Indications
Probing is a mini-operation that is prescribed when absolutely necessary. First, the doctor will advise the patient to do a jerky massage in the area of the blockage and drip medicinal drops, and only after that - probing. It is advisable to conduct a bacteriological examination of purulent discharge in order to prescribe suitable drops.
Indications for sounding:
- an infant with dacryocystitis older than 5 months;
- the eye is constantly watering, lacrimation intensifies on the street;
- inflammation in the area of the nasolacrimal duct has become chronic;
- Treatment with massage and drops gives a short-term effect, the eye continues to fester.
Sometimes infants have the blockage removed at 1-3 months if the child’s health worsens or the temperature often rises. In other cases, the operation is postponed for up to 6 months for the following reasons:
- sometimes massage helps restore the patency of tears;
- By this age, tears are produced in full, and the lacrimal canal is fully washed. This speeds up recovery after surgery and reduces the risk of relapse.
Probing procedure
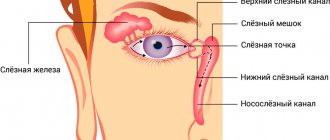
Before birth, the baby has no communication between the nasal cavity and the tear duct. It is closed by a thin membrane, which breaks through at the time of birth. The canal itself is closed in utero with gelatinous contents, which after birth, when the child screams and breathes independently, is removed from the duct and enters the nose. If the membrane does not rupture and the contents are not drained, obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct occurs with dacryocystitis - inflammation of the nasolacrimal duct. The eyes become watery, inflamed, and suppuration occurs. If conservative measures with massage and the use of drops do not help, probing of the canal is necessary - restoration of patency due to mechanical action, insertion of a special probe into the canal. It breaks the membrane and removes the plug.
Contraindications
An absolute contraindication for sounding is a deviated nasal septum. This pathology requires surgical intervention, as it can cause chronic dacryocystitis.
Relative contraindications:
- acute respiratory infection or acute period of disease of the ENT organs;
- phlegmonous dacryocystitis of the newborn;
- phlegmon of the lacrimal sac.
Exacerbation of the infectious process causes swelling of the nasal mucosa, so surgical intervention during this period is not advisable.
If the lacrimal sac becomes infected with pathogenic microorganisms, phlegmon forms. This is an inflammation of connective tissue and fiber with the formation of pus. A dangerous pathology requires urgent hospital treatment. Probing is recommended after the inflammation has completely subsided.
Preparation for the procedure
The diagnosis of “dacryocystitis” is made by an ophthalmologist, but the operation will require consultation with other specialists:
- an ENT doctor to rule out a deviated nasal septum;
- pediatrician to exclude infectious processes in the child;
- anesthesiologist if general anesthesia is required.
In addition, be sure to do a urine test and a blood clotting test.
The child should not be fed 3-4 hours before the procedure to avoid vomiting.
Probing, rinsing the nasolacrimal ducts
NEWBORN
Children with a family history of ametropia, premature babies, newborns born in difficult labor, as well as children whose parents suffer from general somatic diseases should be examined by a pediatric ophthalmologist in the maternity hospital or, if this was not done, immediately after discharge from it.
In the absence of pathology, the baby should be shown to a pediatric ophthalmologist for the first time at 1-2 months. In addition to an external examination, including assessment of the extraocular muscles, completeness of eyelid closure, and the condition of the nasolacrimal ducts, an examination of the fundus with a wide pupil is necessary. Of course, a newborn cannot read letters, but at the ArtOptics Clinic, thanks to the unique German autorefractometer PlusoptixA09, it is possible to check the refraction (optics) of a child. This will allow us to establish the presence of congenital ammetropia (myopia, hypermetropia or astigmatism) and identify the baby at risk for this pathology. Doctors at the ArtOptics Clinic will develop an individual observation plan for you.
The second very common problem in infants is neonatal dacryocystitis . You should see a doctor if your baby has the following symptoms:
1. Watery eyes when the baby is not crying.
2. Redness at the inner corner of one or both eyes.
3. The appearance of purulent discharge from the eye, or even just the adhesion of pus on the eyelashes in the morning.
OBSTRUCTION OF THE NOSLACRIMAL TRACT. PROBING
After the birth of a child, all tear drainage paths must be clear for tears. However, it happens that elements of embryonic tissue may remain in the lumen of the nasolacrimal duct, which interferes with the outflow of tears from the lacrimal sac. This leads to the tear starting to stagnate. Watery eyes appear.
The main symptoms of obstruction develop by two months, when the lacrimal gland begins to actively function. Since microorganisms that have entered the palpebral fissure are not removed, purulent inflammation of the lacrimal sac may occur - dacryocystitis.
Usually, parents begin treatment on their own - instill antibacterial drops, rinse with tea or chamomile decoction. Such treatment can improve the situation or even completely remove purulent discharge. However, after its cancellation, everything repeats again. This happens because the main cause of the disease has not been eliminated.
Treatment of dacryocystitis in newborns consists of two stages. The first stage is to massage the lacrimal sac. It is carried out by the mother after each daily feeding. The younger the child, the more effective the massage. After the massage, toileting of the eye cavity is necessary to remove purulent discharge. Doctors at the ArtOptics Clinic will teach you this procedure and select the necessary medications, taking into account the age and condition of the baby.
If there is no effect from the massage, then proceed to the second stage - probing the nasolacrimal ducts. It is better to perform probing at 3-4 months. If treatment is delayed, long-term inflammation leads to a decrease in the elasticity of the lacrimal sac and the risk of fistula formation.
As a rule, this manipulation is performed on an outpatient basis. Under anesthesia, a special sterile probe is inserted into the lacrimal canaliculus and passed through the lacrimal ducts. After which the lacrimal ducts are washed with an antiseptic solution. This procedure leads to a complete cure of the child. Repeated probing is required only in rare cases. You will also be prescribed antibiotic instillation at home for a few days. Many parents are needlessly very afraid of this procedure.
To carry out probing you need:
— examination by a pediatric ophthalmologist at the ArtOptics Clinic or referral from a clinic at your place of residence.
- the child must be healthy.
- if preventive vaccinations were carried out, at least 2 weeks should pass after them.
- You must bring an outpatient card.
- passport of one of the parents for concluding an agreement.
— probing is carried out by appointment by phone. (351) 734 94 96.
- Do not feed the baby 1 hour before the procedure.
— after 1 week you will be scheduled for a second examination, which is free of charge.
The cost of sounding according to the price list.
Execution Process
The operation is performed in the hospital by an ophthalmologist who practices surgery. The process takes no more than 5 minutes.
The manipulation is carried out in the operating room. For adults and infants up to one year old, local anesthesia in the form of anesthetic eye drops is used. The baby is swaddled tightly so that he does not break out and harm himself. A child older than one year is given general anesthesia, since it is impossible to restrain him, and it will not be possible to persuade him to undergo the procedure due to his age. In a hospital setting, a child becomes hysterical, even when there is no pain.
Sounding is carried out according to the following plan:
- The patient is given local anesthesia.
- The doctor uses a special instrument (Bowman probe), which is placed in the lacrimal punctum on the lower eyelid, unfolds and enters the nasolacrimal duct, moving towards the nose. The eyelid is kept taut.
- Having felt an obstacle in the path of the probe, the doctor relaxes the lower eyelid and breaks through the mucous plug.
- Using a cannula, the nasolacrimal duct is washed with saline and antiseptic.
- The result of the operation is checked using a colored liquid that is dropped into the eye. A cotton swab is placed in the nasal passage. The coloring of the swab means that the duct is free.
Upon completion of the operation, the patient is discharged home. During the recovery period after probing, it is advisable to avoid hypothermia. The doctor will show you how to properly massage after probing and instill anti-inflammatory drops.
Under favorable conditions, one procedure solves the problem, and repeated intervention is not required.
Risks
In fact, the procedure is quite safe, because everything is carried out under anesthesia; all you need to do is take care of the child after the operation, that is, do not forget about massages, drips of antibacterial drugs and monitor the condition of the eyes. Parents can also choose a more experienced attending physician, so that he definitely does not misfire.
If the child catches a cold in the near future after the operation, then the suppuration will recur, otherwise there are practically no relapses. Therefore, eye probing in newborns is considered the most effective, fastest and safest method.
Possible complications
Treatment of dacryocystitis using a probe should not be delayed if attempts to cope without surgery do not produce results. The disease carries the risk of such complications:
- chronic eye diseases;
- lacrimal sac abscess;
- the need to use general anesthesia for probing in a child over 1 year of age;
- the occurrence of phlegmon of the orbit of the eye;
- spread of infection (brain abscess, sepsis).
This diagnosis should not be underestimated, since the consequence of untreated dacryocystitis can be loss of vision, and in severe cases, death.
Probing is done only as prescribed by an ophthalmologist. You can carry out the procedure in the hospital on a first-come, first-served basis, or make an appointment at a medical center and have the operation performed at a convenient time. In Moscow, probing the lacrimal canal can cost from 500 to 7,000 rubles, the average price is 2,000 rubles. for one eye.
Indications for probing
It is a fairly normal thing for newborns to develop some eye problems. The reason for this can be hidden in many things, be it allergies, infection or problems with the tear duct. Sometimes the symptoms are revealed in the maternity hospital: lacrimation, redness, discharge of purulent masses, souring of the eyelids. But, most often, the cause of all this is conjunctivitis, which can be treated with simple rinsing and some medications.
But if this is not the reason, then most likely it’s all in the child’s lacrimal duct. To find out the diagnosis, you need to contact a pediatric ophthalmologist, who can easily determine the cause and prescribe the appropriate treatment. As a rule, probing of the lacrimal canal in newborns is prescribed.
Checking for problems with the tear duct is carried out as follows. The doctor drops a harmless solution, colored in a noticeable color, into the baby's eye, after which a cotton swab is inserted into the baby's nose. If there are no problems, the tampon will turn the color of the solution, otherwise there is a blockage, so you will have to treat it with probing.
Video: Obstruction of the tear duct
Aznauryan Igor Erikovich, MD, pediatric eye surgeon, pediatric ophthalmologist, head of a specialized system of children's eye clinics.