- Common symptoms in children
- Course of the disease in infants
- Prevention in infants
- The course of the disease in infants
- Symptoms in infants
- How to treat influenza in children
- Precautionary measures
Flu in children: symptoms
A small child cannot explain how he feels. Therefore, you must independently determine the onset of the disease. Usually in children it is acute, the temperature suddenly rises to 39oC and above.
Clinical symptoms of influenza:
- feeling of chills,
- fever,
- cough,
- headache,
- sore throat,
- pharyngitis,
- nasal congestion,
- diarrhea,
- rhinoconjunctivitis,
- mental changes,
- dizziness,
- Pain in the eyes,
- vomit,
- myalgia,
- cervical lymphadenitis,
- wheezing in the lungs.
In the first 2–3 days after infection, no painful changes are visible, but as the virus spreads, the patient’s condition sharply worsens. In practice, this can mean: the baby has just been playing calmly, and now the mood has deteriorated, and the forehead and body have become hot.
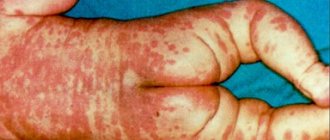
Unlike acute respiratory viral infections, influenza syndromes affecting the respiratory tract are not sharply expressed at first and are manifested by difficulty in nasal breathing, slight rhinitis, dryness, and sore throat. The child may complain of chills, aches throughout the body, pain in the eyes, photophobia, headache, and sore throat. Patients experience weakness and fatigue. Intoxication syndrome dominates over catarrhal syndrome on the first day of illness. The so-called hemorrhagic syndrome is manifested by nosebleeds and a rash on the body.
A dry, painful cough and nasal discharge usually begin only on the second day. Due to intoxication, appetite decreases and vomiting may begin. In severe cases, toxicity can affect the central nervous system, causing delusions, seizures and hallucinations. If an alarming situation arises, you must immediately call a doctor, give the child warm water, change him into dry clothes, put him to bed and measure his temperature.
At temperatures above 38°C you must:
- Give antipyretics.
- Provide rest and bed rest.
- Drink plenty of warm water, weak tea, fruit juice.
- If there is a chill, warm the child.
- At 39.5-40°C, the child should not be wrapped.
- If it is above 40.4°C call emergency helpiv
How long is the incubation period of ARVI in children from one to 3 years old?
With ARVI in young children, a more severe course and deeper penetration of viruses are observed. On average, the period after which signs of the disease begin to appear in children when infected with acute respiratory viral infections is shorter than in adults, which is associated with the characteristics of the immune system, as well as with the structure of the organs of the respiratory system: their larynx is shorter than that of adults.
For example, parainfluenza manifests itself after only 2-4 days, and the onset is violent, with a sharp increase in body temperature and obvious signs of intoxication. The voice becomes hoarse, the child complains of a sore throat, and is bothered by a cough. Body temperature rises to 38ºC and above. In children aged one to three years, infection can lead to the development of false croup - acute laryngeal stenosis. Symptoms of this disease include a barking cough, a wheezing voice, and noisy breathing. Also, young children may develop obstructive bronchitis and other complications that require immediate medical attention.
The main difference between parainfluenza and influenza is that parainfluenza does not cause large epidemic outbreaks. The influenza epidemic develops quite acutely, since the incubation period for influenza is even shorter - 12-24 hours.
With adenovirus infection, children under two years of age may experience not only catarrhal symptoms, but also abdominal symptoms - diarrhea and abdominal pain. Also, a sick child may experience decreased appetite, sleep disturbances, pale skin and a bluish discoloration of the nasolabial triangle.
In order to prevent the development of complications, it is necessary to seek help from specialists at the first signs of the disease.
Flu in babies
Children from 0 to 6 years old are especially susceptible to viral infections of the respiratory system. At this age, the body cannot yet fully resist infection, since it does not have a developed immune defense. At an early age, any virus is perceived by the child’s body as new, so children get sick especially seriously and for a long time. Annual epidemics bring new strains of influenza. Children have virtually no chance of avoiding infection without effective protection. Particularly high-risk groups include: infants (newborns) and children under two years of age, as well as pregnant women, the elderly, and people with chronic diseases.
Flu in a child under three years of age will most likely be treated in a hospital. Older children are usually treated at home under the supervision of a doctor. To avoid infecting other family members, it is necessary to provide the patient with separate dishes and care items, frequently ventilate the room, change linen and carry out wet cleaning. Dishes used by the patient must be boiled or disinfected. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap after each contact with someone who is sick. Family members should wear masks and remember to change them every two hours, throw away disposable ones, and wash and iron reusable ones on both sides.
Treatment should begin immediately after the first symptoms appear. It is important to inactivate the influenza pathogen with antiviral drugs that prevent the penetration and reproduction of the virus in the cells of the respiratory tract and prevent the further development of the pathological process. As a rule, complex therapy is prescribed, in which many doctors include interferon drugs, whose task is to fight viruses and restore one’s own immunity. The antiviral effect of interferons is explained by the suppression of viral reproduction in the initial phase of the synthesis of specific proteins. Treatment of influenza in children involves diet, regimen, drug treatment using etiotropic, pathogenetic, symptomatic therapy, immunotherapy and immunocorrection, as well as preventing complications and the formation of residual effects.
How to understand that the threat has passed? – Recovery criteria: persistent normalization of temperature for 3 days or more; absence of intoxication and inflammation in the respiratory tract; normalization of blood counts.
Children at risk
Children from big cities are at particular risk. This is due to several factors. Firstly, almost all such children attend organized groups - kindergartens and schools, and many also attend various developmental courses and sports sections. Since the influenza pathogen is highly virulent (infectious) and is transmitted by airborne droplets (by coughing, sneezing and talking), it spreads at lightning speed in such groups. Once one sick child coughs at school, a few days later a significant portion of his classmates will be at home with a high fever.
The decrease in the immunity of the children's population of large cities also contributes to the spread of the influenza and ARVI epidemics. It is caused by both the polluted air of the metropolis and the characteristics of the diet, which is not always healthy and nutritious. Often, the child’s immunity is undermined by the parents themselves, who unreasonably, without a doctor’s recommendation, prescribe dietary supplements, antibiotics, adaptogens and other drugs.
Therefore, it is not surprising that from year to year the number of frequently and long-term ill children increases. In some regions, such problems are observed in more than half of the child population.
Meanwhile, a single comprehensive approach to the treatment and prevention of frequent respiratory diseases in children in healthcare has not been developed. This leads to an additional deterioration of the epidemic situation during the cold season.
To prevent the disease, there are preventive vaccinations. They are really effective, but they do not help in all cases. This is due to the high variability of the virus - its antigens (surface proteins that are recognized by the immune system) are constantly changing. Vaccines contain only a limited set of antigens and are effective only against viruses containing them. In addition, vaccination serves only as a preventative measure, and if the disease has already developed, treatment is necessary.
But the flu is caused by a virus, not a bacteria. This means that antibiotics are absolutely ineffective against it. There are no drugs that kill the virus that has entered the body. Therefore, the task of destroying the influenza pathogen falls entirely on the immune system.
One of its most important components of antiviral immunity is the production of interferons. These substances change the functioning of cells in such a way that they become immune to the virus and do not participate in its reproduction. In addition, under their influence, immune cells – lymphocytes and macrophages – are activated.
The more interferons are produced, the easier the course of the disease will be, the faster recovery will occur and the lower the risk of complications. However, the body is not always able to quickly respond to the introduction of a virus. Especially if it is a child’s body with reduced immunity.
Prevention of influenza in infants
Children under 5 years of age are at particular risk for ARVI, for the prevention of which broad-spectrum antiviral drugs come to the fore. Over the past 20 years, extensive experience has been accumulated in the use of the drug VIFERON in the treatment and prevention of ARVI. Starting from the birth of a child, VIFERON gel can be used as preventive measures against influenza. The drug has an effect already at the “gate” of infection, because very often it enters the body through the nose. Thanks to the gel base, VIFERON has a prolonged effect, so it is enough to apply it to the nasal mucosa only 2 times a day.
Flu in infants
Infants receive from mother's milk not only a balanced complex of vitamins, enzymes, minerals and trace elements, but also the ability to resist viral and bacterial infections due to passive immunity. However, viruses can still invade a child’s body. This is especially true for artificial infants who are not protected by a natural barrier in the form of mother's milk, premature and weakened children. Influenza is very dangerous: the likelihood of death in newborns is 2-3 times higher than in others. Flu in a baby under one year old can lead to serious complications, as it affects the nervous and cardiovascular systems and has a detrimental effect on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
The goal of therapy is to alleviate the condition and minimize the risk of complications. Naturally, only a pediatrician who observes your child can develop the best treatment regimen.
One of the drugs that can be used to treat infants is VIFERON in the form of suppositories (rectal suppositories) at a dosage of 150,000 IU according to a schedule of 1 time in 12 hours, the course is 5 days. Premature newborns with a gestational age of less than 34 weeks are recommended to use the drug VIFERON 150,000 IU daily, 1 suppository 3 times a day after 8 hours.
In order to recognize the signs of influenza in time and take action, you need to know some features, for example, that catarrhal symptoms (cough, runny nose, redness of the throat) in children may be completely absent, and the temperature may rise only on the second day. Lethargy and lack of appetite, moodiness, and tearfulness should alert you.
During stressful periods for a baby, breastfeeding should not be stopped, as it contains a high concentration of antibodies that help strengthen the child’s body’s defenses. If your baby has difficulty sucking at the breast due to a stuffy nose and weakness, feed expressed milk from a bottle. It is advisable to exclude from the diet of a nursing mother any foods that cause digestive disorders in the baby, so as not to burden his immune system. If the mother is sick, we must try not to infect the baby. There is no need to stop breastfeeding and boil your expressed milk. You cannot put your child in your own bed; he must sleep in a separate crib; Be sure to sterilize pacifiers and bottles, avoiding contact with your utensils. A nursing mother should wear a protective mask before feeding, wash her face and hands with soap, wash her breasts, and of course, undergo treatment.
Flu symptoms in infants
The child, experiencing pain, worries, starts screaming and kicks his legs. A child who has the flu does not sleep well, often wakes up, and cries. The baby may completely lose appetite, give up or not take the breast at all. Due to swelling of the nasal mucosa, the baby breathes with his mouth open, the skin is pale; With a lack of oxygen, a slight blue discoloration may appear around the nose. During the flu, infants and newborns often experience nausea and vomiting, and stool consistency is disrupted. At the peak of the temperature, the pain increases, which can provoke an attack of colic, bloating and cramping in the tummy. At temperatures above 38C, children have seizures.
How to treat influenza in children
To treat influenza in children, antiviral drugs are used that act directly on the cause of the disease - viruses. During diagnosis, a smear, blood and urine tests are taken to determine the presence of infection. If a virus is detected in the body, the doctor may prescribe VIFERON suppositories (suppositories) in a dosage of 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 2 times a day after 12 hours every day for 5 days*. According to clinical indications, therapy can be continued. The break between courses is usually 5 days.
*Premature newborns with a gestational age of less than 34 weeks are recommended to use the drug VIFERON 150,000 IU, 1 suppository 3 times a day after 8 hours every day for 5 days.
The reluctance of young patients to take medications with a specific taste and/or consistency (tablets, syrups) can interfere with treatment. Therefore, the form of the drug in the form of rectal suppositories is very convenient, because their small size facilitates easy and painless administration. It is advisable to start therapy aimed at combating viruses from the first hours of the disease, when it is actively multiplying, so the speed of action of the drug is one of the important properties. Due to the dense network of blood vessels in the rectum, absorption of the drug occurs quickly, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract, which makes it possible not to tie treatment to the meal schedule and not overload the baby’s stomach and liver.
Flu treatment
Treatment of influenza is carried out by three groups of drugs: immunostimulants (containing vitamin C), antiviral drugs (neuraminidase and M2 inhibitors), immunoglobulins (serums) and interferon drugs. It is worthwhile to approach their use wisely, because these are potent drugs with side effects.
In general, flu treatment should not be left to chance. Doctors have gained sufficient experience to effectively fight the disease, and usually recommend several proven medications that fight the virus, help the immune system and relieve the most unpleasant symptoms.
One of the important conditions for recovery from the flu is bed rest. A sick person undermines his immunity, weakens the body even more and becomes a carrier of infection. Therefore, if you are sick, bed rest and a doctor’s recommendation will get you back on your feet as quickly as possible.