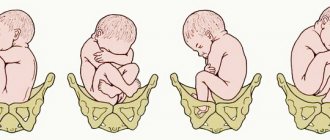
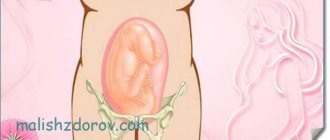
The position of the fetus is determined by the location of its longitudinal axis to the length of the uterus. When they are placed along the same line, this position is physiological. The baby is placed along the uterus, and one of its round parts (the head or pelvic end) is placed towards the cervix.
What is the transverse position of the fetus? This diagnosis indicates that the baby is located across the uterus. Its axis is located at a right angle to the axis of the uterus. In this case, the position is not determined. The baby's head and pelvis are located above the crests of the pelvic bones.
Causes.
This anomaly can be caused by various factors that contribute to excessive or, conversely, insufficient activity of the baby in the womb. The main reasons for the anomaly:
- hypotonia of the abdominal muscles;
- oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios;
- fetal hypotrophy;
- tumors of the uterus and pelvic bones;
- increased myometrial tone;
- risk of spontaneous abortion;
- large fruit;
- clinically narrow pelvis;
- multiple births;
- abnormal attachment of the placenta;
- fetal development abnormalities;
- structural defects of the uterus (bicornuate, saddle-shaped).
Symptoms.
If the fetus is not positioned correctly and there are no other pathologies, pregnancy in most cases proceeds favorably. There are no pathological symptoms. External signs may indicate an abnormal position of the fetus:
- spherical shape of the uterus;
- transversely stretched abdomen;
- the height of the uterine fundus increases slowly and does not correspond to the gestation period;
- abdominal circumference is higher than normal;
- the baby's heartbeat can be heard at the level of the mother's navel;
- The baby's pelvis and head are located on the sides of the abdomen.
How to understand how the baby lies in the mother's belly
You can find out how the baby lies in the mother's belly using an ultrasound examination. In the early stages, when the fetus is too small, it is impossible to independently determine its location.
Determining the baby's position by heartbeat
The placement of the child can be determined by the contractions of the heart muscle. It is believed that a heartbeat below the mother's navel indicates that the baby is lying upside down. If the heart is heard at the level of the navel or slightly above, the baby is positioned head up. In the early stages, there is no need to worry, since the baby’s position can easily change. For such a study, you will need an obstetric stethoscope: with its help you can understand how the baby is positioned at home.
How to determine the location of the fetus yourself by kicks
Based on the characteristics of the movements, the expectant mother can independently determine how the baby is positioned.
If shocks are felt under the ribs, the baby lies with his back forward. In this case, most often the stomach and navel protrude forward. If the tremors are felt in the front part, the stomach has become flatter, the baby’s back is on the side of the mother’s back. To independently determine the position of the baby, a woman needs to pay attention to which part of the abdomen the baby is pushing into.
If the tremors are felt above the navel, the fetus lies head down; in the third trimester this is a good sign.
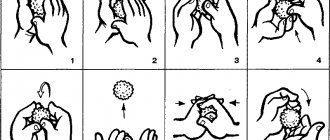
Determining the position of the baby using the abdominal map
A map of the abdomen also helps to understand the location of the fetus. It can be used from the 30th week: the baby at this stage does not become too active, his position does not change much. It is better to draw a map after a visit to the gynecologist: the doctor will determine by palpation where the baby’s pelvis and head are. A woman also needs to carefully monitor sensations: it is possible to determine the position of the child by movements.
Belly map
Non-toxic paint should be used for painting. The doll will help determine the position; It is better to use one that imitates a baby for greater accuracy.
First, determine the position of the head and pelvis. It is better to use data obtained from a gynecologist: this will increase accuracy. But you can try to determine it by some signs, your own feelings. Then the heartbeat is determined. You need to use paint to mark in which part of the abdomen it is heard. After this, the woman notes the movements: this will help to detect the location of the arms and legs. They may be bent or straightened, making them difficult to identify.
This method is auxiliary and helps to determine at home how the baby lies in the uterus.
Why is the transverse position of the fetus dangerous for the mother and fetus?
Diagnosing an abnormal position of the fetus in the early stages of pregnancy should not be a cause for panic, since there is a high probability of its change to longitudinal. If this does not happen, the main danger is that when the baby is positioned transversely in the uterus, most pregnancies end in premature birth. Therefore, women with this diagnosis are carefully monitored and hospitalized in advance.
In the absence of timely medical care, the transverse position of the fetus can lead to the following complications:
- premature rupture of amniotic fluid;
- massive bleeding;
- neglected transverse position - loss of small parts, driving of the shoulder into the small pelvis, limited movements of the child;
- uterine rupture;
- infection with subsequent development of chorioamnionitis, sepsis, diffuse peritonitis;
- hypoxia or asphyxia of the fetus;
- birth of a twin fetus - occurs when the uterus is hypertonic and intense contractions, when the fetus is bent in the chest area, the birth of a live baby in this case is unlikely.
How should the fetus be positioned depending on the week of pregnancy?
The position of the baby in the early stages depends on where the egg is implanted. Most often it is implanted to the back wall of the uterus; this position is considered the best, since the woman begins to feel movements earlier, and it is easier for the doctor to track the fetal pulse. Less commonly observed is the location on the anterior wall of the uterus; it is a variant of the norm and does not cause dangerous deviations.
A low position can be dangerous. If this option is noted for placing the baby in the stomach for weeks until 31-32 weeks, the doctor does not consider it a deviation: often the baby moves to the upper parts of the uterus. In cases where this does not happen, the doctor diagnoses placenta previa, which is an indication for a cesarean section.
The position of the baby in relation to the birth canal may also be different. In the early stages it can easily change; up to 32 weeks, the norm is a constant change in the position of the fetus. However, before birth, the baby should lie head down; otherwise complications will arise. It is better if the back is pressed against the anterior uterine wall, the position will be longitudinal (the line from the tailbone to the back of the baby's head is parallel to the uterine axis).
The oblique and transverse position is considered incorrect in the later stages.
At what time does the issue of presentation become relevant?
Since the fetus is constantly moving and changing its location in space, in the first and second trimesters you should not worry if the ultrasound results show that the baby is lying head up or perpendicular to the birth canal. The child will have time to move many times.
In the third trimester, the fetus increases greatly. The space in the uterus becomes insufficient for active movements. By week 34, the baby most often takes its final position. At this stage, it is important that the baby is positioned head down. If a pelvic or transverse presentation is noted, complications are possible; this phenomenon is observed in approximately 4-6% of cases. If the position of the baby in the stomach at this stage is incorrect, the doctor prescribes a caesarean section.
Gymnastics with the transverse position of the fetus.
Until 34 weeks of gestation, the position of the fetus is unstable, so there is a high probability that the baby will be placed longitudinally. For this purpose, expectant mothers are prescribed corrective gymnastics during the period 30-31 weeks. This is a group of exercises that help correct the incorrect position of the fetus.
Most often recommended:
- lie on the floor, bend your legs and rest your heels on the floor, raise your pelvis above head level;
- “cat” - get on all fours, while inhaling, raise your tailbone and head, and bend your lower back, while exhaling - the opposite movements;
- take a knee-elbow position, the pelvis is placed above the head - hold for up to 20 minutes.
These exercises are performed for 1-1.5 weeks three times a day. During this period, the fetus must acquire the correct position. If this happens, the stomach must be secured with a bandage.
Correct position while sleeping is also important. The baby is more accustomed to being head down, so the mother should sleep on the side on which the baby's head is located.
Corrective gymnastics is contraindicated in the following cases:
- abnormal placement of the placenta;
- multiple births;
- umbilical cord abnormalities;
- scar on the uterus;
- presence of bloody discharge from the vagina;
- abnormalities of amniotic fluid;
- severe chronic diseases of women;
- increased uterine tone;
- uterine fibroids.
How to independently determine the position of the fetus in the uterus and distinguish cephalic presentation from breech presentation?
Most expectant mothers are interested in knowing where the baby is located in their tummy. And the closer the birth is, the more important this information becomes for the mother in labor. The position and presentation of the fetus affects the course of the upcoming birth . In some of these options, childbirth through the female natural birth canal is contraindicated. Not every doctor will undertake a natural birth with a breech presentation, and a cephalic presentation of the fetus does not always provide a guarantee. The doctor, of course, will help determine the baby’s presentation, but sometimes it’s simply unbearable to wait for the next appointment, especially if the mother hopes that the baby will turn over and take a more favorable position. But how to understand how the fruit lies? How to independently determine the position of the fetus in the uterus, how to understand whether the baby has turned over? Calculating the position of the baby yourself is not at all as difficult as it might seem. By the way, this is a great way to get to know your child better.
It makes sense to make attempts to determine the position of the baby in the uterus only after the 30th week of pregnancy. Naturally, the longer the period, the more clear how the fetus lies, so if you cannot determine the presentation of the baby, you need to try again in a week - the next attempt will certainly be successful! In addition, up to 33-34 weeks of pregnancy inclusive, the position of the baby in the uterus may change, the baby may roll over. After 34 weeks of pregnancy , it usually becomes stable, that is, the baby remains in the position in which it will be born.
____________________________
Content:
1. How to determine the position of the fetus yourself: listen to the heartbeat
2. How to independently determine the position of the fetus: make a map of the abdomen
3. How to distinguish a cephalic presentation of a fetus from a breech presentation?
4. Upside down - backwards, or how to tell if the fetus has turned over, and how to make the baby turn upside down?
5. Why can’t I independently determine the baby’s position?
Video
We recommend reading
____________________________
Top
· How to determine the position of the fetus yourself: listen to the heartbeat
The easiest way to independently determine the position of the fetus in the uterus is to find out exactly where its heartbeat is best heard. To do this you will need a very ordinary stethoscope, a little patience and good luck. Your goal is to catch the beat-like sounds of your heartbeat at a rate of 120-160 per minute. It is better to start listening from the left lower segment of the abdomen - in this place you can hear the heartbeat of most babies who are “in place.” You don’t have to limit yourself to the front surface of the abdomen - in some positions of the child, the heart can be heard more clearly if the stethoscope is applied to your side. The heartbeat is best heard in the place where the baby's upper back is located.
This method is very useful when it is necessary to understand whether the fetus has turned over for birth into a cephalic presentation from a breech presentation. Find the place where his heart beats most audibly, and by doing exercises every day that help the baby roll over, watch whether the baby's position in the uterus changes. With a breech presentation of the fetus, it will be slightly higher than with a cephalic presentation.
Top
· How to independently determine the position of the fetus: drawing up
a map of the abdomen.
This method allows, without the help of ultrasound, to independently determine the position of the fetus in the uterus, and draw up a so-called detailed “map” of the abdomen. Its essence, in short, is this.
First, observe the baby’s movements (what is their nature, direction, in what part of the tummy you feel them). After this, take a supine or semi-lying position and gently feel the baby through the abdomen while the uterus is relaxed. This way you can create a “map” of the abdomen, where you can note the following observations:
- where the strongest kicks are felt - these are the baby’s legs, - where light movements with a small amplitude are felt - there, most likely, the arms are located, - where the large protruding area similar to the head is located - this is the baby’s butt, - on which side is your tummy more smooth and firm - this is the back, - where the doctor or you heard the heartbeat - there is the upper part of the baby’s back.
For convenience, you can even draw a conditional “map” and consult it to understand whether the fetus turned over by the scheduled date, and how exactly it turned over.
Top
· How to distinguish a cephalic presentation of a fetus from a breech presentation?
One way or another, you will feel the protruding part of the child from above. To determine the position of the baby in the uterus, to figure out whether it is the butt or the head, you need to understand that only the neck and back extend from the head, but also the legs from the baby’s butt. You can actually feel the legs if you are persistent, or feel them when the baby kicks. In addition, listen for yourself or remember where the doctor last found the sound of a heartbeat - if it was from below, then the child lies head down, and if from above, then with his buttocks down.
Top
· Upside down - backwards, or how to tell if the fetus has turned over, and how to make the baby turn upside down?
To begin with, I would like to draw your attention to the fact that cephalic presentation of a child is not an unambiguous indicator for a successful natural birth. There are other, no less significant factors in the position of the fetus. In particular, it is important to understand how the fetus lies in relation to the back, that is, where the child’s back is facing - towards the mother’s back, or towards the stomach? If in recent months the baby most of the time lies with his back to his mother’s back (the so-called “posterior presentation”), then, most likely, he will begin to be born from this position. But childbirth in this case may be longer, more painful, and with a high degree of probability may end in a caesarean section.
You can determine the position of the baby in the uterus by observation: if you can’t find the baby’s back when you feel your abdomen, this means that it is facing your back. In this case, it makes sense to try to “persuad” the baby to roll over. The back is the heavier part of the baby compared to the arms and legs, so it usually tends to turn down on its own - all that remains is for the mother to take the desired position. In recent decades, women have led a much less mobile, less active lifestyle and, especially during pregnancy, spend a lot of time in a half-sitting or half-lying position, largely because of this, gravity pulls the child's back down - towards the mother's back. That is, in order for the baby to roll over, the mother needs to move more actively and more often take positions in which the force of gravity will pull the back of the fetus towards the mother’s belly - any straight positions, as well as poses with the body tilted forward, standing on all fours, swimming .
In order for the fetus to turn over in the uterus after 31 weeks of pregnancy from cephalic to breech presentation , the following exercises are recommended:
1. Lie on your right side, lie there for 10 minutes, and then quickly turn over to your left side and after 10 minutes again to your right. Repeat the exercise 3-4 times in a row several times during the day, before meals.
2. It is recommended to stand in the knee-elbow position for 15-20 minutes daily.
3. The turning of the fetus is facilitated by exercise in the pool.
4. If the baby turns over on his head, it is recommended to wear a bandage for a couple of weeks so that the correct position of the fetus is fixed.
Performing such exercises has contraindications, which include: complications during pregnancy (gestosis in pregnant women, threat of premature birth), placenta previa
, scar on the uterus as a result of a cesarean section in the past, uterine tumors.
Previously, they tried to correct the breech presentation of the fetus, which they call manually, by externally rotating the fetus - through the abdomen, the doctor tried to move the baby’s head downwards. Today, this is being abandoned because the method has low efficiency and a high percentage of complications, such as premature birth, premature placental abruption, and poor condition of the child. If the breech presentation of the fetus persists, then the pregnant woman is sent to the hospital 2 weeks before the expected date of birth. There, under supervision, a delivery plan is drawn up that is most favorable in the given situation.
Top
· Why can’t I independently determine the baby’s position ?
In some cases, it can be difficult to determine the position and presentation of the baby in the uterus. If there is a lot of amniotic fluid, if the placenta is attached to the anterior uterine wall, the hands will be less able to “see”. It can be problematic to determine the presentation of the fetus on your own, if the mother is plump - the fat layer prevents you from feeling anything. If your stomach constantly tenses from trying to independently determine the position of the fetus in the uterus, it is better not to undertake such searches - in this case, you will not be able to obtain reliable information, but it is easy to have an adverse effect on the baby. The baby is best palpated during the last two months of pregnancy.
Of course, a professional can very quickly and accurately determine the position of the fetus in the uterus. But mothers have one advantage - the baby is always with them, and they can do this much more often, and feel what is called the gut. As a rule, one or two weeks of attempts make almost any mother an expert in this matter, and, being attentive, you can easily determine the presentation and position of the baby in the uterus.
Then, when the baby is born, his body will be more familiar and you will handle him with more confidence. And during pregnancy, it is much more pleasant to feel the baby’s movements when you understand how he makes them and what exactly he is doing now - where are the arms, where is the leg, where is the butt, etc. Then it’s a pleasure to answer the question “how is he doing?” - “Everything is fine with him, he moves as usual, in the morning he actively stretched his legs, he lies head down, and here he has a back, you want to touch...”
Yana Lagidna, especially for
MyMom . ru
To the top
And a little more about how to independently determine and change the position of the fetus in the uterus, video:
Top
Similar articles:
Preparing for childbirth → Breathing during childbirth: breathing technique during contractions and pushing
Preparing for childbirth → Pregnancy and childbirth: breathing during childbirth. Breathing exercises to ease childbirth
Preparing for childbirth → Joint childbirth: pros and cons. Should my husband be present at the birth?
Preparing for childbirth → The process of childbirth: periods when a child is born. Pregnancy and childbirth, video course
Preparing for childbirth → Position and presentation of the fetus during pregnancy: pelvic, cephalic, transverse,…
Childbirth with a transverse position of the fetus.
If the position of the fetus does not change, then natural childbirth is not recommended and most often a planned caesarean section is prescribed.
Natural childbirth is possible with a low baby weight, but even then it is necessary to monitor the dilation of the cervix. If the dilatation does not allow birth on its own, then an emergency caesarean section is prescribed.
In the case of premature birth with a transverse position of the fetus, a decision is usually made on an emergency caesarean section.
Surgical intervention in the case of a transverse position of the fetus is quite justified, because there is a significant risk of complications during natural childbirth.
The transverse position of the fetus entails many difficulties, but they can be easily avoided if you follow all the instructions of your obstetrician-gynecologist.