What does a head clause mean?
The duration of the gestation period for a baby is 40 weeks according to the obstetric calculation period and 38 weeks according to the embryonic development calendar. During this time, the fetus changes its body position many times. In the early stages of gestation, the baby floats freely in the amniotic fluid, because its size is now still very small. The baby turns over, somersaults, lies with his buttocks or head down.
From about 7-8 months, the child takes a constant body position. Now the fetus is already quite large, so it is difficult for it to turn over, the walls of the uterus prevent it. By 34-35 weeks, the baby takes a certain body position and after this period it extremely rarely changes its position.
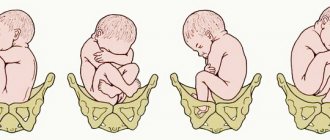
In most cases, approximately 80-85% of babies are in the head down position. Let's try to figure it out - is this good or bad? This position is considered correct and most favorable for childbirth. If the toddler is positioned with his pelvis down, there is a chance that he will roll over, but they are insignificant. With a cephalic presentation, the baby is unlikely to turn over with its bottom down or turn across the uterus. The anterior view of presentation can be seen in the photo.
Causes of pathological types of cephalic presentation on the part of the mother and fetus
Causes of pathological presentation of the fetus on the part of the woman:
- narrow pelvis of a pregnant woman;
- too weak tone of the uterus, irregular compression of its sides;
- excess amniotic fluid;
- second or more births;
- multiple pregnancy;
- uterine fibroids;
- saddle or bicornuate uterus;
- the presence of a septum in the body of the uterus.
Causes of pathological position on the part of the fetus:
- tumor of the baby’s neck or thyroid gland;
- too small, or vice versa, very large head, which is associated with diseases.
Correct head position
When diagnosing a cephalic presentation of a baby, a specialist must pay attention to the features of the position of the baby’s body relative to the central axis of the cavity of the reproductive organ, as well as to how the fetal limbs are positioned. In obstetric practice, there are such types of cephalic location of the fetus as occipital, anterior cephalic, frontal and facial.
For safe delivery, a flexed occipital presentation is considered optimal. The baby will walk head first as it passes through the birth canal. The small fontanelle will be the point of advancement. This is precisely the option provided by nature. Due to the fact that the back of the head is the largest, the remaining parts of the body will pass through the birth canal much easier.
With this body position, the baby's neck will be in a bent position during childbirth. The baby will not be able to straighten it, thereby causing injury. This is exactly the scenario observed in most cases of natural childbirth.
What does cephalic presentation of the fetus mean?
When the fetus is in the cephalic position in the womb, its head is directed towards the internal os of the cervix. The cephalic presentation of the fetus is designed so that the baby's head, as the largest part of the body, will be the first to move along the birth canal. This will allow you to leave the uterus and other parts of the baby’s body without injury or complications. Usually, up to 30 weeks, the position of the fetus in the uterus is quite variable, but by the 35th week, most fetuses are characterized by cephalic presentation.
A woman may not immediately find out what cephalic presentation of the fetus is. Most often, in the first half of pregnancy, a woman can behave quite freely. But if breech presentation is further determined, then the likelihood of complications during childbirth increases: timely breaking of water, prolapse of the baby’s limbs and umbilical cord, pathologies during childbirth, fetal asphyxia, infection, prolonged passage of the baby. During such births, there is a high probability of postpartum hemorrhage, to prevent which the woman in labor is given intravenous oxytocin and methylergometrine. In this case, the woman should observe bed rest as much as possible. The expectant mother is recommended to lie on her side, where the back of the fetus is facing.
Classification of incorrect cephalic presentation
If the baby's head is at the wrong angle in the woman's pelvis, it can cause some problems during childbirth. The scenario for the development of events here will depend on the angle at which the neck is bent, as well as on the professionalism of the doctors.
Let's consider several options for the head position of the fetus.
Anterocephalic (first degree of head extension)
With this position of the baby’s body, the point of advancement of the child along the birth canal is not the small fontanel, but the large one. This leads to the fact that the area of advancement of the head along the birth canal will be larger, therefore, it will be more difficult for the fetus to pass. With this position, natural childbirth is quite possible, but it may take longer and be more painful. Can complications arise from this? Yes they can. Most often, this is a weakening of labor. Due to the cessation of contractions, the labor process may be delayed, which often causes fetal hypoxia. With this development of events, doctors may decide to perform a Caesarean section.
Frontal (second degree of head extension)
With this position, the most voluminous part of the fetal head enters the woman’s pelvic area. We can say that the baby will make his way into the world around him with the frontal part. Often this makes labor very difficult.
The risk of developing birth injuries greatly increases. Spinal injuries occur most often. As for the woman, the danger for her lies in ruptures of the uterus and its cervix, as well as the perineal area. It is believed that stimulation of labor with this position of the child’s body is extremely dangerous.
Facial (third degree of head extension)
The most unfavorable position of the baby's body for childbirth. In this case, the baby’s passage through the birth canal will be with the chin forward. That is, the main point of passage of the fetus through the birth canal is the chin. Natural childbirth with this position of the baby is possible only under certain conditions:
- The child is small in weight and size.
- The woman has a wide pelvis.
- There are no pathologies in the fetus.
In this case, the risk of birth injuries will not exceed the risks that are possible with frontal presentation.
To prevent injury to the fetus and mother, such women most often undergo a Caesarean section.
Degree 3 - facial presentation.
Facial presentation is the extreme degree of maximum extension of the fetal head. The axial point of advancement along the woman’s birth canal is the fetus’s chin. During childbirth, the initial emergence of the baby's head is observed, and after the back of the head. In this case, the probability of giving birth naturally is 50/50%. Successful spontaneous childbirth is possible if the fetus is small and the mother has a wide pelvis; in other cases, obstetricians resort to caesarean section.
The main reasons for an extensor cephalic presentation of the fetus include a narrow pelvis in the expectant mother, uterine fibroids, anomalies in the structure of the uterus - all this significantly takes away the space of existence of the fetus. Other causes may include polyhydramnios or placenta previa, a flabby abdominal wall, and more.
Causes of fetal malpresentation
As obstetric practice shows, the extensor posture of the baby’s body is rare. A caesarean section is required in no more than 2% of cases. It is unlikely that it will be possible to accurately identify the reasons for this finding of the baby. It is believed that the following conditions can provoke the problem:
- Narrow pelvis in a woman in labor.
- Tumors in the uterine area.
- The presence of scars in the area of the reproductive organ.
- Uterine fibroids.
- Polyhydramnios.
- Saddle or bicornuate uterus.
It happens that a fibroid or neoplasm in the uterine area is located in its lower segment. This leads to the fact that the baby will try to turn into the most comfortable position for himself. This will lead to the fetus having an extensor posture. Sometimes incorrect body posture may be due to the fact that the placenta is located too low. Genetic predisposition plays an important role. If the family has already had such problems, the likelihood of a repetition of the scenario is quite high.
If the birth is not the first and the peritoneal wall is in a stretched state, the extension position also occurs.
Features of preventing complications during childbirth
If a woman has any abnormal changes in the health of her gynecological organs, then there is a very high probability of a difficult birth that will require surgical intervention. For such women, a very careful diagnosis of the condition of the fetus, its location, and placement aspects is required. A woman in labor is most often placed on a hospital stay to avoid additional stress and irritation in the environment of everyday life. In addition, during this time, detailed rational tactics for childbirth are developed. With early detection of a complicated fetal presentation, the woman has time to prepare for a cesarean section, in which case the likelihood of subsequent psychological distress is reduced.
Head presentation with low placentation
In obstetric practice, the placenta is a temporary organ that develops in a woman during pregnancy. This organ is formed at 12-13 weeks of gestation. During a normal pregnancy, the placenta is located at the bottom of the reproductive organ. Sometimes the fertilized egg is attached in the area of the anterior or posterior wall, closer to the uterine os. This leads to the development of low placentation.
This condition requires careful management of pregnancy, as it often causes various complications. The danger of low placentation is as follows:
- Bleeding, development of anemia in women.
- Compression of blood vessels, which can lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus and deviations in its physical and mental development.
- Poor blood circulation in a child as a result of placental abruption.
- Risk of premature birth.
- Difficulty in lowering the head into the pelvis, which complicates natural childbirth.
- Large blood loss during Caesarean section.
- Blocking of the birth canal by the placenta.
Often, a low location of the placenta causes an extensor cephalic presentation of the fetus, which leads to the development of various problems during childbirth. The birth will take place naturally or the patient will undergo surgical intervention, which depends on the characteristics of the child’s position in the womb.
What are the options for cephalic presentation of the fetus?
The cephalic presentation of the fetus, in which the longitudinal position of the child remains clear and stable, contributes to the formation of several options for the location of the fetal head: facial, frontal, anterior, occipital.
The flexion occipital presentation is considered the safest and most comfortable for the child. In this case, the small fontanelle on the baby’s head will act as the axial point of movement along the birth canal. The cephalic presentation of the fetus in the occipital version implies such a movement of the child through the mother’s birth canal, in which the baby’s neck will be bent and its birth will begin precisely with the appearance of the back of the head. This option applies to up to 95% of births.
But the bends of the cervix during cephalic presentation of the fetus can be quite varied. Therefore, doctors distinguish 3 main degrees of extension presentation:
Diagnostics
You can understand how the baby is located in the mother’s womb using ultrasound and external palpation of the pregnant woman’s abdomen. An experienced specialist can preliminarily diagnose the position of the child’s body by measuring the height of the uterine fundus and palpating the baby’s head. If the presentation is breech, the doctor can feel the baby's pelvis above the pubis. Unlike the head, it is less mobile and soft. If the baby lies in a transverse position, the head can be felt on the left or right.
In addition, body position is determined by listening to the heart rate. If the head is located below, the heartbeat can be heard in the lower abdomen of the pregnant woman. When the head is at the top, the heart can be heard in the woman's navel.
Even the most competent doctor cannot determine the degree of extension of the head by measuring the height of the uterine fundus and palpating the abdomen. This is impossible from a physiological point of view.
Position of fetuses in twins
With twins, vaginal delivery is possible if both fetuses are in the cephalic presentation, or if the first (which is closer to the exit from the uterus and will be born first) is in the cephalic presentation, and the second in the breech. If, on the contrary, the first is in a breech presentation, and the second is in a cephalic presentation, the situation is unfavorable, since after the birth of the pelvic end of the first fetus, the babies can get their heads caught.
When determining the transverse position of one of the fetuses, the issue is resolved in favor of a cesarean section.
Even with a favorable position of the fetuses, the question of the method of delivery for twins is decided not only based on the position, but also depending on many other factors.
Features of the course of labor
According to medical statistics, if the baby’s cephalic extension position is incorrect, delivery in most cases occurs naturally. The optimal position is considered to be occipital presentation. At the same time, childbirth is easy and with minimal risks for mother and baby. While passing through the birth canal with the back of the head forward, the child turns and the back of his head is directed towards the womb, and the front part turns towards the sacrum of the woman in labor. As soon as the head emerges from the vagina, the baby's face turns toward the mother's thigh. The body then exits easily and with little risk of injury.
Anterocephalic presentation
If the fetus is not positioned correctly, labor management becomes more complicated. They can last longer, and the risks of various complications increase. Often stimulation of contractions is required. This is necessary to prevent oxygen starvation of the baby.
In some cases, a special tool is used - obstetric forceps. In modern obstetric practice, forceps are recommended to be used only in extreme cases, as they often injure the newborn.
Facial presentation
With this position of the baby's body, childbirth takes place under the careful supervision of doctors. In this case, the newborn will come out of the vagina with his chin forward. The task of obstetricians is to try to prevent possible injuries to the baby. If the risk of injury is high, an emergency decision to perform a Caesarean section may be made.
Frontal presentation
If a woman has a frontal extensor cephalic presentation, a Caesarean section is recommended. This is due to the fact that the risk of injury to a child is very high. In addition, there is a serious threat of rupture of the mother’s reproductive organ. During natural childbirth, which can happen when it starts early, the labor process can be very prolonged and contractions can weaken.
An experienced specialist can stimulate the baby's body to turn manually, but this often provokes spinal injuries in the newborn. The main danger is that the baby may remain disabled for life.
Longitudinal presentation
Often the mother experiences an oblique presentation of the fetus. In this case, the baby's head is on the left or right. In this case, childbirth is recommended to be carried out by Caesarean section. With natural delivery, the risk of injury to the mother and newborn is very high.
If the baby is not positioned correctly in the mother's womb, the woman is recommended to go to the hospital at another 36-37 weeks. This will help prevent spontaneous birth and the development of various complications.
Approaches to diagnosing cephalic presentation of the fetus
Gynecologists begin to monitor the cephalic presentation of the fetus from the 28th week of pregnancy. A general examination is performed by placing the doctor’s open right palm over the symphysis. In this position, a dense round part is felt, which is the fetal head. Head presentation is indicated by its placement above the entrance to the pelvis. The fetal head is very mobile in the uterine waters. Therefore, doctors practice additional vaginal examination.
With the help of gynecological ultrasound, the position of the fetus, its position, position, position, and appearance of the fetus are determined. Having specified such details, the woman counts the baby’s heartbeat under the navel.
It is very important to accurately diagnose fetal presentation, which mainly affects the birth scenario.
The standard correct option for childbirth includes birth with an occipital anterior cephalic presentation of the fetus. With such a diagnostic result, the mother in labor should not worry about the correspondence of the birth canal and the size and shape of the fetal head. This type of birth is the safest, since the baby’s chin is hidden inside the body closer to the baby’s chest. Thanks to the correct bending of the head, the birth canal is less injured, since the baby's head is located in the smallest possible way. In addition, there is an additional inversion of the fetus, in which the face turns to the mother’s sacrum, and the back of the head is directed towards the symphysis pubis.
All other options for childbirth are distinguished by their complexity due to the unfolded cephalic presentation of the fetus. The baby turns the back of his head towards the sacrum. In this case, labor is significantly delayed, which can cause fetal asphyxia or the development of weak secondary labor. In such a situation, care and experience from obstetricians is very much required.
The mechanics of labor during anterior cephalic presentation of the fetus is accompanied by the passage of the baby's head, following the movement of the large fontanel. Obstetricians are required to have perseverance, the ability to wait, but also to respond urgently in critical situations if there is a danger to the life and health of the mother or child.
After diagnosis of frontal cephalic presentation of the fetus, delivery occurs mainly through surgical intervention. For a woman, such childbirth is very painful. Natural childbirth with such indications threatens with deep ruptures of the birth canal and genital organs. At the beginning of labor with a frontal cephalic presentation, gynecologists try to perform an additional rotation of the fetus, but if this attempt is impossible, then they resort to a cesarean section and a craniotomy is performed.
Diagnostic indicators for the normal course of labor with a facial cephalic presentation are the wide size of the woman’s pelvis, the small size of the fetus, the body’s tendency to active labor, and the baby’s chin facing forward. In this case, special attention is paid to the dynamics of labor, the state of health of the mother in labor, and the fetal heartbeat is carefully measured based on cardiotocography and phonocardiography. If, with a facial cephalic presentation, the chin is the dominant point in the direction of movement, then a cesarean section is immediately required. In this case, there are very great threats to the baby’s life. If the fetus is stillborn, a craniotomy is performed immediately.
Gymnastics for turning a baby
As already mentioned, the baby can turn over in the womb many times until about the seventh month. After 30-34 weeks, the baby takes a permanent position. To stimulate the correct position of the baby's body, a woman can perform some simple exercises.
Here are a few of them:
- Lie on your right side, stay in this position for 30-60 seconds, breathe deeply. Turn to the other side. Perform 3-4 repetitions.
- Lie on your back, place a pillow under your pelvis. The legs should be above the pelvis in a bent position. You need to stay in this position for 15-20 minutes. Repeat the exercise daily.
- Take a knee-elbow position. You should remain in this position for 10-20 minutes. If it is immediately difficult to stand for that long, start with a few minutes.
These simple exercises will help your baby take the right position, which will make natural childbirth much easier.
Gymnastics to turn the fetus over are permitted only after consultation with a specialist. If there are contraindications, performing the exercises is strictly prohibited.
"Coup" plan
If your due date is approaching and your baby is still in the wrong position, don't panic. You should never panic at all, especially if you are pregnant. There is an action plan!
Step 1. Corrective gymnastics...
... will help “persuade” the baby to take the correct position before childbirth. It is carried out after 24 weeks or at certain times in the third trimester. General contraindications to any set of exercises: threat of miscarriage, placenta previa. But there are other features of pregnancy in which doing gymnastics can be dangerous. Before performing any (!) exercises, be sure to consult your doctor!
With breech presentation
- Lie on your side, but not on a soft surface. Lie on one side for 10 minutes, turn to the other, lie down for another 10 minutes. Turn from side to side 3-4 times. Such simple exercises should be performed 2-3 times during the day.
- Lie on your back with your pelvis raised. To do this, place pillows under your legs and lower back. The legs should be 20–30 cm higher than the head. You can spend 10–15 minutes in this position 2–3 times a day.
- Take a knee-elbow position. Stay like this for 15–20 minutes. Repeat 2-3 times a day.
What happens: When performing such exercises, the motor activity of the fetus is stimulated, and it gets more opportunity to turn.
In transverse (oblique) position
- Lie on your side in accordance with the position of the fetus: the head on the left - on the right side, on the right - on the left. The legs are bent at the knee and hip joints. Lie down for 5 minutes.
- Take a deep breath, turn to the opposite side. Lie down for 5 minutes.
- Straighten the leg (in the 1st position - the right one, in the 2nd position - the left one), the other leg remains bent.
- Grab your knee with your hands and move it to the side opposite to the position of the fetus. Bend your torso forward. With your bent leg, describe a semicircle, touching the anterior abdominal wall, take a deep, extended exhalation and, relaxing, straighten and lower your leg.
What happens: A slight mechanical “pushing” of the baby by the muscles into the correct position.
Step 2: Additional steps
- In the transverse position, it is recommended to sleep on the side where the fetal head is located.
- With a breech presentation, turning the baby head down stimulates swimming (after consulting a doctor!).
Step 3. Visit to an osteopath
After the 35th week, a doctor in a hospital setting can rotate the fetus (in transverse and oblique cases, less often in breech presentation). During the entire “operation,” the condition of the mother and child is monitored. The procedure has contraindications and a high risk of complications and injuries, so it is performed in extreme cases.
Step 4. Consolidate the result
As soon as the efforts have been crowned with success and the little “striker” has decided to take the correct position, it is important to help him “get a foothold.” To do this, purchase a prenatal bandage, wear it throughout the day and do a special exercise (consult a doctor!).
Sit on the floor, spread your knees to the sides and press them as close to the floor as possible. Press your feet together. Stay in this position for 10–15 minutes. You can do this several times a day.
What happens: stretching of the ligaments and muscles of the pelvis, which promotes the insertion of the head into the pelvis.
Preventing complications
To avoid various complications in the mother, it is necessary to properly manage the pregnancy. In this case, the woman must be registered with a doctor and visit a doctor regularly. This is especially important in the second and third trimester. Under no circumstances should an expectant mother refuse to take tests or undergo other examination methods.
By the beginning of the third trimester, it is advisable for a pregnant woman to choose a maternity hospital and a doctor who will be present at the birth. A woman can choose any maternity hospital that is nearby. It is very important to trust your doctor. To choose a specialist, it is recommended to take into account his professional activities and reviews of other patients. In addition, it is important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Eat right and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Walk outdoors more often.
- Drink enough fluids.
- Get more rest.
- Try to eliminate stress and anxiety.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Sign up for courses for expectant mothers.
- Regularly attend antenatal clinics.
- Treat acute and chronic diseases in a timely manner.
- Plan your pregnancy correctly.
Following these simple tips will help you carry and give birth to a healthy baby. A woman should set herself in a positive mood and try to focus on her health and the health of her baby. We wish you good health and an easy pregnancy.
All information that you received by reading this article is for informational purposes only and cannot be used as an inducement to take any action.
Birth tactics for cephalic presentation
The best position for an easy and safe birth is considered to be the cephalic occipital presentation, where the crown of the head is turned anteriorly. In this position, childbirth has a favorable outcome, since it occurs in accordance with the natural parameters of the mother’s pelvis and the size of the fetus.
With the occipital type of presentation, the baby's chin is pressed against the chest, and the small fontanelle is turned in the direction of the birth canal. It is this bending of the head that makes its size slightly smaller, which makes it easier for the fetus to pass during childbirth. Moving forward, the baby makes rotational movements. Inside the birth canal, the occipital part faces the pubic symphysis, and the face faces the sacrum. At the moment of teething and exit, the child turns over again and straightens his head. Thus, the baby, as it were, pushes his way out with the force of his head and neck, while his face is turned towards the mother’s thigh. After the head, the shoulder girdle, torso and legs are expected.
If the initial position was posterior (the back of the head is facing the mother’s sacrum), forward movements in the birth canal may be longer. Here the doctor must ensure that the child does not experience asphyxia, and the mother does not experience weakness in labor. If such dangerous conditions are suspected, the doctor may decide on artificial stimulation or the use of obstetric forceps.
With anterior cephalic presentation, the delivery tactics are similar to the previous one and are more expectant in nature.
With a frontal position of the child, the prognosis for natural childbirth is often unfavorable - there is a high probability of ruptures in the mother, the formation of fistulas, death or asphyxia of the fetus. A cesarean section is indicated for the woman in labor.
In case of facial presentation, labor should be conducted expectantly, carefully assessing the dynamics of labor, the condition of the woman in labor and the fetal heartbeat. In most cases, before delivery, the doctor decides in favor of a cesarean section.
Childbirth
Delivery is determined individually. During the birth process, the position of the baby's head may change. The parietal passes into the occipital, and with extension - into the frontal.
Longitudinal cephalic presentation can cause premature rupture of amniotic fluid. The possibility of spontaneous childbirth and cesarean section has the same risks.
If the view is not occipital, then birth lasts longer. This increases the likelihood of injury and hypoxia of the child.
If the baby's head enters the pelvis, labor may sharply weaken in some patients. This is a very dangerous condition that threatens childhood death.
To eliminate the danger and help the newborn, doctors use special obstetric forceps. In emergency cases, you may need to use a vacuum extractor. This is a special device that allows you to pull the child out of the genitals.
If the expectant mother has a small pelvis and the baby is large, gynecologists recommend a surgical method of delivery. This is especially true with frontal presentation.
Unattended childbirth poses a high risk of injury to mother and baby. It is important for the doctor to perform the operation before the fetal head enters the pelvis.
In the facial position, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, oxygen deficiency, and prolapse of the umbilical cord may also occur. Birth takes a very long time. It is important in this process that the head does not take a frontal position - this is an indication for an emergency caesarean section.
When birth takes place naturally, the skull adapts to the birth canal and slightly changes its shape. It recovers on its own only some time after birth.
Classification
Head presentation of the fetus during pregnancy has a certain classification. It is determined by a specialist in the last stages of gestation. Gynecologists highlight the main characteristics of the location, which are very important:
- view - how the child is turned;
- position – direction to the right or left (for example, the first indicates a turn to the right).
Changes may occur at any time. The birth of a small life is unpredictable.
Occipital
This type is considered the most successful. The head is tilted down towards the chest, and the face is turned towards the spine of the expectant mother.
The baby comes into the world through the cervix with the back of the head. This is the narrowest part. This position is safe and has little risk of injury. The process proceeds largely without damage.
Anterocephalic
Anterior cephalic presentation is also called parietal presentation. In this case, the fetus is turned towards the genital tract by a large fontanel.
His head is not tilted to his chest enough and is held straight. Initially, the crown of the head will emerge through the birth canal.
The woman in labor can cope on her own or will need surgical intervention. It is necessary to strictly control this process, since at any moment there may not be enough oxygen and a threat appears.
Facial
It is observed very rarely. This position is accompanied by a strong deviation of the child’s skull back, and the back of the head is pressed to the back. Exit to the light is done face forward, nose and chin.
The mother has a chance to give birth on her own, but if necessary, a caesarean section will be performed. The gynecologist makes a decision individually, taking into account the labor activity of each patient.
This is influenced by the following factors:
- pelvic structure;
- fetal weight;
- intensity of contractions.
Considering all the data, facial presentation is dangerous. It often causes injuries to the newborn's spine. Mainly observed during repeated and multiple gestations.
Frontal
Frontal cephalic presentation of the fetus is extremely rare and very dangerous. Occurs in 1-2% of expectant mothers. At the same time, the child’s neck straightens, and he is directed towards the exit by the frontal part.
The danger is that the passage through the birth canal is carried out by the widest parts of the head. In this case, natural delivery is prohibited, so only cesarean section is performed.