Possible reasons
Yellowness of the sclera appears due to the following systemic pathologies:
- Infectious hepatitis. A liver disease in which the liver is damaged or its functioning is impaired. The acute stage of the disease develops during the first 6 months after infection and is practically asymptomatic. In severe cases, the baby is hospitalized. A child becomes infected from the mother during pregnancy or after birth through contact with a carrier of the disease.
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome. There are 2 types of the disease. This is familial jaundice caused by unconjugated, non-hemolytic hyperbilirubinemia. A congenital disease is an inherited disorder of pigment metabolism associated with the absence or low activity of glucuronyl transferase in liver cells. With type 1 pathology, newborns die at 1 year of life, some live up to 30 years. Death occurs from bilirubin encephalopathy. The disease occurs equally among boys and girls. The duration of treatment for patients with type 2 syndrome is higher.
- Enzymopathic jaundice. The disease is characterized by hereditary pigmentary hepatosis, which is caused by a violation of the transport of bile pigment from parenchyma cells to bile. The type of inheritance is autosomal recessive. Dabin Johnson syndrome is manifested by increased fatigue, pain in the right hypochondrium, diarrhea, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, and poor appetite. In some children, the disease is asymptomatic and manifests itself after several decades.
There is also a normal (physiological) form of the disease. Newborns suffer from this form of jaundice due to the early stage of liver development. It appears when the child is 2–4 days old.
Breastfeeding can cause jaundice when the baby doesn't get enough breast milk to flush out the bilirubin. This type of illness often goes away when the milk comes in.
We recommend reading: Blue whites of the eyes
Sometimes substances in breast milk cause a newborn's intestines to retain bilirubin rather than excreting it in the stool. This form of jaundice disappears by 12 weeks of age.
Yellowing of the whites is rarely associated with ophthalmological diseases. But you should know that this symptom is caused by tumors, pinguecula (benign formation on the protein membrane) and pterygium (abnormal growth of the mucous membrane of the eye, red and whitish), cysts. In infants, yellow eyes indicate an allergic reaction.
What is pathological jaundice
The disease most often manifests itself during the first days after the birth of the baby. Pathological jaundice is called hyperbilirubinemia, since it is characterized by an increase in bilirubin levels to very high levels due to disturbances in the functioning of the body of the baby or mother.
The disease is divided into several types:
- conjugation (appears on days 3-4);
- hemolytic (accompanied by massive breakdown of red blood cells);
- obstructive (develops with partial or complete obstruction of the biliary tract);
- parenchymal (occurs with lesions of the liver parenchyma).
It is not always possible to accurately determine the cause of the disease. The development of the disease is accompanied by factors such as breastfeeding, prematurity, and severe weight loss.
In approximately 10% of cases, jaundice is pathological.
Symptoms of jaundice
Jaundice is a common and usually harmless condition in newborn babies, causing yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. Other symptoms of the disease:
- yellowing of the palms of the hands or soles;
- yellow urine (a newborn baby's urine should be colorless);
- yellowness appears 1–3 hours after birth, becoming more intense within 3–4 days;
- symptoms either disappear or begin to appear more actively;
- stool becomes light in color;
- hematomas appear on the baby’s skin;
- in rare cases, vomiting is observed.
During the diagnosis, the doctor will find an enlarged liver and spleen. The child's general condition worsens, the baby becomes lethargic and capricious.
Why do the whites of the eyes turn yellow?
As the famous saying goes, eyes are the mirror of the soul. However, not everyone knows that the appearance of the eyeballs often indicates the condition of the internal organs and health in general.
For example, a symptom such as yellow whites of the eyes can be a sign of very serious diseases. Why are the whites of the eyes yellowish?
Causes of yellow whites of the eyes
The main causes of yellow sclera of the eyes:
- Diseases of the liver and biliary tract - the whites of the eyes are colored with a yellow pigment, which is formed due to the breakdown of a large number of red blood cells. This pigment is bilirubin, which for some reason (hepatitis, cholelithiasis) is not excreted from the body;
- Helminth infections - parasitism of helminths (opisthorchis, echinococcus) in the liver can cause closure of the lumen of the bile ducts, which provokes obstructive jaundice;
- Physiological jaundice of a newborn - after birth, the baby’s red blood cells actively disintegrate, and liver enzymes are not yet mature enough to cope with the resulting bilirubin;
- Melanomas and conjunctivitis of a malignant nature are pathologies of the visual analyzer;
- Bad habits, including alcohol abuse, smoking, consumption of large amounts of spices, fatty, smoked foods;
- Overstrain and fatigue.
Overvoltage
Prolonged stress on the visual analyzer can be a provoking factor for yellowing of the sclera. Occurs in the following cases:
- Prolonged work on a personal computer;
- Chronic lack of sleep;
- Long reading in a supine position;
- Working with small details in low light.
In such situations, yellowness of the eyes is accompanied by pain, a feeling of dryness and pain, and “the presence of sand.” A person cannot concentrate his gaze on a specific object and complains of headaches and dizziness.
Bad habits
Tobacco smoking is perhaps one of the most harmless reasons why the whites of the eyes may turn yellow. As you know, tobacco smoke contains a large amount of toxic substances.
When in contact with the eye, smoke has a harmful effect on the tear film and conjunctiva, as a result of which they can become cloudy or even yellow. However, it must be said that this does not happen to every smoker.
Neoplasms of the eye
Pinguecula and pterygium are benign neoplasms of the eye. They arise as a result of lipid metabolism disorders and do not pose any threat to health. At the same time, pinguecula and pterygium tend to grow and can become a serious cosmetic defect.
Infectious eye diseases
The whites of the eyes may turn yellow if a person has recently had infectious keratitis or severe conjunctivitis. The fact is that during the course of the disease, microscopic defects appear on the surface of the conjunctiva and cornea, after healing of which yellowish scars remain.
It should be noted that this phenomenon can remain for life or disappear without a trace when using keratoprotectors - drugs that accelerate the regeneration (restoration) of the cornea.
Liver diseases
Sometimes yellowed whites of the eyes are the first symptom of hepatitis and other liver diseases.
The coloring of proteins is caused by the breakdown products of bilirubin, an enzyme that is produced by the liver for the normal functioning of the hepatic system. In this case, the skin and visible mucous membranes will turn yellow.
A similar picture will be observed in all viral hepatitis, Gilbert's syndrome (hereditary increase in the concentration of bilirubin in the blood), malignant neoplasms of the liver
Diseases of the biliary tract
The eyes may turn yellow as a result of obstructive jaundice, a disease that is accompanied by obstruction (blockage) of the bile ducts (for example, in the case of cholelithiasis). As a result, bile accumulates in the cavity of the gallbladder, and its breakdown products penetrate into the blood and give the skin and mucous membranes a specific yellow-lemon coloration.
Parasitic diseases
This refers to opisthorchiasis and echinococcosis. The favorite location of these parasites is the liver. Together with the blood flow, the parasite larvae penetrate the hepatic ducts.
Once there, they tightly attach to the wall of the ducts and form cysts in which further development of the parasite occurs.
Over time, the cyst grows, compresses the hepatic ducts and causes an attack of hepatic colic, one of the symptoms of which is yellowing of the sclera (the whites of the eyes).
Now you know why the whites of the eyes turn yellow in adults, but why does scleral jaundice occur in children?
Jaundice in newborns
Yellow whites of the eyes are observed in almost every newborn soon after birth. This is due to the insufficient maturity of the baby’s liver enzyme systems. In a newborn, the yellow whites of the eyes go away on their own, without medical intervention.
Physiological jaundice in a newborn is not a pathology. This is the baby’s body’s reaction to adapt to environmental conditions. Appears in every second newborn.
During the prenatal period, the child's body receives a large number of red blood cells from the mother. When born, the formed elements of the blood disintegrate massively, resulting in the release of bilirubin.
The liver enzymes of a newborn are not able to bind bilirubin with proteins in order to remove it from the body due to their immaturity. The baby's sterile intestines are also not a contributing factor for the excretion of pigment in feces.
Physiological jaundice disappears during the first 10 days of life. If yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes persists for a longer period, the baby should be taken to a pediatrician to assess the condition and prescribe therapy.
However, there is a second reason for yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes in a baby - hemolytic disease of newborns. It develops in the event of an immunological conflict due to incompatibility of the Rh factor or blood group. This is a very serious condition that threatens the child’s life and requires emergency care.
Yellow spot on the white of the eye
This phenomenon is not a symptom of irreversible changes and is not a cause of decreased visual acuity.
Pinguecula is a thickening of the mucous membrane of a benign nature, which does not have a tendency to malignant degeneration. It is considered one of the signs of age-related changes in the conjunctiva. Frequent cases are the appearance of a yellow spot simultaneously on the whites of both eyes.
Pterygium is a formation (growth) in the form of a yellow film, localized in the inner corner of the eye (on the white of the eye). Its appearance is provoked by physical factors (ultraviolet radiation, strong wind, dry or hot climate).
A dermoid cyst is a dense yellow capsule, the contents of which are fatty deposits. Has the ability to increase in size.
A nevus is a yellow spot that can appear in any corner of the sclera of the eye. The shade of the formation reaches brown.
Horner-Trantas spots are a disease that is accompanied by the appearance of small dotted yellow spots in the form of millet grains that occur against the background of allergic manifestations.
DrVision.ru
Consequences
You cannot self-medicate; even with the physiological appearance of the disease, it is recommended to be observed by a pediatrician. Having started the pathology, the child will have the following disorders:
- poisoning of internal organs;
- neurological abnormalities;
- partial deafness, in some cases the baby completely loses hearing;
- possible cirrhosis of the liver;
- immunity is greatly reduced.
Jaundice is not a serious problem in most healthy children. However, very high levels of bilirubin are dangerous. They can damage the newborn's brain.
The risk of serious complications from high bilirubin levels increases if the baby is premature. But jaundice is diagnosed before bilirubin levels become high enough to cause this type of damage.
What happens if jaundice is not treated?
Severe forms of jaundice, if not treated promptly, can lead to a baby's blood transfusion.
The concentration of harmful substances increases, and the liver cannot cope with cleansing the body. This is very dangerous because nervous system disorders may occur.
Infant jaundice, unlike adults, is not contagious! This is not viral hepatitis, and a child with jaundice is sometimes prescribed only activated charcoal.
Remember that infant jaundice is not a defect! Your pediatrician will help you make a diagnosis if symptoms occur. Physiological jaundice in newborns is not dangerous, unlike hemolytic disease, so you should not panic, but it is better to trust specialists in matters of the baby’s health.
Diagnostics
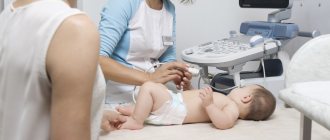
Diagnosis is carried out in the clinic. The child is sent for inpatient treatment. He is under the supervision of medical personnel until the attending pediatrician establishes the exact cause of the disease.
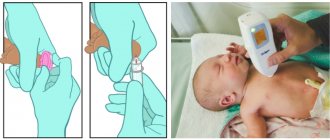
To determine the level of bilirubin, blood is taken from the child. The analysis is carried out several times so that the doctor can verify the accuracy of the result obtained.
Then the condition of the skin is examined. The initial diagnosis is made based on the color of the skin and the whites of the eyes. To confirm the disease, urine and stool tests are performed.
The doctor will need information about the course of pregnancy and childbirth. This information is important to establish the correct diagnosis. If necessary, parents of the sick baby are given a referral to visit an endocrinologist and surgeon.
What will be offered at the hospital?
You can often see yellow whites of the eyes in newborns. When this condition passes depends entirely on the cause. If the jaundice is physiological, then within a week the color of the eyes and skin will normalize. If the cause is pathological changes in organs, then treatment will take longer. Such jaundice will require hospitalization of the baby and mother, where a course of treatment will be offered.
Depending on the cause, the baby may be prescribed procedures that combine therapeutic techniques, which include the following:
- choleretic;
- antibacterial;
- antiviral;
- immune;
- detoxification.
As the experience of doctors and reviews of parents shows, such methods in combination usually give good results. There are practically no complaints about the deterioration of the child’s well-being and the occurrence of complications. However, you need to be prepared for the fact that at first the baby’s well-being may be unsatisfactory.
Treatment
Often no treatment is required. Mild jaundice goes away on its own in 1–2 weeks. In case of severe illness, the baby is hospitalized; the child must be under the supervision of medical personnel around the clock. Treatment is carried out if tests show a very high level of bilirubin in the baby’s blood.
There are 2 main procedures that are carried out in the hospital to quickly reduce its amount:
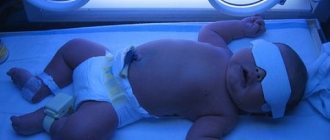
- Phototherapy. The child is placed under special lamps or on a light-producing blanket. The baby only wears a diaper and a mask to protect his eyes. Light helps the body get rid of excess bilirubin. Converts bilirubin into a form that is easily broken down by the liver. Phototherapy lasts 1–2 days. If the bilirubin level is very high, treatment can be carried out at home. It is important that your baby gets plenty of breast milk or formula. If phototherapy does not help and the bilirubin level in the baby's blood continues to rise, a blood transfusion may be required.
- Exchange transfusion. The procedure is prescribed in severe cases. Exchange transfusion is performed if serum bilirubin is more than 350–428 µmol/l. The procedure involves simultaneous infusion of donor blood while collecting the recipient's blood. The baby's blood is removed from the bloodstream and simultaneously replaced with donor blood. It is performed through 2 veins to prevent clotting during a long procedure. The baby's blood is removed from one, and donor blood is poured into the other.
Cause and investigation
It is always necessary to determine exactly why the whites of the eyes of newborns are yellow. Further therapy depends on the diagnosis. So, if the cause is a Rh conflict, then it is advisable to carry out a transfusion of blood or its components. Next, the baby may be recommended a course of antibiotics and physiotherapy. If the jaundice is of a mechanical type, then surgical intervention will be required.
If there are failures in the production of bilirubin, the baby may be shown photo procedures. Their essence is to place the child under a special lamp that works on the principle of sunlight. As a result, the baby’s body begins to intensively produce vitamin D, which successfully copes with increased bilirubin. Typically the course is 96 hours under the lamp.
For some pathologies, doctors may prescribe courses of intravenous glucose and the administration of activated charcoal. Glucose is necessary to activate the liver, and the sorbent removes the remaining unprocessed bilirubin naturally along with feces.
Prevention
To prevent jaundice in a baby, the mother should lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid infections and treat them in a timely manner, and eat right.
You can reduce the risk of your baby developing the disease by feeding your newborn 8–12 times a day for the first few days. Feed on demand.
Actively attaching a newborn to the breast promotes the active functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and hepatobiliary system. This helps your baby urinate and defecate regularly, which helps remove excess bilirubin from the body.