Human embryonic development
During development, the embryo goes through several stages. At first it is called a zygote, a fertilized egg with a diploid set of chromosomes that are received from the parents.
Baby in the womb
At the second stage, the cell is fragmented into blastomeres. The result is a ball of small cells, inside of which a cavity appears and a single-layer embryo that looks like a ball. The cavity is called blastula, and the wall is called blastoderm.
It is recommended to become more familiar with the features of embryo development in order to better understand how this process occurs.
Morula stage
The development of the human embryo continues, and on the 4th day the embryo is normally compacted and a morula is formed. The embryologist notes the percentage of compacted blastomeres and the presence of fragmentation. With further development of the embryo, the outer cells of the morula divide faster than the inner ones, as a result of which the outer cell layer (trophoblast) is separated from the inner accumulation of cells (inner cell mass-ICH), maintaining connection with them only in one place. A cavity (blastocoel) is formed between the layers, which is filled with fluid. How does the development of a human embryo proceed day by day?
Periods of human development during pregnancy
A person inside the womb goes through several stages of development. Each of them is considered mandatory, and she expects all future babies.
Stages:
- The union of germ cells obtained from parents. They are necessary for the formation of the zygote.
- The division of a zygote, which has already formed, into blastocysts.
- Development of germ layers, as well as the beginning of the formation of all internal organs.
- Development of organs and tissues.
- Formation of organ systems.
To put it simply, the life of an embryo inside the womb is divided into three important periods: fertilization, embryonic and fetal.
How a person changes in the stomach
Embryonic lasts from the second week to the eighth, and fetal begins from the 9th week. Every month the baby looks more and more like a baby, although at first he looks vaguely human.
Fertilization
During fertilization, the two sex cells of mom and dad must fuse. This process involves one egg and about 300,000,000 sperm, and only one of them is considered the winner. During this process, the diploid set of chromosomes will be restored. The parent cells must unite, which will determine the sex of the future baby. As a result of fertilization, a zygote will appear.
This process takes place in the fallopian tube, directly in the ampullary part. At first, the germ cells interact with each other at a distance, then they come closer together. The egg secretes substances that attract sperm. They are able to fertilize under the influence of a secretion that is synthesized in the female tract.
Fertilization
Cell contact occurs, after which the egg is activated. It begins to rotate, and an acrosomal reaction occurs.
After this, the male cell must penetrate under the mother’s shell, after which fusion is observed. From this moment on, a special shell appears on the eggs, which prevents the penetration of other sperm.
Embryo implantation day
Only on the 7th day from the moment of conception the embryo is implanted directly into the endometrium. This process is usually called implantation, and it is considered quite complex. The duration is about 40 hours, after which the embryonic period of development begins.
Embryonic period of human development
Some women still have no idea that conception was successful. At the same time, a new life is already developing in the body of the expectant mother. Some women may suspect changes have occurred in their body. Let's say that menstruation does not begin on a specific date and there is a delay.
After this, the woman can take a test and it will show two lines. At this stage, the baby’s heart is already contracting.
Germ
At the moment, the body of the mother and the embryo is extremely sensitive to external factors. We are talking about the influence of medications, toxins, infections, radiation, etc. It is important to protect yourself as much as possible in order to successfully go through this period. A woman is obliged to take care that the baby is fully formed.
It is useful to know how the embryo is currently developing in order to understand what changes are occurring in the body. A woman will understand what to prepare for, as well as how to protect her unborn child.
Fetal period of human development
The fertile period begins at 9 weeks, as soon as conception occurs. The obstetric period will be two weeks longer than the development time of the embryo. The fetal period will end with the birth of a person, and from that moment on he will be considered a newborn.
From the 11th week of obstetrics, the embryo will be called a fetus. It is almost completely formed, organs are laid inside, tissue differentiation is taking place. The baby has a direct relationship with the mother’s body due to the emerging placenta.
Although the laying of organs has already completed, there are several important periods. From weeks 15 to 20, the fetal brain will grow and develop. From 20 to 24 weeks, the functional systems of the body are formed, as well as the genitourinary apparatus.
Child development - from 1 week to one year
Intrauterine development: from the 1st week of pregnancy to childbirth
Intrauterine development of a person lasts an average of 40 weeks. During this time, a single-celled organism - a zygote - develops into a little person. What changes occur to him on the path of formation?
pregnancy development, intrauterine development
During pregnancy, every woman is interested in everything that happens in her body during the 9 months of bearing a child. During this time, a single-celled organism - a zygote - develops into a little person. What changes occur to him on the path of formation?
The gestation period is 40 weeks or 10 obstetric months, each of which consists of 28 days. The countdown of pregnancy itself begins from the first day of the menstrual cycle. Thus, the development of a child from the moment of fertilization lasts not 40 weeks, but approximately 38.
How does the human embryo develop?
At the moment, scientists continue to study how the human embryo develops from the moment of conception. Expectant mothers can get acquainted with what changes the future baby will have to face.
Future baby
The initial stage is considered one of the most important, because at this time the embryo is formed and organs are laid down. Scientists have described this process in detail, and anyone can familiarize themselves with it.
1-2 days
Once the parent cells unite, a zygote will appear. It divides by mitosis into cells called blastomeres. This process occurs slowly at first, but then speeds up.
Blastomeres are formed of two types: light and dark. The first ones are built in a single layer around the dark ones, and the trophoblast appears from them. It is considered a connecting element between the embryo and the maternal body. Thanks to him, the future baby will eat during development.
From the dark blastomeres, the embryoblast appears, which is considered the precursor of the human body. There will also be extraembryonic organs.
3-4 day
After the zygote appears, a cluster of blastomeres form a morula. It is at this time that a bubble with a cavity forms. Over the course of three days, the blastocysts are transported through the tube into the uterine cavity. At the same time, trophoblast and embryoblast cells develop. The size of the baby is minimal - only 0.2 mm.
5-6 day
The blastocyst will be located in free form in the uterus for two days. Her cells fill the embryo with nutrients, as the woman’s tissues decompose.
The birth of a new life
Embryoblast cells are located on the blastocyst. Now the embryo is completely ready to attach to the wall of the uterus.
Embryo development by week - embryonic period
From the second week the embryonic period of development begins. It will last until the end of the 8th week of pregnancy, if you count according to the obstetric period, then this will be the 10th week. The embryo does not stop developing, and it is constantly improving. Expectant mothers can learn in detail how the fetus develops.
Embryo development at 2 weeks
The amniotic sac appears from the blastocyst, and this is observed on average 8 days after conception. By day 11, the chorion is already created - the membrane of the embryo, which appears before the placenta. On day 12, the baby is still being implanted and gastrulation is now beginning.
Embryo development is in full swing. As for gastrulation, this is a complex process in which the tissues of a future person grow and change. The primitive streak appears from these cells and is considered the precursor of the head process.
What does an embryo look like?
At the same time, the circulatory system is actively being formed, namely, blood vessels and blood cells. Blood appears in the yolk sac. Now the embryo is connected to the placenta by a stalk.
Embryo development at 3 weeks
After 15 days from the moment of conception, the unborn baby has already grown to 0.4 mm, but it is still too small. The notochord appears, and at this time the perichordal plate is formed. The baby itself has a three-layer structure.
By day 17, the embryo is already growing and its length is up to 1.5 mm. The indicator may be less, this is not critical. It has a pear shape with a wide head end. The neural plate appears, as well as the first groove. The entire nervous system develops from it.
By day 21, a person is already stretched out, and the head becomes wider than the body. A thickening of the mesoderm appears. Chorionic villi are created.
At the end of this week, the heart is already being laid, and it looks like 2 tubes, and for now they exist separately from each other.
A preference appears, and after a short period of time it is reduced. The embryo itself continues to actively develop.
Embryo development at 4 weeks
Now the baby’s size is already 2.5 mm, but it could be less. The unborn baby is growing rapidly. By the end of this week it will already reach 5 mm.
Now the embryo looks like the letter “C”. It’s still difficult to recognize him as a person, but soon he will become like mom and dad. Cells of the nervous system have already appeared in the head, and the eyes and ears have also begun to form.
Now the separate pipes have closed; they are needed for the formation of the heart muscle. Blood flow appeared in different parts of the body, and at 3 weeks valves and partitions appeared in the heart.
Baby in the womb
The epithelial tissue of the digestive tube has already continued its development. The digestive system appeared, more precisely, organs such as the pancreas and liver. The esophagus, trachea, and respiratory tract have already formed from the epithelial tissue of the pharyngeal intestine.
At the end of this period, arms and legs will already be formed, but for now these are just the beginnings. Now the top layer of skin is emerging, muscles and the skeletal system are forming.
Now three bubbles of the brain will appear, and the lens of the eye will also form. The rudiment of the tongue has appeared, and in the picture you can see the primary area of the mouth.
The baby’s thyroid gland is actively developing, as well as the digestive system and respiratory tract.
Embryo development at 5 weeks
The size of the baby is about 7 cm. It is curled in the form of an arc, the bend of the neck is already noticeable. The upper limbs gradually lengthen, and hands appear.
The brain and heart are now growing rapidly, as well as the spinal cord. The eye lens develops rapidly, and the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland grows.
You can already notice the esophagus, which quickly separates from the tracheal area. The lungs are already located on both sides of him. The bladder and kidneys are now developing.
Embryo development at 6 weeks
At week 6, the unborn baby reached 13 mm in length. In the first days you can already notice the primary face. The outer ear has also formed. The eyelids began to close, and the pits of the nose appeared. Now the oral cavity is emerging, the esophagus is growing.
The embryo slowly straightens its back, and skeletal ossification is observed. The facial muscles are formed, as well as the lower jaw. The arms were perfectly formed, but the hands were not yet perfect.
At this stage, the diaphragm is formed, the liver and genitals develop.
Embryo development at 7 weeks
The embryo has already grown to 28 mm, but the figure may be less - about 17. The shape visually resembles an arc. The face and skull are now actively forming, and the lower jaw is easily identified. Still, the top one cannot yet be seen.
Fetus in the stomach
The hindbrain begins to improve, and the ureters lengthen. Feet develop on the lower limbs.
Embryo development at 8 weeks
At this stage, the embryo increases to 40 mm. The baby's head becomes straighter, his eyes develop, but they are still on the sides of the skull. The ears are set low, and nostrils have appeared in the hemispheres. The inner ear is still developing.
The development of the skeleton and muscles is taking place, and right now the baby is already making its first movements, but for now he does not control them. By the end of this week, the formation of the heart is completed.
Now the tongue is almost completely formed, taste buds have appeared, and teeth have formed. The bones of the hard palate fuse, and the intestine moves into the abdominal cavity. The development of the genital organs is taking place, and now the baby is expecting degeneration of the tail.
Fetal development by week of pregnancy
Each of us was such a cell, and all our “parameters”: the structure of all the proteins of the body, gender, blood type, eye color, leg size, taste and future talents are determined by the genetic code, 46 chromosomes. Then the person only grows and develops, receiving oxygen and nutrition. He is destined to live 9 months in the womb and about 90 years outside her womb. From the very moment of conception, each person is a unique being that has never existed in history and will never exist again!
The story of a new life, full of dramatic collisions, begins even before the fertilization of the egg by the sperm - in the female and male genital tract. The female reproductive tract consists of the fallopian tubes, or oviducts, the uterus and the vagina. One free end of the fallopian tube is expanded like a funnel and is equipped with numerous long outgrowths-villi, forming a kind of fringe. The movement of the villi creates a flow of fluid (mucus) towards the uterus. In the middle of the menstrual cycle, a mature egg is released from the ovary and ends up in the abdominal cavity (this process is called ovulation). At this very moment, the funnel with its fringe drives it with a current of mucus inside the fallopian tube. Wave-like contractions of the walls of the oviduct slowly carry the entire contents of the fallopian tube into the uterus. If for some reason the egg lingers longer than expected in the abdominal cavity, it can be fertilized there. This leads to the development of an ectopic (peritoneal) pregnancy, which is dangerous to the health and even life of the woman.
After a day, at most two, the egg reaches the wide part of the tube - the ampulla. This is the most suitable place for fertilization. Nature does not provide for any waiting: either the egg is fertilized and the embryo moves along the oviduct, or the unfertilized egg dies.
The second part of this great drama of the emergence of a new life - or rather the prelude to it - begins in the male reproductive gland - the testis, where male reproductive cells - sperm are formed. With the flow of seminal fluid, male reproductive cells are transported to the epididymis, and here their final maturation, accumulation and storage occur. When sperm is ejected (ejaculation), the seminal fluid concentrate is diluted with secretions from other male sex glands - the seminal vesicles and prostate. There are 50-170 million sperm per 1 ml of sperm (ejaculate), which is 10-20% of the ejaculate volume. At least 70% of sperm must have normal motility in the female genital tract. However, spermatozoa begin to move purposefully only once they are in the woman’s genital tract, outside of which they are not characterized by directed movements at all.
A medical analysis of semen composition is called a spermiogram. Quantitative spermiogram indicators are very important in the diagnosis and treatment of male infertility, since, although one sperm fertilizes the egg, a decrease in their concentration in the sperm significantly reduces the likelihood of this event. The volume of ejaculate and the number of sperm in it are very sensitive to the effects of all kinds of harmful influences: deteriorating environmental conditions, smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction. Over the past half century, the average concentration of sperm in the seminal fluid of healthy men has decreased by half. Once in a woman’s reproductive tract, male reproductive cells remain ready for fertilization for an average of two to three days.
In a woman, the formation of an egg most often takes from 17 to 40 years. The sperm development cycle is much shorter - only 68-74 days. In both women and men, sex cells, having matured, leave the places of their formation (gonads) and travel along the genital tract to the place of meeting and fertilization. The reproductive cells of a man and a woman are completely different in their structure, and in the process of fertilization they are assigned virtually opposite, although complementary, roles. However, the volume of hereditary material (the number of chromosomes in the nucleus) in both the female and male reproductive cells is exactly half of the chromosome set of any other cell in the body. When germ cells merge, their nuclei also unite, and the new organism receives a complete set of chromosomes.
The mother cell, the egg, is one of the largest cells in the body. It carries a supply of nutrients in the form of the yolk (containing proteins, fats and carbohydrates), which is enough for the embryo for the first 3-4 days of a very intensive life. The female reproductive cell itself is not capable of movement.
The sperm is smaller than the egg, its distinctive property is mobility. We can say that this is the nucleus of a cell with chromosomes, which has one “oar” - a flagellum. Many cells of the human body move over considerable distances, but only the sperm has such a perfect “engine”, which allows it to first leave the body of its owner and then head through the woman’s reproductive tract to the meeting point with the egg.
The speed of movement of human sperm is estimated at 30-50 μm/s (remember: one micrometer, or micron, is one millionth of a meter). The flagellum itself is used for targeted movements on the last leg of the journey: in the fallopian tube and during the process of fertilization. The fusion of germ cells occurs strictly in a certain part of the fallopian tube, in its ampulla. In this case, the egg is transferred only a few centimeters, while the sperm travels a considerable distance, first along the sperm duct of the man, then along the genital tract of the woman.
Initially, 2-3 ml of seminal fluid is injected into the vagina. Under optimal conditions, 30-60 minutes after ejaculation, sperm enter the uterine cavity, and after 1.5-2 hours - into the ampulla of the fallopian tube. During fertilization, the female reproductive cell secretes substances that “attract” sperm and indicate to them its exact position. One egg is “found” by many sperm at the same time. They attach to its shell and, with the movement of their flagella, cause the egg to rotate. Having loosened the egg shell in this way, the sperm then dissolve it with special substances.
After one sperm manages to penetrate the egg, its shell becomes impenetrable for the rest. The nuclei of the sperm and egg merge, the paternal chromosomes form a single set with the maternal chromosomes.
After about a day, the development of the embryo begins. Eight to ten days later, the absence of menstruation can indicate to a woman that she is pregnant.
First stages of development
pass during the movement of the embryo through the fallopian tube.
A fertilized egg is divided into 2, 3, 4, 7, 12, 16 cells, etc. This process takes 4-5 days.
On the seventh day, a dividing lump, consisting of approximately 100 cells, is embedded in the wall of the uterus. This process is called implantation
and is considered the first critical period during pregnancy (in total, doctors usually distinguish three critical periods of pregnancy; about the second and third, see below), since implantation can be prevented by any discrepancies in the activity of the mother’s body, stress, anxiety, and heavy physical activity.
Details about the development of the fetus and the feelings of the expectant mother by week of pregnancy - Pregnancy Calendar
| Approximate gestational age | Fruit length | Fetal weight |
| 5 weeks pregnant | 5-8 mm | |
| 6 weeks pregnant | 10-14 mm | |
| 7 weeks pregnant | 17-22 mm | |
| 8 weeks pregnant | 28-30 mm | |
| 9-12 weeks of pregnancy | 5-8 cm | 10-45 g |
| 13-16 weeks of pregnancy | 9-16 cm | 60-200 g |
| 17-20 weeks of pregnancy | 18-25 cm | 250-450 g |
| 21-24 weeks of pregnancy | 25-29 cm | 500-820 g |
| 25-28 weeks of pregnancy | 31-34 cm | 900-1300 g |
| 29-32 weeks of pregnancy | 37-40 cm | 1400-2100 g |
| 33-36 weeks of pregnancy | 43-45 cm | 2200-2900 g |
| 37-38 weeks of pregnancy | 47-49 cm | 3000-3400 g |
| 39-40 weeks of pregnancy | 50-51 cm | 3400-3600 g |
In the third week of pregnancy
After conception, the nervous system of a new person is formed, and his heart begins to work. At this time, an ultrasound specialist sees how the heart beats and can judge the condition of the fetus by the heartbeat.
The period of formation of all internal organs (mainly from the third to sixth weeks of pregnancy) is considered the second critical period of the child’s intrauterine development.
In the fourth week of pregnancy , the embryo grows rapidly, its size approximately triples. The formation of internal organs occurs: lungs, stomach, liver, pancreas, endocrine glands. The rudiments of eyes and ears appear. The formation of the placenta begins.
The fifth week is marked by intensive growth of the brain, development of the bronchi and lungs. The kidneys, rectum, and bladder are formed. By the end of the week, the upper limb becomes shovel-shaped and the lower limb becomes flipper-shaped. The length of the embryo reaches 6 mm.
During the sixth week of pregnancy, the face and fingers are formed. The formation of the outer ear and eyeball begins. The brain grows rapidly, and the rudiments of its parts are formed. The genital organs are formed.
In the seventh week of pregnancy , the upper and lower limbs are formed, the baby floats freely in the amniotic fluid, he can kick his leg and move his head. Its length is about 2 cm. If it continued to grow as quickly as in the second month of intrauterine life, then at birth its weight would be 14 tons, that is, equal to the weight of two large elephants!
A nine-week-old embryo fully becomes a little person. He sucks his finger, can grab an object with his hand, and feels pain. The length of the fruit is about 6 cm.
At eleven to twelve weeks of pregnancy
the child reacts to light, warmth, noise, touch. He is still so small that he could stand on his mother’s little finger, his length barely reaches 8 cm, nevertheless, he has eyelids, nails, he is finally formed and all the child’s organ systems have begun to work. Using ultrasound data, you can determine the sex of the child.
Third to twelfth weeks of pregnancy
- a period of special sensitivity of the embryo to drugs, as well as to the rubella virus. The latter, penetrating the embryo, disrupts the formation of the heart, organs of vision and hearing, and the brain. Alcohol can also cause severe fetal development problems.
Smoking and receiving anesthesia lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus, which carries a risk of miscarriage or the birth of a low-weight baby.
From the fifteenth to sixteenth week of pregnancy
the mother can feel the baby moving. (The timing of the first fetal movement recorded by the mother is very individual. It is believed that women who have given birth feel the movements of the child earlier than first-time mothers.) Physiologically, fetal movements are associated with contraction of the extensor muscles. Their frequency increases with maternal physical activity. Frequent or increased movements may indicate a lack of oxygen. The period of the most intensive movement of the child begins from the 20th week, when he already weighs about 350 g and is 25 cm tall, and continues until the 30-32nd week. As the baby grows, there is less and less space inside the uterus for his movements. At 32 weeks, the baby weighs about 1.8 kg and is 40-42 cm long. He can still roll over, but soon takes the correct position for birth - head down.
From the twelfth week of pregnancy
During pregnancy, the child’s existing organs increase in size and grow, while continuing to develop - after all, the child is not yet able to survive outside the mother’s body. Ideas about viability, this border between life and death of a prematurely born child, have changed a lot recently, approaching the 20th week of development (not so long ago this border was 30 weeks, then 28 and 25). There is a known case where premature birth occurred at the 19th week of pregnancy; the born girl weighed only 510 grams. She survived, but for many weeks she was under special conditions to maintain breathing, nutrition and body temperature.
By the fourth month (sixteenth week of pregnancy)
The placenta (baby place) is formed. It looks like a cake with a diameter of about 18 cm and a thickness of 3 cm. Thanks to the large number of villi, the surface of the placenta reaches 6 m2. The placenta connects the child with the mother’s body and ensures intensive exchange between the blood of the mother and the fetus. Under normal conditions, the blood of mother and fetus never mixes: the placenta creates a kind of barrier between them. Thus, oxygen passes from the mother to the fetus, and carbon dioxide flows in the opposite direction. If for some reason half of the placenta is excluded from metabolism, the fetus dies from oxygen starvation. Water, glucose, salts, amino acids, hormones and vitamins pass through the placenta. Antibodies from the mother cross the placenta and protect the fetus and newborn from infections. The permeability of the placenta is not only a blessing - it is also fraught with great danger, because the placenta is permeable to toxins (including alcohol and drugs), viruses and most medications, and if damaged, it can “pass” microorganisms in the blood to the fetus mother.
In the second half of pregnancy, the fetus's sensitivity to harmful influences decreases. However, the last weeks of intrauterine life of the fetus are classified as the third critical period precisely because the placenta has already stopped growing, and the fetus is significantly gaining weight. Any complications during pregnancy (placental abruption, late toxicosis) during this period may affect the completion of the formation of certain organs (genital, urinary). Throughout pregnancy, the baby is protected from mechanical damage and is in a special aquatic environment - amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid fills the fetal sac - the amnion. Amniotic fluid contains a number of cells that are rejected from the embryo. Therefore, analysis of amniotic fluid obtained through a special puncture (amniocentesis) allows doctors to examine the genetic characteristics of the fetus and identify chromosomal abnormalities in it. The amnion ruptures during childbirth when the water breaks. The well-known expression “born in a shirt” indicates a severe complication during childbirth, when a child is born covered with the amniotic membrane. Previously, this often ended in the death of the child (due to lack of oxygen), so the person who survived such a situation was considered lucky.
In the fifth - sixth month (20-28 weeks of pregnancy)
The child's body is covered with germinal fluff - lanugo. These delicate fine hairs fall out about a month before birth, with the exception of scalp hair, eyebrows, and eyelashes. The child is growing quickly and moving actively. The formation of vernix lubrication is a white, fat-like substance that protects the baby during childbirth. The baby's skin is red and wrinkled due to a lack of fatty tissue underneath.
The seventh month (28-31 weeks of pregnancy) is different in that the baby establishes a rhythm of sleep and wakefulness. He can wake up in the morning with his mother and greet her with quite violent tremors. It is believed that it is from the seventh month that the child takes part in the emotional life of the mother. By the end of the seventh - beginning of the eighth month, the child begins to hear and see. Fatty tissue forms under the skin. The child swallows amniotic fluid and sometimes even begins to hiccup. Babies born in the seventh month of pregnancy are most likely to survive.
In the eighth month (32-35 weeks of pregnancy )
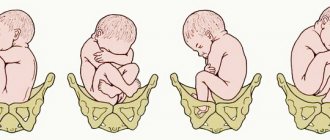
the baby gains weight and height; there is more fatty tissue under the skin, the baby is “rounded”; the baby is already cramped in the uterus, his movements are limited. He stops “twirling” and takes a position with his head down, preparing for birth.
Ninth month of pregnancy (36-40 weeks of pregnancy)
- time of final preparation for birth. The baby's head is pressed against the entrance to the pelvis. Primary stool, the so-called meconium, accumulates in the child’s intestines. In boys, the testicles descend into the scrotum. A special substance is formed in the lungs - surfactant - which prevents the lungs from collapsing - the baby is ready to take his first breath. By the end of the ninth month, the skull has the largest circumference compared to other parts of the body, therefore it is the circumference of the skull that determines the size of the child and the mother’s pelvis. This is important when deciding whether a caesarean section is necessary. Typically, birth occurs 280 days after conception (40 weeks). It seems that it is the baby who “makes the decision” that it is time to be born. He is ready to make the difficult journey through the birth canal. Now the child and mother are not one, as they were during the previous nine months. The child is able to survive outside her body, but it will still take him a lot of time to learn to live independently.
Almost all life support systems of a child will go through the stage of final formation after birth. Thus, during the first six months of life, the body’s immunological defense system uses antibodies obtained from mother’s milk, and only by one and a half years the immune system begins to work “in full force.” The kidneys' excretion of salts and protein metabolism products becomes effective by the end of the child's first year of life, which is why it is so important to control the amount of salt and protein in the baby's food. Liver function is fully formed by two years. The formation of the nervous system is one of the slowest processes in the body. For example, intensive development of the cerebral cortex is completed by the age of seven. The reproductive system matures on average by 15 years. And by the age of 25, skeletal growth stops.
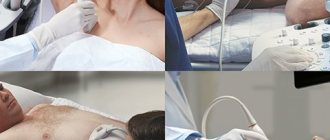
What does a human embryo look like on ultrasound: ultrasound examination
When doctors began performing ultrasound examinations, future parents had the opportunity to look at their unborn baby. Typically, the first study is carried out for a period of 10 to 14 weeks. At the same time, the woman’s blood is taken for detailed analysis.
As a rule, women do not look at the embryo before this period, because this requires specific indications. Let’s say you are sent for testing in case of an ectopic pregnancy, in preparation for terminating this condition. Also, if there is a suspicion of a frozen pregnancy or if there are painful symptoms, an ultrasound scan is prescribed.
Ultrasound
It is difficult to say definitively whether this study has a negative effect on the embryo. There is no exact data on this matter.
Is it possible to take a photo of an embryo?
Young parents often want to keep a photo of the embryo as a souvenir, because for them it is a significant event. A similar shot is taken at different stages of pregnancy, and this allows you to see the intrauterine life of a little person.
Nowadays, many people want such a unique photo, and it is placed in the family photo album. We can definitely say that on an ultrasound, even at 8 weeks of pregnancy, you can see the baby, examine his body, limbs, and even recognize his heartbeat.
To ensure the highest quality ultrasound possible, it is performed through the vagina. You can also scan through the anterior abdominal wall.
Ultrasound image
Now all young parents can look at their baby on an ultrasound, because the equipment allows this to be done. You can also get a unique photo that will be two-dimensional or three-dimensional. 7
When does a human embryo begin to be called a fetus?
An embryo is a baby in the early stages of pregnancy. To be more precise, up to 8 weeks, if you count the period from the moment of conception. After this, it is called a fruit.
When the third month of pregnancy begins, women note that their health has changed significantly. Many people are worried about toxicosis, headaches, heartburn and swelling. Dizziness may occur, and this condition is considered normal for the first trimester.
The belly of most mothers is not yet noticeable, and it is really still small. Already in the second trimester, others will be able to visually determine the patient’s special condition. Mommy just has to wait for the second trimester, and at that time her health will become better. Toxicosis will disappear, the dizziness will stop, and the weakness will pass.
Embryos are studied in detail by scientists, and specialists are concerned directly with their formation. The first trimester is considered the most dangerous for the mother, because complications most often occur at this time. For this reason, it is worth visiting a doctor in a timely manner and undergoing tests if you do not want to face negative consequences.
Entering the third trimester: what lies ahead
Your baby is growing and taking up quite a bit of space these days. During the third trimester of pregnancy, you may urinate more frequently or experience leg cramps as the fetus puts pressure on nerves in your hips and back. The pregnancy honeymoons are over and parenthood is on the horizon. Now it's time to take good places in the kindergarten, look for a doctor for your child, and also create a registry for him.
Week 28
Your baby's vision is developing, so he may sense slight filtering from the outside. The baby can already blink, and his eyelashes have already grown. Now it resembles a large eggplant.
Week 29
Your baby's muscles and lungs are busy getting ready to function in the outside world, and his head is growing to make room for his developing brain. Now your baby resembles a butternut squash.
Week 30
Your baby is surrounded by amniotic fluid. It grows and requires more space inside the uterus. Your baby is now the size of a large cabbage.
31 weeks
Your baby can now turn his head from side to side. A protective layer of fat accumulates under the skin, filling the arms and legs. Your baby is currently the size of a coconut.
Week 32
You're probably gaining about a pound a week. The child is fully formed, and his body has become more proportional. Thanks to the fat layer, the baby looks plump. It now resembles a large turnip.
Week 33
The bones in your baby's skull have not yet been fused. This allows you to push your head through the birth canal. They will not be completely fused until adulthood. Your baby is now the size of a pineapple.
34 week
Your baby's central nervous system is maturing, as are his lungs.
Now your baby is the size of a melon.
Week 35
Your baby's kidneys are fully developed and his liver can process some waste products. The size remains the same.
Week 36
Your baby gains about 30 grams per day. It also loses much of the fuzz that covers its body, as well as the waxy substance. Your baby is now the size of lettuce heads.
Week 37
Your date is very close. Although your baby looks like a newborn, he is not quite ready for the outside world yet. Over the next two weeks, his lungs and brain will be fully mature.
Week 38
Do you want to know the color of your child's eyes? His pupils are not fully pigmented, so if he is born with blue eyes, they may change to a darker color within a year. Now your baby resembles a leek.
Week 39
Your baby's physical development is complete, but he is still busy with his development. It will need the fat to help regulate its body temperature in the outside world. Now your baby resembles a mini watermelon.
At 39 weeks your baby will be considered full term.
40 week
Most likely you will already give birth at this time. But at the discretion of the doctor, if necessary, you can safely continue your pregnancy. Your baby is now the size of a small pumpkin.
41 weeks
Your baby is now considered late. Post-term pregnancy more than two weeks past your due date can put you and your baby in danger and cause complications. As a rule, during this period they intervene with a caesarean section.