What is the timing of teething?
Milk teeth erupt at a certain period in a child’s life. Not all parents know how long this lasts. It is important to determine the exact timing in order to understand what causes hyperthermia. The following main periods are distinguished:
- 5-6 months - first the lower, then the upper incisors appear, usually they erupt one by one;
- 9-11 months - upper lateral incisors;
- 12-13 months - lower lateral incisors;
- 12-16 months - chewing teeth, molars;
- 16 months - upper and lower canines;
- 18-24 months - second molars;
- 7-10 years - indigenous elements;
- 14 years and older - wisdom teeth.
Absolutely all teeth appear by 2-2.5 years. If a child's body temperature rises in the first 2 months after birth or after 3 years, this is not due to teething. With hyperthermia in the period from 4 months to 2.5 years, the indicators usually do not exceed low-grade fever.
The temperature does not rise above 38.5 degrees and lasts for a short time.
As a result of eruption, 16 teeth should appear. If parents have counted this number, this means the process has stopped. When the body temperature rises with all these teeth present, eruption is impossible. Then they look for the cause in an infectious or viral disease or other pathologies.
Every parent worries about their child and many begin to panic when he or she develops symptoms of some disease. Parents are not doctors, but they should know the general signs of disease in order to identify it from the very beginning of development and take treatment and preventive measures. Read more in the article: “Rubella in children - information for parents.”
Ways to alleviate a child’s condition without drugs
The methods listed below can be used as an independent measure if the child’s body temperature does not rise above 38.5ºC. If the thermometer reading is higher, then they can be combined with taking medications.
Ventilation of the room where the child is located
The air temperature in the room should not be higher than 22–23ºС. To maintain this regime, it is necessary to ventilate the room at least 3-4 times a day for 10-15 minutes. Naturally, the child must be dressed or taken out of the room for the ventilation period.
Ventilate the room more often
You should not leave your baby in a draft or lower the thermometer readings by leaving the baby under the fan. This can cause pneumonia.
Air humidification
Along with ventilation, air humidification should also be carried out. Humidity should not be less than 40–50%. Such indicators can be achieved by using special humidifiers, as well as by carrying out wet cleaning of the room. Floors, shelves, and toys must be treated.
You can use special humidifiers to humidify the air.
Maintaining optimal air humidity and temperature serves as a good prevention of viral and infectious diseases, helps strengthen the immune system, alleviate the child’s condition and accelerate the recovery process.
Drink plenty of fluids
This is important, because when the body temperature rises, the body becomes dehydrated, loses fluid, the water-salt and mineral balance is disturbed, and intoxication occurs. In addition, with such a symptom, children often refuse to eat, which aggravates the state of general weakness and malaise, because the body has nowhere to draw strength and energy from.
You need to give your baby food often and in small portions. You can give drinking water, fruit drinks, juices. If the baby is breastfed, then he needs to be put to the breast more often and under no circumstances should he be weaned from it during this difficult period.
During this period, it is important to give your child water to avoid dehydration.
If you give sweet drinks, then be sure to wipe the baby’s gums and tongue with special napkins, gauze or a silicone brush. Remember that sugars are a good environment for pathogenic bacteria, which, if they come into contact with damaged gums, can provoke a pathological inflammatory process and even cause caries on emerging teeth.
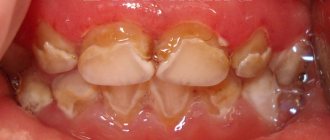
Signs of teething in a baby
Teething occurs normally in a child. That is, it is a physiological process. If you examine the baby’s oral cavity, you can see the following main signs:
- strong secretion of saliva that flows from the child’s mouth (this is a protective reaction of the body aimed at eliminating pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity);
- gums swollen, hyperemic;
- refusal to eat;
- chewing foreign objects, for example, TV remote control, toys;
- disorder of stool formation accompanied by diarrhea;
- Teeth may be visible on the gums, indicating their approach.
No other foreign formations should appear in the mouth. The child becomes whiny and irritable. He constantly demands the breast or bottle for food. This calms him down. Strong crying occurs throughout the day, but intensifies at night.
If the temperature is associated with teeth, immediately after teething the low-grade fever will end. This distinguishes it from a cold. The indicator will return to normal, the child will stop crying often and being restless. The condition is often observed during the eruption of fangs. But in some children it can appear on all teeth.
The substance codeine is obtained semi-synthetically from opium. When compared to other substances in terms of action, codeine is similar to morphine. It has a pronounced therapeutic effect, but if the recommended dosage is significantly exceeded, it becomes a drug. Read more in the article: “Cough tablets with codeine.”
What temperature should be lowered in an infant?
Let us immediately note that you should not lower the temperature to 38 °C, allowing the immune system to cope with the change in the body on its own. Parents should regularly monitor the general condition of the baby. If the temperature has risen above this level and the child is constantly crying or lying exhausted, you should not ignore its increase, because protein begins to coagulate in the baby’s body.
Many mothers complain that their children’s teething temperature reaches 38-39°C. In these cases, you should monitor the thermometer readings at least once every 2 hours. A high temperature in a baby is a symptom not only of teething, but also of a concurrent cold or infectious disease. In any case, it is worth calling your local pediatrician to examine and listen to the child.
Category Children Published by Mister stomatolog
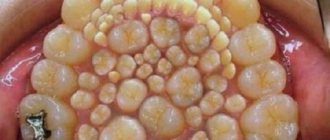
Teething symptoms in older children
By the age of 7-8 years, the second stage of teeth appearance begins. The milky elements fall out and are replaced by radical structures. This process is tolerated by children much easier than in infancy. There is practically no pain syndrome, since there is already a hole in the gum and it is not damaged. But the following discomfort signs may develop:
- aching sensation in the mouth;
- severe itching in the gums;
- insomnia or taking a long time to fall asleep at night;
- lack of concentration, absent-mindedness;
- swelling of the cheek;
- in rare cases, a slight rise in temperature to 37-37.5 degrees.
Negative signs in the child quickly disappear. But it is important to ensure that infection does not penetrate into the hole where the baby tooth used to be. If a child has a tendency to pathology, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with furatsilin, chamomile, and other herbal antiseptics. Most products not only have disinfectant properties, but also relieve inflammation.
Typically, the filling of the oral cavity with radical elements occurs closer to 10 years. In some children the process may occur delayed. But most cases end quickly and painlessly.
How long does the temperature last
When a new tooth, and especially a canine tooth, is emerging, hyperthermia is common. But here we are talking only about averages. If a child develops a real fever, it is imperative to contact a specialist as soon as possible.
The temperature of 37ºC, which most often accompanies the appearance of fangs in babies, can be left undisturbed. In this way, the body fights the inflammatory process, which guarantees rapid healing of the wound around the tooth. But given that no medications will be used, hyperthermia may drag on.
As for how long the temperature lasts during teething, the duration may be different for each child. It all depends on how strong the baby’s immune system is, whether there are concomitant illnesses and how many teeth have erupted. There are also cases when the temperature can remain at 37ºC for up to a week. This happens when several teeth are cut at once. Nevertheless, such phenomena are quite rare. Generally, hyperthermia during the appearance of teeth, including fangs, lasts no more than 3 days.
Signs of pathologies in the mouth
More often in infants, increased salivation and low-grade fever mean teething. This is not always true. If the following symptoms appear, it is recommended to look for the disease:
- coating on the tongue (gastritis, colitis);
- white growths on the gums (stomatitis);
- bad breath (pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract, tonsils, adenoids);
- small or large wounds caused by mechanical damage, infection;
- bleeding of soft tissues;
- severe swelling of the cheek caused by the accumulation of exudate in the inner part of the tissue (for example, with flux).
Symptoms develop due to bacterial or fungal infection. Children at this age often chew on foreign objects and toys. If they have sharp edges, there is a high risk of mechanical damage to the gums.
If you are unsure of the cause of the child’s negative condition, it is better to consult a pediatrician.
It is important to identify the infectious process in a timely manner so that bacterial or fungal infection does not spread throughout the internal tissues. This is fraught not only with damage to the mucous membrane, but also with the development of purulent formations. Pathologies are more difficult to treat and are more difficult for the child to tolerate.
When fever is a reason to see a doctor
When teething, the immune system is weakened, so the baby can easily become infected with acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, rotavirus infection and other diseases. This is already dangerous and requires seeing a doctor. To recognize the pathology, it is important for parents to know how many days the temperature lasts, to what levels it rises and what symptoms are accompanied.
If the temperature rises to 39–40ºС, is poorly controlled by antipyretics and quickly rises again, lasting for more than 2–3 days in a row, then this is a serious reason to consult a doctor. Often other signs of serious illness are added to the temperature. Let's list them:
- fever and cramps,
- vomiting and diarrhea that is black or green mixed with blood,
- dry frequent cough, wheezing and gurgling during breathing, difficulty breathing,
- sticky white, yellow or green nasal discharge
- long-term refusal to eat: more than 1 day,
- putrid odor from the mouth,
- the presence of ulcers and ulcers in the mouth,
- general malaise, weakness,
- pale skin, cold hands and feet,
- the child has a history of chronic diseases.
If you have additional symptoms, you should consult a doctor.
In all of the above cases, you should not hesitate to consult a doctor, as they may indicate not only a banal ARVI or poisoning, but also stomatitis, candidiasis, internal diseases of the body, or an exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Signs of wisdom teeth erupting
Teething does not always happen in children. When it comes to wisdom teeth, the age is determined from 14 years and older. Usually the process is completed by 30-35 years. The molars are large in size and slowly move up the soft tissues. This causes the following negative symptoms in patients:
- increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees;
- an increase in body temperature above 38 degrees, if the eruption of wisdom teeth is accompanied by suppuration of the soft tissues due to the proliferation of infection;
- inability to chew food because the tissues are swollen;
- extensive swelling of the cheek;
- the lesion hurts at any time of the day, but the discomfort intensifies after eating food due to prolonged chewing;
- runny nose caused by the accumulation of immune cells in the nasopharynx during inflammation in the oral cavity.
Most wisdom teeth erupt very slowly. Then the inflammation develops less, the swelling is minimal. If the process occurs at a rapid speed, acute pain occurs. Wisdom teeth are dangerous not only because of their eruption, but also because of the tendency of this area to form gum pockets filled with purulent exudate. This happens when food gets under the gum.
In rare cases, molar eruption may be pathological. For example, the molar is not turned up, but to the side. It damages the adjacent tooth as it grows. It is recommended to remove such elements in a timely manner. They are detected using radiography.
Comments
Do children have fever when their permanent teeth are coming in?
Mom_Olya (06/01/2020 at 16:08) Reply to comment
- Children whose permanent teeth are cutting rarely suffer from an increase in body temperature against this background. However, the temperature begins to rise if an infection occurs, the child gets sick with ARVI or other diseases.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (06/07/2020 at 09:21) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Diagnosis confirmation
Parents will not always be able to understand why their child’s temperature has risen. Then it is recommended to consult a pediatrician to confirm the diagnosis. At an early stage, pathologies are easier to eliminate. Hyperthermia does not always occur against the background of teething.
When it comes to small children whose baby teeth are just developing, X-rays are not taken.
Excessive radiation negatively affects health. You just need to get examined by a pediatrician or dentist. If the temperature persists for more than 3 days, other negative symptoms occur, a smear is taken to determine the presence or absence of infection. When the doctor cannot accurately determine the cause, the condition continues to worsen, an x-ray is prescribed.
For older children, the range of diagnostic procedures has been expanded. For their age, acute pain when the root elements occur is not typical. The following diagnostics are recommended:
- examination by a pediatrician or dentist;
- radiography of the jaws;
- bacterial culture of a nasopharyngeal swab;
- opening of swollen gums if internal suppuration is suspected.
After completing the diagnosis, the correct treatment is prescribed. Thanks to the examination, the cause is accurately understood without giving the child unnecessary medications. If the discomfort and low-grade fever persist after completion of therapy, laboratory and instrumental examinations are repeated.
What to do when the temperature rises?
If a child develops hyperthermia due to teething, no specific treatment is required. The condition passes quickly, but many children have a hard time bearing it. If only a slight low-grade fever develops, antipyretics are not used.
In rare cases, the temperature may rise above 38 degrees. Only then do doctors allow the use of antipyretic drugs. The following medications are used:
- Nurofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug based on ibuprofen, which simultaneously reduces body temperature, eliminates inflammation and pain;
- Paracetamol is an antipyretic with much fewer side effects than NSAIDs.
Most medications that eliminate teething hyperthermia contain ibuprofen or paracetamol. They may differ in name, but the active substance remains the same. It is important to choose the right shape. For children under 3 years of age, a syrup form is recommended. After this age, tablets are used. Injections are not used during teething.
Antipyretics are used in a short course. Excessively long use leads to adverse reactions. This is especially true for NSAIDs, they negatively affect the gastrointestinal tract.
What can be the temperature during teething?
As for whether there can be an elevated temperature in children during teething, this phenomenon is not uncommon. But real fever when teeth appear in a child is rarely observed. Basically, these are average indicators that are not life-threatening, but nevertheless cause very unpleasant symptoms, including aching joints, muscle pain, increased drowsiness and moodiness. When baby teeth appear, infants may have a temperature of 37.5ºC. This is a temperature that, according to most, does not require medical intervention. Minor hyperthermia does not cause serious discomfort, so you just need to monitor the baby’s health and periodically take measurements to know for sure that the indicators have not risen to higher levels. It is possible that the temperature will simply return to normal, but there are also cases when hyperthermia can remain at an average level for quite a long time, and then the thermometer readings begin to rapidly creep up. This is already a reason for concern and the use of special antipyretics.
In some children, the temperature immediately rises to 38ºС - this is already the point when it is worth using medications.
It is advisable to use drugs that have already been used before and did not cause adverse reactions in the baby. If possible, if the temperature rises from teething to more than 38ºC, you should consult a doctor.
In the case when a child immediately develops a temperature of 39 ºС, you should definitely call an ambulance. Sharp hyperthermia to very high values is not typical for teeth, including canines. Therefore, most likely, we are talking about some kind of disease, possibly a very dangerous one. Therefore, there is no need to waste time. It is better to consult a doctor immediately to get the correct diagnosis and treatment.
How to help with teething?
Measures of treatment and assistance with teething depend on the age of the patient. If it is a baby, the condition is difficult to tolerate. Many drugs are not available for this group of patients. For adult children, completely different therapy is prescribed. All methods are listed in the table.
| Method of therapy | Young children | Older children or adults |
| Painkillers | Anesthetic gels applied to the gums. For example, Kalgel, Kamistad. They act locally, so the risk of side effects is reduced | Topical gel applied to the gums. If the pain is unbearable, take a non-opioid analgesic. NSAIDs relieve pain, fever, inflammation (Ibuprofen) |
| Herbal decoctions | The method is rarely used; it is impossible to predict allergies. Use chamomile or calendula lotions. They have a disinfecting, anti-inflammatory effect | Rinse your mouth with a decoction of chamomile, calendula, celandine, and oak bark. |
| Rinse with antiseptics | Not applicable | Furacilin, Chlorhexidine. Destroy pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity, preventing infection of the socket |
| Doctor's help | Not used, teeth erupt on their own | If eruption is difficult, use a scalpel incision in the gums. The method is used for purulent infection |
If a runny nose, diarrhea, or hyperthermia persists after the tooth appears, look for another cause. Conditions require different treatments. For example, using antibiotics.
Why is teething accompanied by hyperthermia?
When a tooth erupts, an inflammatory reaction occurs at the site of gum damage. Immune cells accumulate in this area to protect this part of the mouth from bacteria and fungi. This forms swelling. Chewing becomes difficult and appetite disappears.
Severe pain, the influence of the immune system, and constant lack of sleep in the child lead to an increase in body temperature. It can last 1-3 days. But this is where it always ends and goes back to normal. This distinguishes it from pathologies that form in the oral cavity.
Low-grade fever (value 37-37.5 degrees) is not eliminated in any condition. It means that the body is fighting against some damaging factor, therefore it activates all its forces. Even if the condition is caused by a viral or bacterial infection, antipyretics are not recommended. The same applies to the appearance of new dental elements.
If hyperthermia rises above 38 degrees, it is important to determine the true cause of the condition. When it comes to teeth, use only an antipyretic. If a bacterial infection is present, local or systemic antibiotics are additionally prescribed.
Why is the thermometer creeping up?
When teething, the gums are injured and a local non-infectious inflammatory process occurs, to which the immune system responds by increasing body temperature. This phenomenon cannot be considered dangerous, but it must be treated very carefully, remembering that the baby has weak immunity, which decreases even more during teething.
How many days does high fever last during teething?
During this period, the baby can catch an infection from nearby people or introduce bacteria to the inflamed area, then the temperature will be considered a sign of a disease that requires seeing a doctor and drug treatment.
At a temperature of 38–38.5°C, the body produces interferon, which fights viruses and bacteria. The level of this protein in the blood becomes maximum on the 2-3 day of illness or illness. If the fever is constantly reduced, the body stops producing the amount of protein necessary for a quick recovery, and the painful condition will drag on.