A newborn baby is surrounded by danger on all sides if he is not given proper care. Parents may be alarmed by any sudden illness of the baby, especially when the baby is choking; it is necessary to act promptly, but carefully. The health and life of the baby depend on the correctness of actions.
Why does a baby often choke?
Babies during the newborn period often choke on their own saliva, milk or water. This occurs due to the immaturity of the digestive tract. The baby is not yet able to control everything that comes into his mouth on his own. If the baby is healthy, this goes away by 4-5 months.
The cause may also be congenital diseases of the nervous system in a child (cerebral ischemia, pathology of the peripheral nervous system, birth injuries (with impaired brain function).
Main reasons
There are many reasons why a baby may choke and begin to suffocate (asphyxia). These factors pose a serious danger to the child and a tragedy for the parents.
A baby may choke on his own saliva due to increased salivation during teething.
- The baby often chokes in the first months of life, since he is not able to control his breathing and eat at the same time, so he choke on breast milk, artificial formula, and water. Such feeding methods are new for a newborn, so it takes time until he learns to perceive them correctly so as not to choke.
- A baby may choke if there are problems with the nervous and endocrine systems. Diffuse goiter causes frequent coughing, excessive production of saliva, and as a result, the baby gags. If this happens regularly, it is better to consult a neurologist and endocrinologist. Also, problems with the thyroid gland can be determined by the results of screening of newborns in the maternity hospital.
- The baby may choke when burping after feeding. Therefore, the baby can be put into bed only after he has burped.
Note! Regardless of whether burped after feeding or not , in the first months of life he should be put to sleep strictly on his side, alternating between them for safety. If a baby regurgitates leftover food, he will not choke on it.
After regurgitation
, the risk of the baby choking is minimal.
- Pieces of food or a foreign body have entered the baby's respiratory tract. This happens if parents practice early complementary feeding (4-5 months) or do not take care of their baby’s toys. It is important that small objects such as rattles, bread crumbs and other adult food do not get into his hands.
- The baby often gags if his nose is stuffy. The cause of this can be a physiological runny nose or a runny nose of a cold nature. If you hear sniffling, sniffling of the nose or the presence of mucus in it, you need to ease your breathing with the help of vasoconstrictor drops Naphthyzin, Vibrocil, and then continue feeding.
Advice! Do not shake the child when he is coughing as if he is choking, this can lead to a severe coughing attack . A cough indicates that the baby's airways are clear. To make it easier, you can lightly tap on the back.
When you need a doctor: signs that a child is choking
A baby may choke on a small toy, food, or milk
You can determine that a baby has choked on something by looking at some symptoms, and if you notice them, it is important to immediately provide first aid:
- wide eyes indicate fear of the baby;
- the child tries to take a breath, but to no avail, while his face acquires a bluish tint; tries to take a breath, but to no avail, while his face takes on a bluish tint;
- the baby vigorously waves his arms and legs;
- you can’t hear a cough or cry, because a foreign object is bothering the baby and blocking the access of air to the respiratory tract;
- whistling and wheezing are heard in the throat;
- There is a lot of saliva in the oral cavity;
- loss of consciousness from lack of oxygen.
These signs require immediate action to save the child's life. At this moment, an urgent call for an ambulance is necessary, and until it arrives, take personal control of the situation.
Children say! They read the fairy tale “Kolobok” to my brother. The book was with pictures and colorful. In the middle of this story, looking at this Kolobkov illustration, he asked:
-Who cut off this head?
Massage and ventilation
Artificial ventilation of the lungs is carried out using the “mouth to mouth” method.
After inhaling and pressing your mouth to the child’s mouth, blow air into his lungs, while pinching the victim’s nasal passages. The frequency of insufflations during resuscitation of children under one year of age should be 38–40 exhalations per minute, for older children - 20–24 exhalations.
After finishing the inflation, you need to make sure that the baby’s chest is lowering. If the air does not enter the lungs, but does not come out into the stomach and back, then with each blowing the upper part of the abdomen will rise.
Photo: AiF
Indirect cardiac massage will help maintain at least minimal blood circulation.
The child should lie on a hard surface (bench, floor). To improve blood flow to the heart, elevate his legs and place something under them.
If the child is under 8 years old, place the palm of your left hand on the lower third of the sternum along the midline and apply rhythmic pressure at a frequency of 80-90-100 times per minute. The sternum should bend under your hand by 2.5–3.5 cm.
For children over 8 years old, massage is performed with both hands: place your left palm on the lower third of the sternum, place your right palm on top and press on the sternum with a frequency of about 80 movements per minute so that the sternum moves by 4-5 cm. Keep your arms straight!
If two people provide assistance, then one of them “breathes” and the other performs a cardiac massage; from time to time they should replace each other. You need to act in the following rhythm: 30 pressures on the chest, then 2 blows into the airways.
When providing assistance alone, the rhythm of actions is maintained: 30 to 2. Resuscitation should be carried out for 25–30 minutes or until the ambulance arrives.
Do not forget about the need to warm the victim: remove wet clothes from him, wrap him in a blanket.
By the way
Signs of the effectiveness of resuscitation measures: disappearance of cyanosis, pallor, marbling of the skin; the appearance of a pulse in large vessels (carotid, femoral); constriction of the pupils; the appearance of spontaneous breaths.
Baby choked on milk
To prevent the baby from choking on milk during feeding, the mother must follow some rules:
- choose the right position for breastfeeding; the baby cannot be in a strictly horizontal position;
- first express the milk that has arrived so that streams of milk do not pour out on their own;
- Be sure to exclude the presence of foreign objects in the child’s mouth (crumbs of bread, leftover fruit).
When your baby does choke on milk and you hear a cough, there is nothing to worry about. The child is normal, but if the baby begins to choke, urgently begin to restore his breathing. See instructions below.
If a baby chokes on milk or leftover food after feeding, it is important to act immediately
A child chokes on saliva: how to deal with this?
The causes of increased salivation in newborns and infants up to one year old are different: from teething to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system.
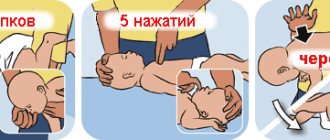
When the baby begins to choke, you need to turn his back to you, then press your hand on the stomach area. Next, tilt the baby forward a little and pat your palm between the shoulder blades.
You can also clear the airways of saliva while lying down:
- Place the baby on the back, with the head lower than the body (place a bolster or pillow under the back);
- Using two fingers (index and middle), you need to make 5 presses under the baby’s sternum. Make sure that after pressing the chest is completely leveled.
First aid if a newborn chokes
You need to act in strict sequence. First of all, try to open the baby’s mouth and look where the foreign object or food remains are located. If this fails, carefully turn the baby upside down by the legs and lightly pat the palm of your hand between the shoulder blades. If this does not help and the situation is getting out of control, we proceed to emergency measures.
Blueness of the baby's facial skin indicates that the baby has stopped breathing
Instructions for rescuing a choking child
The main rule is absolutely no panic!
- We turn the baby over with his tummy down and place him on his forearm so that his face is in your palm and below his butt.
- Carefully, between the shoulder blades, we make five pushing sliding movements from the lower back to the chest, provoking muscle contraction and the release of the object from the respiratory tract.
- When the previous steps did not help, we turn the baby upside down and apply five pressures on the sternum.
- Observing the blueness of the skin of the face, we begin mouth-to-nose artificial respiration; with each inhalation, place your palm on the child’s chest. This is necessary in order to feel whether air is entering the lungs. At the same time, the baby's chest should rise.
Be sure to look at the photo instructions.
Correct position for a baby during first aid after choking
Note! The listed actions must be performed without delay until the ambulance team arrives. It is important that at least some of the air gets into the little patient’s lungs.
What to do if the child begins to choke?
If your child is coughing, he should be encouraged to continue coughing. Trying to help your child in any other way may push the object deeper into the throat. However, if the child cannot breathe, it means that the object has completely blocked the child's airway and immediate action is necessary. You should call emergency services as soon as possible.
If your child is under 1 year old, you can do the following:
- Place the child face down on the adult's arm so that the head is lower than the body. Make sure the baby's head is supported and in a safe position. Avoid putting pressure on the baby's back or neck.
- Using the palm of your other hand, deliver five strong blows between your shoulder blades. The spanking should be strong enough to help dislodge the object from the child's airway.
- If the object does not move, place the child on a hard surface. Place two fingers on your baby's chest at about heart level and press five times at a fast, firm pace to supply oxygen to the body.
- Continue alternating back blows and chest thrusts until help arrives.
If the child becomes unresponsive or unconscious, you need to focus on providing oxygen to the child's body and do the following:
- Place your baby on his back on a firm, flat surface with his head and neck in a neutral position.
- Place two fingers in the center of the baby's chest and apply firm pressure. Repeat 30 times at a speed of about 100 thrusts per minute.
- After 30 chest thrusts, check to see if the object comes out. If not, give the child oxygen. Breathe lightly into your baby's mouth twice.
- Alternate between 30 pushes and two breaths until help arrives.
What parental behavior is unacceptable?
In a dangerous situation, when a baby often chokes on food or foreign objects, it is necessary to act correctly. However, not every mother follows exactly all the measures in a panic. It should be remembered that you should not knock a choking newborn on the back if he is in an upright position. These actions provoke the foreign body to move even deeper into the respiratory tract.
It is not recommended to remove the object from the baby’s throat yourself using different objects or hands. This often makes the situation worse, leading to tragic consequences. Such actions are permissible if the foreign body is still in the oral cavity.
Water in the lungs
It is advisable to pull a drowning person out of the water with the help of a rope, a stick, a lifebuoy... A drowning person is always in a state of panic and can grab the lifeguard with a death grip and drag him with him to the bottom. Therefore, when rescuing a drowning person, do not forget about your own safety.
If a person falls or jumps into cold water, he experiences a reflex spasm of the glottis, and water does not enter the respiratory tract. The cause of death in this case is mechanical asphyxia - oxygen starvation. And although they will say about such a person that “he drowned,” this type of drowning is called “dry” or asphyxial. If the victim was able to be immediately removed from the water, then in most cases it is possible to bring him back to life with the help of artificial respiration.
True, or “wet” drowning occurs as a result of water entering the lungs. Before starting artificial respiration, it is necessary to clear the upper respiratory tract of water, sand, silt, and vomit. The rescuer goes down on one knee, and on the other knee puts the victim head down on his stomach and inflicts 3-4 push-like blows between his shoulder blades.
Don't try to remove all the water from your lungs. This requires extra time that you don't have right now. The main thing is to bring the child back to life with the help of resuscitation measures, and the water will resolve later.
Security measures
In order to prevent a newborn and a child up to one year from getting food into the respiratory tract, preventive measures should be observed. To do this, be sure to keep an eye on:
- the baby’s health condition (after all, nasal congestion and Quincke’s edema can also cause suffocation
- ensure perfect cleanliness in the room where the child spends most of his time; no small objects are allowed within the child’s reach;
- when introducing complementary foods, it is advisable to give the baby chopped fruits and vegetables or give food in a nibbler (a device for safe complementary feeding);
- From infancy, teach your baby not to take toys or various objects into his mouth, do not allow him to play around during feedings;
- do not force the baby to eat if he does not want to, it is also important not to offer him cookies, fruits, bagels during play;
- delay the introduction of bakery products into complementary foods until the last minute;
- Do not feed your newborn in a strictly horizontal position; the head should be slightly elevated.
It is unacceptable to tilt the baby too much to clear the airway.
Prevention
You can reduce your child's risk of choking by:
- Feed the baby only in the presence of an adult, do not feed it in the car or crib
- feed the child in a sitting position, not allowing him to play while eating
- keep small items out of reach
- Do not give your child toys with small parts, especially in a stroller or crib
- do not give children popcorn, chips, candy, chewing gum
- attend an infant first aid and CPR class
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
E. Komarovsky urges parents not to be nervous in this situation; panicky behavior frightens the baby even more, which causes the movement of a foreign object or food deep into the respiratory tract.
Due to improper actions, bacterial pneumonia may develop after food debris enters the respiratory system. This is due to the fact that pieces of food or milk may have entered the lungs. Therefore, E. Komarovsky recommends not to experiment, but to provide first aid according to the instructions.
For more detailed information, watch our video, in which E. Komarovsky comprehensively reveals the topic of how to help a baby if he has choked on water, milk or a foreign small object.
What to do if there is water in a child’s lungs?
Let's look at a case where there is still water in the lungs, and talk about how to eliminate this problem.
In this case, it matters where exactly the child swallowed the water. If it was an open body of water, in which, in addition to water, there is also sand and dirt, then there are almost certainly remnants of these substances left in the child’s mouth, and they need to be removed there. If a child takes a sip of water in the bath, then most likely the oral cavity will be clean and no additional procedures will be needed to clean it. In order to remove dirt from the child’s mouth, you need to wrap gauze around your finger and use it to carefully remove any remaining mucus and dirt from the child’s mouth.
In order for the water to leave the lungs, you need to turn the child facing the floor and rest his chest on his knee. This will allow the baby's head to hang down and allow water to escape. In order to facilitate the passage of water from the lungs, you need to pat your back with your hand or apply a little pressure on it. Such actions are also appropriate if the child is choking (young children can choke on milk)