Ultrasound in the CIR group of companies (Center for Immunology and Reproduction)
Average size of the uterus in the first trimester of pregnancy
| Date of last menstruation (weeks) | Time at conception (weeks) | Length (mm) | Width (mm) | Anterior-posterior size (mm) | Perimeter (mm) | Area (mm2) | Volume (mm3) |
| 5 | 3 | 71 | 50 | 40 | 150 | 2170 | 74000 |
| 6 | 4 | 80 | 57 | 45 | 158 | 2330 | 94000 |
| 7 | 5 | 91 | 68 | 49 | 167 | 2770 | 119000 |
| 8 | 6 | 99 | 74 | 52 | 179 | 3086 | 152000 |
| 9 | 7 | 106 | 78 | 55 | 187 | 3828 | 183000 |
| 10 | 8 | 112 | 83 | 58 | 199 | 4368 | 229000 |
| 11 | 9 | 118 | 89 | 62 | 210 | 5138 | 287000 |
| 12 | 10 | 122 | 95 | 66 | 222 | 5794 | 342000 |
| 13 | 11 | 135 | 102 | 70 | 234 | 6809 | 365000 |
Average size of the fertilized egg in the first trimester of pregnancy
| Date of last menstruation (weeks) | Time at conception (weeks) | Inner diameter (mm) | Area (mm2) | Volume (mm3) |
| 5 | 3 | 18 | 245 | 2187 |
| 6 | 4 | 22 | 363 | 3993 |
| 7 | 5 | 24 | 432 | 6912 |
| 8 | 6 | 30 | 675 | 13490 |
| 9 | 7 | 33 | 972 | 16380 |
| 10 | 8 | 39 | 1210 | 31870 |
| 11 | 9 | 47 | 1728 | 55290 |
| 12 | 10 | 56 | 2350 | 87808 |
| 13 | 11 | 65 | 3072 | 131070 |
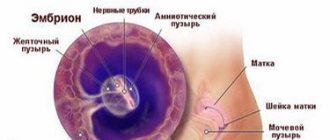
Formation of the fertilized egg
The first stage of the cycle that a reproductive cell goes through is the release of the egg from the follicle. Usually 3-4 follicles mature, but only one egg passes through a woman's fallopian tubes during ovulation.
The growth and development of a new life begins with the fusion of an egg and a sperm. Immediately after ovulation and fusion, a protective membrane forms around the egg.
This outer protective layer around the embryo will later develop into the amniotic sac containing amniotic fluid.
In the early stages of pregnancy, during an ultrasound, you can see the formation of an ovoid shape of small diameter. This is the fertilized egg. The first stage of its development is the morula, consisting of 12-32 blastomeres formed as a result of division of the zygote, which turn into a compact ball.
As the cells multiply, the embryo continues to move through the fallopian tubes until it attaches to the mucous wall inside the uterus. After this, the outer layer of the membrane begins to produce hCG (chorionic gonadotropin hormone), which is one of the first indicators of a woman’s pregnancy. All this time, the fetus is fed from the internal resource of the egg. In the process of further development, the attachment site is transformed into the placenta. At this time, to prevent infection, a mucous plug is formed, which closes the entrance to the uterus. This whole process takes about two days. If the embryo does not attach to the wall of the uterus, then a miscarriage occurs along with menstruation at the end of the cycle, and often the woman does not even know that she was pregnant. In the next cycle, the egg is released from the follicle again, ovulation occurs, and the whole process is repeated again.
What does a fertilized egg look like, structure:
- Villous membrane, chorion;
- Amnion (amniotic sac or membrane of water);
- Embryo.
It is difficult to see exactly what the fertilized egg looks like even with the help of an ultrasound. Due to its small diameter, the embryo is difficult to detect inside the uterus if a woman is pregnant for less than a month.
It happens that even at a period of 6-7 weeks the embryo is not visible inside the egg - this may indicate a non-developing pregnancy. An empty ovum is quite rare and is often a symptom of genetic disorders in the woman or her partner.
Average size of the embryo in the first trimester of normal pregnancy
| Date of last menstruation (weeks) | Time at conception (weeks) | Coccygeal-parietal size (mm) | Biparietal size (mm) | Yolk sac diameter (mm3) |
| 5 | 3 | 3 | — | — |
| 6 | 4 | 6 | — | 3 |
| 7 | 5 | 10 | — | 4 |
| 8 | 6 | 16 | 6,0 | 4,5 |
| 9 | 7 | 23 | 8,5 | 5,0 |
| 10 | 8 | 31 | 11,0 | 5,1 |
| 11 | 9 | 41 | 15,0 | 5,5 |
| 12 | 10 | 53 | 20,0 | 6,0 |
| 13 | 11 | 66 | 24,0 | 5,8 |
Anomalies in the development of the ovum at 5 weeks of pregnancy
The ovum, unfortunately, may have developmental abnormalities, the causes of which may be chronic diseases of the mother, intrauterine infections and heredity.
Experts consider the following factors to be developmental anomalies at 5 weeks of pregnancy:
- The fertilized egg is deformed. A change in shape occurs with premature partial detachment of the placenta, due to a violation of the tone of the uterus. Timely diagnosed deformation of the ovum, as well as normalization of the tone of the uterus, often leads to the return of the ovum to its correct shape and subsequently does not threaten the life of the fetus and the woman;
- Location anomaly. The fertilized egg is attached to the internal pharynx, more precisely in its lower part;
- Violation of the implantation process. Anomaly of egg attachment to the endometrium of the uterus;
- Violations of magnitude. The size of the fertilized egg does not correspond to the parameters required for this period;
Experts say that a 4-5 week ovum often has developmental anomalies, but timely diagnosis often makes it possible to maintain the pregnancy and give birth to a healthy baby.
Relationship between the coccygeal-parietal size (CPR) and the duration of pregnancy (based on the last menstrual period)
| KTE, mm | Weeks + days | KTE, mm | Weeks + days | KTE, mm | Weeks + days |
| 7 | 6+3 | 32 | 10 | 57 | 12+2 |
| 8 | 6+4 | 33 | 10+1 | 58 | 12+3 |
| 9 | 6+6 | 34 | 10+2 | 59 | 12+3 |
| 10 | 7 | 35 | 10+2 | 60 | 12+4 |
| 11 | 7+2 | 36 | 10+3 | 61 | 12+4 |
| 12 | 7+3 | 37 | 10+4 | 62 | 12+5 |
| 13 | 7+4 | 38 | 10+5 | 63 | 12+5 |
| 14 | 7+5 | 39 | 10+6 | 64 | 12+6 |
| 15 | 7+6 | 40 | 11 | 65 | 12+6 |
| 16 | 8 | 41 | 11 | 66 | 13 |
| 17 | 8+1 | 42 | 11+1 | 67 | 13 |
| 18 | 8+2 | 43 | 11+2 | 68 | 13+1 |
| 19 | 8+3 | 44 | 11+2 | 69 | 13+1 |
| 20 | 8+4 | 45 | 11+3 | 70 | 13+2 |
| 21 | 8+5 | 46 | 11+3 | 71 | 13+2 |
| 22 | 8+6 | 47 | 11+4 | 72 | 13+3 |
| 23 | 9 | 48 | 11+5 | 73 | 13+3 |
| 24 | 9+1 | 49 | 11+5 | 74 | 13+4 |
| 25 | 9+2 | 50 | 11+6 | 75 | 13+4 |
| 26 | 9+3 | 51 | 11+6 | 76 | 13+5 |
| 27 | 9+3 | 52 | 12 | 77 | 13+5 |
| 28 | 9+4 | 53 | 12+1 | 78 | 13+5 |
| 29 | 9+5 | 54 | 12+1 | 79 | 13+6 |
| 30 | 9+6 | 55 | 12+2 | 80 | 13+6 |
| 31 | 10 | 56 | — | — |
Internal diameter of the fertilized egg
The fertilized egg is a kind of oval or round sac. At short stages of pregnancy, an ultrasound examination can reveal the shell of the egg itself without the embryo, which will begin to be visible no earlier than in the middle of the first trimester. The embryo itself, during a normal pregnancy, is visualized at 6-8 weeks. Then the baby's heart can be heard. In the first trimester, an ultrasound scan is required. If any pathological deviations from the norm of the fetus or uterus have been identified, the specialist will be able to prescribe the correct treatment. The diameter of the ovum is a rather variable figure, but relatively stable, therefore, in case of deviations or concerns about the abnormal course of pregnancy, the pregnant woman should undergo a control ultrasound examination with a break of two weeks. The internal diameter of the ovum or SVD also makes it possible to determine the duration of pregnancy and set an estimated date of birth. But here you should take into account the medical error, which is 7-14 days. This means, if your estimated due date is October 16, then the baby may be born from October 2 to October 30. More accurate data is provided by measuring the coccygeal-parietal development of the fetus, the thickness of the fetal nuchal space, the biparietal and fronto-occipital size of the fetal head.
Relationship between biparietal size (BDS) of the fetal head and gestational age (based on last menstruation)
| BPR (mm) | Duration on average (weeks) | Fluctuation range (week) | BPR (mm) | Duration on average (weeks) | Fluctuation range (week) |
| 17 | 10,6 | 9,6—11,5 | 58 | 23,5 | 22,7—24,4 |
| 18 | 10,9 | 9,9—11,8 | 59 | 23,8 | 23,0—24,7 |
| 19 | 11,2 | 10,2—12,1 | 60 | 24,1 | 23,3—25,0 |
| 20 | 11,5 | 10,5—12,4 | 61 | 24,4 | 23,7—25,4 |
| 21 | 11,8 | 10,8—12,7 | 62 | 24,7 | 24,0—25,7 |
| 22 | 12,1 | 11,1—13,0 | 63 | 25,1 | 24,3—26,0 |
| 23 | 12,4 | 11,4—13,3 | 64 | 25,4 | 24,6—26,4 |
| 24 | 12,7 | 11,7—13,6 | 65 | 25,7 | 25,0—26,7 |
| 25 | 13,0 | 12,0—13,9 | 66 | 26,0 | 25,3—27,0 |
| 26 | 13,3 | 12,3—14,2 | 67 | 26,3 | 25,6—27,4 |
| 27 | 13,6 | 12,6—14,5 | 68 | 26,7 | 25,9—27,7 |
| 28 | 13,9 | 12,9—14,9 | 69 | 27,0 | 26,3—28,0 |
| 29 | 14,2 | 13,2—15,2 | 70 | 27,2 | 26,6—28,4 |
| 30 | 14,4 | 13,5—15,4 | 71 | 27,6 | 26,9—28,7 |
| 31 | 14,7 | 13,8—15,7 | 72 | 27,9 | 27,2—29,0 |
| 32 | 15,0 | 14,1—16,0 | 73 | 28,2 | 27,5—29,4 |
| 33 | 15,3 | 14,4—16,4 | 74 | 28,5 | 27,9—29,8 |
| 34 | 15,6 | 14,6—16,7 | 75 | 28,9 | 28,2—30,3 |
| 35 | 15,9 | 14,9—17,0 | 76 | 29,2 | 28,5—30,8 |
| 36 | 16,2 | 15,2—17,3 | 77 | 29,5 | 28,8—31,3 |
| 37 | 16,5 | 15,5—17,6 | 78 | 29,8 | 29,2—31,8 |
| 38 | 16,8 | 15,8—17,9 | 79 | 30,6 | 29,5—32,3 |
| 39 | 17,1 | 16,1—18,3 | 80 | 31,1 | 29,8—32,8 |
| 40 | 17,4 | 16,4—18,6 | 81 | 31,6 | 30,0—33,3 |
| 41 | 17,7 | 16,7—18,9 | 82 | 32,1 | 30,5—33,8 |
| 42 | 18,0 | 17,0—19,2 | 83 | 32,6 | 31,1—34,2 |
| 43 | 18,5 | 17,3—19,5 | 84 | 33,6 | 31,6—34,8 |
| 44 | 19,0 | 18,2—19,7 | 85 | 33,7 | 32,1—35,3 |
| 45 | 19,4 | 18,5—20,0 | 86 | 34,2 | 32,7—35,8 |
| 46 | 19,7 | 18,8—20,4 | 87 | 34,7 | 33,2—35,9 |
| 47 | 20,0 | 19,2—20,7 | 88 | 35,2 | 33,7—36,1 |
| 48 | 20,3 | 19,5—21,0 | 89 | 35,7 | 34,2—37,1 |
| 49 | 20,6 | 19,8—21,4 | 90 | 36,4 | 34,7—38,1 |
| 50 | 20,9 | 20,1—21,7 | 91 | 37,3 | 35,3—39,1 |
| 51 | 21,3 | 20,5—22,0 | 92 | 38,1 | 35,8—40,1 |
| 52 | 21,6 | 20,8—22,4 | 93 | 38,9 | 36,9—41,1 |
| 53 | 21,9 | 21,1—22,7 | 94 | 39,7 | 37,6—42,1 |
| 54 | 22,2 | 21,4—23,2 | 95 | 40,5 | 38,3—43,1 |
| 55 | 22,5 | 21,7—23,6 | 96 | 41,3 | 39,6—44,1 |
| 56 | 22,8 | 22,1—23,7 | 97 | 42,1 | 39,6—45,1 |
| 57 | 23,2 | 22,4—24,0 | 98 | 42,9 | 40,3—46,1 |
Pathologies of the ovum
When studying the fertilized egg with echography, pathologies can be detected already in the early stages. The absence of an embryo inside the membrane, an “empty egg” or anembryony, may indicate a non-developing pregnancy that will end in miscarriage or purging.
A picture that shows a discrepancy between the sizes of the growing embryo and egg in the absence of a heartbeat may indicate fetal fading, which also leads to miscarriage.
For example, if the embryo is much smaller than the membrane or the size of the bubbles is too small for the given period, then with a high degree of probability a miscarriage will occur at the end of the cycle.
The most common cause is chromosomal changes during conception, either congenital or caused by external influences. For example, a woman, not knowing about pregnancy, takes pills, drinks alcohol or is exposed to other harmful influences, which leads to serious pathology in the development of the fetus and miscarriage. Deformation of the ovum is not always a pathology, and in most cases is caused by increased uterine tone in the first period of pregnancy. Often the tone is accompanied by slight bleeding and pain in the lower third of the abdomen.
This problem can be solved with medication; pills are prescribed to reduce the number and intensity of contractions of the uterine muscles and hormonal pills to keep the fetus inside.
In case of detachment of the ovum in the case of a small affected area, hormonal treatment is carried out. For a woman during this period, bed rest in a hospital setting is required.
An ectopic pregnancy is characterized by the fact that the fertilized egg develops in an unintended place: in the fallopian tubes or ovaries. The main manifestation is heavy bleeding. It is impossible to save such a pregnancy, since the growth and development of the embryo in the fallopian tube leads to its rupture and serious consequences for the woman’s health.
During screening at 12 weeks, the nasal septum is measured. If the bone is less than 2.5 mm in length or is absent, doctors can make a preliminary diagnosis: trisomy 21 or Down's disease. In this case, the woman herself will be able to decide whether to continue the pregnancy.
In rare cases, two embryos are found in the fertilized egg at once - this is not an anomaly, but a factor indicating the presence of twins. A similar situation occurs when two bubbles are found in a woman’s uterus at once. In the latter situation, the chorions of both membranes in the future form placentas, with the help of which each fetus is fed separately. In the first case, the embryos will be nourished from one placenta. Detection of twins in the early period is often not confirmed, and the study gives reliable results only at 6-7 weeks of pregnancy.
Average sizes of the fetal chest at different stages of pregnancy (according to the last menstruation)
| Duration (weeks) | Dimensions (mm) | ||||
| transverse | anterior-posterior | average | perimeter | area (mm2) | |
| 15 | 28 | 30 | 29 | 90 | 588 |
| 16 | 34 | 32 | 33 | 99 | 768 |
| 17 | 38 | 36 | 37 | 111 | 972 |
| 18 | 41 | 38 | 39 | 117 | 1200 |
| 19 | 44 | 44 | 44 | 132 | 1452 |
| 20 | 48 | 44 | 46 | 138 | 1587 |
| 21 | 50 | 48 | 49 | 147 | 1875 |
| 22 | 53 | 50 | 52 | 156 | 2028 |
| 23 | 58 | 53 | 56 | 168 | 2352 |
| 24 | 59 | 56 | 57 | 181 | 2523 |
| 25 | 62 | 60 | 61 | 183 | 2724 |
| 26 | 65 | 63 | 64 | 192 | 3072 |
| 27 | 69 | 66 | 67 | 201 | 3468 |
| 28 | 73 | 70 | 72 | 219 | 3888 |
| 29 | 76 | 72 | 74 | 228 | 4107 |
| 30 | 78 | 74 | 76 | 234 | 4332 |
| 31 | 81 | 77 | 79 | 243 | 4563 |
| 32 | 83 | 79 | 81 | 249 | 4810 |
| 33 | 85 | 82 | 83 | 255 | 5292 |
| 34 | 88 | 85 | 86 | 264 | 5547 |
| 35 | 91 | 89 | 90 | 273 | 6075 |
| 36 | 94 | 90 | 92 | 282 | 6348 |
| 37 | 97 | 92 | 94 | 291 | 6627 |
| 38 | 98 | 94 | 96 | 294 | 6912 |
| 39 | 99 | 96 | 98 | 297 | 7203 |
| 40 | 101 | 97 | 99 | 303 | 7498 |
Average dimensions of the abdominal cavity of the fetus (gestational age - at the last menstruation)
| Duration (weeks) | Dimensions (mm) | ||||
| transverse | anterior-posterior | average | perimeter | area (mm2) | |
| 14 | 26 | 20 | 23 | 72 | 396 |
| 15 | 30 | 24 | 27 | 78 | 548 |
| 16 | 34 | 25 | 32 | 96 | 760 |
| 17 | 40 | 32 | 36 | 108 | 972 |
| 18 | 44 | 36 | 40 | 120 | 1210 |
| 19 | 50 | 40 | 45 | 138 | 1452 |
| 20 | 52 | 41 | 47 | 140 | 1600 |
| 21 | 55 | 43 | 49 | 144 | 1728 |
| 22 | 59 | 49 | 54 | 162 | 2180 |
| 23 | 63 | 52 | 57 | 168 | 2350 |
| 24 | 68 | 55 | 62 | 186 | 2880 |
| 25 | 73 | 60 | 66 | 198 | 3260 |
| 26 | 77 | 62 | 69 | 204 | 3675 |
| 27 | 81 | 65 | 73 | 216 | 3888 |
| 28 | 84 | 68 | 75 | 228 | 4107 |
| 29 | 86 | 71 | 79 | 240 | 4330 |
| 30 | 89 | 75 | 82 | 248 | 5042 |
| 31 | 93 | 79 | 86 | 259 | 5547 |
| 32 | 97 | 82 | 89 | 270 | 6074 |
| 33 | 100 | 84 | 92 | 278 | 6348 |
| 34 | 102 | 86 | 94 | 288 | 6625 |
| 35 | 104 | 88 | 96 | 290 | 6912 |
| 36 | 107 | 92 | 99 | 300 | 7495 |
| 37 | 110 | 94 | 102 | 306 | 7803 |
| 38 | 113 | 97 | 105 | 310 | 8425 |
| 39 | 116 | 98 | 107 | 324 | 8748 |
| 40 | 118 | 100 | 109 | 325 | 9074 |
| 41 | 119 | 101 | 110 | 327 | 9192 |
| 42 | 119 | 102 | 111 | 330 | 9408 |
Average length of long bones at different stages of pregnancy (according to last menstruation)
| Duration (weeks) | Length (mm) | |||
| femoral | humeral | ulnar and radial | tibia and tibia | |
| 14 | 16 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| 15 | 19 | 18 | 16 | 16 |
| 16 | 22 | 21 | 19 | 18 |
| 17 | 24 | 24 | 22 | 21 |
| 18 | 28 | 27 | 24 | 23 |
| 19 | 31 | 30 | 27 | 26 |
| 20 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 29 |
| 21 | 37 | 36 | 32 | 32 |
| 22 | 40 | 39 | 33 | 34 |
| 23 | 43 | 42 | 35 | 36 |
| 24 | 46 | 46 | 37 | 39 |
| 25 | 48 | 46 | 39 | 41 |
| 26 | 51 | 48 | 41 | 43 |
| 27 | 53 | 48 | 43 | 45 |
| 28 | 55 | 50 | 45 | 47 |
| 29 | 57 | 53 | 47 | 50 |
| 30 | 59 | 54 | 49 | 52 |
| 31 | 62 | 55 | 52 | 54 |
| 32 | 63 | 56 | 54 | 55 |
| 33 | 65 | 58 | 56 | 57 |
| 34 | 66 | 60 | 58 | 59 |
| 35 | 67 | 62 | 61 | 60 |
| 36 | 69 | 64 | 62 | 62 |
| 37 | 70 | 65 | 64 | 63 |
| 38 | 72 | 67 | 66 | 65 |
| 39 | 74 | 69 | 67 | 67 |
| 40 | 77 | 71 | 69 | 70 |
Tags: ultrasound