What is ringworm?
Ringworm is an infectious skin disease caused by the parasitic fungi Microsporum canis and Trichophyton tonsurans, it is part of the group of ringworms that primarily affect the skin, hair and nails. This is an infectious dermatological pathology caused by dermatophyte fungi. It is also called dermatomycosis, scab, micro- and dermatophytosis.
Doctors distinguish several types of ringworm, depending on the location, nature of the course and the causative agent.
The main types of the disease are:
- chronic or ringworm of smooth skin;
- surface;
- ringworm of the nail plate;
- infiltrative-suppurative.
Since ringworm is caused by two types of fungi, in medicine it is diagnosed as microsporia and trichophytosis. These fungi have persistent pathogenicity, pronounced virulence and often cause acute diseases with varied clinical manifestations.
A disease caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum canis is microsporia. Depending on the location, there is microsporia of smooth skin and microsporia of the scalp.
Trichophytosis is caused by the activity of the dermatophyte Trichophyton tonsurans, which, through the anthroponotic route of infection, causes inflammation of the scalp and smooth skin, and through the zootroponotic route, inflammation in the deep layers of the dermis, accompanied by suppuration.
The presence of fungal spores does not always provoke damage to the skin and its appendages. The transition of the fungus from an inactive state to a pathogenic state is facilitated by metabolic and endocrine disorders, immune diseases, hypovitaminosis or vegetative-vascular dystonia. This increase in the pathogenicity of dermatophytes provokes an exacerbation of inflammatory processes, the spread of the fungus through the blood and lymph flow.
The disease is weakly expressed during the development of a latent infection and when localized in previously affected areas, and the high virulence of the fungus is formed during a relapse, gradually decreasing during the course of the infection.
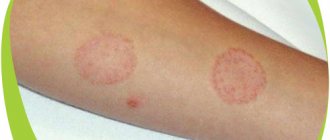
Symptoms of ringworm: At the end of the incubation period, itchy ring-shaped spots of red-pink color appear on the skin, on the surface of which bubbles appear, after which a crust and peeling remain. The hair at the site of the lesion breaks and falls out.
Normally, the immune system is able to cope with the pathogen and prevent its activity, but there are a number of factors that increase the risk of ringworm, namely:
- skin microtraumas;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- prolonged contact with the source of infection;
- high humidity and air temperature;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases, etc.
In a situation where there is an adult or child with lichen at home, it is necessary to take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of its spread, namely:
- use separate towels and bed linen;
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap, especially if you touched the patient’s things;
- use gloves when touching areas of disease;
- undergo examination and take tests to identify pathogens, etc.
The main method for diagnosing ringworm is the use of a Wood's lamp, under the light of which the affected areas acquire a characteristic greenish glow. Microscopic examination and culture of skin and hair scales are effective to confirm the diagnosis.
Timely diagnosis and a properly selected treatment regimen can effectively eliminate ringworm in children and adults, preventing its spread. The pathology is prone to relapse, since the presence of spores of viable fungi can cause repeated damage. It is extremely important to complete the course of treatment and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
Causes
Ringworm in infants is an infectious disease. It is caused by Microsporium or Trichophytia fungi. Pathological pathogens are transmitted in the following ways:
- From animals to humans. Ringworm affects cats and dogs, most often stray ones. A child can become infected if they come into contact with animal hair.
- From a sick person to a healthy one. The source of infection is the hair and desquamated scales of the patient's epidermis.
- Through everyday things. You can become infected through household items on which particles of the skin and hair of an infected person accumulate, as well as the fur of sick animals. Fungi can live in the external environment for quite a long time.
Pityriasis rosea in infants is a fairly rare disease. It is more common in children aged 2 to 12 years. However, there are cases of Zhiber's disease in infants. This pathology is an infectious-allergic process. Its exact reasons are unknown. There is an assumption that the causative agent of this form of lichen is one of the strains of the herpes virus.
However, a viral infection is only a trigger for Gibert's disease. All manifestations of this pathology are an allergic reaction to waste products of microorganisms. Children with weakened immune systems most often get sick. The following factors can provoke Zhiber's disease in a child under 1 year of age:
- hypothermia;
- previous colds and childhood infections;
- transition from breastfeeding to artificial formula;
- administration of vaccines;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- start of complementary feeding;
- insect bites.
Pityriasis rosea is not a contagious disease and it is impossible to become infected with it from a sick person.
Pityriasis versicolor (varicolored) is an infectious pathology of a fungal nature. The causative agent of the disease is an opportunistic microorganism of the genus Pityrosporum. It is found on the skin of many people, but causes pathological manifestations only when immunity declines. The following factors contribute to the proliferation of fungus:
- the child’s stay in a humid and hot climate;
- use of linen and diapers made of synthetic fabrics;
- uncontrolled treatment of the baby with antibiotics and vitamins;
- hereditary predisposition.
This form of lichen is rarely transmitted from person to person. However, the possibility of infection cannot be completely excluded. Infection usually occurs through very long and close contact with a sick person.
How is ringworm transmitted?
Ringworm is transmitted in two ways:
- from a sick animal – zoonotic with an incubation period of one week;
- from an infected person – anthroponotic with an incubation period of up to 6 weeks.
Children are at risk because they most often come into contact with the carriers of the pathogens of this disease - cats and dogs. Children's skin is characterized by low density of the stratum corneum and weak protective properties of the water-lipid mantle. The stratum corneum prevents the penetration of the fungus into the layers of the skin, since its spores are located between the horny scales, and the water-lipid mantle forms a barrier to the penetration of pathogens.
The infection is also transmitted by non-compliance with personal hygiene standards and the use of other people's personal belongings containing fungal spores (hats, combs, bed linen, etc.).
Causes of deprivation in a child
Mostly, lichen infection among children occurs in groups - preschool institutions, school, extracurricular activities.
A very common method of infection is contact with an infected pet; therefore, it is very important to teach children not to touch stray kittens and puppies without visible skin abnormalities; the animal may be recently infected or carry pathogenic fungi.
In addition to contact, there are several factors that together can cause the development of lichen:
- Reduced immunity;
- Hot season - high temperatures are a favorable environment for the pathogenic activity of fungi and infections;
- Diseases of the endocrine system;
- Avitaminosis;
- Incorrect selection of children's skin care cosmetics and detergents;
- Frequent skin injuries - children lead an active lifestyle, so it is sometimes difficult to prevent frequent injuries, as a result of which the protective functions of the skin are weakened.
- Using other people's personal items - combs, hairpins, hats, etc.;
- Wearing clothes made of synthetic fabrics;
- Frequent allergic reactions.
Cases of infection through soil are very rare; if a child has a weak immune system and the soil is oversaturated with fungal spores, there is a possibility of infection.
Find out more
How does ringworm begin?
Favorable conditions contribute to the introduction and reproduction of a pathogenic fungus in the skin, triggering the infectious process. In the initial stages, this period is asymptomatic. After which the development of the pathology acquires clinical manifestations, the signs of which depend on the stage of the pathology.
The stages of the infectious process during the development of ringworm are:
- incubation period;
- period of mushroom growth;
- refractory stage (period of insensitivity, rest);
- regression.
In the skin, the fungus forms branched mycelium, which gradually invades new areas of the skin, while old lesions become the location of its spores. This period of fungal growth is determined by the rapid increase in the colony of the pathogen, active division of skin cells and the high rate of exfoliation of the affected epidermis.
Since most often the growth of the colony outstrips the rate of change of the stratum corneum, the infectious process spreads. An intense immune reaction (inflammation) in the lesion is displayed in the form of a red ring, which, in the chronic course of mycosis, becomes the permanent residence of the pathogen.
Gibert's disease
Rash with pityriasis rosea is most often localized in the shoulders, abdomen, groin, as well as on the arms and legs. The following characteristic signs of Zhiber's disease can be noted:
- First, a swollen spot (maternal plaque) appears on the skin. It is pink in color and most often forms on the stomach or between the shoulder blades. Subsequently, new smaller rashes appear around the maternal plaque.
- Then yellowish or brown scales appear in the center of the spot. In the middle of the rash, severe peeling of the skin is noted.
- The flaky area in the center of the spot eventually sinks and forms a dent surrounded by a red ridge. Doctors call this type of rash ring-shaped.
- Over time, the scales fall off and the skin color evens out.
Skin itching is observed in 50% of children. Pityriasis rosea does not cause a deterioration in the baby’s well-being. However, this pathology can worsen after exposure to ultraviolet radiation. There have often been cases where the child underwent treatment and the rash completely disappeared. But after being exposed to the sun's rays, a recurrence of pityriasis rosea occurred in the infant. In the photo below you can see ring-shaped rashes on the skin due to Gibert's disease.
What does ringworm look like?
Clinical manifestations of ringworm depend on the type of pathogen, course and stage of the disease. Dermatophytes secrete enzymes and toxins that destroy keratin protein (they feed on it), so the severity of symptoms directly depends on the ability of fungi to produce these substances.
Common symptoms of ringworm on the scalp are:
- hair thinning;
- the appearance of localized peeling of the skin;
- redness of the epidermis;
- hair breaking off at the root;
- the appearance of small bubbles with cloudy contents along the edges of bald patches, after opening which yellow crusts form.
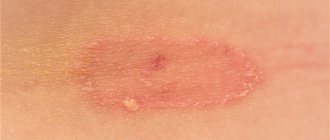
Ringworm of smooth skin includes the following symptoms:
- pronounced itching;
- the appearance of round red spots;
- light epidermis at the site of damage, surrounded by gray scales;
- the edges of the damaged area consist of pink-red bubbles;
- growth of the lesion in diameter.
The chronic form of the disease is accompanied by the presence of microscopic blisters on the affected areas, the formation of scars after their opening and severe itching. In a situation where the site of the lesion is the nail plate, its separation, discoloration and thickening are observed.
Ringworm of the infiltrative-suppurative form is characterized by the appearance of large bright red spots up to 10 cm in diameter, the outer surface of which is lumpy and uneven, and purulent follicles form along the edges. Pain, swelling and hyperemia of the affected areas are also observed.
The appearance of the first signs of the disease requires a mandatory visit to a dermatologist. The lack of qualified treatment can lead to the rapid spread of infection throughout the body and cause a number of complications: tissue scarring, death of hair follicles, allergic reactions and the addition of a secondary infection.
Pityriasis rosea
This lichen received its second name in honor of Gibert, the Frenchman who discovered it. It poses a threat to children aged five to twelve years. It is considered quite dangerous because it is very easily and quickly transmitted between children.
First, a small pink spot appears and begins to peel off. After this, a rash begins to appear around him, which spreads in all directions. This is accompanied by quite severe itching, due to which children often scratch the affected areas until they bleed, which is very dangerous.
How is ringworm treated?
In each case, treatment for ringworm should be selected individually, since its composition and duration have their own specifics and are determined by the type, location and stage of the pathology.
Only prescriptions from a dermatologist are effective; they take into account the current clinical picture, the characteristics of the patient’s physical health and his age.
Therapy is aimed not only at relieving the symptoms of the pathology, but also at inactivating the pathogen. The chronic form of the disease also provides support for the immune system, normalization of metabolism and hormonal levels.
The following groups of drugs are used to treat ringworm:
- systemic and local antimycotics;
- antiseptic solutions;
- multivitamin complexes.
Pityriasis versicolor
In pityriasis versicolor, the maternal plaque looks like a yellowish-pink spot. The rash forms around the hair follicle on the body. There is no swelling of the skin in the affected area. The spots most often appear on the chest and back. In rare cases, the rash is localized to the lower extremities, scalp and buttocks. Small rashes often merge into one large spot.
Pityriasis versicolor in infants is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- The color of pink spots changes as the pathology develops. They first become red and then dark brown. Then the color of the rash becomes brown. Therefore, pityriasis versicolor is often called versicolor.
- The fungus destroys the stratum corneum of the skin. That's why the spots peel off. When scraped, scales resembling bran or shavings are easily separated from the rash.
- There is slight itching in the area of the rash.
After recovery, the rash disappears. However, the places where the spots were previously located remain depigmented for a long time. These areas do not tan when exposed to ultraviolet light. This symptom is due to the fact that the fungus disrupts the functioning of melanocytes - skin cells responsible for pigmentation of the epidermis.
This disease may resemble vitiligo or psoriasis in its manifestations. Therefore, it is very important to carry out a differential diagnosis of pityriasis versicolor in infants. In the photo you can see skin pigmentation disorders after suffering a pathology.
How long does it take to treat ringworm?
The treatment process for ringworm is lengthy, usually taking at least six weeks, with systemic therapy lasting mainly 15-25 days.
The effectiveness of therapy is assessed using laboratory tests. In a situation where tests indicate a significant decrease in the number of fungal spores after 2 weeks of a medication course, it is necessary to continue the chosen treatment. In some cases, fungal shedding can last for several months.
After the signs of pathology disappear, you need to scrape the epidermis three times in previously damaged areas:
- immediately after completion of therapy;
- 7 days after therapy;
- after 2-3 months.
The result of therapy is considered successful if all three tests show negative results.
How to treat lichen versicolor?
When treating this disease in infants, doctors use local antifungal ointments:
- "Ketoconazole";
- "Bifonazole".
Pustules and inflammation may appear on the child's skin. This usually occurs when bacteria attaches to a fungal infection. In such cases, it is necessary to use not only antifungal agents, but also ointments with zinc or salicylic acid.
The course of treatment takes about a week. After the rash disappears, the drugs are applied to the skin for another 3 days.
This disease does not pose a great danger to the body. The rash disappears without a trace after a course of treatment for lichen in an infant. In the photo below you can see the treatment of the baby's skin with antifungal agents.
How to treat ringworm in children?
Treatment of ringworm in a child is the responsibility of a pediatric dermatologist, since the characteristics of the child’s body require special doses and composition of medications.
Hygiene and child care are also important elements of pathology therapy:
- boiling and ironing clothes in contact with affected areas of the skin;
- treating household surfaces with disinfectants to prevent the spread of spores;
- frequent change of bed linen;
- washing in the shower rather than the bath, etc.
Prevention of deprivation in a child
To prevent the development of the disease in a child, the following tips should be followed:
- Teach children not to come into contact with stray animals.
- Teach the rules of personal hygiene - washing hands, not using other people’s personal belongings.
- Do not use detergents with aggressive ingredients in the composition for bathing children, do not abuse antibacterial agents, select cosmetics (oils, creams, powders) taking into account the characteristics of the child’s skin.
- Strengthen immunity.
- If you have an allergy, eliminate the cause of its occurrence, use clothes made from natural fabrics.
- The child's diet should be balanced.
If a child is infected with lichen, you should pay special attention to underwear and bed linen, wash in hot water, and iron after drying. After complete recovery, you need to be tested again to prevent a relapse.
Can I go to work or school with ringworm?
The presence of this diagnosis requires isolation of the patient from the team for at least two weeks. In schools and other children's institutions, it is mandatory to notify parents for timely detection of the disease in other children.
The disappearance of ringworm symptoms and 3 negative tests for the presence of fungus are a reason to return to school or work.
If a dermatomycosis infection has been detected in a team, then to prevent pathology, you can use antifungal shampoos for some time, carry out wet cleaning with the addition of antiseptic solutions, and strictly observe personal hygiene.
- Treatment of lichen in Kharkov;
- treatment of lichen in Uzhgorod;
- treatment of deprivation in Sumy;
- treatment of lichen in Poltava;
- treatment of lichen in Odessa;
- treatment of deprivation in Nikolaev;
- treatment of lichen in Mariupol;
- treatment of deprivation in the Dnieper.
1
0
0
Article rating:
3.8 out of 5 based on 5 ratings
Author: Mangusheva Victoria Yurievna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist. Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category. Work experience more than 10 years.
Diagnostics
If a baby has a spot on the skin, then it is necessary to show the child to a pediatric dermatologist as soon as possible. At the initial visit, the doctor examines the baby’s skin using a Wood’s lamp. In the light of the device, the affected areas turn greenish.
Rashes with different forms of lichen may be similar to the manifestations of other diseases. In order to differentiate the pathology, scales are scraped from the spot. The resulting material is sent to the laboratory for microscopy. The analysis helps determine the type of pathogen and the form of lichen.
The timely detection of pathological signs and treatment of lichen in infants depends on correct differential diagnosis. In the photo below you can see how a child’s skin is examined by a dermatologist.
An iodine test is used as an additional diagnostic method. The doctor lubricates the scaly spots with an iodine solution. Increased looseness of the skin is noted in the affected areas, and the epidermis absorbs the drug well. Therefore, the spots are painted in a more intense color than healthy areas.
What is lichen
The term lichen in a child is understood as a collective concept meaning a fungal and viral disease. The classification includes several types of pathology, differing in course, causes and external manifestations. Ringworm on the skin of a child occurs more often under the age of 14 years.
When the first unusual rash appears, parents should contact a dermatologist, infectious disease specialist, or pediatrician as soon as possible. This is due to the high degree of contagiousness of the disease. For this reason, sick children pose a great threat to the people with whom they come in contact.
Viral and fungal lichen requires timely initiation of treatment. Advanced forms are difficult to treat, and it takes a lot of time. Depending on the type, ringworm may resolve on its own. Some variants of the disease return again with the same symptoms, while others become chronic.
The incidence rate increases significantly in the summer and autumn seasons. During this period, specific signs appear and treatment of lichen must be comprehensive in order to eliminate the manifestations in a short time.
The most favorable period for the development of the disease, according to Dr. Komarovsky, is a warm time, when optimal conditions are created for the reproduction and spread of infection. Heat, moisture in the environment, and increased sweating help increase the permeability of the skin. This makes it easier for the infection to break through the protective barrier. Symptoms of lichen in newborns and older children appear when the body's defenses against pathogenic microorganisms are insufficient.
Ringworm
The presented form is not common in childhood. Its etiology is varied and in some cases, it is not possible to determine the source. The causes and treatment are closely related. Medicines are prescribed after identifying the factor that provoked the development of the disease. The etiology of lichen planus consists of the following options:
- hereditary predisposition;
- drug intoxication;
- autoimmune factors;
- allergic lichen;
- neurogenic form;
- viral infection.
There are several forms along the way - acute, subacute and chronic.
Symptoms
The onset of the disease occurs differently in each child. Lichen planus appears after 7-10 days against a background of general malaise, weakness and loss of appetite in the form of a rash. For other patients, this form of development of the disease is not typical and they develop specific elements without affecting their well-being.
The most favorite places for rashes of red lichen are identified:
- underbelly;
- on the fingers;
- in the lumbar region;
- on the butt;
- elbow bends;
- on the feet;
- axillary fossae.
Ringworm most often does not appear on the head, which becomes one of the main distinguishing features. The rash consists of papules that do not have a cavity inside. They have an umbilical depression in the center of their elements and a polygonal shape.
Varieties
The types of diseases are striking in their diversity. Undoubtedly, for parents, especially young and inexperienced ones, the question is relevant: what does lichen look like in children? And of course - what are the symptoms and how to treat lichen?
It should be noted that most cases of the disease occur in children. And this is understandable. The reason is the restlessness and curiosity of the little ones, as well as the significant location of their communication. Everything is interesting to them. I want to try everything, cuddle and caress.
And as soon as we talk about a new cat or dog that has appeared in the yard, then expect a skin “epidemic”. They will immediately catch this infection and will certainly “reward” each other with it.
It is not for nothing that it is included in the TOP 10 anti-rating among all dermal diseases.
Types of lichen with names, contagiousness and ways of communication:
| Variety | Transmission path | Degree of aggression |
| Pink | Personal contact | Minimal. Some dermatologists are inclined to believe that it is not contagious at all. |
| Flat red | Not fully studied | Minor. There is a risk of transformation into squamous cell malignancy. |
| Colored (pityriasis) | Personal contact | Low and low risk. |
| girdling | Personal contact | High. Especially during the rash stage. |
| Shearer | Personal contact | Extremely high. |
Types of lichen in children in the photo:
Flat red
girdling
Pityriasis
Shearer
Shearer
If the doctor writes microsporia in the diagnosis of a skin disease, then you can rest assured that your child “won” the jackpot and became the owner of ringworm. We understand that this is not entirely appropriate sarcasm. Although it is not a fact that it was the Microsporum fungus that provoked the pathology.
The fungus Trichophyton tonsuran has no less vile properties. Such dirty tricks can be expected from him. Remember, at the beginning of the article we talked about causal diversity.
There can be several ways of infection:
- Tactile contact (through the senses of touch) is the simplest and most common channel, because with the help of it your child learns about the world.
- Using other people's personal items: comb, towel, bedding in kindergarten, soft toys, etc.
- On the street, in the yard, on a walk in the park, through contact with grass, leaves, hay, where the fur of sick animals can become embedded. In the same way, pathogenic fungi can end up in a sandbox or soil.
Ringworm in children in the photo:
Anthropophilic trichophyton may not begin to manifest its sinister essence immediately, but only two or more weeks after contact with an infected object. This makes it much more difficult to identify the location and subject (source) of danger. Although no more than 7 days can pass from the moment of infection directly from the animal.
It is extremely important to see and recognize symptoms at an early stage and prevent the transformation from acute to chronic form:
- A distinctive visual sign of a problem is an inconspicuous round spot. This is how a maternal plaque is formed. How and where on the body it will choose a convenient place for further development is difficult to say. This can be anywhere on the child's head, neck or face. Carefully examine the entire baby - the number of spots will increase very quickly. When mature, the plaque gives some swelling on the body.
- Further, peeling and disturbing, obsessive itching will appear around the affected area.
- A clear sign of trichophytosis are characteristic spots on the hair. This is how the fungus “decorates” the scalp.
- Parents should not ignore enlarged lymph nodes and fever - these are also symptoms of an early stage.
There can be not only a different immune response of the body to the causative agent of the disease. The forms of flow are also radically different from each other.
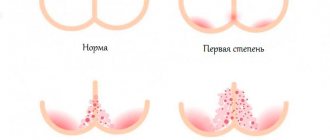
| View | Description | Affected areas |
| Surface | The disease is mild. There is subtle damage to the dermis. With a progressive development trend, the spots increase in size. | Neck, face, areas of the head covered with hair. Another location of the body is rarely affected. |
| Chronic. | Dark spots appear on the head. Their diameter does not exceed 10 mm. The surrounding scars peel off. The hair color takes on an unnatural color: from bluish to pinkish. The affected area expands its boundaries, the contours become blurred. Itching and an unaesthetic appearance of the skin appear. | Lichen in a child is localized on the temporal and occipital parts, elbows, head, and less often in other places. |
| Infiltrative-suppurative (deep) | Only infected animals are capable of causing this problem. Signs:
| Almost always this is the scalp. |
It is important to know that the disease develops successfully in the presence of the following favorable conditions:
- A painful condition characterized by a chronic lack of vitamins is hypovitaminosis.
- Diseases in the active phase.
- Chronic infection.
- Reduced immune resistance.
- Skin injury.
Causes and treatment of microsporia in a video from Dr. Malysheva:
Pink
This phenomenon has another name – Zhiber’s disease and refers to an infectious-allergic pathology of the dermis. The idea that it is contagious is wrong. The disease can develop only in conditions that are comfortable for it - a cold and problems with the immune shield.
That is why the peak of diseases occurs in early spring and late autumn, when the vitamin warehouse is empty, immunity decreases and the likelihood of problems associated with colds increases.
This circumstance objectively indicates the seasonality of the disease.
The definitive causative agent is not known for certain. Although most dermatologists say that the culprit of the problems is the herpes virus type 7. It is he who is characterized by such deceit. But in the other camp this opinion is not accepted unambiguously.
Causes? They were briefly discussed above.
But there are other negative accompanying factors:
- Skin damage.
- Recent infections and colds.
- Stress, although this applies more to adults, of course.
- Pathology of metabolic processes.
- Allergic reaction to vaccinations and medications.
- Frostbite or sunburn.
- Poisonous insect bites.
In general, the background of the course of the pink “disgrace” is characterized as favorable, but it will be useful for parents to know some of the “individual” features of this disease:
- At the initial stage, you should be alert not only to the deterioration of the child’s general condition: lethargy, drowsiness, pain in the joints and head. The main thing that should immediately catch your eye is the appearance on the forehead, legs, neck, elbows, and back of a huge pink formation rising above the skin. This is the decisive sign - maternal plaque.
- It remains on the body for up to ten days, showing amazing “fertility.” The result of her work is small daughter spots.
- After a week they will turn yellow, begin to wrinkle and peel.
- Once peeling is complete, the spots change color. They can darken or become lighter.
- After two months, the spots will disappear without leaving a trace.
Pityriasis rosea in a child in the photo:
Parents should know:
- The disease occurs extremely rarely in children. And then, this is favored by an infection that has penetrated the intestines and, not surprisingly, by routine vaccination.
- Gibert's disease can occur in an atypical form - without the formation of a maternal plaque. On a baby's bottom, lichen may appear as a result of physical abrasion from a washcloth or clothing, or excessive sunbathing.
Video from an expert:
girdling
Herpes zoster, also known as herpes zoster, is definitely a viral disease that covers almost all areas of the skin with a painful rash.
In 90% of cases, the abdomen, chest and pelvis are affected. In addition, it is he who causes chickenpox, in other words, chickenpox.
Having penetrated the body in early childhood, the virus continues to stay for a long time, until favorable conditions arise, which are characterized by the following circumstances:
- Infectious diseases.
- Excessive ultraviolet exposure (summer tanning).
- Abnormal hypothermia or overheating of the body.
- Unbalanced diet and lack of vitamins.
Therefore, you need to understand that chickenpox and shingles are two troubles of the same nature.
Speaking about the “ferocity” of the Herpes Zoster virus, it is necessary to significantly emphasize its contagiousness and virulence, i.e., almost 100% probability of damage when it enters the body.
For a baby to “catch” the virus, banal everyday contact with a sick person is enough, because the airborne communication channel is the most favorable for this infection.
However, we can talk about more dramatic cases. And this applies to expectant mothers.
If in the third trimester she, God forbid, gets sick with herpes, then there is an extremely high probability that the newborn will develop herpes after birth. Although it is possible that it will make itself felt on the baby’s body a few weeks after birth.
Symptoms that should prompt you to see a doctor immediately:
- A debilitating malaise.
- Weakness turning into chills.
- An exorbitant increase in temperature, crossing the 39° mark.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
- Severe headaches and body aches.
- Nausea progressing to vomiting.
The following stages are distinguished:
- After entering the body, viruses from the nerve node endings rush to the surface of the dermis.
- After two days, spots that closely resemble swelling form in the areas most affected by the invisible enemy.
- Already on the fourth day, the swelling transforms into extremely painful transparent blisters.
- At the same time, the lymph nodes become enlarged.
- After seven days, the blisters begin to dry out and form a crust.
- The end of all periods of the disease: the first symptoms, the formation of bubbles, their drying out and falling off occurs in about a month.
The above clinic is typical for 90% of cases.
But there are also atypical forms, which are characterized by:
- Muscle weakness.
- Formation of blood fluid in blisters.
- Formation of a single large bubble, instead of a scattering of small ones.
- There are cases when preliminary rash is completely absent.
- Extensive damage to the skin around the eyes, with temporary loss of vision (ocular form).
- The same is true for the auricular form, where the concha is affected and hearing is lost.
Important! Parents need to be prepared and not panic when a little patient may exhibit pseudosymptoms of encephalitis, keratitis, stomatitis, iridocyclitis or conjunctivitis. Only a doctor can make a final diagnosis!
Video from Dr. Malysheva:
Flat red
Experts do not have a uniform interpretation of the reasons for this phenomenon.
The majority is inclined to the autoimmune nature of the motivating factors, naming the likely “culprit” - this is therapy, during which the uncontrolled use of medications occurs, such as:
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Pain relievers: Diclofenac, Aspirin, Ibuprofen and similar medications.
- ACE inhibitors, reducing renal and heart failure.
- Antimalarials.
Please understand correctly – this is not anti-advertising. Just be extremely careful when giving your baby medications. Especially strangers or without doctor’s recommendations.
Speaking about other motivating triggers, part of the medical fraternity is inclined to reduce the problem to gastrointestinal pathology, as well as a treated (untreated) infection in the mouth.
Numerous clinical symptoms of this skin disease sometimes make diagnosis difficult in children, but parents need to be aware of them.
There are several forms, the most common:
| Clinical form | Symptoms and description |
| Typical | The first signs of lichen planus in a child or adult are the appearance on the body of a monoform rash, identical in size and shape. These are red flat plaques up to 5 mm in size. During further transformation, they are able to connect and create a large location of the lesion. In every fourth case, the affected area is the oral or vaginal mucosa in girls. |
| Warty | Hyperkeratosis (pathological thickening) forms on the body. Its color is usually brown or purple. This formation vaguely resembles warts. The front of the shin is a favorite area. |
| Atrophic | The affected area experiences a process of atrophy with significant thinning of the skin. If the disease affects the scalp, it is often accompanied by baldness. Dangerous consequences are the scars and scars that may remain after recovery. |
| Pemphigoid or vesicular | Its characteristic symptomatology is the appearance of vesicular formations filled with bloody intercellular fluid. Vesicles can develop to large sizes - up to 10 mm in diameter. Most often, bullae (transformed vesicles) “sit down” on the feet or legs. |
| Moniliform | This is a very specific form with an exclusive rash. It attacks in a group at once and decorates the neck, elbows and outer surface of the hands with a necklace-shaped rash, sparing the rest of the skin. |
| Pigmented | This form is characterized by dry hyperpigmentation of the skin. |
| Pointed | After infection, papules form on the body, and a thickening is called hyperkeratosis in the form of a spike. The neck, shoulder blades and legs are most often affected. |
| Ring-shaped | The geometry of the rash resembles a circle. The spread occurs from the center to the periphery. |
| Erosive-ulcerative | It is distinguished by a generalized attack on the oral cavity - erosion and painful ulcers. |
Lichen ruber in a child in the photo:
Colored (pityriasis)
This type of skin pathology “appropriated” such cheerful names for itself - colored, solar fungus, multi-colored, but this did not add joy to either children or parents. To say the least, the disease puts pressure morally, causing psychological trauma.
The disease is of fungal etiology with a seasonality bias. During the period of active sun, the spots are the brightest; in winter, the “beauty” fades away.
The disease does not pose a danger to health, but we repeat - internal discomfort is obvious.
Children whose skin suffers from ringworm are most often at risk.
An amazing fact - the majority of the planet's inhabitants are carriers of an opportunistic fungus from the line of yeast-like mycotic organisms. But why do only a select few become the object of attention from the disease?
There are a number of reasons for this:
- Endocrine imbalance.
- Deficiency of immune resistance.
- Pathology of the digestive structure.
- Functional skin problems.
- Excessive sweat production and its exclusive chemical composition.
The disease manifests itself in various forms:
| Form of the disease | Symptoms |
| Spotty-flaky | Pinkish-yellow spots appear at the base of the hair follicle (bulb). Formations with an unusual color can be located on the neck, chest and abdomen. As they develop, they merge into a single affected field. Some time later, their color changes to red, brown and brown. A little later, peeling appears, the so-called “chips” effect. There is no itching with this pathology. After recovery, the previously affected areas do not tan and look like painful white islands. |
| Follicular | Papules appear on the surface of the skin in the area of the back, arms, legs and chest. Their size does not exceed 5 mm. But the distinguishing feature of this form is painful itching. |
| Inverted | Skin folds are a favorite location. In these places, redness and peeling of the dermis occurs. Itching is possible. |
Pityriasis versicolor in a child in the photo:
In terms of symptoms, white is similar to pityriasis. Although it is less common, it has the same fungal etiology. And after itself it leaves the same unpleasant white spotty surface.
Lichen alba in a child in the photo:
But it is distinguished by several exclusive features:
- painful itching at the site of the white spot;
- pain;
- getting the affected surface wet;
- in rare cases, the course is accompanied by inflammation of the affected areas.
After reviewing a significant part of the types of disease, the reader may be slightly confused and a logical question will arise: and yet, how to distinguish lichen from dermatitis or allergies and not confuse a spot that looks like lichen with a real fungal disease?
The table below will help you figure this out:
| Symptoms | Lichen | Allergy |
| Rash on the body | Skin spots have a strictly defined location. At first they are single and located at some distance from each other. Affected areas are diagnosed in specific areas: stomach, back, scalp, feet, neck or genital area. | The location of the rash cannot identify the system - it randomly covers the body. The spots vary in size. They always have the appearance of swelling, merging with each other, forming a single area, but can be located separately. |
| Itching | Only when infected with ringworm or lichen planus does painful itching occur. | Allergies are always accompanied by itching. Treated exclusively with symptomatic therapy. |
| Heat | Almost all types of similar skin phenomena are accompanied by a temperature abnormality. | For older patients, hyperthermic syndrome is extremely rare, which cannot be said about children - it is rather a common occurrence. |
| Enlarged lymph nodes | This symptom is characteristic of all types of fungal skin diseases. | As a rule, allergies do not affect biological filters. |
Shingles
The disease is caused by the herpes virus. Children over the age of 12 are prone to it. Symptoms of shingles appear only in those who have already had chickenpox. From this moment on, type 3 virus remains in the body for life. A number of predisposing factors contribute to the appearance of the disease:
- frequently ill children;
- newborns;
- with oncology;
- in the presence of chronic diseases;
As soon as the immune defense becomes insufficient, the herpes virus, which is in a dormant state, begins to actively manifest itself.
Symptoms
It is not immediately possible to recognize herpes zoster in children. Elements often appear on the leg and torso. The following signs are characteristic:
- Increase in body temperature.
- Chills.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Burning, stinging or itching in the areas where the rash appears.
- Decreased appetite.
At the beginning of its development, the first signs in the form of ARVI may appear. After 1-2 days of development of nonspecific symptoms, lichen colds begin to actively manifest themselves. Pink bubbles appear along the nerves (intercostal spaces are a common location for rashes). Gradually they merge. After a week, the elements dry out and the surface becomes covered with crusts.
Knowing everything about lichen, parents should exclude the possibility of scratching the elements on the child’s skin. At an older age, he needs to explain this. The presence of an open wound in an infant when scratching will lead to a secondary infection. Against the background of reduced immunity, it will begin to actively multiply, which will result in the addition of concomitant pathology.