severe abdominal pain is recorded. Body temperature often increases.
To confirm the diagnosis, a biochemical blood test should be performed, feces and vomit should be examined to determine the pathogen. Only after this can treatment begin.
Attention! Salmonellosis or suspicion of it is a reason to immediately seek medical help. With this pathology, the disease quickly leads to dehydration and poisoning of all body systems, which can cause the death of a small patient.
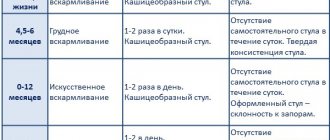
Stool consistency and frequency
Norm
In infants, stools are more frequent and softer. With the introduction of complementary foods, the frequency and consistency of stools change significantly, becoming denser.
Peculiarities
- The consistency and frequency of a baby's stool depends very much on the type of feeding.
- A breastfed baby's stool is mushy, homogeneous, and the frequency is equal to feedings. The frequency of stools also decreases in breastfed children with the introduction of complementary foods.
- A bottle-fed baby's stool is much denser (pasty), but not yet formed like an adult's. The density of stool is closely related to its frequency. Those who have artificial stools have less frequent stools - perhaps up to once a day, sometimes up to once every two days; they are more often bothered by constipation. The problem of increased stool density requires more attention from the pediatrician, and sometimes nutritional correction.
- The stool becomes less frequent and denser with the appearance and increase in the volume of complementary foods and becomes formed in a child who eats from the common table - your baby has grown up!
Important!
- Dense, rare (less than 2 times a week), large-diameter stools are diagnostic signs of constipation. Constipation is not always accompanied by pain, and therefore a small part of parents turn to the pediatrician immediately.
- The specialist’s recommendations may relate to the nutrition of the child and/or mother, but it is possible to prescribe laxatives in this case - there are children’s medications, you should not be afraid of them.
- Try to do without frequent interventions in the “life of the rectum” - therapeutic enemas and suppositories. There is a ready-made complex rectal preparation (a special form for children), it is used in addition to laxatives if their effect is insufficient.
Alarming symptoms, you should immediately contact your pediatrician!
- Viral and bacterial infections. Loose and frequent (10 or more times per day) stools. The most common cause of this condition is viral and bacterial intestinal. The danger of loose stool is the very rapid dehydration of a small child. In this case, independent or late treatment is unacceptable!
- Lactase deficiency (lack of enzyme in the child’s intestines that digests milk sugar, lactose). In this case, loose stools are a) associated with feeding, b) have a foamy appearance and c) are accompanied by pronounced anxiety of the child. In most cases, the baby will “outgrow” this problem in the first six months of life, and the pediatrician will help cope with temporary difficulties by prescribing lactase medications.
- Poisoning, taking medications (usually antibiotics), and other digestive diseases can also cause loose stools, so you shouldn’t figure out the reasons on your own. Time is precious in this case.
Preventive measures
The introduction of complementary foods must be correct and timely
- A nursing mother must follow a diet.
- It is important to regularly see a pediatrician; if any alarming signs occur, immediately report it to the doctor.
- Artificial formulas should be carefully selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the child.
- Timely and correct introduction of complementary foods.
- Correct diet for toddlers, no overeating.
- Gradual introduction of foods that may cause allergic reactions.
As you can see, there are many reasons why a baby’s stool may change color to green. It's better to play it safe and consult a pediatrician. Do not forget that some factors influencing changes in stool may be dangerous for the child’s body and require early diagnosis.
What does the shade and consistency of green stool tell us?
Based on the degree of color saturation and density of green feces, one can judge the reasons for the changes:
- deep green: normal; depends on the food range; dark green, loose stools in infants may be a consequence of lactase deficiency;
- light green, yellow-green: normal indicator; impaired lactation or lack of breast milk with hind fat milk;
- black-green: typical only for newborns, in other cases it is a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract, a nutritional error;
- deep green: lack of hindmilk, food pigmentation;
- green foam: lactase deficiency, low fat content of milk during breastfeeding;
- mushy: normal indicator;
- green stool with mucus, watery, liquid, too hard stool: deviation of the gastrointestinal tract, development of the disease.
The reason for panic among parents should be the general deterioration of the baby’s condition.