Development of the fertilized egg
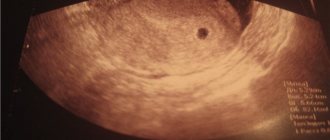
The fertilized egg can be detected on the seventh day of missed menstruation. What is a fertilized egg? A fertilized egg is formed after the fusion of an egg and a sperm. If it is located in the uterus, then we can talk about intrauterine pregnancy. If the doctor who conducts the ultrasound examination does not see the fertilized egg, then we can say with confidence that pregnancy has not occurred. Sometimes a specialist sees a fertilized egg in the tube and speaks of a tubal pregnancy. During an ultrasound, the shape, size and location of the fertilized egg are determined. Given its size, it is possible to determine the gestational age with an accuracy of one week.
Can there be two embryos in a fertilized egg?
Very often, women cannot distinguish between two, at first glance, identical concepts - twins and twins. In medical reference books on obstetrics and gynecology, a clear description of each of the definitions is given, with a description of the differences between twins and twins. This and another situation can be described by one concept - multiple pregnancy, but in the case of twins, after fertilization, the fertilized egg divides, in each of which two embryos develop separately.
If such division did not occur, or fertilization occurred twice in one egg, the development of embryos will take place in one fertilized egg, which indicates the presence of twins.
Development of the fertilized egg by week of pregnancy
If you perform an ultrasound in the third to eighth week of pregnancy, you can see that the fertilized egg looks like an oval or circle. And when a bubble formed by the yolk sac that nourishes the egg is visible in its cavity, we can talk about five or six weeks of pregnancy. At this stage of development, the fertilized egg measures from one and a half to two and a half centimeters. At this stage, you can see the embryo, which looks like a strip five centimeters long and is located next to the fertilized egg. Of course, it is not yet possible to determine the parts and structure of the fetus, but the baby’s heartbeat is already being recorded. His heart beats at a frequency of 145 - 220 beats per minute. Cells undergo a process of differentiation, they determine which of them will be responsible for what in the future. During this period, the fetus is already developing a neural tube. By the seventh week, the embryo detaches from the surface of the fertilized egg. It looks like the letter "C". You can also see the formed umbilical cord in the egg. And the most interesting thing is that during this period it is already possible to examine the head, torso and rudiments of the limbs.
The irregular shape of the fertilized egg, when it resembles a bean, indicates that the pregnant uterus is in good shape. If a woman does not have pain, then she should not be especially afraid. However, if at the same time there are unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen, pain, then this should serve as a reason for urgently taking emergency measures.
Beginning of pregnancy - development of the fertilized egg
A fertilized egg is 1 mm – such a small size, but what a significance this bubble already has! The correct determination of the gestational age in the first weeks, the diagnosis of a frozen pregnancy, and the determination of the state of the embryo in dynamics depend on how many mm the fertilized egg has.
When an expectant mother first comes for an ultrasound, she is usually given a conclusion “early pregnancy” and is recommended to undergo a re-examination in a month. In this case, the conclusion may already include such a parameter as the size of the fertilized egg. It is according to this that the ultrasound doctor is guided when determining the gestational age - after all, obstetricians will count the period from the first day of the last menstruation, and ultrasound sometimes indicates the period from conception (i.e., the age of the fetus). It should be remembered that we are all different, and the development of pregnancy is also different for everyone. Therefore, the article provides average data, which may differ slightly from the real ones. A 1 mm ovum is detected already in the fourth obstetric week of pregnancy - around this time the next menstruation should have occurred. Thus, mommy may not yet suspect the birth of a new life, but it can already be seen on an ultrasound. Usually, if a 1 mm ovum is detected, it is recommended to undergo a re-examination in a couple of weeks - it will be possible to assess the dynamics of its growth, see the heartbeat and determine the exact duration of pregnancy. The fertilized egg is 3 mm - it acquires this size in just a couple of days of development. By this moment, the yolk sac has already begun to form, which is clearly visible on ultrasound - it allows you to differentiate the fertilized egg 3 mm from the fluid bubble in the folds of the uterine mucosa. Thus, a 3 mm fertilized egg in the uterine cavity allows one to accurately determine the presence of pregnancy. If an ultrasound reveals a gestational sac of 3 mm, but the embryo is not visible, there is no need to panic, at this time it simply has not yet had time to develop, and it should not be visible. In just a few days, the fertilized egg will increase in size, and not only the embryo, but also its heartbeat will become noticeable. If pregnancy is diagnosed by ultrasound, a 4 mm ovum will be visible by the end of the fourth obstetric week. The rudiments of the fetal organs - liver, pancreas, lungs - begin to form. The most important organ that is formed at this stage of pregnancy ( fertilized egg 4 mm ) is the heart. In just a couple of days, the heart will begin to beat, and it will be possible to note with relief that the fetus is developing, the pregnancy is progressing! The fertilized egg is 5 mm - it reaches this size by the last day of the fourth week of pregnancy. At this stage, sometimes it is already possible to see the embryo by ultrasound, although its size is no more than a millimeter. A 5 mm fertilized egg is the borderline of the transition from the fourth to the fifth week of pregnancy. The fertilized egg is 6 mm - this is its size that indicates that the fifth week of pregnancy has begun. At this stage, two important events occur - the heart and blood vessels of the embryo are actively forming, and the formation of the nervous system occurs. The embryo reaches a size of 1.5 mm, sometimes at this stage the beating of a tiny heart is already noticeable. Thus, a fertilized egg of 6 mm is a reason to talk about a developing pregnancy. A 7 mm ovum is approximately the middle of the fifth week of pregnancy. The fertilized egg and embryo grow quite quickly, increasing by at least 1 mm every day. A fertilized egg of 7 mm indicates that the embryo is also growing, its organs are forming. If the ultrasound report describes a gestational sac of 7 mm, this usually corresponds to about ten days of delay. However, do not worry if you have a delay of more than two weeks, and the ovum is 7 mm - most likely, ovulation occurred with a delay, and therefore fertilization too. Literally in a day, an 8 mm gestational sac will be visible on an ultrasound scan - this is approximately 5 obstetric weeks and four days. The baby continues to grow along with its shells, and soon it will have limbs. A fertilized egg of 8 mm is an indicator that the sixth week of pregnancy will begin in a few days. A 9 mm gestational sac can be distinguished by ultrasound at 5 weeks and 5 days. Thus, a 9 mm fertilized egg is determined by the end of the fifth week of pregnancy - at this time, the germ cells continue to actively divide, forming the anlage of future organs. A 10 mm ovum is detected at the very end of the fifth week. By this moment, the embryo already has a neural tube with a thickening at its end - this is the future brain. A gestational sac of 10 mm indicates that the formation of the heart and blood vessels is almost complete. A 12 mm ovum is the beginning of the sixth week of pregnancy. At this stage, experienced ultrasound specialists can already determine the fetal heartbeat, although its size is only 2 mm. A gestational sac of 12 mm is an opportunity to catch the pulsation of your baby’s formed heart on an ultrasound. A 13 mm gestational sac is visualized at six weeks and three days. At this point, the baby's heart rate is at least 150 beats per minute. A gestational sac of 13 mm usually allows for good visualization of the embryo. The fertilized egg is 14 mm - it reaches this size by the end of the third day of the sixth week. The baby's arms and legs begin to appear, while still in their infancy. A fertilized egg of 14 mm usually allows you not to worry about the presence of a frozen pregnancy - the embryo is actively developing. A 15 mm gestational sac is visible at 6 weeks and four days. The baby's brain and nerve fibers are formed. If the fertilized egg is 15 mm, a face is already forming, indentations form in place of the eyes, and folds form in the area of the nose and mouth. Fertilized egg 16 mm - corresponds to a period of six weeks and five days. At this point, the digestive system, the rudiments of cartilage and the spleen begin to form. The fertilized egg is 16 mm - at this size, the embryo already has three intestinal loops, the rudiment of the esophagus and stomach. A fertilized egg of 17 mm indicates the close end of the sixth week. If an ultrasound reveals a gestational sac of 17 mm, finger buds begin to form in the embryo. A fertilized egg of 18 mm is determined at the very end of the sixth week. Usually, by the time an 18 mm ovum is formed, muscle tissue has formed in the fetus and it begins to respond to external signals. reaches 19 mm A 19 mm fertilized sac usually contains a fetus measuring at least 5 mm, clearly visible on ultrasound. The fertilized egg is 20 mm – this is the second day of the seventh week. The baby’s brain is actively developing, and a genital tubercle is formed (from which the genital organs will form in the future). The fertilized egg is 20 mm – usually at this moment the mouth and nostrils become visible. The ovum is 21 mm – the fetal face and brain continue to form. A fertilized egg of 21 mm indicates the size of the fetus is at least 8-10 mm. Fertilized egg 22 mm - mid-seventh week of pregnancy. A visible gestational sac of 22 mm allows you to stop calling the baby an embryo - now it is a full-fledged fetus!
Low fertile egg
The egg is usually attached to the fundus or body of the uterus. In some cases, ultrasound reveals a low location of the ovum. Many women are afraid that with a low-lying ovum they will not be able to carry a pregnancy to term. In this case, do not panic. A woman has every chance of maintaining a pregnancy if the egg is low, because in later stages of pregnancy the placenta migrates upward on its own in 95% of cases. And in the other five percent, physical activity should be reduced, and during childbirth, a doctor who knows that a woman’s ultrasound has detected a low gestational sac will definitely help her.
How is the fertilized egg released?
An incipient abortion is also called detachment of the ovum. It is prematurely rejected from the wall of the uterus. If an abortion occurs, the fertilized egg is released with blood. The question is often asked: “Is it possible to see for yourself that the fertilized egg has come out?” There is only one answer: “No!” If a woman suspects that she has had an abortion for one reason or another, she should definitely immediately contact a gynecologist.
How do you know if the fertilized egg has come out? After a medical abortion, it sometimes remains in the uterus. This can only be detected by repeating the ultrasound examination. If the suspicion is confirmed, in no case should you treat yourself using any old-fashioned methods; you should urgently contact a gynecologist. The fertilized egg that remains in the uterus should be removed.
Problems with the development of the fertilized egg
During the period of nidation (introduction of the fertilized egg with the help of chorionic villi into the uterine mucosa), a number of problems may arise. Due to the fact that successful implantation of the fertilized egg depends on the speed of its movement along the fallopian tube, if the membrane of the fertilized egg moves too quickly, it may not have time to fully form, which prevents the egg from attaching to the uterine wall and leads to termination of pregnancy (miscarriage of the fertilized egg ).
Cases of low attachment of the fertilized egg, which may indicate a cervical (ectopic) pregnancy, also require constant monitoring. In this situation, surgical intervention is performed, since the development of this type of pregnancy poses a threat to the woman’s health, including removal of the uterus.
If pregnancy is terminated, you need to carefully ensure that the egg comes out completely. The remains of the fertilized egg are removed by scraping the walls of the uterine cavity. In cases where the cause of the miscarriage remains unknown, a histological analysis of the fetal egg is performed.
Remnants of the fertilized egg remaining in the uterine cavity after a miscarriage can lead to the development of an infectious process, the treatment of which will require antibacterial therapy.
Another complication that can result from the remaining fertilized egg is bleeding.
A “false egg” that appears during an ectopic pregnancy and differs on ultrasound in the shape and width of the walls is an accumulation of blood or glandular secretion of the fallopian tube.
One of the serious developmental pathologies is an empty ovum, which appears due to a number of reasons: the age of the mother, the presence of genetic disorders, taking medications that are contraindicated during pregnancy. It must be taken into account that at 1-2 weeks of pregnancy, an empty ovum is the norm (the fetus at this stage is simply visually indistinguishable), while the presence of this pathology at a later stage leads to a medical termination of pregnancy.
How to remove the fertilized egg?
In order to remove the fertilized egg from the uterine cavity, instrumental or digital emptying of the uterine cavity is performed. Digital removal of the fertilized egg or its elements is more painful; when used, there is a risk of infection from the vagina, however, its advantage is that the risk of perforation of the uterine wall is minimized. The instrumental method requires less effort during surgery, reduces the risk of infection of the uterus, it is less traumatic, but when used there is a danger of perforation of the uterine wall. Both operations should be performed under short-term anesthesia or local anesthesia with potentiation.
Normal development of the ovum indicates an adequate pregnancy. Every modern woman who wants to become a mother in the future must consult a doctor in a timely manner, undergo an ultrasound examination, monitor her own health and properly monitor the intrauterine development of the fetus. This contributes to the normal course of pregnancy and the birth of a full-fledged healthy baby.
gynecology, useful