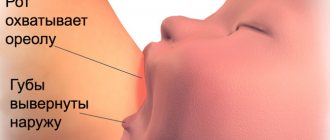
Appearance time
From the first days of pregnancy, women's breasts begin to prepare for lactation, and certain changes occur in the hormonal background. This leads to the fact that from the moment the baby is conceived, the production of colostrum begins.
- Almost always, a woman in the first trimester (up to 12 weeks) does not feel or notice this, because the amount of this nutrient fluid is minimal. However, there are cases when the appearance of colostrum is the first sign of a woman’s pregnancy. It depends on the individual characteristics of the organism.
- In the second trimester (from 13 to 28-30 weeks), colostrum production begins more actively, and many women notice yellowish sticky droplets on their clothes. These discharges may not be daily, appear regardless of the time of day and have different amounts (from 1 drop to 1-2-5 ml).
- The third trimester (from 30-31 weeks until birth) in most women is accompanied by the release of colostrum in varying amounts. It acquires a less saturated color, but its amount does not change significantly.
Breast discharge during pregnancy is associated with several environmental factors:
- emotional situations (both stress and positive moments);
- taking a hot shower;
- after prolonged sexual intercourse;
- after massage of the mammary glands;
- hot drink (water, tea or other drinks).
information After birth, colostrum becomes even more transparent, but still retains its yellow color and chemical composition. It is secreted for the first 3-7 days, after which it is replaced by mature white milk with a slightly different composition.
Myths and facts about colostrum
Often girls believe that fluid should appear shortly before giving birth. When discharge occurs in the 1st or 2nd trimester of pregnancy, they begin to become very worried and fear a miscarriage. However, this phenomenon is normal. The time of release of the first drops depends on individual characteristics, diet, and genetic predisposition.
There is another misconception: women think that a large amount of discharge and its early appearance indicate that later there will be a lot of milk, and, accordingly, problems with lactation will not arise. But this is not true: the amount of colostrum does not affect future breastfeeding, and its absence is not a sign of a problem.
Sometimes women, noticing the appearance of drops on their bra, believe that they are pregnant. This is not always the case, however: fluid may be released before menstruation.
Properties of colostrum
The yellow secretion of the mammary glands performs a number of functions:
- Saturation of the child’s body with immune cells (proteins). The baby’s immune system begins to work from 6 months after birth, therefore, starting from the oral cavity, the necessary cells are detached from the colostrum, which are involved in protecting the child from pathological microorganisms coming from the environment.
- Colonization of the intestines with beneficial microflora (bifidobacteria and lactobacilli). It promotes the absorption of milk and other products that the child will receive, normalizes the baby’s bowel movements, and prevents the proliferation of pathological microorganisms.
- Accelerating the excretion of meconium (original feces that fills the entire intestine of a newborn baby) and preparing the intestines for the arrival of the first portions of milk.
- Binding of excess bilirubin from the baby’s blood and intestines, which prevents the development of jaundice.
- Enriching the child with essential vitamins and minerals, which are essential from the first days of life for the physiological development and growth of tissues and organs.
- Saturation of the baby's blood with antioxidants, which help adapt to a new environment, especially in the respiratory system.
- Acceleration of the maturation of the intestinal epithelium due to growth factors (cortisol, insulin, insulin-like growth factor - IGF, epidermal growth factor - EGF).
important Colostrum is extremely nutritious and is extremely necessary for a child in the first days of life.
During its production during pregnancy, it accumulates many nutrients and has an ideal composition, starting from the first breastfeeding in the delivery room.
Norm and deviations
Despite the fact that colostrum is actively produced from the first stages of pregnancy, not every woman can observe its release. This is no cause for concern. It is quite possible that the lobules and ducts of the mammary gland have a fairly dense network and these drops of yellow liquid do not require release, or that there are few provoking factors and they are quite rare. The absence of colostrum during pregnancy in some women is considered a physiological norm , as is its appearance in the early stages of pregnancy.
Small or rare release of colostrum, its absence, or, conversely, a large amount of it, does not indicate the amount of milk after the birth of the baby. These are two different processes with different influencing factors and even hormonal levels.
Quite rare, but it is possible that a minimal amount of blood inclusions may appear in colostrum during pregnancy. In the absence of any other symptoms, this is also within the normal range. The ducts gradually expand, the mammary gland is rebuilt, and this can periodically lead to the rupture of small capillaries and the release of blood.
Between the second and third trimester, a woman may feel itching in the mammary glands and slight bloating, pressure from the inside. This indicates an even greater opening of the ducts, the movement of colostrum through the ducts and the active preparation of the breast for lactation. In this situation, also in the absence of other symptoms, there is no reason to sound the alarm and consult a doctor.
dangerous However, there are also variants of pathological conditions when the help of a medical professional may be required.
Breast discharge accompanied by pain
This may indicate the development of an inflammatory process in the mammary glands. To avoid purulent mastitis and contamination of milk when feeding your baby, you should promptly seek help from your local obstetrician-gynecologist and undergo a course of anti-inflammatory therapy.
If the release of colostrum is accompanied by nagging or cramping pain in the lower abdomen or in the sacrum and lumbar region, this indicates increased tone of the uterus and there is a risk of premature birth. This is due to an excess of oxytocin (a hormone that is actively involved in labor and prevents the development of postpartum hemorrhage). In this case, hormone replacement therapy is necessary. The doctor selects the drug and its dosage depending on the woman’s oxytocin levels.
Colostrum with blood
If the bleeding is quite profuse and is accompanied by pain in the mammary glands, uterus, or poor health in a pregnant woman, then you should immediately consult a doctor. This condition can be caused by the development of inflammatory processes, the risk of premature birth, or the growth of a neoplasm (both benign and malignant). The doctor will order a mammogram, magnetic resonance imaging and laboratory testing of blood and colostrum.
Foul odor of colostrum
Colostrum acquires the smell due to the active development and reproduction of a bacterial infection in the mammary glands. This may be accompanied by pain, fever, general weakness, or be asymptomatic. To treat this condition, it will be necessary to undergo a course of antibiotic therapy, with the most gentle effect on the baby. If you do not take appropriate medications, there is a high risk of fetal infection. And if there are several days left between the moment of infection of the mammary gland and birth, the child may be infected through breast milk during feeding.
Colostrum in the absence of pregnancy
It is quite a rare occurrence when there is no pregnancy, but colostrum is released from the mammary glands. This may be due to increased levels of oxytocin or prolactin, the development of an inflammatory or tumor process.
important If this condition occurs, you should immediately contact a gynecologist to avoid serious consequences of the disease.
What to do if you have colostrum leakage
There are no hard-to-follow rules for the production and excretion of colostrum. Caring for the mammary glands is quite simple:
- Wearing a specialized bra for pregnant and lactating women (made of natural fabrics, soft material, appropriate size, not pinching the breasts).
- Washing the mammary glands with clean warm water 1-2 times a day, without using soap (to prevent cracks, inflammation and colonization of microorganisms).
- Using a soft towel to wipe or blot the mammary glands (without sudden or rough movements, avoiding pain and chafing).
- Apply specialized pads between the underwear and nipples (you can use regular cotton pads, gauze, handkerchiefs). Change them regularly to avoid the development of infection.
- Do not massage the mammary glands (this will speed up lactation and increase uterine tone).
- Do not express colostrum (this will speed up lactation and increase uterine tone).
- Use moisturizing creams (this will prevent stretch marks on the breasts and reduce the risk of cracked nipples, both during pregnancy and lactation).
- Follow the rules of a balanced diet (reduce carbohydrate intake - flour products made from refined wheat flour, sugar, potatoes and white rice, consume large amounts of animal and plant proteins, fruits and vegetables, and increase fat intake 1 month before giving birth).
dangerous In case of pathological impurities, pain, poor health, uneven enlargement of the mammary glands, you should immediately contact your local gynecologist in charge of the pregnancy.
In this case, it is recommended to undergo a full examination and the necessary treatment to avoid complications and infections of the baby and mother.
Colostrum in non-pregnant women
Colostrum can be produced not only during pregnancy and lactation, but also after the period of feeding the baby for 1-2 years. The sudden appearance of colostrum, not associated with pregnancy and recent feeding of the child, may mean that the content of hormones - oxytocin and prolactin - has increased in the woman’s body. And here you shouldn’t wait and think for a long time: you should immediately run to a mammologist. What can the unexpected appearance of colostrum in the mammary glands signal?
- hormonal imbalance in the body;
- mastitis (in this case pus is released);
- fibroadenoma and other tumors.
Important: In cases of taking contraceptives, some women experience periodic release of colostrum before the start of the menstrual cycle. However, it is worth taking a blood test to make sure there are no diseases.