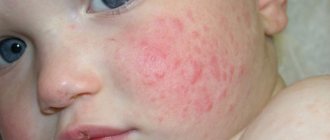
Infectious inflammation of the eyes sometimes occurs immediately after the birth of a child. The disease is easy to recognize by external signs. If you start the treatment prescribed by your doctor on time, the disease will pass quickly and without consequences.
Conjunctivitis is a disease that can be one of the first to appear after birth. The bacterial inflammatory process sometimes begins within 1 month of life. The biggest danger of conjunctivitis in a 1-month-old child is complete loss of vision. Therefore, it is extremely important, as soon as signs of inflammation appear, to immediately seek help from a specialist.
Causes of conjunctivitis in infants
If the disease develops immediately after the child is born, it could be caused by:
In this article
- Causes of conjunctivitis in infants
- Types of conjunctivitis in a month-old baby
- Symptoms of conjunctivitis in infants
- Dacryocystitis in newborns
- Treatment of conjunctivitis in a one-month-old baby
- Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in infants
- Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in infants
- Treatment of allergic eye inflammation in newborns
- Prevention of ophthalmic inflammation in newborns
- Infected amniotic fluid. Since during pregnancy, mother and child have a single blood flow, it is possible for the fetus to become infected with an intrauterine infection. Infection also occurs during passage through the birth canal.
- The presence of gonorrhea in the mother. The causative agent of gonorrhea, the microbe gonococcus, enters the baby’s conjunctival sac when its head passes through the birth canal.
- Violation of sterility during childbirth.
- Failure to comply with the rules for caring for a newborn.
Conjunctivitis in a one-month-old baby sometimes develops after discharge from the hospital if family members who have contact with the baby do not comply with basic sanitary standards.
Types of conjunctivitis in children
Conjunctivitis of various etiologies is among the most common ailments in children.
In this article
- Types of conjunctivitis in children
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Bacterial conjunctivitis
- Dacryocystitis
- Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in infants under one year of age
- Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in children
- Prevention of childhood conjunctivitis
The causative agents of the disease spread through household contact and airborne droplets, and infants in the first year of life still have very weak immunity and are not able to sufficiently resist infections. Viral infection can occur when visiting a public place, from parents, while bacteria from dirty hands easily enter the mucous membrane of the eyes. Depending on the cause that caused the development of conjunctivitis in a child under one year old, several types are distinguished.
- Allergic. Eye inflammation develops when the conjunctiva is irritated by various substances. At this age, this most often occurs, for example, when introducing a new type of food. Allergies can also occur to medications, hygiene products, and insect bites.
- Bacterial. The most common type of conjunctivitis in children, which they often become infected with from a sick mother during childbirth (blennorrhea of newborns, chlamydial conjunctivitis), as well as when various microorganisms get into the eyes.
- Viral. It is provoked by various microorganisms, in particular adenoviruses, enteroviruses, etc.
- Dacryocystitis. Occurs due to obstruction of the lacrimal canaliculus. This eye pathology can be treated quite successfully with timely measures taken.
A common symptom for all types of eye inflammation is redness and swelling of the inner lining of the eyelid, but each of them also has its own characteristics. Let's look at the causes and symptoms of various types of conjunctivitis, as well as dacryocystitis in babies under one year old.
Types of conjunctivitis in a month-old baby
The main types of conjunctivitis in infants are:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- allergic.
The difficulty in recognizing conjunctivitis in a child is that the baby is deprived of the opportunity to talk about his feelings. If something is bothering him, parents can only understand it by his behavior. Usually the baby begins to rub his eyes, turn away from the light, and cry for no reason. As the disease progresses, external signs appear. Conjunctivitis will be indicated by redness and swelling of the eyelids, and purulent discharge. During sleep, mucus blinds the eyelids, making it difficult for the child to open his eyes.
As you might guess, bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria, and viral conjunctivitis is caused by viruses. Microorganisms and infectious agents quickly provoke disease, since the immune system of a 1-month-old baby is not able to actively resist infectious attacks.
The most common causative agents of inflammation are the following bacteria: gonococcus, chlamydia, streptococcus, staphylococcus.
This type of conjunctivitis is characterized by purulence from the eyes. Chlamydia and gonococci, which a child can become infected with during childbirth, are very dangerous. They can lead to complete destruction of the cornea and, as a result, loss of vision. Such consequences are unlikely, since parents usually immediately notice the symptoms of the disease and begin treatment.
Viral conjunctivitis in newborns is provoked by pathogens such as adenovirus, herpes virus, enterovirus, etc. But more often, infants catch it from adults with colds. In a baby, conjunctivitis can become one of the concomitant diseases when infected with an acute respiratory virus. ARVI, as is known, is transmitted by airborne droplets, so a newborn is exposed to infection while in the same room with a sick person.
If the cause of conjunctivitis is an allergy, then the first signs appear the very next day after contact with the allergen. Pathology can be caused by children's hygiene products - soap, shampoo, as well as medications. When there are animals in the house, their fur can cause allergies in the newborn.
In infants, internal organs are at the stage of formation, so viruses or bacteria that enter the body can lead to disruption of their functioning.
Causes of conjunctivitis in children
Most often, inflammation of the eyes in children is of infectious origin.
Less commonly, inflammation is caused by exposure to allergens and external irritants. Each type of conjunctivitis has its own characteristics. Bacterial conjunctivitis predominates in children. Most often these are pathogens such as:
- staphylococcus;
- streptococcus;
- Pneumococcus;
- conditionally pathogenic flora from the skin of the hands;
- gonorrheal and chlamydial staphylococcus (in newborns, at birth through the natural birth canal when the mother is infected).
Bacteria can come not only from the external environment, but also from nearby purulent foci with otitis media, tonsillitis, pyoderma, and sinusitis.
Although tears have a certain antimicrobial activity, with a decrease in immunity, due to trauma or mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, inflammation is possible when the nasolacrimal duct is blocked. Viral infections can also cause conjunctivitis. Among them:
- flu;
- herpes simplex;
- adenovirus;
- measles;
- enterovirus;
- chickenpox.
With viral conjunctivitis, there may also be signs of pharyngitis, rhinitis, and tonsillitis.
Allergic conjunctivitis is usually provoked by pollen (with hay fever), less often by animal dander, food or medications.
Some types of conjunctivitis are contagious; outbreaks are typical in children's groups, especially among children who are in close contact with each other. Defects in caring for the baby, poor nutrition, dry air, and bright lighting increase the risk of conjunctivitis.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis in infants
By external signs, different types of inflammation are easy to distinguish from each other. However, it must be remembered that different types of conjunctivitis sometimes have similar symptoms. Thus, suppuration from the eyes occurs in both bacterial and viral types of the disease. In the first case, this is a distinctive feature; in the second, it indicates a neglected form.
With bacterial inflammation, symptoms appear first in one eye, and after a while - in the second. When the disease is of an allergic or viral nature, signs of pathology appear in both eyes at once.
Characteristic symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis are photophobia, burning and itching, and tears flow from the baby's eyes all the time. But, like a viral one, it can be accompanied by a runny nose.
Before starting treatment, you need to correctly identify the causative agent of the disease. This is very important because the choice of therapy depends on the cause. For example, recommended drugs for the treatment of one type of inflammation may be contraindicated for another type of pathology. The child’s body, which is at the stage of formation, cannot be a field for experimentation. He is susceptible to any kind of influence, so all doctor’s recommendations should be taken very seriously.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis in children
The manifestations of viral, microbial infections and the symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis are slightly different.
They are often accompanied by additional symptoms – runny nose, cough, fever and malaise. Any conjunctivitis provokes:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- redness of the white of the eye or both;
- increased lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- feeling of sand or burning in the eyes;
- spasm of the eyelids;
- the appearance of crusts on the eyelashes.
Children often rub their eyes, are capricious, cry, and may have a low temperature.
Sometimes vision may deteriorate during the acute period of the disease. It is restored after the conjunctivitis is eliminated. With bacterial conjunctivitis in children, one eye first becomes inflamed, then after 1 - 2 days the second one. Mucopurulent or viscous cloudy discharge, sticking of the eyelids and abundant crusting on the eyelashes are typical.
With viral conjunctivitis, both eyes are inflamed at once, there is a fever, runny nose and signs of a cold. Swelling of the eyelids, copious mucous discharge, and sticking together of the eyelids after sleep are typical.
Allergic conjunctivitis is similar to viral conjunctivitis, but without the symptoms of a cold. The eyes are swollen, the eyelids are swollen, and there is typically a watery discharge from both eyes.
Dacryocystitis in newborns
Separately, it is worth considering a disease such as dacryocystitis, which is often mistaken for conjunctivitis in a month-old baby. Its symptoms are similar to those that appear during an eye infection, but the cause of the pathology is completely different. It is associated with such a phenomenon as obstruction of the lacrimal ducts in newborns.
During the formation of the respiratory system of the embryo in the womb, the lacrimal canal is closed with a thin film. This anatomical feature prevents amniotic fluid from entering the respiratory system. After being born, the baby takes in air and begins to cry for the first time. Under pressure, the epithelial septum ruptures, making passage through the lacrimal ducts free. If this does not happen, then, like a cork, the film clogs the channels, preventing tears from passing through. As a result, stagnation and inflammation of the lacrimal sac occurs.
The liquid that we used to call tears performs an important function. It washes the eyeball, washing away bacteria from it. In the absence of pathology, tears enter the lacrimal sac through the canaliculi, and from there into the nasal cavity. The blockage causes tears to accumulate in the lacrimal sac, causing inflammation. It is often accompanied by constant lacrimation and purulent secretion. Therefore, many parents mistake dacryocystitis for conjunctivitis.
When several days have passed and treatment of conjunctivitis does not improve, it is necessary to recheck the diagnosis.
Dacryocystitis cannot be cured without the intervention of an ophthalmologist. In some cases, massage can help. But if mechanical action does not produce results, a specialist will perform a painless procedure in the medical office to remove the plug in the tear ducts.
Conjunctivitis
Allergy
Herpes
Fungus
4487 06 November
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Conjunctivitis: causes, classification, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory disease of the outer mucous membrane of the eyeball and the inner surface of the eyelids of various nature.
Conjunctivitis is the third most common eye disease, and in children the infection is often bacterial in nature.
According to the definition used by Russian ophthalmologists, conjunctivitis is irritation of the conjunctiva of the eye in response to various factors, manifested by redness (hyperemia), swelling and itching of the eyelids, often complicated by visual impairment due to the spread of the pathological process to the cornea - the outer shell of the eye (with the development keratoconjunctivitis).
Causes of conjunctivitis
The causes of conjunctivitis include failure to comply with personal hygiene rules (infections enter the eye mucosa through dirty hands), decreased local and general immunity, the presence of allergic diseases, as well as the use of lenses, improper care of them and the use of damaged or expired lenses.
Classification of conjunctivitis
According to
the duration of the flow,
they are distinguished:
- Acute – symptoms of the disease last less than 4 weeks.
- Chronic – the disease lasts more than a month.
For the reason
that caused conjunctivitis:
- Viral (the main causes are adenovirus, human herpes virus, enterovirus, molluscum contagiosum virus, etc.).
- Bacterial. Typically, bacterial forms of conjunctivitis develop as a result of the addition of a secondary infection to an existing viral conjunctivitis. Children are diagnosed more often than adults. Bacteria that cause the development of this pathology include Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae, gonococcus, and streptococcus.
- Allergic. Allergic conjunctivitis can be either an independent disease or observed together with other allergic manifestations (for example, hay fever). The following types of allergic conjunctivitis are distinguished: seasonal (for example, when weeds and trees bloom), year-round (if the allergen constantly circulates in the air - animal dander, dust mites), contact (for example, an allergic reaction to decorative cosmetics).
- Physical (due to physical or chemical exposure). When the mucous membrane of the eye is exposed to a chemical (low-quality cosmetics, household chemicals, etc.) or a physical agent (light of excessive intensity, radiation, mechanical impact on the mucous membrane of the eye), nonspecific inflammation develops.
- Autoimmune (urethro-oculosynovial syndrome, for example, with genitourinary or intestinal infections).
Symptoms of conjunctivitis
Regardless of the cause, conjunctivitis always begins acutely.
The occurrence of photophobia most often indicates involvement of the cornea in the process, which is fraught with a significant decrease in vision in the absence of proper treatment.
Viral conjunctivitis
- Herpetic conjunctivitis first affects one eye, then the infection can spread to the second. The development of the disease is sluggish, the symptoms are not clearly expressed. The appearance of swelling and redness of the eyelid is characteristic; there may be typical herpetic blisters with transparent contents; when a secondary infection occurs, a mucopurulent discharge appears.
- Adenoviral infection (pharyngoconjunctival fever) is an acute disease accompanied by a runny nose, fever, sore throat with possible enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes. Eye damage is usually gradual - first one eye is affected, and after 72 hours - the second.
- With conjunctivitis caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus, mucus secretion from the eye and the formation of nodules with a concave center on the eyelids are disturbing.
- Viral conjunctivitis is also characterized by rapid spread in crowded groups (in kindergartens, schools).
Bacterial conjunctivitis
A distinctive symptom is the difficulty of opening the eyelids after sleep due to copious purulent discharge; in the early stages of the disease, the appearance of white threads when opening the eyes.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is characterized by sharp redness of the conjunctiva of the eye, a burning sensation in the eye, a feeling of a foreign body (sand), and the appearance of pathological discharge (pus).
In newborns, gonococcal conjunctivitis can develop due to infection during childbirth. Most often appears on the 2nd–5th day of life. A similar picture occurs when a child is infected with chlamydia.
Allergic conjunctivitis The development of symptoms of the disease occurs immediately after contact with the allergen or after a short time (up to 48 hours). There is profuse lacrimation. Over time, the secretion thickens, when a secondary infection occurs, it becomes cloudy and purulent. The patient complains of itching, burning in the eyes, redness of the eyelids (the lesion is often symmetrical (both eyes at once)). Soon these symptoms may be joined by a runny nose (this is due to swelling of the nasolacrimal duct), photophobia (if the cornea is involved in the process), and decreased visual acuity.
According to the course of the disease, acute allergic conjunctivitis is distinguished (if contact with the allergen is one-time or very rare, such a disease passes quickly, in mild cases it is enough to simply stop contact with the allergen) and chronic (in this case the contact is regular, the symptoms are wave-like and less pronounced - more often with allergies to house dust mites).
Physical conjunctivitis
Symptoms of this disease develop immediately after exposure to an irritating agent: burning, discomfort, itching, sensation of a foreign body in the eye, lacrimation, redness of the eyelids and eyeball.
Urethro-oculosynovial syndrome
Urethro-oculosynovial syndrome (previously called Reiter's syndrome) develops in response to the penetration of sexually transmitted infections (in particular, chlamydia) into the body, autoimmune inflammation, when the body's own cells of the synovial membrane of the joint, the mucous membrane of the eye and the urethra are perceived by the body as foreign. In addition to the eye symptoms of conjunctivitis, the patient is concerned about pain and swelling of large joints. Conjunctivitis is often purulent in nature. It is possible to develop iridocyclitis - inflammation of the middle (choroid) membrane of the eye, including the iris, which causes pain in the eyeball and its hyperemia (redness), clouding of the cornea, lacrimation and photophobia are characteristic.
Diagnosis of conjunctivitis
Diagnosis of the disease is based, first of all, on examining the affected eye and collecting anamnestic data to identify the factor that caused the development of conjunctivitis. An obligatory part of diagnostic measures is checking visual acuity. If necessary, scrapings of the conjunctival mucosa are taken (in particular, to identify the DNA of microorganisms), culture of pathological discharge from the eye, including an expanded spectrum of antibiotics and to identify molluscum contagiosum. Consultations with related specialists (for example, otolaryngologist, allergist, rheumatologist, etc.) are often required.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in a one-month-old baby
The doctor will tell you exactly how to treat conjunctivitis in a one-month-old baby. Only a specialist can recommend medications for the treatment of conjunctivitis in a one-month-old baby. After examination by an ophthalmologist and receiving prescriptions, therapy is carried out at home. With the exception of difficult cases when hospitalization of a small patient is required.
Treatment of bacterial and viral conjunctivitis begins with rinsing. You can wipe your baby’s eyes with boiled water or pharmaceutical saline solutions. Infusions of various herbs are also suitable. Chamomile flowers are most often used for these purposes. They are poured with boiling water and allowed to brew for 20-30 minutes. After the solution has cooled, it should be filtered so that small particles of grass do not get into the baby’s eye.
During the day, the eyes are washed 4-5 times and always before each use of medications. There are several rules that should be followed during the procedure:
- both eyes are wiped, even if there are symptoms of the disease in only one;
- a separate cotton pad is used for each eye;
- the solution should not be too cold or hot;
- movements are performed from the outer corner to the inner.
Conjunctivitis in a 1-month-old child is treated with drops and ointments, sometimes tablets and injections are used. Local medications are instilled behind the lower eyelid. Ointments are applied in the same way.
The drugs are instilled in accordance with the doctor's recommendations, usually 1-2 drops in each eye 4-5 times a day. Ointments are usually recommended to be applied before bedtime.
List of ointments for bacterial conjunctivitis
For bacterial conjunctivitis, it is most important to apply the ointment to the eyes. Drops can be used during the day, but the infection can re-spread during the night, eliminating their effect. The ointment is placed under the lower eyelid or applied in a thin layer to the inner corners of the eyes.
Tobrex
The main active ingredient is tobramycin. This is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that destroys bacteria and also prevents them from reproducing. The drug is absorbed into the tissue, therefore it is used for bacterial infections of the conjunctiva, cornea, and eyelids.
Tobrex is used 3 times a day for no more than 7 days. After this time, the bacteria develop resistance to the main active ingredient, so if the disease continues, the doctor will need to replace the medicine with an analogue with a different active ingredient.
The main advantage of the product is the possibility of its use for small children, starting from 2 months from birth.
Tetracycline ointment
The main active ingredient is tetracycline, which destroys bacteria by inhibiting their growth. Tetracycline ointment is active against most opportunistic microbes, as well as salmonella and chlamydia. The medicine can be used for children only after reaching 8 years of age.
It is recommended to place the medicinal substance under the lower eyelid or on the inner corner of the eyes 3 times a day. Adverse reactions occur quite rarely. Sometimes there may be a slight decrease in the quality of vision, which quickly passes. Allergic reactions are also possible.
Erythromycin ointment
The main active ingredient is erythromycin, which destroys gram-positive bacteria. Erythromycin ointment effectively fights the inflammatory process of an infectious nature in the eyes. It must be used 3 times a day for no more than 7 days.
With an excessively long course of therapy, patients develop a secondary infection in their eyes, which will be resistant to many antibiotics.
Eubetal
A complex product containing betamethasone, tetracycline and other active ingredients. This composition provides anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. That is, the drug is applicable both for bacterial infections and during allergic manifestations.
The drug is used with caution for children, as it contains a hormonal substance that can cause adverse reactions. That is why the product is used for no more than 7 days.
During therapy, the medicine destroys most pathogenic microorganisms, helps eliminate swelling, inflammation, and redness.
It is not recommended to use the drug for pregnant and lactating women, as well as for patients suffering from glaucoma.
Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in infants
The selection of medications for children can only be entrusted to a professional. It will not be possible to do without medications. In some cases, such as bacterial conjunctivitis, antibiotics will be required. Most often, bactericidal drugs are prescribed when there is purulent discharge. Usually prescribed:
- "Fucitalmic" is a topical agent. Helps eliminate the inflammatory process and has antiseptic properties. Available in the form of drops, ointment and gel.
- "Albucid" is an antimicrobial drug. To treat children, a weak 20% solution is used. Quickly eliminates the inflammatory process.
- "Vitabact" is an antiseptic. It is not an antibiotic, therefore it is indicated for use in the treatment of children from birth.
Erythromycin and tetracycline ointments are also used. These mild antibiotics are the least toxic, therefore they are allowed in the treatment of infant conjunctivitis. They have a wide spectrum of action, fight pathogenic bacteria and relieve inflammation.
Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in infants under one year of age
For each type of pathology, their own medications are used. To diagnose the causative agent of the disease, the doctor takes a smear from the conjunctival cavity and then determines its sensitivity to various antibiotics. Only after this does he prescribe antibacterial drugs for the eyes.
"Albucid"
The most common eye drops for children of any age, starting from birth, which effectively eliminate the symptoms of the disease. They contain sulfonamide, an active antimicrobial substance. "Albucid" is also used to treat blenorrhea and purulent ulcers.
"Tobrex"
The active ingredient is tobramycin. This is a strong antibiotic that suppresses protein synthesis in the cells of microorganisms, disrupting their active functioning. Copes with most pathogens of bacterial conjunctivitis. Adverse reactions such as allergies and urinary disorders are possible. In case of such phenomena, you should consult a doctor to change the medicine.
"Vigamox"
The active ingredient is moxifloxacin 0.5%, which belongs to the fluoroquinolones and has an extended bactericidal effect. If there is severe discharge of pus, you can use an additional antibacterial ointment, for example, Erythromycin 1%. It has proven its effectiveness in forms of the disease that are difficult to treat (fungal, gonococcal, diphtheria and others). The ointment should be used after administering all the drops three times a day for 7-10 days, after which see a doctor.
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in infants
Therapy for viral conjunctivitis excludes the use of antibiotics, since bactericidal drugs do not destroy viruses. In this case they are completely useless. This type of conjunctivitis is treated with antiviral drugs. Typically, eye drops are used:
- "Ophthalmoferon" is an antiviral and anti-inflammatory agent;
- "Aktipol" is a drug with an antiviral effect that accelerates tissue regeneration.
Sometimes Anaferon tablets are used in treatment. The drug is allowed to be used from 1 month of life, but in some cases the doctor prescribes it for the treatment of a child up to 1 month.
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in children
Viral pathology usually develops against the background of ARVI or influenza. and in both eyes at once. Outbreaks of viral conjunctivitis often develop into epidemics. Antiviral drugs are used to eliminate the symptoms of this disease in children.
"Ophthalmoferon"
Their active ingredients are recombinant interferon 2-alpha and diphenhydramine - thus, antiviral and antihistamine effects are achieved simultaneously. For the treatment of children under one year of age, it is advisable to use Oftalmoferon when the first signs of the disease appear.
"Poludan"
A drug that enhances the synthesis of interferon, which significantly reduces the manifestations of viral eye inflammation in children. The main substances in these drops are polyadenylic and polyuridylic acids. The recommended dose for instillation is 1-2 drops three to four times a day. Already on the third day after starting to use Poludan, improvements in the condition are noticeable, irritation, redness of the eyes, and lacrimation disappear.
"Aktipol"
Antiviral drops that produce interferon in the body, which helps to significantly strengthen its own immune defense. The use of this medicine helps eliminate swelling and redness of the conjunctiva, reduce itching and irritation. "Aktipol" also has a keratoprotective effect, promoting the healing of corneal tissue. Since the product is applied topically, the main active ingredient - aminobenzoic acid - is well absorbed, contributing to a rapid therapeutic effect.
Treatment of allergic eye inflammation in newborns
Conjunctivitis in a 1-month-old child is treated by eliminating the allergen. Contact of the baby with the object that caused the allergic reaction should be excluded. The inflammation often goes away on its own. Older children are prescribed antihistamines. But they are contraindicated in the treatment of newborn babies.
Only a doctor can tell you how to treat allergic conjunctivitis in a 1-month-old child. If the inflammation does not go away soon after eliminating the allergen, you need to go to the hospital. When conjunctivitis is accompanied by swelling of the face, neck, lips, and respiratory tract (Quincke's edema), it is necessary to immediately take the child to a medical facility. In the hospital, if necessary, the baby can be given antihistamines and hormonal drugs intravenously.
Lotions will help relieve your child's symptoms. Allergic conjunctivitis can be treated only after consultation with a doctor.
Prevention of ophthalmic inflammation in newborns
A newborn baby requires special attention and care. The baby must be carefully cared for. Everyone who comes into contact with the baby must maintain hygiene. An integral rule in a family where a baby is born should be regular hand washing with soap.
After discharge from the maternity hospital, a nurse visits the mother and baby. The health worker will tell you in detail how to comply with sanitary standards at home and list the procedures that the baby should carry out daily.
Conjunctivitis in a one-month-old baby, with proper treatment, goes away quickly and does not cause complications.