Types of hyperopic astigmatism
In medicine, a classification of the disease is accepted according to the form of refractive error in two perpendicular meridians:
- Simple hypermetropic astigmatism (H) - the distortion passes along one meridian, and in the other the refraction is normal.
- Complex hypermetropic astigmatism of both eyes (CH) – the child’s refraction is distorted along two meridians. In this case, one may have farsightedness, and the other may have myopia or also farsightedness. The child sees a very distorted picture because there is a high degree of refractive power pathology. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24637486 Kulp MT, Ying GS, Huang J, Maguire M, Quinn G, Ciner EB, Cyert LA, Orel-Bixler DA, Moore BD; VIP Study Group Associations between hyperopia and other vision and refractive error characteristics // Optom Vis Sci. 2014 Apr;91(4):383-9. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000223
Prevention of myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism
The child's visual system requires increased attention from adults. In many cases, refractive errors can be corrected, and sometimes even prevented, if attention is paid to prevention. It is important to control the level of lighting - reading and studying is permissible only in bright light, using table lamps and other point light sources. It is important to monitor the duration of visual stress in children and alternate them with physical exercise and other activities.
A good way to prevent myopia, farsightedness and astigmatism is therapeutic exercises for children's eyes, which is especially useful for schoolchildren and those children who like to play on the computer. Simple exercises relax the eye muscles, relieve tension and spasm, increase blood circulation and improve nutrition of the visual organs. To maintain normal intraocular pressure, it is useful to massage the eyeballs in a circular motion through closed eyelids.
If you are just preparing for the birth of a child, then it is important for a pregnant woman to monitor her condition, nutrition and habits during pregnancy. The correct lifestyle of the expectant mother will greatly reduce the risk of having a child with congenital farsightedness or astigmatism. If one of the parents has refractive errors, it is important to show him to an ophthalmologist immediately after the birth of the baby.
Preventative visits to a pediatric ophthalmologist should be made at least once every six months. If the doctor finds irregularities, he may schedule a different visit schedule. In any case, regular examinations by an ophthalmologist are the most effective prevention of eye diseases and refractive errors at any age.
Degree of disease development
Hypermetropic astigmatism is classified into degrees depending on how light is refracted in the meridians of the eyes. In accordance with this symptom, three degrees of the disease are distinguished:
- Weak – up to 3 units, the most common and treatable.
- Average – 3-6 units.
- Strong - over 6 units - the result of serious disorders on the cornea.
This disease is treatable, but the greater its degree, the worse the prognosis and the more difficult it is to achieve a good result. The disease, detected at an early age, allows vision correction with positive results; in adults the prognosis is much worse.
Causes of the disease
Farsighted astigmatism can be congenital or acquired.
The congenital form is determined by genetic predisposition, that is, the disease is transmitted to the child from the parents or one parent. In this case, visual impairments are detected already from birth.
If hypermetropia is within 0.5 diopters, then this is conditionally the norm. Above 1 diopter – the likelihood of disease progression.
Causes of acquired disease:
- eye surgeries;
- eye injuries;
- subluxation of the lens;
- inflammatory eye diseases;
- diseases of the teeth or jaws, due to which the wall of the orbit is deformed;
- diseases of the cornea, which are accompanied by a violation of the limiting membrane - ulcer, cataract, etc.
Clinical manifestations of childhood astigmatism
Astigmatism in one or both eyes can occur in a child at any age. Parents need to be observant and attentive, listen to the baby’s complaints and not miss the following symptoms that indicate the presence of refractive errors:
- The baby often squints when looking at objects and tilts his head;
- When walking, the child does not feel very confident, often stumbles and stumbles;
- He has difficulty reading because he cannot focus his eyes and see the letters.
Complaints that can be heard from a small patient with astigmatism are as follows:
- Insufficient image clarity near or far;
- Distortion of objects;
- Feeling of discomfort and rapid eye fatigue;
- Headaches due to eye strain;
- Duplication of objects.
It is important to remember: children adapt to visual impairments quite quickly, so parents may not learn about them from the child himself. That is why it is so important to undergo preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist in a timely manner.
Diagnostic methods
After a physical examination, the pediatric ophthalmologist may order the following tests:
- Visometry – determination of visual acuity using a table.
- Ultrasound of the eyeball - contact ultrasound.
- Biomicroscopy is a visual examination of the tissues and optical media of the eye. Based on the contrast between illuminated and unlit areas. Allows you to examine in detail the iris, cornea, lens, anterior chamber of the eye, central areas of the fundus, and vitreous body.
- Skiascopy - the eye is illuminated by a beam of light that is reflected from the mirror, and the doctor observes the movement of shadows in the pupil area.
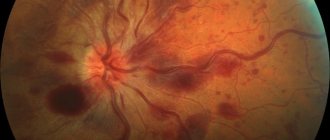
- Ophthalmoscopy – examination of the fundus of the eye.
- Computer keratotopography - prescribed in difficult cases, involves obtaining a color map of the ocular surface, a hardware-based technique, non-contact and painless.
Diagnostics
To diagnose hypermetropic astigmatism, it is not enough to establish the fact of visual impairment. Ophthalmologists have to figure out in which plane and along which meridians the refraction of the light beam is disrupted. For this purpose, a complex of instrumental and physical studies is used, including:
- visometry - a standard measurement of visual acuity in each eye, identifying the nature of visual dysfunction;
- autorefractometry – determination of the curvature of the cornea;
- duochrome test - a study using color filters that help identify the hypermetropic type of refraction (refraction of light inside the eyeball);
- biomicroscopy - examination of the structures and membranes of the anterior pole of the eye using a slit lamp, which identifies possible contraindications for certain types of vision correction;
- Snellen and Raubichek test - specific studies using figures and the light flux directed through them, which make it possible to determine the leading meridians and the degree of change in the refractive power of the eyes;
- keratotopography - computer diagnostics of the surface of the eye with measurement of the thickness and curvature of the surfaces of the cornea, changes in the sphericity of which may indicate astigmatic manifestations;
- optical or ultrasound pachymetry - studies that help determine the curvature of the anterior sphere of the eyeball in order to select contact lenses.
Computer methods are considered the most informative in terms of diagnosing anomalies. They allow you to identify changes not only in the cornea, but also in the internal structures of the eyeball that affect refraction, without pain or discomfort.
Home tests
To determine the disease, there are many schematic tests that can be found on the Internet. Some you can do yourself:
- Siemens Star test - a circle with a diameter of 10 cm is displayed on a computer monitor, which is formed from 54 black rays, the background is white, the rays are the same in size and color. The test is carried out in the morning, the brightness of the monitor should be medium. The child takes off his glasses or contacts and moves 5 m away from the screen. First, he closes one eye and looks at the picture for 2-3 seconds, then closes the second eye and looks again for 2-3 seconds. Then you need to look at the picture with both eyes. With astigmatism, the lines visually thicken, bend, their contrast changes, and an oval or shapeless image appears in the center of the circle.
- “Straight Lines” test - with astigmatism, the child sees straight lines drawn or created on a computer as curved.
- Test “Dark lines” - on the monitor you need to draw a circle consisting of straight dark lines, like rays. The child takes the test without taking off his glasses. You need to sit in front of the drawing at a distance of 35 cm, look, closing one eye. All lines should normally be sharp and distinct, equally dark. With astigmatism, some lines are normal, while others are lighter and blurred.
How to recognize symptoms of astigmatism in children?
Parents should carefully monitor the development of the child’s visual organs and pay attention to the peculiarities of visual perception. He should be taken to the doctor immediately if the following symptoms are noticed:
- the child squints when looking at both long and short distances;
- complains of eye fatigue while reading or writing;
- has difficulty reading text, cannot identify some letters;
- tilts his head to the side in an attempt to get a better look at the object.
If such signs are present in children, you can also conduct a mini-test at home to check for astigmatism. To do this, experts advise doing the following. You need to take a sheet of paper with a clear graphic black and white design, then place it in front of the child’s face at arm’s length and ask him to close one eye. Next, check how well he sees all the lines or strokes (by pointing to them), find out if any of them seem lighter than the rest.
If the answers to the questions are affirmative, this may indicate the presence of astigmatism with some degree of probability. During the examination, the ophthalmologist will use instruments to identify the degree and type of this disease.
Treatment of hyperopic astigmatism
The disease is corrected in two ways - with glasses or contact lenses or surgically.
Spectacle correction
This correction does not eliminate the defect itself, but forcibly changes the refraction, restoring visual acuity. Children under 3 years of age cannot wear glasses carefully. Therefore, correction is possible with specially shaped hard contact lenses. If the degree of the disease is weak, then the cornea can be given the correct shape in this way.
Children over 3 years old are prescribed glasses to prevent further development of the disease.
Surgery
Farsighted astigmatism can be completely eliminated only by surgical methods. There are different types of interventions that restore vision:
- Infrared coagulation (thermokeratocoagulation) is carried out using a heated needle. This needle is used to make pinpoint burns on the cornea. After this, coagulation (folding) of collagen occurs in the center of the cornea, due to which the central part becomes more convex, and flat on the periphery. As a result, refraction is restored throughout the entire cornea.
- Laser coagulation is the effect of a laser beam on the center of the cornea to correct its shape.
- Hypermetropic laser keratomileusis - small incisions are made on the cornea using a laser beam to gain access to the middle layers of the cornea. Corrections are made on them. This is one of the most advanced operations with good results.
The operation is recommended after 18 years of age. At an earlier age, surgical intervention is indicated only for a high degree of farsighted astigmatism.
After the operation, within a few days the child sees well and his vision is completely restored.
Methods and effectiveness of treating astigmatism in children
Treatment of childhood astigmatism is usually carried out with conservative methods. Until approximately 18 years of age, the eyeball grows, so surgical manipulations or laser correction are carried out only if there are serious indications. If you start treating astigmatism on time and strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, the pathology can be corrected and the development of complications can be prevented.
- Spectacle correction.
- Contact lenses.
- Night lenses.
Sometimes a doctor may prescribe treatment for childhood astigmatism using orthokeratological correction. It involves wearing hard lenses at night to correct the curvature of the cornea. By putting on these lenses before bed, your child will be able to see much better during the day. However, this method is only suitable for low degrees of astigmatism up to 1.5 diopters.
- Laser correction.
Sometimes, on the recommendation of a doctor, a child’s astigmatism is treated with laser correction. The procedure takes about 15 minutes and is performed under local anesthesia. After such treatment there is no need for sutures, and the rehabilitation period is practically absent. According to experts, within a couple of hours after laser correction, vision will noticeably improve, and after 7-14 days it will be completely restored.
For each little patient, the doctor selects an individual treatment regimen that will help achieve the best results. The main task of parents is to bring their child to see a doctor as early as possible.
Prevention methods
There are no special ways to prevent hypermetropic astigmatism. It is necessary to protect the eyes from injury and promptly treat diseases of the anterior part of the eye and lens. Regular eye exercises and courses of vitamins to strengthen vision will also be useful. Source: E.P. Tarutta, O.V. Proskurina, N.A. Tarasova, G.A. Markosyan Analysis of risk factors for the development of myopia in preschool and early school age // Health Risk Analysis, 2021, No. 3, pp. 26-31
Sources:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24637486 Kulp MT, Ying GS, Huang J, Maguire M, Quinn G, Ciner EB, Cyert LA, Orel-Bixler DA, Moore BD; VIP Study Group. Associations between hyperopia and other vision and refractive error characteristics // Optom Vis Sci. 2014 Apr;91(4):383-9. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000223.
- E.P. Tarutta, O.V. Proskurina, N.A. Tarasova, G.A. Markosyan. Analysis of risk factors for the development of myopia in preschool and early school age // Health Risk Analysis, 2021, No. 3, pp. 26-31.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an ophthalmologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Biomicroscopy of the anterior segment of the eye | 500 rub. |
| Selection of glasses with plain lenses | 600 rub. |
| Subconjunctival injection (1 eye) | 500 rub. |
| Removal of a foreign body from the conjunctiva, from the eyelids | 800 rub. |
How can you tell if your child is developing astigmatism?
Unlike adults, children cannot always complain of decreased vision clarity and other problems. Therefore, one can suspect astigmatism in a preschooler based on indirect signs.
- The child often suffers from dizziness and headaches concentrated in the frontal region.
- Children with astigmatism may avoid reading or even just looking at pictures.
- Trying to “catch the focus,” the child squints his eyes and turns his head at different angles when looking at objects.
Such symptoms are not a clear indication of the presence of astigmatism, but should be a reason to show the child to an ophthalmologist.