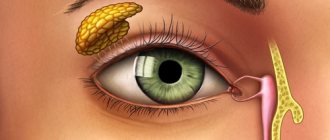
In what cases do doctors use needles to irrigate the tear duct?
In medical practice, the problem of obstruction of the lacrimal canal is often encountered. The danger of the pathology lies not only in the discomfort it brings to the patient; for example, the eyes can continuously water, which interferes with the normal functioning of the visual apparatus. With obstruction, bacteria and viruses harmful to the body are activated, which find themselves in a favorable environment for development and reproduction. As a result, infectious diseases may develop.
You can eliminate congestion in the tear ducts by introducing a special liquid into their cavities. Filling occurs under slight pressure. Washing can be prescribed for diagnostic purposes and as targeted therapy for a number of ophthalmological diseases, such as:
- Corneal ulcerations requiring sanitation of primary foci of infection;
- Slight stenosis of the lacrimal canals and nasolacrimal duct;
- Congenital or acquired dacryocystitis in the first days of a baby’s life;
- Other inflammatory processes in the eye area.
Depending on the throughput, a specialist during the procedure can diagnose the condition of the lacrimal canal, identify incipient pathologies, unwanted protein and other deposits.
If there is no blockage, the liquid administered under slight pressure should come out freely through the nose. During the procedure, doctors use special sets of instruments, including needles for rinsing the tear duct.
Symptoms
Obstruction of the lacrimal canal is the first stage of the disease.
Signs:
- suppuration of the corner of the eye, possible gluing of eyelashes with pus;
- profuse lacrimation for no reason.
If you do not consult an ophthalmologist in time, the disease develops and enters the second stage - blockage of the canal occurs (stenosis). In this case, the tears stagnate and harden. This phenomenon can occur in one eye or two. If further failure to seek medical help occurs, dacryocystitis occurs - a more dangerous pathology in which the canal is completely clogged. Causes loss of vision.
Signs:
- vision decreases;
- blood “strings” in the lacrimal sacs;
- purulent discharge;
- swelling and inflammation of the eye;
- redness and heat in the eye;
- painful sensations on palpation;
- profuse lacrimation;
- The density of the lacrimal sac increases and it increases in size.
Cellulitis of the lacrimal sac may develop - acute purulent inflammation followed by death of eye tissue.
Obstruction of the tear duct is easily confused with other ophthalmological diseases:
- Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye.
- A corneal ulcer is the destruction of corneal tissue.
- Eye stye is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash.
- Blepharitis is a chronic inflammation of the eyelids.
- Demodectic mange is an infection of the eyeball by parasites.
- Allergic manifestations with whitish discharge from the eyes.
Therefore, at the first symptoms of a lack of patency in the tear duct, you need to contact an ophthalmologist and undergo an examination. Only a specialist will determine the disease and treatment method.
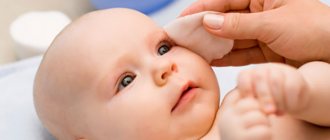
Lacrimal duct lavage in newborns
Due to the physiological characteristics of the structure, the nasolacrimal ducts of a baby can be blocked to a greater extent by a gelatinous film, which should self-destruct 15 days after the birth of the child. In standard cases, this process is not facilitated by medication - it occurs independently under the influence of tears.
However, the film does not always dissolve naturally, which may indicate its excessive density or a congenital anomaly in the structure of the skull or tear ducts. In such cases, doctors recommend postponing rinsing the baby's lacrimal canal. As a rule, the procedure should be delayed until the child is at least 2 months old. In some cases, ophthalmologists prescribe a special massage to the baby, which helps clean the tear ducts without additional intervention. In the first stages of therapy, the child's mother can massage the required area on her own. The set of exercises is not that complicated. For example, after each feeding, the mother massages the baby’s tear duct up and down with force 6-10 times. However, it is important to perform the massage correctly. It must be preceded by a mandatory consultation with a specialist.
If a set of exercises does not help, the lacrimal canal is washed in newborns. During medical intervention, before the procedure begins, the doctor administers local anesthesia to the child for pain relief.
A special rinsing kit is then used, which may include:
- Conical instrument (Zakhil probe);
- Bowman's probe, which has a pointed base (with its help, the doctor pierces the gelatinous film that interferes with the outflow of tear fluid);
- Special blunt needles, etc.
Before surgery, the lacrimal canals are disinfected with a solution. The final stage of washing involves disinfection by introducing antibiotics, which subsequently eliminates the risk of inflammation and the development of infectious diseases.
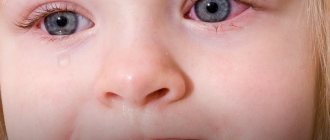
Symptoms of tear duct obstruction in infants
Signs of pathology in infants are the same as in adults.
The very first symptoms that are important not to miss:
- causeless lacrimation in the baby;
- redness of the area around the eyes (one or both);
- purulent discharge, more abundant at night.
Pus sticks together the newborn's eyelashes, making it impossible for him to open his eyes. Subsequently, dacryocystitis develops with symptoms similar to those of an adult.
Lacrimal duct rinsing in adults
Doctors can diagnose blocked tear ducts in patients of any age. Most often in adults, the procedure is performed for diagnostic purposes. Using this method, it is possible to determine the percentage of passive patency of the lacrimal ducts (in some cases, the diagnosis is carried out several times).
Problems with patency in adults are more difficult to eliminate than in infants. In this case, neither probing nor massage helps. Due to the tightly formed tissues, the only way to restore tear flow is repeated rinsing.
If a thick film blocks the tear ducts, as a rule, simple rinsing is not prescribed. In the appropriate situation, surgical intervention is advisable.
As with newborns, the patient is given antibiotics after the procedure to prevent complications. The drugs are taken during the rehabilitation period. They can be in the form of nasal sprays or drops.
Treatment of blocked tear ducts
The best treatment for blocked tear ducts depends on the cause. Your eye doctor will recommend trying the least invasive option first and then choosing what works for you and when to move on to other treatments.
Below are common treatments for blocked tear ducts.
Blocked tear ducts in babies
For many newborns, tear duct blockage resolves during the first year of life. However, there are cases when treatment is necessary. The first treatment for blocked tear ducts in infants involves dilation (gently widening the duct), probing, and lavage. If this does not help, the ophthalmologist will sometimes insert a dilation probe to further widen the canal.
Blocked tear ducts in adults
Blocked tear ducts in adults usually indicate narrowing or other problems that do not go away on their own. The first stage of treatment is the same as for infants: dilatation, probing and lavage.
If there is no response to less invasive treatment, surgical stenting and intubation are performed by inserting a tube to keep the tear duct open.
As always, you should talk to your eye doctor if you are experiencing symptoms or concerns. Your eye doctor examines your eyes regularly and also identifies problems that arise between regular exams and helps you decide on the best treatment options.
Symptoms
There are a number of signs of problems in the functioning of the lacrimal ducts. These may be symptoms such as:
- Excessive tear production;
- Swelling, pain in the corners of the eyes;
- Infections, inflammations, and also disturbing a person for a long time;
- Mucus accumulation and excessive secretion.
In addition to the listed symptoms, patients with obstruction often complain of blurred vision. If the above symptoms appear, the right decision would be to seek qualified help. Timely treatment, preceded by early diagnosis, will help get rid of undesirable consequences.
Indications for the procedure
The main indication for washing the lacrimal canal in children under one year of age is considered to be recurrent dacryocystitis. It is characterized by accumulation of tear fluid in the corners of the eye, inflammation, suppuration and the formation of crusts on the eyelashes. In addition, washing is indicated for diagnostic purposes, using a special dye to determine the patency of the ducts. Therapeutic rinsing is also indicated after probing surgery - to eliminate the infection and remove remnants of gelatinous plugs.
Contraindications
As with any other procedure, there are some contraindications for washing the lacrimal ducts. Thus, the operation is not performed on people who have hydrops of the lacrimal sac or purulent inflammation of the eyes (hydropsus and phlegmon, respectively). Rinsing is not prescribed if the patient is diagnosed with a stretched lacrimal sac (it contains mucus) due to the risk of spread of pus. In a number of other cases, the procedure is not considered dangerous and does not require additional care, but during the healing period you will have to stop wearing soft contact lenses and other types of them (the use of glasses with diopters is recommended to correct refraction).
Rinsing the tear ducts is a safe method of diagnosis and treatment that does not injure the tissue. Ophthalmologists do not recommend delaying the examination, since the corresponding disorders are easier to eliminate in the early stages of development.
The website of the online store Ochkov.Net presents a wide range of contact correction products. From us you can order products from well-known brands such as Acuvue, Biomedics, Hera and others.
Rehabilitation
Inpatient observation, regular dressing changes, and antibiotic therapy to prevent postoperative infection are indicated for a week. The sutures are removed on day 5-6.
It takes about a month for the tissue to completely heal. During the rehabilitation period, the eyes and nasal mucosa are washed. Routine medical supervision is indicated. It is contraindicated to visit swimming pools, baths, and beaches. You should also refrain from intense physical activity.
If severe chronic dacryocystitis is not treated correctly, stretching of the lacrimal sac, abscesses and phlegmon develop. As a result, corneal ulcers, tissue necrosis, purulent encephalitis and meningitis are possible. The inflammatory process spreads further according to the type of erysipelas with an increase in temperature and an increase in regional lymph nodes.
To consult with an operating ophthalmologist in St. Petersburg, call us at SM-Clinic.
How to get rid of the disease
Purulent exudate from the eye is often confused with conjunctivitis, so for dacryocystitis in newborns, treatment does not need to be done at home, relying on the experience of grandmothers. Don't play with your baby's vision; it's better to seek help immediately. It is very important to make an accurate diagnosis as early as possible so as not to aggravate the matter with surgical intervention.
Usually, drug and antibacterial therapy is prescribed, as well as a special massage of the area of edema, which helps to break through the blockage of the nasolacrimal duct. Your doctor will teach you how to do a massage correctly during your consultation.
If there is no effect, probing is performed (washing the lacrimal canal in an infant), mainly after 3 months of age. After a year of life, probing is performed under anesthesia.
Under local anesthesia, a thin probe is inserted into the baby's lacrimal canaliculus, and the canal is washed with an antiseptic solution. The surgeon then prescribes antibacterial drops after the operation. If there is no positive result, the procedure is repeated.
Of course, when the tear duct is clogged in a newborn and treatment is started immediately, a cure is possible using only drops and massage. This happens in about 65% of cases. In other cases, surgical intervention is required - probing of the nasolacrimal canal.
Preparing for washing
If no conservative measures help eliminate dacryocystitis, the doctor prescribes lavage of the lacrimal canal in children 3 years old under local anesthesia. The intervention is indicated from an early age; before it begins, the doctor instills drops with anesthetics into the area of the inner corner of the eye. During the procedure, a set of rinsing tools is used:
- a conical probe that is inserted into the lacrimal canal;
- pointed Bowman probe to remove gelatinous film;
- blunt needles.
Symptoms of tear duct obstruction
Obstruction of the lacrimal ducts can occur in one or both eyes at the same time. In turn, the symptoms of this pathology may manifest themselves due to blockage of the drainage system or as a result of a subsequent infection.
In general, obstruction of the lacrimal ducts is accompanied by:
- profuse lacrimation;
- frequent inflammatory processes of the eyes;
- painful swelling in the inner corner of the eye;
- discharge from the eyes;
- presence of blood in tears;
- blurred vision.
If you encounter one or all of the above symptoms, you need to consult an ophthalmologist as soon as possible to conduct a full examination of the visual organs and determine the cause of the pathology.