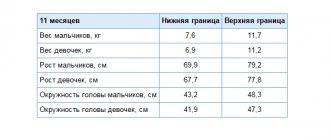
Age crises and appetite
Problems with appetite in children often worsen during age-related crises. From birth, the child feels the mother’s responsibility for the process of feeding him. The first attempts at manipulation begin when the baby is weaned from the breast or bottle. This reaction is quite normal and indicates the formation of a healthy psyche in children.
There may also be an age-related crisis of the year, when the child begins to eat much worse and refuses those foods that he previously ate with pleasure. In this case, you should not spend a lot of time persuading the baby at the table. It is best to offer him food at another time.
After this comes the crisis of three years. If at the age of one the child is sure that he is an adult, then at the age of 3 he decides that he is very small. This leads to protests and hysterics, including during meals. Sometimes such whims are caused by a lack of attention at the table.
What if these movie characters had children? AI showed what they would look like
On March 2, unmarried people will find out their fate. Miriamna Kikimora will help
Scientists have created a glowing bright green tattoo
In the period from 3 to 5 years, the child’s body begins to develop very slowly, which is why the baby needs very little food, and he begins to eat worse.
Reasons for refusing to eat
It is very important to understand why a child refuses to eat in order to find a solution to the problem, and not a way to get rid of its symptoms. Sometimes the baby wants to eat, but cannot eat in peace due to health problems.
- For example, if the baby has inflammation of the oral cavity, any meal turns into torture.
- It is also difficult for a baby with a stuffy nose to eat, who cannot breathe normally while absorbing food.
- Problems with the gastrointestinal tract often lead to digestive disorders, in which abdominal pain occurs after every meal.
Wrong selection of dishes can also cause poor appetite. If food causes discomfort to the baby due to too high or low temperature, as well as an unpleasant overly spicy or salty taste, even severe hunger may subside.
If none of these problems deprive your baby of his appetite, illness may be the reason for his refusal to eat.
At elevated temperatures and other manifestations of infections, the body concentrates its energy on maintaining the functioning of the organs responsible for the immune system, so appetite naturally decreases.
During illness, it is important to listen to the needs of the child’s body, which knows best when and how much food it needs.
It is the restoration of appetite that in most cases is a sign of recovery.
Stereotypes
Many people believe that if a child is fat, then he is healthy, and if he is thin, then he is sick. However, in fact, there are certain norms for the weight and height of children that should be adhered to. Excess weight, just like pathological thinness, does not indicate health.
There is also an opinion that what is beneficial for an adult is also beneficial for a child. However, this is a misconception. The child's organs are not yet sufficiently developed, and the food that adults consume can negatively affect his health.
Some parents believe that if the child has not eaten anything, then let him eat at least something. This is a fairly common stereotype. In any case, you need to feed your child only healthy and wholesome foods.
We feed according to age
Let's start with the fact that in fact, a child's eating habits are laid before birth. Increasingly, doctors and psychologists are sharing observations that foods that the expectant mother liked during pregnancy are very likely to be the baby’s favorites as well. And, conversely, what is unloved by the mother will be rejected by the child.
The thing is that the mother’s emotional reaction to a particular product is transmitted in the form of a signal to the fetus, as a result of which ideas about what is tasty and tasteless are formed even before birth. The relationship is not always so primitive, otherwise we would love everything the same as our parents, but there is a significant amount of truth in this - apparently, other factors also influence, which we have not yet studied and taken into account.
But dislike for certain types of food and incorrect behavior are transmitted with a much greater “guarantee”, and therefore, if the mother ate healthy foods “because I don’t want to,” then the child will most likely choke on them.
Remember how you forced yourself to eat cottage cheese, which you didn’t like, but you “had to” - doesn’t this remind you of your current tense relationship with your own child’s milk porridge? The stereotype of eating “under duress”, without pleasure, is an extremely tenacious thing, passed down from generation to generation, and therefore, even at the stage of expecting a baby, it is worth thinking about eating something that is not only healthy, but also to your taste. It is worth learning to find compromise options, and not force the body with unloved food - so as not to pass this unhealthy baton on to the child.
The next moment is the beginning of feeding the newborn. It has been noticed that breastfed babies have almost no problems with refusing food at the stage of infancy - unless the mother ate something “forbidden”, which distorted the taste of breast milk and made it unpleasant for the baby. But those who are bottle-fed have more difficulties.
- Firstly, it is not a fact that the child will like the first mixture chosen: sometimes parents have to go through several options until they find one that suits the baby’s taste and does not cause allergies.
- Secondly, no matter how perfect the formula is , it still cannot replace breast milk in terms of nutritional value, and therefore bottle-fed babies more often receive early complementary feeding than infants.
But early does not mean more effective and healthy: often the little one’s digestive system is simply not yet ready for more “adult” food, and therefore problems with the stomach and stool begin. So, if babies these days receive their first complementary foods on average at 6 months, then artificial babies receive their first complementary foods a month and a half earlier. But if the child is not ready for innovations, then the likelihood of rejection of new food will be much higher.
It is also important where exactly this first complementary feeding was started. Parents often make the mistake of offering their baby fruit first and only after some time - vegetables. The fact is that fruits are “tastier” than vegetables - they are simply sweet, and therefore some kind of zucchini or cauliflower after them seems simply tasteless.
Therefore, it is more correct to start with vegetables, and hypoallergenic ones - these are the same zucchini and cabbage, and also broccoli and pumpkin. But it is better to introduce the taste of apples, pears and other fruits to the child after vegetables - then there is a much higher chance that the child will eat all of the above.
And only then do we introduce vegetable soups, fermented milk products, cottage cheese and meat. Food that is not appropriate for one’s age, as we already know, is poorly digested, complicates the functioning of the digestive system and, instead of benefiting the child, brings problems. And if food is a problem, then inevitably sooner or later it will begin to cause disgust and rejection, that is, as a result we will get a child who “does not like” to eat.
Causes of poor appetite
Among the most common reasons are the following:
- nervous state of the nursing parent;
- snacks;
- excessive persistence when feeding;
- chase with a spoon throughout the apartment.
Also, a child may not eat well due to lack of physical activity or nervous overexcitability.
“I was going to get married”: Nadezhda Babkina spoke about her lover in Astrakhan
Some children clean their houses at will: how do their parents instill this in them?
Four zodiac signs under which people with a “light hand” are born
There are several ways you can encourage your child to eat food. Here are a few such recommendations.
Solving the problem of snacking
Most nutritionists and pediatricians unanimously anathematize snacking: they interrupt appetite, distort a child’s eating habits, disrupt proper eating behavior, supply extra calories, and so on. This is all true - there is no point in arguing.
But sometimes force majeure circumstances arise when you simply do not have time to prepare lunch or dinner on time, or there is no way to get home or a decent cafe on time to have a full meal. In this case, you can’t do without a snack - the whole point is what exactly is considered a proper snack and what the child should be taught to eat.
Another life hack on how to feed a small child is to give him food, food that increases his appetite.
It turns out that there are not only harmful snacks, but also “correct” ones that improve appetite and supply vitamins and microelements. These are vegetables, fruits and nuts. They are easy to transport, they do not need heating or cooling, they store well even in hot weather - in short, they have a lot of advantages.
Therefore, if your child whines: “I want to eat,” and lunch is far away, it is better to accustom him to fresh carrots, cucumbers, apples, walnuts or hazelnuts from early childhood. Because children, accustomed to buns and cookies, will simply ignore such an offer, alas.
Nuts, by the way, are high-calorie and therefore they are more suitable as a replacement for a missed lunch or breakfast: after eating nuts, the child may not be hungry for the next meal (the same applies to hearty bananas).
However, one way or another, the very principle of snacking is permissible only in emergency cases. Normally, the child should not eat anything between meals, because in this case he is in a state of permanent satiety and the need for “normal” food, he simply does not feel the need for a full meal.
Snacking is often resorted to by overly kind-hearted mothers who are not confident in their parental authority, who have “surrendered to the mercy of the winner” in the fight with a spoon, but cannot allow the child to go hungry, and therefore go along with the children’s begging for tasty things (and at the same time, about their desire to be “good”, not prohibitive, democratic - well, this is how these mothers understand the above concepts, unfortunately).
But in fact, a child who did not eat lunch was simply not hungry, did not feel the need for food, and the only thing he needs to be given is time to get hungry, and not a “yummy” food in order to deceive his own body.
Why do parents force their child to eat?
Some parents are accustomed to living by certain stereotypes and act with their children in the same way as they did with them in childhood. Adults try to determine for themselves what the baby needs and in what quantities.
Some parents perceive a child's refusal to eat as a sign of disobedience. And some believe that if children refuse to eat, it means they are sick.
Why is my baby having trouble eating?
Psychologists note the connection between a child’s behavior and his diet. Typically, a child behaves poorly if he goes without food for a long time or receives an excess of sweet foods (snacks of candy or cookies). The reason for this is changes in blood sugar levels.
The rise in blood sugar releases insulin, then the sugar is quickly used up, levels drop sharply, and stress hormones stimulate the return of sugar from the liver, raising blood levels again.
Such changes in sugar levels lead to the child’s mood constantly changing. To be convinced of these sugar races, it is enough to remember any children's party with an abundance of sweets, at which it is not possible to calm the children down.
The feeding method proposed below is suitable for many children from 1.5 to 3 years old, but especially for small children and hyperactive children, for whose parents it will not only be a way to feed the fidget, but also an opportunity to correct the child’s behavior. This method is called “grazing.” However, when your baby eats this way, it will minimize mood swings related to blood sugar levels.
What is the danger?
Force-feeding your baby can cause food aversions and create unhealthy eating behavior in the future. This can lead to bulimia or anorexia.
The consequences of such feeding can be both physiological and psychological problems. Physiological ones include metabolic disorders, spasms of the digestive system and disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Psychological problems include stress, changes in behavior, neuroses, and fears.
Experts have named habits that, if abandoned, can extend your life by 10 years.
No one needs: the fate of Jewish women scientists who fled from the Nazis to the USA
Exercising just 11 minutes a day in the evening can ensure longevity
How to encourage a child to eat?
You need to play outdoor games with your baby, because the more energy he spends, the hungrier he gets.
You can go to the beach and have fun with your child. However, you need to remember the basic safety rules.
Sometimes you need to let children fast for a little bit so that their appetite wakes up. When they want to eat, they will let you know about it.
It is necessary to exclude junk food from the child’s diet. This will allow him to enjoy healthy food.
Appetite increases in fresh air. That is why, if a child does not want to eat, you need to go for a walk with him.
Proper feeding
Playing “airplane” and “spoon for mom” is normal, as is disguising some foods so that the child will eat them.
In this case, it is only important for adults to keep under control their desire to feed the child to satiety. The main task of parents is still to buy healthy food, cook it, preserving the vitamins, and serve it in a form that is attractive to the child. By being flexible and listening to their child's individual needs, parents can reduce stress and enjoy shared meals with their children more.
What should parents do?
If a child does not like a certain product, then you need to offer it to the baby up to 10 times at intervals of a month. This product can be offered in a variety of forms. If this is followed by a categorical refusal, then it is worth replacing this product with another with similar properties or composition.
It is important to develop a feeding schedule, and you should not give food while watching TV or during entertainment activities. Parents should serve as an example for their child.
Found a violation? Report content