Causes of inguinal hernia
If the pathology is congenital, then a pocket of the peritoneum (blind) protrudes and enters the scrotum using the inguinal canal. When the testicle is placed inside the scrotum, the process begins to grow. This happens before the baby is born. If there is no obliteration process, then the inguinal canal remains open. And when the pressure in the abdominal cavity rises, the organs located inside the body begin to fall out. An external type channel ring acts as a gate. The hernial sac is an appendix of the peritoneum; this can also include the ovary, uterine tube, omentum, and loops located in the intestines.
The causes of inguinal hernia in children vary. Often pathology appears due to heredity. Statistics show that 12% of children with this diagnosis live in families where one of the relatives also had a similar pathology. Both parents could even have an inguinal hernia.
An inguinal hernia in children can be acquired, but such cases are less common. Their development can be triggered by the following situations:
- excess weight;
- weight loss that happens too quickly;
- the child moves little;
- lifting weights;
- diseases associated with the respiratory system. During this, a cough is observed, which is quite severe;
- constipation that has become chronic.
Inguinal hernia
What is an inguinal hernia?
An inguinal hernia is the prolapse of tissue or an organ from the abdominal cavity (omentum, loop of intestine, ovary in girls) through the wide inguinal canal.
Inguinal hernias in children are congenital. The main role in the formation of inguinal hernias in children is played by the “vaginal process”. This is a protrusion of the peritoneum, which during intrauterine development is involved in the process of lowering the testicle from the retroperitoneum into the scrotum. It is the disruption of the process of obliteration (fusion) of the vaginal process that creates the prerequisites for the formation of hydrocele, inguinal hernia or spermatic cord cyst in boys. In girls, an inguinal hernia can form as the uterus descends into the pelvis.
Inguinal hernias occur in approximately 5% of newborns. It is much more common in premature infants than in full-term infants. Boys more often than girls. There are bilateral hernias.
- 1) Dropsy of the testicular membranes
- 2) Inguinal hernia
- 3) Spermatic cord cyst
What does an inguinal hernia look like?
Typically, a small child will develop a “swelling” (protrusion) that increases with crying and fussing and may disappear when calm.
In older children, a hernia may appear when coughing or physical activity.
Strangulated inguinal hernia.
Incarceration is compression of the contents of the hernial sac, which leads to impaired circulation and necrosis (death) of tissue.
In boys, the loop of intestine is most often strangulated, and in girls, the ovary with the fallopian tube.
The hernial protrusion becomes dense, painful, and cannot be reduced into the abdominal cavity. The child becomes restless, refuses to eat, and may experience vomiting and fever. In this case, urgent surgery is necessary.
Delay in seeking medical help can lead to serious complications.
Treatment of inguinal hernias.
The only radical method of treating an inguinal hernia is surgery. Modern methods of pain relief allow surgery to be performed at any age. There is no point in postponing the treatment of an inguinal hernia, since it will not disappear on its own, and over time the tissues of the inguinal canal change and require more complex plastic surgery. But there are relative contraindications (prematurity, severe concomitant diseases - cardiological, neurological, etc.). In these cases, the operation is postponed to an older age (6–12 months).
Methods of surgical treatment:
1) Open surgery.
A small incision (1-2) cm is made in the groin area and the hernial sac is bandaged. The operation is performed under general anesthesia (mask anesthesia) and lasts approximately 15 minutes. Complex plastic surgery of the inguinal canal is not required. This reduces the trauma of the operation and after 3-4 hours the child can be discharged home. Atraumatic, intradermal sutures are applied with a self-absorbing thread.
2) Laparoscopic surgery.
Laparoscopy is one of the new and advanced trends in surgery. This is a surgical method that allows the doctor to perform surgery without a large incision, using small 3-5 mm punctures of the abdominal wall. The intervention is carried out using special medical equipment, which makes it possible to see organs and tissues on a color screen under high magnification, and through additional punctures to carry out surgical intervention with special elegant instruments.
Advantages of laparoscopy:
- perfect cosmetic result (no incision)
- eliminates surgical trauma to the elements of the spermatic cord
- Laparoscopic access allows you to identify cleft processus vaginalis on the other side and perform herniorrhaphy (suturing the hernia) on both sides
3) Video-assisted herniorrhaphy
- a relatively new method of surgical treatment of inguinal hernia, combining the advantages of open and laparoscopic techniques:
- requires minimal time investment,
- low-traumatic,
- good cosmetic result,
- efficiency is high.
According to our data (about 60 operations), the relapse rate does not exceed the rates of open and laparoscopic herniorrhaphy.
Classification and forms of inguinal hernias in children
What matters here is the location of the inguinal hernia in children. There are three options - on the right side, on the left side, on both sides. If we talk about girls, then half are diagnosed with bilateral inguinal hernias. If we take boys into account, the bilateral form is observed in only 10%, a hernia on the left side is diagnosed in 30%. Most often, boys suffer from a right-sided inguinal hernia.
It is usually located inside the inguinal canal. It initially enters the inner ring located in the groin. Practice says that it is rarely possible to note the presence of a direct hernia. This pathology occurs when the abdominal wall in front is characterized by the presence of muscle defects. And it is because of this that the hernia protrudes.
In male children, with an inguinal hernia, the sac sometimes descends into the scrotum, and this contributes to another point. We are talking about an inguinal-scrotal hernia; it comes in two types - funicular and testicular.
How does an inguinal hernia manifest itself?
An inguinal hernia manifests itself as a swelling in the inguinal or inguinal-scrotal area, which increases with activity and restlessness of the child. When you press on this tumor-like formation, it disappears - the hernia is “reduced.”
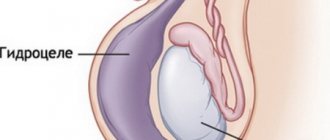
The spread of swelling to the corresponding half of the scrotum may indicate the presence of an inguinoscrotal hernia or testicular hydrocele.
In many cases, parents themselves may suspect an inguinal hernia and confirm their fears when visiting a doctor.
If swelling appears in the groin area, you should immediately consult a specialist in order to diagnose the hernia in time and distinguish it from a spermatic cord cyst and hydrocele. In doubtful cases, it is advisable to perform an ultrasound examination of the scrotum and inguinal canals (ultrasound).
Symptoms of inguinal hernia in children
The main symptom of an inguinal hernia in children is a protrusion that resembles a tumor. It is located in the groin. When a child strains, screams, coughs or cries, the protrusion becomes large. When the baby is calm, then the size decreases. There are even situations when the protrusions disappear.
With a similar pathology, which was found in boys, the scrotum is deformed, since there is a sac inside it. If we take girls into account, then the sac is placed in the labia, the latter becomes thicker.
During the pathology, the child feels pain in the groin or abdomen (bottom). Painful sensations can also be localized in the sacrum or lower back. Because of this, an inguinal hernia in an infant provokes crying and whims. If the child is older, then they tell the parents that he has pain in the lower abdomen.
Causes of inguinal hernias
There are many causes of inguinal hernias in children. The main ones are: congenital defects, weakness, underdevelopment of the muscles and connective tissue of the abdominal wall, defects of the vaginal peritoneum.
In the presence of these factors, spontaneously or due to physical stress (excessive crying in infancy, heavy lifting by older children), sudden movements, constant constipation and other reasons that cause an increase in intra-abdominal pressure, various hernias are formed.
The main reason for the formation of an inguinal hernia is associated with the physiological descent of the testicle and its passage through the inguinal canal in boys and fixation of the round ligament of the uterus in the inguinal canal in girls. Thus, there is a congenital predisposition to inguinal hernia.
Diagnostics
An inguinal hernia in young children can be noticed by parents or a specialist when examining the patient.
During palpation, the doctor can determine the protrusion. It has a certain consistency, which is elastic and soft. If the pathology is not very serious, then the contents of the hernia can be easily reset into the abdominal cavity. A rumbling sound is heard when repositioning. This suggests that the intestinal loops are located inside the pouch. After this process is completed, the doctor probes the ring located outside. It's expanded.
To clarify the presence of an inguinal hernia in children, they are sent for the following examinations:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and its organs; they also examine the scrotum, groin canals, and pelvis;
- cystography;
- irrigography.
Diagnosis of the disease
As a rule, there are no difficulties in determining pathology. Initially, a visual examination with palpation is performed, during which the doctor evaluates the location of the protrusion, consistency and size. If necessary, testing is carried out: the child is asked to bend over, cough, and strain his stomach.
Additionally, in the diagnosis of inguinal hernia in children, the following are used:
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, pelvic organs in girls and scrotum in boys;
- X-ray examination with contrast agent.
A thorough examination allows you to differentiate a hernia from other diseases with similar manifestations: lymphadenitis, cysts, hydrocele, and other neoplasms.
Treatment of inguinal hernia in children
Today, bandages and adhesive bandages are not used to cure a hernia in the groin; conservative methods are used.
If the course of the disease is uncomplicated, then the pathology is removed as planned. But the child must be over 6 months old at that time. During an operation to remove an inguinal hernia in children, the surgeon identifies the hernial sac, ligates it and cuts it off. Afterwards, work continues with the hernial orifice, they are provided with plastic surgery. To do this, use tissue that belongs to the patient or can use a special mesh made of propylene.
When it comes to surgical removal of an inguinal hernia in a child, the classic open method is used. Another option is laparoscopic technology. The second option is used more, since during such an operation soft tissues are not seriously injured and blood loss is minimal. In addition, the child’s rehabilitation period is not that long.
In the case of boys, this operation should be carried out especially carefully. Otherwise, there is a risk that the vessels of the testicle and the ducts that carry the seed will be injured. If this happens, then in children, after treatment of an inguinal hernia, the testicles may then atrophy, and in the future the man may be diagnosed with “infertility.”
When girls develop a strangulated hernia, this indicates the need for urgent surgical intervention. Otherwise, the ovaries and uterine tubes may die. For infant boys who are only a few months old and who have been noted to have infringement, conservative therapy is initially prescribed. Her goal is to repair the hernia. For this, there are certain clinical recommendations for inguinal hernia in children:
- the child is placed in a warm bath or a heating pad is placed in the lower abdomen;
- drugs are administered intramuscularly. We are talking about drugs that have an antispasmodic effect;
- put the child on the bed and lift his pelvis.
If the inguinal hernia does not return to its place after such treatment, then surgery should be performed urgently. There are already certain differences regarding the operation. First, the surgeon examines the organs and their viability. We are talking about those organs that are contained in the hernial sac. They can be adjusted in one case - there is no doubt associated with the ovary, omentum, intestine, or their viability. If the specialist still doubts, then resection is performed.
Indications for surgery
The absolute reason for emergency surgical intervention is a strangulated hernia - a dangerous complication that, without timely help, threatens the lives of children. With it, there is a gradual necrosis of the structures that are inside the hernia due to the cessation of blood circulation in them. This is accompanied by severe intoxication and severe pain in the abdominal area.
Emergency assistance is needed for acute intestinal obstruction. It is formed if intestinal loops get into the hernial sac, resulting in an obstacle to the movement of feces.
In all other cases, even with a mild degree of the disease, a planned operation to remove an inguinal hernia in children is performed.
Possible consequences and complications
The main complication that a hernia in the groin leads to is strangulation. This happens when the contents of the hernia are compressed by the inguinal ring (outer). This can provoke a consequence of an inguinal hernia in a child, such as ischemia of those organs that are strangulated.
Infringement is caused by coughing, which is quite strong, flatulence, and constipation.
The following signs will help you understand that an inguinal hernia has been strangulated:
- pain in the groin area. If the child is very small, he will cry and at the same time pull his legs towards his stomach;
- During palpation, the protrusion becomes tense and painful. It won't be possible to straighten it;
- many times the child vomits and feels sick;
- the stomach is bloated;
- the baby cannot go to the toilet normally, he passes gas, but with a delay.
If surgery for an inguinal hernia in a child is not performed in time, peritonitis may occur.
The ovary, its tissue, is particularly sensitive to ischemia. This indicates the possibility of developing ovarian necrosis. Eggs may also die. This applies even to situations where the infringement is short-lived.
This pathology poses a danger to men and their reproductive system. 5% of boys experience testicular atrophy after strangulation.
Types of inguinal hernias
Doctors distinguish several types of inguinal hernias. First of all, it should be said that hernias can be congenital and acquired. Congenital is a hernia with which the child was born. It forms during pregnancy or childbirth. Acquired hernias occur later, in the postpartum period.
There are unilateral and bilateral hernias. With a unilateral hernia, protrusion of organs occurs only through one inguinal canal (such hernias are left- and right-sided). Hernias on both sides at the same time are quite rare; they are characterized by damage to both inguinal canals and are more dangerous than unilateral ones.
In the case of an indirect inguinal hernia, the internal organs exit through the internal inguinal ring directly through the external inguinal canal. We are talking about direct inguinal hernias when the hernial protrusion comes out through the internal inguinal fossa. If there are several independent hernia formations in one inguinal canal, then such hernias are called combined (for example, in the case of a combination of oblique and direct forms of hernia).
A cord hernia is called when the protrusion is at the level of the spermatic cord. The inguinoscrotal form of the disease is characterized by the fact that the hernia is partially located in the scrotum. The diagnosis of a recurrent hernia is made in case of recurrence of the disease (unfortunately, no treatment method provides a 100% guarantee of preventing relapses).
In practical medicine, all hernias are divided into strangulated and non-strangulated. The first case is a direct indication for urgent surgical intervention (impaired blood flow in the strangulated organ quickly turns into tissue necrosis).
Forecast
Today, treatment of inguinal hernias in children is carried out in a hospital setting. The patient can be discharged almost immediately or the next day. The treatment does not end there; treatment continues on an outpatient basis.
As for relapses after surgery for an inguinal hernia in a child, this happens rarely (1%). This is usually diagnosed in babies whose mother did not carry to term during pregnancy, or after emergency intervention.
Complications of hernia repair can be noted very rarely. The following points should be included here:
- inability to have children;
- highly fixed testicles;
- testicular lymphostasis;
- lymphocele.
How is surgery for inguinal hernia performed on children?
Conservative methods of treating the disease are practically not used, since the effectiveness of such methods is extremely low, and the risk of strangulation of the hernia is high. The only correct solution is surgical removal of the formation.
There are two options for hernioplasty:
- open access;
- using laparoscopic equipment.
The optimal method of surgery is chosen by the doctor based on examination data, the child’s age and possible risks. The type of intervention determines how long the operation for an inguinal hernia in a child lasts. The operation time can vary from 30 minutes to an hour, taking into account anesthesia. Regardless of the chosen method, deletion occurs according to a certain algorithm:
- incision of the hernial sac and restoration of the anatomically correct location of internal organs and tissues;
- suturing of the hernial orifice;
- strengthening the inguinal canal or the patient’s own tissues.
All manipulations are performed under general anesthesia.
In modern pediatric surgery, laparoscopic hernioplasty is considered the preferred method of treatment. It is less invasive: minimal blood loss and small incisions reduce the risk of complications and shorten the recovery period. In some cases, it is possible to perform an open operation on a child to remove an inguinal hernia in the scrotal area. The doctor determines the method of performing the operation individually in each specific clinical case.
Prevention
When it comes to preventive measures that will prevent a child from having a hernia in the groin area, it is worth mentioning the following:
- the child must eat rationally;
- You should always control your body weight;
- treat constipation in a timely manner;
- treat diseases associated with the respiratory system that provoke coughing;
- physical activity must be present. But it is important to choose loads that will correspond to the child’s muscle strength and his age.
Symptoms of inguinal hernias
Inguinal hernias are quite simple to diagnose, but it should be remembered that they can often begin with almost no symptoms, and this makes them very dangerous.
The most common symptoms of this pathology are: a protrusion or swelling in the groin area that is visible to the eye and palpable to the touch. The child may complain of pain, discomfort, or, at a very early age, cry, scream, or react painfully to touch in this area. A very important diagnostic sign is the cough symptom - a change in the size and shape of the hernia during coughing. If the bladder exits through the inguinal canal, problems with urination will arise.
Very dangerous and unpleasant symptoms develop with complications of the disease. Strangulation of a hernia (impossibility of returning protruded organs back into the abdominal cavity) is the main complication of hernias. It is manifested by severe pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, lack of passage of gases from the intestines, difficulty urinating, fever, and general weakness.
How to make an appointment with a pediatric surgeon
If you think that your girl children have an inguinal hernia, then you should make an appointment with a specialist. He will study the clinical picture, conduct tests, examine the child and make the correct diagnosis. We are talking about such a specialist as a pediatric surgeon.
If necessary, he will prescribe surgery for an inguinal hernia in a child. It doesn't last long. To come to an appointment with a pediatric surgeon, you need to make an appointment in advance. You need to choose one of the most suitable options. You can leave a request on the website; call +7(495)995-00-33. The clinic is located in the center of Moscow, at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane 10.
Is it necessary to operate on an inguinal hernia?
Most often - yes. Unlike an umbilical hernia, which often disappears on its own in children under 2 years of age, a protrusion in the groin is a common indication for surgery. You should not postpone an appointment with a pediatrician, because this disease is accompanied by the risk of strangulation and damage to internal organs.
However, not in all cases it is necessary to operate immediately. If the patient is young, the size of the hernia is small, and the risk of strangulation is low, the pediatrician at the clinic may apply conservative treatment and recommend that parents postpone the operation until the patient is 1 year old, or for some other optimal period. Therefore, you should always start by making an appointment with a pediatric surgeon in the clinic where the child is being seen, and then, having developed a strategy for solving the problem together with the doctor, go to the hospital one day for the operation.
Treatment methods for inguinal hernias
Unfortunately, the only effective treatment for inguinal hernias is surgery. In the case of uncomplicated forms of the disease, surgery can be performed as planned. But if a hernia is strangulated, the patient needs urgent surgical intervention.
Today, doctors have 5 types of surgical operations aimed at treating inguinal hernias:
- The operation according to the Lichtenstein method using a special artificial mesh to strengthen the abdominal cavity at the site of hernia formation is practically not used in children.
- The Trabucco operation is a modified form of the Lichtenstein method using a mesh made of a special, very strong and rigid material; it is not used in children.
- Endoscopic hernioplasty is a minimally invasive intervention performed under the control of specialized endoscopic equipment. This approach allows us to minimize all risks associated with the operation. It is laparoscopy (endoscopic hernioplasty) that is the method of choice in modern surgery of inguinal hernias.
- Obstructive hernioplasty is a subtype of endoscopic hernioplasty, which allows you to close the hernial orifice with a special mesh prosthesis.
- The fifth type of operation, which involves the use of monoblock implants made of polypropylene materials, is not used in children.
If an inguinal hernia is diagnosed in a child, preference is given to minimally invasive surgery. In some cases, laparotomy operations are performed to strengthen the inguinal canal using one’s own tissue. Such treatment requires less material resources.
Since surgical intervention is rarely performed urgently, you need to remember some rules of behavior aimed at preventing complications while waiting for surgery. Excessive physical exertion should be avoided and heavy objects should not be lifted or carried. And most importantly, you should not postpone surgical intervention - the only way to solve the problem.