What is ringworm?
Ringworm is an infectious skin disease caused by the parasitic fungi Microsporum canis and Trichophyton tonsurans, it is part of the group of ringworms that primarily affect the skin, hair and nails. This is an infectious dermatological pathology caused by dermatophyte fungi. It is also called dermatomycosis, scab, micro- and dermatophytosis.
Doctors distinguish several types of ringworm, depending on the location, nature of the course and the causative agent.
The main types of the disease are:
- chronic or ringworm of smooth skin;
- surface;
- ringworm of the nail plate;
- infiltrative-suppurative.
Since ringworm is caused by two types of fungi, in medicine it is diagnosed as microsporia and trichophytosis. These fungi have persistent pathogenicity, pronounced virulence and often cause acute diseases with varied clinical manifestations.
A disease caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum canis is microsporia. Depending on the location, there is microsporia of smooth skin and microsporia of the scalp.
Trichophytosis is caused by the activity of the dermatophyte Trichophyton tonsurans, which, through the anthroponotic route of infection, causes inflammation of the scalp and smooth skin, and through the zootroponotic route, inflammation in the deep layers of the dermis, accompanied by suppuration.
The presence of fungal spores does not always provoke damage to the skin and its appendages. The transition of the fungus from an inactive state to a pathogenic state is facilitated by metabolic and endocrine disorders, immune diseases, hypovitaminosis or vegetative-vascular dystonia. This increase in the pathogenicity of dermatophytes provokes an exacerbation of inflammatory processes, the spread of the fungus through the blood and lymph flow.
The disease is weakly expressed during the development of a latent infection and when localized in previously affected areas, and the high virulence of the fungus is formed during a relapse, gradually decreasing during the course of the infection.
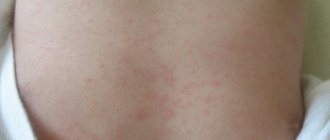
Symptoms of ringworm: At the end of the incubation period, itchy ring-shaped spots of red-pink color appear on the skin, on the surface of which bubbles appear, after which a crust and peeling remain. The hair at the site of the lesion breaks and falls out.
Normally, the immune system is able to cope with the pathogen and prevent its activity, but there are a number of factors that increase the risk of ringworm, namely:
- skin microtraumas;
- lack of vitamins and microelements;
- prolonged contact with the source of infection;
- high humidity and air temperature;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases, etc.
In a situation where there is an adult or child with lichen at home, it is necessary to take preventive measures to reduce the likelihood of its spread, namely:
- use separate towels and bed linen;
- wash your hands thoroughly with soap, especially if you touched the patient’s things;
- use gloves when touching areas of disease;
- undergo examination and take tests to identify pathogens, etc.
The main method for diagnosing ringworm is the use of a Wood's lamp, under the light of which the affected areas acquire a characteristic greenish glow. Microscopic examination and culture of skin and hair scales are effective to confirm the diagnosis.
Timely diagnosis and a properly selected treatment regimen can effectively eliminate ringworm in children and adults, preventing its spread. The pathology is prone to relapse, since the presence of spores of viable fungi can cause repeated damage. It is extremely important to complete the course of treatment and follow all doctor’s recommendations.
- Gallery
- Reviews
- Articles
- Licenses
- Vacancies
- Insurance partners
- Partners
- Controlling organizations
- Schedule for receiving citizens for personal requests
- Online consultation with a doctor
- Documentation
This is a skin and hair disease caused by fungi of the genus Microsporum. This disease is highly contagious.
Children aged 4-11 years old are more likely to get sick, this is due to the fact that children under 2 years of age and adults have an acidic sweat reaction, and acid prevents fungi from multiplying. But with a decrease in immunity, if there are microtraumas on the skin (scratches, abrasions), anyone can become infected, regardless of age.
Infection occurs from animals (cats and dogs), which may have manifestations of the disease or may be carriers of the infection without obvious manifestations, and from people who have manifestations of the disease. Moreover, you can become infected both through direct contact with an infected animal or person, and through objects and things contaminated with skin flakes or hair (fur) containing the pathogen.
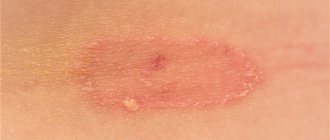
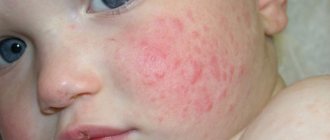
When infected, round pink or red lesions with a clear boundary appear on the skin, which quickly increase in size and number. Over time, they fade in the center, while a brighter rim remains along the edge, the lesions resemble rings. On the surface of the lesions, whitish or grayish peeling and crusts are observed, and there may be bubbles with liquid. If the process is localized on the scalp, then in the foci under the influence of a fungal infection, the hair breaks off at a height of 3-5 mm (which is why the disease is popularly called “ringworm”), and bald spots are formed. Subsequently, the lesions can merge with each other, forming intricate patterns; infected skin flakes can again fall on the skin in the center of the ring, which leads to the formation of a new lesion - a “ring within a ring”. The rashes are most often accompanied by itching and cause discomfort to the baby.
The diagnosis of microsporia can only be made by a pediatric dermatologist; to do this, you first need to take a scraping and culture from the lesions on the skin for fungi. Some other skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, may have similar manifestations, so treatment is prescribed only after receiving tests. If you suspect ringworm, immediately contact a pediatric dermatologist; do not self-medicate, as the tests will be unreliable.
Treatment for microsporia is quite long. The duration depends on the number and size of the lesions, as well as on whether the hair is affected. If the scalp is affected, the hair in the area of the lesions is shaved 1-2 times a week as it grows back. During the treatment process, a scraping for the fungus is also taken every 5-7 days. And only after three negative results can we talk about recovery. After healing, the rashes disappear, leaving no traces behind, and the hair in the lesions is completely restored.
If microsporia is detected in one of the family members, it is necessary to carefully examine all household members and pets, as well as all people who have been in contact with the infected person. Attend school, preschool institutions, sports clubs, etc. Sick children are prohibited. All personal hygiene items (sponges, towels, combs) must be individual, other people should not use them. Things worn by a baby infected with microsporia must be washed at a temperature of at least 60 degrees and ironed, this also applies to bed linen. It is recommended to boil items that the child has used, including hard toys, for 10-15 minutes. Furniture and hard surfaces should be wiped with disinfectants.
Preventing infection is not easy. But for prevention purposes, make sure that your child does not come into contact with unfamiliar animals on the street or at a party, and also carefully observe basic rules of personal hygiene.
Make an appointment with a pediatric dermatologist by phone
Services and prices
Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a dermatovenerologist
1,800 rub.
Skin scraping
220 rub.
Taking material for testing for pathogenic fungi of smooth skin
400 rub.
Avdeikina Olga Nikolaevna Dermatovenerologist Experience: 9 years
Make an appointment
How is ringworm transmitted?
Ringworm is transmitted in two ways:
- from a sick animal – zoonotic with an incubation period of one week;
- from an infected person – anthroponotic with an incubation period of up to 6 weeks.
Children are at risk because they most often come into contact with the carriers of the pathogens of this disease - cats and dogs. Children's skin is characterized by low density of the stratum corneum and weak protective properties of the water-lipid mantle. The stratum corneum prevents the penetration of the fungus into the layers of the skin, since its spores are located between the horny scales, and the water-lipid mantle forms a barrier to the penetration of pathogens.
The infection is also transmitted by non-compliance with personal hygiene standards and the use of other people's personal belongings containing fungal spores (hats, combs, bed linen, etc.).
The causative agent of ringworm: what is the cause?
Ringworm is caused by a special type of parasitic fungus called Microsporum. It was due to them that it received its official medical name - microsporia. During its activity, the parasite is capable of forming a huge number of small microscopic spores that affect the skin and give rise to new elements on the skin. There are two variants of this infection, caused by two types of fungi:
- Microsporia caused by Microsporum canis
- Trichophytosis caused by Trichophyton tonsurans.
In addition, there are also several types of fungi that primarily affect animals and occur extremely rarely in humans, only against the background of severe immunodeficiency. Typically, these types of ringworm are relatively mild and do not lead to chronic skin lesions.
Important
Doctors usually classify ringworm as an anthropozoonotic infection - this is a pathology that affects both people and animals. Accordingly, you can become infected both from sick children and from sick animals.
How does ringworm begin?
Favorable conditions contribute to the introduction and reproduction of a pathogenic fungus in the skin, triggering the infectious process. In the initial stages, this period is asymptomatic. After which the development of the pathology acquires clinical manifestations, the signs of which depend on the stage of the pathology.
The stages of the infectious process during the development of ringworm are:
- incubation period;
- period of mushroom growth;
- refractory stage (period of insensitivity, rest);
- regression.
In the skin, the fungus forms branched mycelium, which gradually invades new areas of the skin, while old lesions become the location of its spores. This period of fungal growth is determined by the rapid increase in the colony of the pathogen, active division of skin cells and the high rate of exfoliation of the affected epidermis.
Since most often the growth of the colony outstrips the rate of change of the stratum corneum, the infectious process spreads. An intense immune reaction (inflammation) in the lesion is displayed in the form of a red ring, which, in the chronic course of mycosis, becomes the permanent residence of the pathogen.
What does ringworm look like?
Clinical manifestations of ringworm depend on the type of pathogen, course and stage of the disease. Dermatophytes secrete enzymes and toxins that destroy keratin protein (they feed on it), so the severity of symptoms directly depends on the ability of fungi to produce these substances.
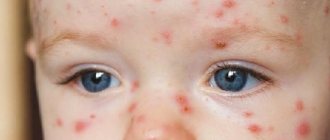
Common symptoms of ringworm on the scalp are:
- hair thinning;
- the appearance of localized peeling of the skin;
- redness of the epidermis;
- hair breaking off at the root;
- the appearance of small bubbles with cloudy contents along the edges of bald patches, after opening which yellow crusts form.
Ringworm of smooth skin includes the following symptoms:
- pronounced itching;
- the appearance of round red spots;
- light epidermis at the site of damage, surrounded by gray scales;
- the edges of the damaged area consist of pink-red bubbles;
- growth of the lesion in diameter.
The chronic form of the disease is accompanied by the presence of microscopic blisters on the affected areas, the formation of scars after their opening and severe itching. In a situation where the site of the lesion is the nail plate, its separation, discoloration and thickening are observed.
Ringworm of the infiltrative-suppurative form is characterized by the appearance of large bright red spots up to 10 cm in diameter, the outer surface of which is lumpy and uneven, and purulent follicles form along the edges. Pain, swelling and hyperemia of the affected areas are also observed.
The appearance of the first signs of the disease requires a mandatory visit to a dermatologist. The lack of qualified treatment can lead to the rapid spread of infection throughout the body and cause a number of complications: tissue scarring, death of hair follicles, allergic reactions and the addition of a secondary infection.
Symptoms of lichen
The clinical picture of the disease directly depends on its form. There are 5 most common variants of lichen: pink, multi-colored, red flat, ringworm, shingles.
- Manifestations of pityriasis rosea. This type is characterized by the appearance on the child’s skin of a single pink plaque with a diameter of 3-4 cm. The formation is prone to peeling and provokes moderate itching. A week after the plaque appears, multiple daughter rashes form on the child’s skin. Pityriasis rosea often affects a child's back, shoulders and abdomen. Often the rash is localized in natural folds and curves.
- Symptoms of versicolor.
Tinea versicolor usually occurs on the child's scalp or upper half of the body. This is one of the few varieties that affects only the upper layer of the epidermis and is not transmitted by contact. At the very beginning of the disease, lichen can be suspected by the appearance of small spots of pink, yellow or brownish color. Then the spots that appear gradually grow, forming large lesions with jagged edges. Lichen versicolor got its name due to its distinctive feature: focal rashes can change color over time, becoming dark brown or dark brown spots. In addition, this form has another distinctive feature - the skin elements are not accompanied by itching or burning of the skin, and therefore do not cause the child much discomfort. - Manifestations of lichen planus.
With this form, scaly spots of bright red or dark brown color appear on the mucous membranes or skin of the child. The disease can be identified by severe itching, which significantly reduces the child’s quality of life, and by the characteristic depressions in the middle of each rash. In most cases, formations are localized on the skin in the area of natural folds, stomach and back. After recovery, long-lasting pigment spots may remain at the site of the rash. - Clinical picture of ringworm.
Ringworm is the most common form of the disease in children and adolescents. Pathology develops on the skin, nails, scalp and hair itself. The skin is affected by reddish round spots, accompanied by peeling and itching. If lichen affects the scalp, this is accompanied by the appearance of a fairly large area of baldness, at the edges of which the hair breaks off at a level of 0.5-1 cm from the dermis (taking on a trimmed appearance). In addition to the main formation, multiple small lesions may occur. - Symptoms of herpes zoster.
This form predominantly occurs in older adolescents who have previously had chickenpox. Before the appearance of skin rashes, the patient experiences the following symptoms: weakness, drowsiness, chills, increased body temperature to subfebrile levels. The onset of the disease is often confused with influenza or ARVI.
A few days later, multiple rashes filled with clear liquid content appear on the child’s skin in the area where large nerve trunks and branches pass. Then the bubbles dry out, darken, and become crusty.
How is ringworm treated?
In each case, treatment for ringworm should be selected individually, since its composition and duration have their own specifics and are determined by the type, location and stage of the pathology.
Only prescriptions from a dermatologist are effective; they take into account the current clinical picture, the characteristics of the patient’s physical health and his age.
Therapy is aimed not only at relieving the symptoms of the pathology, but also at inactivating the pathogen. The chronic form of the disease also provides support for the immune system, normalization of metabolism and hormonal levels.
The following groups of drugs are used to treat ringworm:
- systemic and local antimycotics;
- antiseptic solutions;
- multivitamin complexes.
How long does it take to treat ringworm?
The treatment process for ringworm is lengthy, usually taking at least six weeks, with systemic therapy lasting mainly 15-25 days.
The effectiveness of therapy is assessed using laboratory tests. In a situation where tests indicate a significant decrease in the number of fungal spores after 2 weeks of a medication course, it is necessary to continue the chosen treatment. In some cases, fungal shedding can last for several months.
After the signs of pathology disappear, you need to scrape the epidermis three times in previously damaged areas:
- immediately after completion of therapy;
- 7 days after therapy;
- after 2-3 months.
The result of therapy is considered successful if all three tests show negative results.
How to treat ringworm in children?
Treatment of ringworm in a child is the responsibility of a pediatric dermatologist, since the characteristics of the child’s body require special doses and composition of medications.
Hygiene and child care are also important elements of pathology therapy:
- boiling and ironing clothes in contact with affected areas of the skin;
- treating household surfaces with disinfectants to prevent the spread of spores;
- frequent change of bed linen;
- washing in the shower rather than the bath, etc.
Who is at risk for infection?
Sick children and adults, carriers of fungal spores, or affected animals with which children come into close contact can be contagious to children. Most often, lichen is transmitted from street cats and dogs, especially small ones. In them, this infection occurs more easily than in humans; the areas of affected skin may be small and barely noticeable under the skin.
Children often get sick, becoming infected from each other, through close contact or sharing clothing, bed linen, and hygiene items (towels, washcloths, nail files, combs). There is a higher risk of contracting fungal spores in the presence of injuries, cuts, scratches and scratches on the skin, sunburn and dermatitis. When the immune system is weakened, under the age of 3, children get sick more often and more severely.
Can I go to work or school with ringworm?
The presence of this diagnosis requires isolation of the patient from the team for at least two weeks. In schools and other children's institutions, it is mandatory to notify parents for timely detection of the disease in other children.
The disappearance of ringworm symptoms and 3 negative tests for the presence of fungus are a reason to return to school or work.
If a dermatomycosis infection has been detected in a team, then to prevent pathology, you can use antifungal shampoos for some time, carry out wet cleaning with the addition of antiseptic solutions, and strictly observe personal hygiene.
- Treatment of lichen in Kharkov;
- treatment of lichen in Uzhgorod;
- treatment of deprivation in Sumy;
- treatment of lichen in Poltava;
- treatment of lichen in Odessa;
- treatment of deprivation in Nikolaev;
- treatment of lichen in Mariupol;
- treatment of deprivation in the Dnieper.
1
0
0
Article rating:
3.8 out of 5 based on 5 ratings
Author: Mangusheva Victoria Yurievna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, trichologist. Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category. Work experience more than 10 years.