Causes of diastasis after childbirth and provoking factors
The abdominal wall consists of supporting and connecting tissue, including collagen fibers. Due to pregnancy hormones, the tension in the fibers decreases and they begin to stretch, and the abdominal muscles give way to the growing baby. The separation of the rectus abdominis muscles along the midline of the connective tissue connecting them (linea alba) is called diastasis. The linea alba runs from the bottom of the sternum to the top of the pubis and is usually about 1 cm wide. Diastasis can occur anywhere from the top to the bottom of the midline. After delivery, this process will resolve itself and the collagen fibers will regain their normal traction force. However, prolonged stretching or tearing of the fibers may cause the binding tissue to fail to fully repair itself.
Having diastasis is completely normal during the third trimester. However, there are a number of factors that can increase the likelihood of developing a disorder that will be difficult to correct:
- Pregnancy after 35 years
- Already have two or more children
- C-section
- Pregnancy with twins or triplets
- Large baby or increased amount of amniotic fluid
- Incorrect type of load on linea alba during pregnancy
- Constant constipation
- The wrong kind of strength training during or after pregnancy
Protruding and distended navel after childbirth
In the last weeks of pregnancy, the navel often protrudes beyond its “hole”. The growing uterus puts pressure on the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. The skin stretches under the influence of relaxing pregnancy hormones. As a result, after giving birth, a woman discovers that her navel is sticking out. A “hood” of skin hangs over it.
It takes an average of 6-9 months to restore your figure. Over time, both muscles and skin return to normal. But a slightly bulging belly button and overhanging skin may be permanent. This depends on many factors: predisposition to stretch marks, the strength of the abdominal muscles, and the quality of nutrition.
Symptoms and methods for determining the presence of diastasis
Diastasis after childbirth is not accompanied by any pronounced clinical symptoms, but can cause the following unpleasant disorders:
- Problems with posture and increased stress on the spine
- Also, diastasis after childbirth can be complicated by the appearance of a hernia.
How to determine diastasis after childbirth? To identify such changes, you can resort to a simple test at home:
- Lie on a hard surface, such as the floor, bend your knees and place your feet on the surface.
- One hand should be placed behind the head and the other on the stomach, gently touching the midline of the abdomen with your fingers (the line is parallel to the waist, in the navel area).
- Next, you need to take a deep breath and exhale, relax the abdominal cavity and press on it with your fingertips.
- Then you should raise your torso and fix yourself in this position for a few seconds. During this time, you can feel how many fingers fit between the abdominal muscles and determine the “space”.
Such self-diagnosis will allow us to identify the size of the “space” and at least approximately know the degree of discrepancy. The more fingers the “space” has absorbed, the more pronounced the diastasis.
If you find such a “gap” a few weeks after giving birth, there is no need to panic. Over time, the connective tissue will return to normal and elasticity will resume. However, do not forget about special exercises that will speed up the recovery process.
Diastasis usually recovers naturally within the first six months after childbirth. After pregnancy, you can check your diastasis monthly to monitor your progress.
Darkened navel
Pigmentation is more common in dark-haired, dark-skinned women.
Darkening of the navel after childbirth is explained by changes in the hormonal levels of the expectant mother's body. The adrenal cortex secretes a large number of biologically active substances. Changes in navel pigmentation begin in early pregnancy. A brown or black stripe in the navel area is normal - it can be located vertically or horizontally. In some cases, pigmentation is located on the stomach in the form of a smile.
Usually, skin color returns to normal by the time menstruation returns or after breastfeeding ends. Darkening of the navel is not always a sign of hormonal imbalance. When the endocrine system malfunctions, a woman experiences frequent dizziness and insomnia, and notes rapid weight gain or loss.
Exercises for diastasis after childbirth
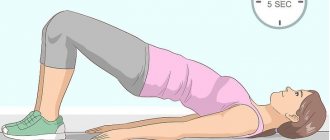
Exercise "bridge"
To perform the exercise, you need to lie on the floor and bend your knees (arms straight along the body). As you inhale, lift your pelvis, hold it for a few seconds and lower it as you exhale. Repeat 10-15 times.
Pelvic floor exercises can help strengthen the deep abdominal muscles because all the major muscles automatically contract as a group. These exercises can be performed in the early postpartum period.
Exercise “squatting near a support”
Stand straight next to the wall, pressing your back against it. Next, you should squat to a 90-degree angle, placing a rubber ball between your legs (if you don’t have a ball, you can use a book or a small bottle of water).
Leg raise exercise
Starting position - lying on the floor, on your back, arms extended along the body. One leg is bent at the knee, the other needs to be raised up and straightened, holding it in the air for 3-5 seconds. Repeat the same with the other leg. You need to reach 3-5 sets of 20 repetitions.
Diagnosis of umbilical hernia in women after childbirth
A hernia is easily diagnosed by visual inspection and palpation. But the rapid progression of pathology after childbirth often requires thorough treatment. And, in order to accurately establish the nature of the hernia that has arisen and its stage, a number of studies are carried out:
- Ultrasound is a study that allows you to assess the size of the umbilical protrusion, understand the structure of its contents, and establish the presence of an adhesive process. Can be performed during pregnancy.
- Tomography is indicated for pronounced signs indicating necrosis, coprostasis or strangulation. The procedure allows you to determine whether there is a threat to other internal organs.
- Herniography is indicated to confirm an inaccurate diagnosis. The patient is injected with a radiopaque mixture and X-rays are taken. After the substance enters the hernial sac, the pinched area is painted a certain color. This allows you to really assess the condition of the abdominal tissues.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy - using an endoscope, the condition of the gastrointestinal tract is studied to determine possible digestive disorders.
Breathing exercises for diastasis
Breathing exercises help retrain the diaphragm, or rather, return it to its normal position and functioning. During pregnancy, the growing uterus seems to push the diaphragm up and it loses the ability to return to its normal position. Since the diaphragm forms the upper part of the core muscles, it is important to retrain it and return it to its original position. Here are some good exercises:
- Lying on your back, with a pillow under your buttocks, raised slightly above chest level, you should take short, shallow breaths into your stomach. This exercise should be done for a minute.
- While sitting, you need to put your hands on your chest and take short and shallow breaths for a minute.
The distance between the two abdominal muscles is not the most important aspect. It is much more important that all the abdominal muscles can work together again, providing quality support to the spine.
Why do women experience umbilical hernia after childbirth?
Impaired muscle elasticity and the occurrence of weakness are due to the anatomical features of the female body, which is often caused by genetic predisposition. But not every pregnancy ends with such a threatening diagnosis as a hernia after childbirth.
For a hernia to develop, a combination of certain circumstances must occur. This:
- tendency of muscles to pathological stretching (physiological weakness of the muscle corset);
- significant expansion of the umbilical ring;
- existing intrauterine pressure, which significantly exceeds the norm.
This condition of abdominal tissue can be caused by one or more of the following factors:
- Multiple pregnancy or one, but very large fetus.
- Complications after natural childbirth or unsuccessful cesarean section.
- Injuries to the abdominal muscles in the past, including from difficult previous births.
- Strip surgeries before pregnancy.
- Congenital connective tissue diseases.
- Muscle weakness and complete lack of physical fitness (women over 30 are at risk).
Important! The cause of intrauterine pressure, which leads to diastasis, can be constipation, prolonged cough, and polyhydramnios.
Prohibited exercises when diagnosing diastasis after childbirth
Before you start working on eliminating diastasis, you should pay attention to exercises that are strictly prohibited. These include the following types of loads:
- Exercises that require you to lie on your back on a fitness ball.
- Yoga, namely poses that stretch the abdominal muscles.
- Using heavy objects or doing barbell exercises.
- A load that involves being on all fours.
Umbilical hernia after childbirth - symptoms
- The first sign indicating the formation of a hernia is a characteristic bulge in the navel area. A woman may not even notice a slight protrusion of abdominal tissue at first, especially if her pregnancy is quite advanced. But the progression of the disease is rapid, so the volume of the hernial sac is steadily increasing. Depending on the stage of the disease, it can fluctuate between 2 cm and 18 cm. But on average, in women, the size of the hernia rarely exceeds 11 cm.
- Symptoms characteristic of a hernia after childbirth include pain. This sign cannot be missed, since the pain becomes more intense and lasts during any physical activity, as well as during coughing or sneezing.
- The third symptom appears very quickly - discomfort in the gastrointestinal tract. In addition to the fact that a large fetus creates pressure on the diaphragm and provokes a lot of inconvenience for a woman, she also develops increased intrauterine pressure. A woman constantly has a feeling of a full intestine, normal bowel movements are disrupted, flatulence develops, and food stops being digested.
Ignoring the first symptoms of a hernia in the abdomen after childbirth leads to complications. A woman may experience:
- infringement of both the hernia itself and nearby muscles;
- inflammation of tissue in the abdominal cavity;
- disruption of the normal movement of feces (coprostasis);
- necrosis (death) of navel tissue as a result of strangulation of a protruding hernial sac.
Necrosis is the most dangerous complication of a hernia after birth above the navel. You can understand that this happened by the characteristic signs:
- severe pain in the umbilical area that appeared suddenly;
- rapid rise in temperature;
- signs of intoxication (dizziness, nausea, weakness);
- strong vomiting;
- loose stools;
- hardening of the contents of the hernial sac;
- the hernial sac becomes hot to the touch.
Important! When the first signs of necrosis appear, the woman is advised to undergo emergency surgery.
Why does pathology develop?
Doctors identify several reasons that may lead to the formation of a postpartum umbilical hernia.
Always come to the fore:
- the presence of a genetic predisposition (most often this means weakness of connective tissues, dysplasia, leading to the inability to fully perform specific functions);
- structural features of the umbilical zone;
- underdevelopment or weakness of the muscular frame of the abdominal wall.
In addition to the main factors, it is customary to identify additional ones that increase the risk of developing pathology, but do not directly lead to it in 100% of cases.
These risk factors include:
- the presence of significant excess weight in women at the time of pregnancy;
- repeating the process of bearing a child after a short break;
- the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity that normally should not accumulate there (ascites);
- frequent stagnation of feces in the intestines, which many representatives of the fair sex face in late pregnancy;
- history of surgical interventions in the abdominal cavity.
With an umbilical hernia after childbirth, a sharp development of clinical signs of the disease is rarely noted. Much more often the disease goes through several stages. It all starts with the appearance of periodic protrusion, which is visible only at the moment of tension, and ends with the formation of a persistent pathology, which can sometimes be eliminated only with the help of surgery.
Signs of illness
What are the symptoms of the disease that appear in the fair sex with an umbilical hernia? First of all, a woman always pays attention to the bulge above or to the side of her navel.
This bulge either appears or disappears completely, without reminding itself of anything. Over time, as the disease progresses, the defect increases in size and ceases to disappear, becoming permanent.
Its appearance no longer depends on whether the woman is currently under stress.
Other important signs of pathology are:
- pain that increases in response to sudden movements, coughing or sneezing;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- attacks of nausea or vomiting that have no clear connection with food intake;
- feeling of discomfort in the abdominal area.
In this case, the patient will complain about:
- the appearance of acute, sudden pain in the peri-umbilical area; the appearance of signs of general intoxication (weakness, fever, drowsiness, etc.);
- hardening of the sac in which the hernia is located;
- an increase in temperature at the location of the pathological bulge.
Methods of treating the disease
Treatment methods for the disease depend on how severe its symptoms are and what stage it is at. If the disease was caught at an early stage of development, it is usually treated with conservative methods. For the most part, doctors recommend wearing a bandage and exercise therapy.
Many representatives of the fair sex are concerned about the question of whether it is possible to pump up the abs with this disease? Yes, it is allowed to do this after childbirth due to an umbilical hernia, but only after all vaginal discharge has stopped.
Two main methods are used:
- implantation, during which a thin mesh is installed using a small incision to fix the area of the spinal ring;
- Gerinoplasty, during which an excessively enlarged umbilical ring is sutured and its walls are strengthened to prevent further development of the disease.
If a woman had surgery for an umbilical hernia after childbirth, then there is no need to fear for her health. Complications are very rare and recovery takes little time. Treatment in the postoperative period includes the use of a special corset, which is selected individually for each patient.
The following options have proven effective:
- applying crushed nettle leaves on a cabbage leaf to the damaged area;
- drinking an infusion of aspen bark, which is infused for an hour, and then drunk several teaspoons three times a day before meals;
- applying a mixture of oak bark and its leaves with wine to the affected area for several hours.
- An umbilical hernia after pregnancy is an unpleasant pathology that every representative of the fair sex can encounter.
- The main thing is to promptly notice the disease that has begun to develop and seek help from specialists.
- If treatment for the disease is started on time and you listen to your doctor, the hernia will not pose any threat to life and health, and getting rid of it will take place without unnecessary hassle.
- Source
- Source:
Symptoms and treatment of umbilical hernia after childbirth
An umbilical hernia after childbirth occurs often, which is associated with changes occurring in the body of the expectant mother. Advanced forms of the disease pose a danger to the life and health of the patient, so it must be promptly identified and treated. The first signs of a hernia may appear as early as the 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
An umbilical hernia after childbirth occurs often, which is associated with changes occurring in the body of the expectant mother.
Causes
The following factors contribute to the development of an umbilical hernia in the postpartum period:
- Genetic predisposition. The risk of protrusion increases if the patient’s close relatives had a similar problem.
- Stretching of the umbilical ring during pregnancy. The abdominal muscles move apart, which contributes to the formation of a hernial orifice. Intestinal loops or the greater omentum fall out through the hole, which is accompanied by dysfunction of the organs.
- Weakness of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall. Hernias are often found in women who prefer to lead a sedentary lifestyle.
- Multiple pregnancy. The abdominal circumference in such cases exceeds the permissible values, which leads to excessive stretching and divergence of the muscles.
- Excess weight. Helps to increase the load on the muscular-ligamentous apparatus, due to which it ceases to perform supporting functions.
- Repeated pregnancy. The risk of developing a hernia increases if a woman becomes pregnant in the first 3 years after giving birth.
- Accumulation of fluid in the abdominal and pelvic cavities. Leads to increased pressure, which pushes internal organs into the umbilical ring.
- Caesarean section, surgical interventions in the abdominal organs. Accompanied by injury to muscle tissue, creating conditions for organ loss.
- Pressure of a large fetus on the anterior abdominal wall.
- Impaired intestinal motility, often occurring in late pregnancy and the early postpartum period.
Symptoms
The development of the pathological process occurs in 3 stages, each of which has its own symptoms:
- The umbilical ring expands, weakened muscles diverge. The abdominal organs periodically fall out into the resulting hole. In this case, a hernial sac with soft filling appears. The protrusion appears during physical activity, coughing, and sneezing. When a woman takes a supine position, the hernia sharply decreases in size. There are no unpleasant sensations at this stage, but you should not refuse treatment.
- If left untreated, the hernial sac fills with connective tissue, which entwines the prolapsed organs and fuses with the peritoneum. Education at this stage of development ceases to increase with physical activity and changes in body position. A woman experiences a dull pain in the navel area, and signs of inflammation of the skin above the protrusion often appear. Unpleasant sensations intensify with movement, coughing and sneezing.
- Further development of the hernia leads to dysfunction of the internal organs. The pain begins to bother the patient at rest. Signs of fecal stagnation appear: cramps in the intestines, false urges to defecate, decreased appetite, weight loss. At the same stage, hardening of the hernial sac and an increase in local and general temperature may be observed.