The appearance of a child’s first teeth is an important event in every family. It brings with it many troubles that are temporary. Fever, loose stools, problems with the digestive system, and anxiety are accompanying symptoms that will not harm the baby. However, every mother needs to know that everything should be within acceptable limits. It is important to monitor the child and react in time to developing deviations.
Symptoms of teething
The very first tooth appears when the child reaches 6 months. This process lasts about two years, or a little longer, depending on the child’s body. Each baby experiences teething differently. For one, everything will be easy and almost painless, for another it will be painful. Each child is unique, so parents should be attentive and monitor the well-being of the baby. When the crowns of the first teeth begin to erupt, the local immune defense reduces its functions. Therefore, pathogenic microorganisms enter the baby’s body, causing physiological stool disorders.
During this period, it is necessary to be attentive to the child’s condition and recognize in time that the appearance of loose stools is not associated with an inflammatory process caused by an infection. During the natural physiological process of teeth formation, symptoms are identified that do not cause harm to health.
Features of feeding and drinking regime of infants during teething
Chickenpox or not? Can diarrhea occur with chickenpox?
If your baby's teething is accompanied by diarrhea, then you need to feed him properly so that there are no problems with digestion.
In such cases, the child is provided with plenty of fluids to prevent dehydration. We have already discussed above why it is dangerous and how it manifests itself. Moreover, if he does not want to drink a lot at once, then you can offer liquid in small doses. For example, give water to drink from a spoon or from a dispenser for antipyretic drugs. If the child is breastfed, then this issue is resolved differently; with artificial nutrition, you cannot change the formula, do not overfeed the child, but if necessary, increase the frequency of feeding.
If the child is more than six months old and has already been introduced to complementary foods, then do not temporarily add anything new to his diet. The baby needs to be fed frequently; food must be thermally processed and thoroughly pureed.
Other feeding tips for teething diarrhea in babies over 6 months include:
- do not let them drink juices;
- do not feed fatty foods;
- vegetables and fruits should not be raw, only after heat treatment;
- do not give the baby anything that would promote fermentation;
- If you are no longer breastfeeding, limit dairy products;
- Light porridges and soups with water are recommended.
When a child suddenly begins to have loose stools, this may not necessarily be due to teething. In such cases, be sure to remember what you fed the baby the day before; loose stools can be caused by inappropriate food. In particular, allergies to certain foods can also manifest themselves in the form of loose stools.
In this case, don’t force your baby to eat if he doesn’t want to, even if he loses a little weight, there’s nothing wrong with that. Over time, the child will meet his own need for food, but dehydration can be dangerous. For this reason, he must be forced to drink, but he cannot be forced to eat. And all other actions must be coordinated with a specialist.
Increased salivation
A natural protective property of the body that disinfects the child’s oral cavity. At a young age, children actively put various objects in their mouths that come their way. Thus, bringing various bacteria into the body, which the immune system fights, releasing large amounts of saliva. This is due to the fact that nature has the property of disinfecting wounds and injuries by wetting with saliva, which contains an antibacterial enzyme (lysozyme). Therefore, excessive salivation is not considered a pathology, but, on the contrary, protects the baby from pathogenic bacteria.
Swelling and redness of the gums
Swelling, swelling, and an increase in the size of the baby’s gums are accompanied by discomfort (pain, itching). At this time, children try to chew on what is within walking distance, thereby trying to eliminate the unpleasant sensations that have arisen. All this is explained by the fact that an inflammatory process occurs in the area of the emerging tooth. Bone tissue forms inside the jaw, so it is necessary to push through the gum to appear on the surface. When swelling and redness are accompanied by profuse salivation, and a white bubble is also detected, this indicates that a baby tooth will soon appear.
Changes in behavior
This period is characterized by changes in the baby’s behavior. Children are capricious, sleep poorly, refuse to eat, and show apathy. This is due to the fact that the appearance of a tooth causes itching and pain, which bring great discomfort. At night, all symptoms become more active and cause concern not only for the child, but also for the parents.
Desire to gnaw
The baby has a need to chew as a result of severe itching and discomfort in the gums. The child puts toys and any other things into his mouth that can relieve the itching sensation. The harder the object, the better it eliminates itching when rubbed against the gums. This whole process is temporary, so the child is constantly looking for a new object that will help relieve unpleasant sensations. Many companies produce special teethers with various cooling effects that help babies go through this period with the least discomfort.
Increase in temperature, appearance of cold symptoms
This is due to the fact that during this period the body tries to produce the required amount of substances that can facilitate the growth of baby teeth. It is also possible that an infection or local inflammation may occur, during which the glands are activated and muconasal secretion (nasal mucus) appears, disappearing after a couple of days. The local inflammatory process provokes the body, which reacts and leads to fever and malaise. The main indicator that there is no serious illness is a temperature not higher than 38 degrees. When teething, sometimes a rash appears on the skin, nasal congestion, and a slight cough, which is caused by a large volume of salivation. A cold may occur less frequently, but this is due to a decrease in the body’s protective functions during periods of active viral infection.
Teething: main symptoms
Examination of the baby's oral cavity will help to partially eliminate the possibility of bowel disorders. Komarovsky and other pediatricians include the following changes as symptoms of teething:
- increased saliva production as a protective reaction against pathogenic microflora entering the body;
- swelling and increase in the size of the soft tissues of the gum shell;
- itching in the area of teething and pain in the gums, trying to eliminate which the child gnaws on various objects, since the pressure they exert on the tissue helps the pain disappear;
- the appearance of discernible contours of the future tooth under the soft tissue shell;
- at the same time, the primary stage of tooth growth in a child may be accompanied by weakness, increased body temperature and general malaise.
Swelling gums
Despite the increase in the size of the soft tissues, their redness and the presence of some loosening of the structure at the site of the tooth exit, one should be very careful about the nature of the swelling. A stressful situation can cause a decrease in immunity, which greatly increases the risk of not only diarrhea, but also infection with pathogenic forms. Alarming symptoms are the presence of inflammatory processes in the child’s oral cavity, if detected, parents should immediately consult a doctor.
Child's anxiety
Changes in the child's behavior, crying and whims are also associated with the pain that the baby experiences when teething. The described symptoms can manifest themselves at night in the form of sleep disturbances, when the intervals between the baby's sleep and wakefulness are reduced. The nervous system of children reacts to stress with increased excitability; during this period, it is important for parents to be sympathetic to the child’s whims and understand their nature.
Fever
Individual symptoms of teething in a baby may include a fever of up to 38°C, a rash and nasal congestion.
An increase in temperature is a reaction of the immune system to a violation of the integrity of the gum structure when a tooth appears. If an elevated temperature in children during the period when teeth are being cut persists for 3 days or more, it is necessary to consult a doctor to determine the cause of the disease. Read also: How the upper teeth erupt
Diarrhea with the appearance of teeth has its own characteristics, which include an increase in the number of bowel movements, the absence of visual and structural changes in the stool. Alarming symptoms include the watery consistency of the child’s discharge, the presence of blood or foreign inclusions in the stool. If the color of the stool changes to black or if it has some kind of green tint, you should consult a pediatrician.
Problems in the digestive system
One of the symptoms of the appearance of baby teeth is loose bowel movements. The stool becomes liquid because the volume of salivary fluid increases, as well as due to the penetration of bacteria that disrupt the microflora of the children's intestines. Regurgitation, flatulence, specific sounds in the stomach that last no more than three days, and bowel movements no more than four times a day are considered normal manifestations of the body. If the symptoms are of a different nature or for a long period, then you should immediately contact your pediatrician.
Important! During the teething period, the immune system weakens its protective functions due to the child's stress reaction. Due to weak immunity, there is a risk of contracting a serious infection, which is why it is worth carefully monitoring the baby and detecting a pathological abnormality in time.
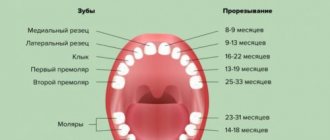
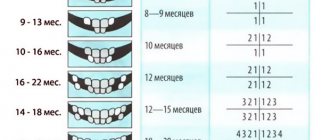
When does the first set of teeth appear?
The process of eruption of the baby’s first teeth depends on his physiological characteristics. But on average, growth begins at six months and ends at two and a half years.
Table. Stages of growth of the first set of teeth.
| Stage | Set of teeth | Approximate eruption interval |
| 1 | Central (medial) mandibular incisor | 6-8 months |
| 2 | Central (medial) maxillary incisor | 7-12 months |
| 3 | Lateral (lateral) incisor of the upper jaw | 12-13 months |
| 4 | Lateral (lateral) incisor of the lower jaw | 12-15 months |
| 5 | Maxillary small molar | 14-18 months |
| 6 | Mandibular small molar | 14-18 months |
| 7 | Maxillary canine | 15-24 months |
| 8 | Mandibular canine | 15-24 months |
| 9 | Large mandibular molar | 20-31 months |
| 10 | Maxillary large molar | 20-31 months |
The main causes of loose stool in a child
Doctors identify the main causes of diarrhea in babies, which are associated with the growth of the first teeth. Normally, all intestinal disorders should not last more than 3 days. If the child’s condition does not improve within this time frame, then it is necessary to urgently show the child to a doctor.
Table. Factors affecting the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
| Cause | Impact |
| Loss of appetite changes the amount of food consumed, but salivation continues. Saliva enters the gastrointestinal tract in large quantities, thereby increasing intestinal motility, diluting stool and causing loose stools. Due to increased salivation, diarrhea occurs up to 4 times a day. | |
| To get rid of the itching of aching gums, the baby puts various objects into his mouth that may contain bacteria. Many bacteria, penetrating into the child’s body, begin to actively multiply. Fermentation occurs in the intestines, followed by diarrhea. In such a situation, watery bowel movements are a way to cleanse the body of pathogenic microorganisms. In some cases, vomiting, chills are observed, and mucus and foam are found in the stool. | |
| When the first baby teeth appear, complementary feeding is introduced. The child is given fruit and vegetable juices, purees, meat purees, and milk, which can cause the development of diarrhea. The body is trying to adapt to new foods, but the digestion is not yet able to accept heavy food, so indigestion occurs. | |
| The body is in a stressful situation, regularly experiencing discomfort, so watery bowel movements are considered a response. |
How long does teething diarrhea last?
Teething diarrhea usually lasts no more than 3 days. During this time, the tooth appears on the surface of the gum, and the symptoms begin to disappear.
If diarrhea is caused by teething, the baby will usually have bowel movements up to 4 times a day. If infected, diarrhea may last longer, up to a week.
If your baby is teething, diarrhea may be accompanied by other symptoms. It is important to ensure that diarrhea is related to this factor. There is no specific treatment for teething diarrhea, but if complications occur, drug treatment is required.
Signs that require medical help
Sometimes a baby may undergo internal processes that are not associated with the appearance of baby teeth. These processes are very dangerous and can cause serious harm to a small organism. Since the child constantly puts everything in his mouth to relieve anxiety associated with teeth growth, pathogenic microorganisms can enter the intestines at this time. An intestinal infection is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- frequent bowel movements in liquid form (more than 5 times a day);
- abdominal pain;
- atypical color of stool;
- blood and mucous inclusions in feces;
- the structure of the stool is watery, foamy;
- frequent vomiting;
- high temperature, more than 39 degrees.
In addition to bacteria, a virus can enter the body, then the symptoms will be similar to a cold, only a few more points will be added:
- mucous discharge from the nose;
- coughing;
- heat;
- redness of the throat;
- weakness and increased sweating.
Important! In case of intestinal and viral infections, a pediatrician is urgently called to your home. The doctor prescribes medications after making a diagnosis. You should not give medications on your own without a doctor’s examination.
How can you tell if diarrhea is caused by teething?
In the case of diarrhea in a child, it is important to determine that it relates specifically to teething. This relationship can be identified by accompanying symptoms:
- swollen and swollen gums;
- restless state;
- drooling;
- increase in temperature;
- the need for hard objects to chew on;
- vomiting.
A bottle-fed baby may have constipation instead of diarrhea. During the appearance of baby teeth, the stool is usually watery and the stool is yellow-brown in color. A distinctive feature is the absence of impurities and excessively unpleasant odor. If there is bloating in the abdomen, peristalsis changes, and pain occurs on palpation, then the matter is not only in the appearance of the first teeth. An alarming factor is also the admixture of blood or mucus, the acquisition of a greenish tint in the stool.
Excessive drooling
Increased salivation provokes diarrhea, because only a small part of saliva flows out of the mouth. The main part of the secreted saliva is swallowed by the baby and causes intestinal peristalsis due to the dilution of feces. A supporter of this version is the best pediatrician of all times, the well-known Doctor Komarovsky. This part of the “aesculapians” believes that such diarrhea does not require any treatment. The tooth will erupt and it will go away on its own.
Any painful sensations in the body are evidence of the development of pathological phenomena. Depending on the specifics of the nerve endings involved in the process, symptoms range from increased body temperature to cutting pain. Read more in the article: “burning in the right side under the ribs in front.”
The saliva of living creatures contains a natural bactericidal component - lysozyme, which acts as an antiseptic and completely disinfects the oral cavity.
Swelling gums
It occurs as a result of inflammation, because bone tissue grows from the inside and is forced to push through the gums in order to crawl out. Swelling and local redness of any area of the gums in a child is as undoubted a sign of teething as drooling. It is especially significant if these two symptoms appear simultaneously.
Redness is always accompanied by the appearance of a white bubble - the precursor of a baby tooth. If a bubble has already appeared, it means that in 2-3 days the outline of the tooth will appear, and all the unpleasant symptoms that accompany teething will go away.
Anxiety and nervousness of the child, insomnia
When a tooth just begins to emerge inside the gum, the baby experiences painful sensations in the mouth, similar to severe itching. They really bother him and cause a change in behavior. A calm child suddenly begins to constantly be capricious and not sleep at night. By the way, it is at night that the manifestation of all these symptoms is activated.
A sweet taste in the mouth can be caused by a wide range of predisposing factors and in most cases indicates that some kind of disorder is beginning to form in the body. Read more in the article: “sweet taste in the mouth: what does it mean.”
Once the outline of the tooth has already come to the surface, anxiety should go away.
The desire to put everything in your mouth
When teething, inflammation of the gums causes itching, and the baby has a desire to scratch the gums. He puts into his mouth everything that comes to hand. And the child does not always get sterile things at hand, but rather the opposite. Therefore, the possibility of introducing an infection into the gastrointestinal tract increases significantly. And the baby’s diarrhea at this time is associated with an infection brought into the mouth by toys, rings, and, in principle, everything that he puts into his mouth. Also quite a digestible version that takes place.
Fever, cold symptoms
Any local inflammation and violation of tissue integrity is always accompanied by a general reaction of the whole body - fever and malaise. During normal teething, the temperature will rise no more than 38°C. It may also be accompanied by skin rashes and nasal congestion, which can also disturb the child's sleep. In rare cases, colds are associated (more often this happens when teething is associated with a period of activation of a viral infection).
Digestive disorders
This may include “fountain” regurgitation, flatulence, “gurgling” in the tummy and liquefied stool. It will last no more than 3 days (for one tooth to come out), and the number of “cleansings” should not be more than three to four times a day.
After analyzing all the symptoms and objectively assessing the baby’s condition, you can decide whether to call a doctor at home, or simply try in every possible way to alleviate the child’s condition and survive these difficult three days of his life.
The main task is to understand whether the “first tooth” is really the cause of the ailment.
Drug therapy for teething
During this period, the main thing is to provide the child’s body with a constant level of fluid so that there is no dehydration. The doctor prescribes medications aimed at pain relief, eliminating inflammatory processes, destroying bacteria and viruses, and maintaining the natural intestinal microflora. It is prohibited to decide on your own what medications to give, since before the age of one year you can cause great harm to the baby’s body.
Complex drugs with analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects
The pediatrician selects a set of products in the form of suspensions, ointments, gels, syrups, suppositories that have antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects. Medicines are also prescribed to relieve pain and allow the child to eat. Some products can be applied at night so that the baby and parents can rest, but the therapeutic effect will still be active.
Table. Analgesics, antipyretics for the appearance of baby teeth.
| A drug | Therapeutic effect | Dosage |
| Efferalgan (syrup, suppositories) | Antipyretic, analgesic | 10-15 mg/kg, 3-4 times a day |
| Paracetamol for children (suspension) | Antipyretic, analgesic | 10-150 mg/kg, 4 times/day |
| Ibuprofen (suppositories) | Antipyretic, analgesic | 5-10 mg/kg, 3-4 times a day |
| Ibufen (suspension) | Antipyretic, analgesic | 5-10 mg/kg, 3-4 times a day |
| Nurofen (suspension, suppositories) | Antipyretic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory | 50-100 mg, 3 times a day |
| Dantinorm baby (solution) | Painkiller | 1 ml, 2-3 times/day |
| Dentokind (tablets) | Painkiller | 1 tablet, 3 times a day |
| Kamistad (gel) | Painkiller | 0.5 cm, 3 times/day |
| Dentinox (gel) | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory | 1-3 drops, 2-3 r/day |
| Cholistal (gel) | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory | 0.5 cm, 2-3 r/day |
| Kalgel (gel) | Analgesic, anti-inflammatory | 7.5 ml, no more than 6 times a day |
| Panadol for children (suspension) | Antipyretic, analgesic | 15 mg, 3-4 times/day |
Important! It is necessary to strictly observe the dosage of the drugs, as well as follow the doctor’s prescription, only in this way the treatment will be effective and will not harm the baby.
Antidiarrheal drugs
Drugs are prescribed by a doctor to eliminate loose stools, as well as to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. The dosage is prescribed by the pediatrician depending on the severity of the disease. The drugs are given ready-made, some need to be diluted with water, but you should always strictly follow the dosage regimen.
Table. Antidiarrheal drugs.
| A drug | Therapeutic effect | Dosage |
| Enterofuril (suspension) | Antimicrobial | 2.5 ml, 2-3 times/day |
| Stopdiar (suspension) | Antimicrobial | 2.5-5 ml, 2-3 r/day |
| Smecta (powder) | Adsorbent, antidiarrheal | 3-6 g/day |
| Enterosgel (powder) | Adsorbent, detoxifying | 2-5 g, 6 r/day |
| Polyphepan (powder) | Adsorbent, detoxifying | 0.5-1.5 tsp, 3-4 r/day |
| Filtrum STI (tablets) | Adsorbent, detoxifying | ? tab, 3-4 times/day |
| Polysorb (powder) | Adsorbent, detoxifying | 2.5-1 tsp, 3 r/day |
Important! Some drugs help remove both harmful and beneficial substances. Therefore, it is necessary to take medications to normalize the intestinal microflora, which are prescribed by a doctor.
Medicines for flatulence
To reduce bloating and gas in the baby, medications are taken that help relax the intestinal muscles, reduce and eliminate gas formations.
Table. Drugs that reduce gas formation and normalize intestinal microflora.
| Drugs | Therapeutic effect | Dosage |
| Espumisan baby (drops) | Reduces flatulence | Prescribed by a doctor |
| Sub-simplex (suspension) | Reduces flatulence | 0.6 ml during feeding |
| Babycalm (suspension) | Carminative, antispasmodic, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial | 10 drops, 3-4 r/day |
| Bobotik (drops) | Reduces flatulence | 20 mg, 4 times/day |
| Linex (capsules) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | 1 capsule, 3 r/day |
| Bifiform (solution) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | Prescribed by a doctor |
| Bifidumbacterin (powder) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | ? package, 1-2 r/day |
| Hilak forte (drops) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | 15-30 drops, 3 times a day |
| Acipol baby (drops) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | 5 drops/day |
| Biobakton (powder) | Normalizes intestinal microflora | 2.5 mg, 2 times/day |
Drugs for dehydration
An important point when dealing with loose stools in an infant is to take medications that maintain normal water levels in the body.
Table. Preparations for dehydration.
| A drug | Therapeutic effect | Dosage |
| Rehydron (powder) | Correction of electrolyte and fluid imbalances | Prescribed by a doctor |
| Glucosan (powder) | Correction of electrolyte and fluid imbalances, elimination of acidosis | 10 ml/kg, 1 r/day |
| Hydrovit (powder) | Correction of electrolyte and fluid imbalances, elimination of acidosis | 3-5 sachets, 1 r/day |
| Reosolan (powder) | Correction of electrolyte and fluid imbalances, elimination of acidosis | 40-50 ml/kg, 1 r/day |
| Citraglucosolan (powder) | Correction of electrolyte and fluid imbalances | Prescribed by a doctor |
Medicines for allergic reactions
Sometimes, with an intestinal disorder, the baby develops a rash (urticaria), itching and redness of the skin. Your doctor may then prescribe medications to relieve symptoms of an allergic reaction.
Table. Antihistamines.
| A drug | Therapeutic effect | Dosage |
| Suprastin (solution) | Antihistamine, antiemetic | Prescribed by a doctor |
| Fenistil (drops) | Antihistamine | Prescribed by a doctor |
| Fenkoral (powder) | Antihistamine | 5 mg, 2-3 times/day |
| Tavegil (syrup) | Antihistamine | 2-2.5 ml, 2 times/day |
Is it possible to prevent diarrhea during teething?
Diarrhea during teething can be prevented in the same way as any other complications. First of all, this concerns compliance with the rules of hygiene both for the oral cavity and in general.
Caring for your first teeth
The child's first teeth are exposed to quite aggressive pathogenic microflora. Moreover, it is often poor oral hygiene that leads to frequent diarrhea in children. It is worth noting that it is necessary to care for your child’s gums even before teeth appear. Especially for this purpose, pharmacies sell special wipes that can be used to wipe the delicate mucous membrane of a child’s gums without fear.
As for the first teeth, they can also be wiped with a napkin. In addition, in pharmacies you can buy special silicone brush pads that are placed on the finger . After a year, you can switch to a toothbrush and children's dental paste. At first, only parents should carry out the cleaning process. For older children, you can buy a special foam mouthwash.
General hygiene during teething
As for general hygiene, in this case experts recommend:
- if the child is breastfed, the woman should pay special attention to breast hygiene,
- when feeding a child with a bottle, it is necessary to regularly boil nipples and bottles, and also wash them using special detergents,
- It is important to wash your child’s hands after a walk. In addition, if the baby is actively crawling, the mother must always have antibacterial wipes with her,
- It is important to ensure that the child does not drink running water. In addition, it is worth remembering that all toys and fruits that reach the baby must be thoroughly washed with boiled water, but not from the tap.
The period of teething is a rather difficult and important period in a child’s life. Any complications raise many questions and concerns among parents. If you are faced with the situation described above, try to show your baby to a specialist as soon as possible. Remember that self-medication can be a direct threat to your child's health.
Natural remedies
The use of medicinal herbs has a beneficial effect on the baby’s body. Using natural ingredients, you can prepare teas that have an anti-inflammatory and restorative effect. At the same time, the manifestation of side effects is minimal. However, you should know that the use of natural remedies is an auxiliary action in the main therapeutic treatment.
Natural remedies that can be used during baby teething include:
- medicinal herbs (chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, mint, chicory, motherwort, black tea). Infusions are prepared from herbs, which are used to treat the oral cavity, make enemas, and also take orally. Such herbs have anti-inflammatory, antiseptic effects;
- massage the gums with a small amount of honey. Honey is a natural antiseptic, it has an anti-inflammatory effect, and at the same time enriches the body with vitamins;
- berries (blueberries, bird cherry). Dry berries are poured with boiling water, and the resulting infusion is given to the child. The infusion has an antiseptic and antidiarrheal effect;
- rice broth. Has a strengthening effect, soothes irritated intestines, reduces gas formation;
- banana. The fruit must be kept in the refrigerator and then offered to the baby. A cold banana perfectly soothes itchy gums, and also, when entering the child’s body, saturates it with vitamins.
Important! Traditional medicine is used only after consultation with a doctor, since many natural remedies have a high percentage of allergens.
How to help your baby?
Intestinal disorders and fever cause a lot of trouble. But itching and swollen gums cause particular discomfort to the child. There are now many remedies available to relieve teething symptoms in children.
- teethers with cooling gel
- dentinox gel
- kamstad gel baby
- dentinorm drops
- Traumeel C ointment
- fenistil drops
- Kalgel
Experienced mothers know that drugs from the pharmacy are not the only help in eliminating the baby’s pain. When a baby is teething, caring parents advise:
- massage your gums with your finger
- wipe your gums with ice wrapped in cloth
- apply a weak soda solution (1 tsp per 200 ml of water) to swollen gums
- chew on a soft, damp terry towel
- invite the baby to chew on a cracker, an apple, a carrot, making sure that the child does not choke
Teething is an important and integral process in your baby’s growing up process. And you can make it as painless and comfortable as possible. Calmness, affection and a sensitive understanding of what your child needs will help you overcome all the difficulties of this period.
Traditional methods
These include herbs. Those that have minimal allergic effects can be prescribed to the baby. The most popular is chamomile. A tablespoon of dry herb is brewed with a glass of boiling water, infused for fifteen minutes and given to the child one teaspoon of the strained solution up to five times a day before meals.
Chamomile has powerful anti-inflammatory properties and plays the role of a mild anesthetic. When bacteria enter the intestines, chamomile acts in its lumen, exhibiting its bactericidal effect, and to some extent is a natural replacement for antibacterial agents.
In addition to chamomile, the following herbs can be used:
- blueberry;
- St. John's wort;
- sage;
- bird cherry;
- mint, etc.
Herbs are by their nature strong allergens, even those that are recognized as suitable for children. The connection of any folk remedy to the main therapy must be discussed with the treating pediatrician, otherwise the consequences can be serious.
Compliance with diet and drinking regime
During the teething period, it is necessary to properly water and feed the baby, since dehydration and lack of nutrients are dangerous to the life and development of the baby. The main rule is little by little, but often. In this way, the body constantly receives vital nutrients.
Dehydration can be noticed by some symptoms:
- dry skin;
- peeling;
- pale skin tone;
- lethargic state;
- urine is rarely excreted;
- change in the color and odor of urine;
- There is an odor of acetone in the mouth.
Depending on the degree of dehydration, the doctor prescribes drugs to regulate the water-salt balance in the body, which are administered orally at home or in the hospital under a drip.
Complementary foods should be used very carefully so as not to provoke new attacks of diarrhea. During this period, you can give a little:
- fruits (banana, pear, peach);
- cereals (rice);
- boiled cow's milk (with caution);
- jelly from fruits and berries.
Fresh juices and fermented milk products are temporarily excluded from the diet, and vegetables are given only boiled in the form of puree.
Mom needs to eat nuts, which will have a strengthening effect through breast milk. Breast milk should be fed more frequently to avoid dehydration. If the child refuses, then in addition to the food, give boiled water using a teaspoon.
What to do and how to treat it?
Treatment of diarrhea in young children is mandatory. How long your stomach upset lasts depends on how quickly you take action. In this case, it is best to seek help from a specialist who can accurately determine whether diarrhea is associated with teeth or indicates another disease. In the event that loose stools are nevertheless caused by the teething period, you can resort to the following treatment methods:
- we will take medications that slow down peristalsis, and the results of treatment will be noticeable almost immediately,
- administration of prebiotics and probiotics. These are drugs that improve intestinal microflora, thereby activating the immune system and reducing the degree of intoxication. You can purchase such products at any pharmacy in the form of powder or drops,
- Provide your child with plenty of fluids. The fact is that prolonged diarrhea can provoke a state of dehydration, which will significantly worsen the child’s condition. In this case, you can drink both ordinary water and natural fruit drinks,
- start giving your child adsorbents. These are drugs that help neutralize the effects of toxins. They help if diarrhea was caused by poisoning or if diarrhea is accompanied by an intestinal infection,
- start taking immunomodulators. This point is especially important for children who are bottle-fed. Products in this category help restore natural immunity and effectively fight pathogenic microflora,
- take vitamin complexes. If the child is still too small and is breastfed, then the mother needs to take vitamins. In addition, a nursing woman should carefully monitor her diet, excluding spicy and fried foods, as well as foods that have a laxative effect, from her diet.
- Give your child a weak decoction of chamomile or sage, which helps stop the inflammatory process, destroy pathogenic microflora and fights diarrhea well. At the same time, it is important to remember the individual characteristics of the body and not give such a drink to children prone to allergies.
Important! If diarrhea does not go away for a long time, call your pediatrician immediately. Most likely the child has an intestinal or rotavirus infection.