Feces are a collection of metabolic waste and undigested food particles. Digestion of food is possible thanks to the digestive enzymes of the stomach, pancreas and bile, as well as beneficial intestinal bacteria. Proteins, fats and carbohydrates are broken down in different parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Feces contain bacteria, small fragments of undigested food, undigested cellulose fibers and metabolic products that the body does not need. The frequency, shape, composition and color of stools change. The color of stool is determined by the amount of bilirubin breakdown products (urobilinogen, stercobilin). Gray feces can appear in both adults and children of any age in the absence of disease.
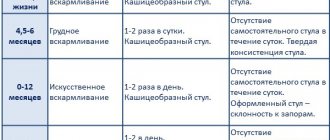
Changes in stool in children
When identifying the sources of disturbances in the normal characteristics of stool, several main ones can be identified:
- medicines,
- food imbalance,
- dysfunction of the liver, pancreas,
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Each person’s digestive processes are individual, and over the course of life these mechanisms undergo significant transformation. In a newborn, the organs of the gastrointestinal tract are just beginning to function; they are immature and cannot fully perform the necessary physiological functions. Gray feces appear in a child precisely because of this imperfection of the child’s body. A baby's diet has a big influence on his feces. When breastfeeding, it is easier for children to adapt to new environmental conditions. The first complementary feeding should meet the required deadlines so that the fragile body does not experience unnecessary stress. Gray stools appear in a child after the first feedings of infant formula.
The food the mother eats also affects the baby's excrement. With large amounts of dairy and plant foods, infants may experience gray diarrhea without any other symptoms. Unfortunately, natural feeding is not always possible. The stool of a bottle-fed baby becomes unstable, its color and consistency may change. However, these adaptive phenomena, in particular gray diarrhea, go away on their own within a few months. This state of a child’s body is absolutely normal for the appropriate age.
At 1 year of age, the child’s digestion stabilizes, and there should no longer be any sudden changes in stool. However, up to 3 years of age, periodic isolated changes in stool should not frighten parents.
After one year, the most common causes of abnormal stool properties are rotavirus gastroenteritis, dysbacteriosis, hepatitis, and bile duct dyskinesia. Timely diagnosis and treatment will help avoid complications.
Causes of changes in stool color
Each person's digestive processes are individual. Throughout life, they constantly change under the influence of a large number of different factors. The reasons for the atypical color of feces are different in adults and children.
Change in color of baby's stool
In infants, the digestive organs are still immature and cannot sufficiently perform all their functions. And that is why the baby often has a gray coloration of stool. Nutrition has a significant impact on their condition and appearance.
If a child is breastfed, then his digestive system gradually adapts to external conditions. The gray color of feces is observed when the child begins to be fed with artificial nutritional formulas.
In healthy children, adaptation of the digestive system is completed within several months after the transition to artificial feeding and the introduction of complementary foods. By the age of one year, the development of the gastrointestinal tract in babies is completed.
Change in stool color in adults
Normally, men and women have brown stool. Discoloration of stool indicates disturbances in the flow of bile into the duodenum.
The following reasons cause gray stool:
- inflammation of the gall bladder;
- blockage or dyskinesia of the biliary tract;
- liver inflammation;
- diseases of the rectum;
- intestinal infection;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- Crohn's disease;
- helminthic infestation;
- tumors in the liver, pancreas or gall.
The appearance of gray feces with a pungent odor indicates the development of severe inflammatory pathologies in the digestive tract. Most often this occurs as a result of pancreatitis or severe putrefactive dyspepsia .
Use of medications
Sometimes gray coloration of stool appears as a result of the fact that a person uses certain medications:
- medicines containing bismuth compounds;
- activated carbon;
- antifungal drugs;
- anti-gout medications;
- antiepileptic drugs;
- Ibuprofen;
- aspirin.
The appearance of dark stool in these cases requires discontinuation of the drug, diagnosis of the patient and the appointment of appropriate treatment.
During pregnancy
The appearance of gray stool during pregnancy may indicate that the pregnant woman eats a lot of fruits and vegetables. If there is no pain and no mucus appears in the stool, then this condition is normal. The problem will disappear if you slightly adjust your diet during pregnancy.
If abdominal pain appears, a change in the nature of bowel movements, or yellowing of the skin, a woman should urgently consult a doctor, because these signs indicate the development of dangerous diseases of the digestive tract.
Conditions requiring attention
The light gray color of a child's stool, close to white, should alert parents. The cause may be a disruption of the bile ducts, pancreas, and liver. These symptoms manifest themselves most clearly in pancreatitis, although such problems do not occur often in children.
If the stool becomes light grayish, mixed with a large amount of mucus or even blood, and turns into diarrhea in a child, you should consult a doctor.
This is how the manifestation of infectious and inflammatory diseases that require specialized therapy begins. Stool that is dirty gray in color, has a mushy consistency, and has an unpleasant, pungent odor in a one-year-old baby indicates the need to diversify his diet. A pediatrician can help with this by providing individual recommendations on proper nutrition for the baby.
Symptoms accompanying stool disorders require special attention:
- pain syndrome (in any area of the abdomen),
- yellowness of the skin and icterus of the mucous membranes,
- increased body temperature,
- nausea and vomiting,
- darkening of urine
- weight loss, loss of appetite,
- bloating, increased abdominal volume,
- noticeable deterioration in the child's condition.
Identification of these symptoms is an indication for immediate consultation with a doctor and undergoing the necessary tests (bacteriological and biochemical analysis of stool, extended coprogram).
Possible diseases
If a child’s stool is gray for a certain period of time, this may indicate the development of certain diseases:
- Pancreatitis. Young children may experience inflammation of the pancreas. The causes of the inflammatory process are as follows: insufficient development of the digestive system, nutrition not appropriate for the child’s age. In children older than one year, pancreatitis can develop with excessive consumption of sweets and flour products. The main manifestations of pancreatitis in children: light shiny stools with a foul odor, abdominal pain, high fever, nausea and vomiting.
- Dysbacteriosis. It develops as a result of the use of antibacterial drugs during pregnancy, treatment with antibiotics, and poor nutrition of the mother. Dysbacteriosis occurs when the balance of microorganisms living in the intestines is disturbed. In this case, the child experiences bloating and abdominal pain, light-colored stools with mucus.
- Hepatitis. Hepatitis A is often detected in children attending school or kindergarten. This form of the disease occurs very rarely in children under one year of age and is caused by poor hygiene. The child's urine becomes dark in color, and the feces gradually acquire a light shade.
- Coloration of stool can be observed with rotavirus infection. The child’s health deteriorates and the body temperature rises. Liquid yellow stool gradually changes color and becomes light after 3-4 days after the onset of the disease.
All these diseases develop when the functioning of the digestive system organs is disrupted. If your child's stool changes suddenly or persists for several days, you should consult a doctor.
Stool disorders in adults
Normally, in healthy people, stool is brown in various shades (from light beige to dark). The color of stool, discolored to light gray or whitish, often signals a violation of the transport of bile into the duodenum. There are enough reasons for such changes:
- cholecystitis,
- dyskinesia or obstruction of the biliary tract,
- hepatitis,
- pancreatitis,
- Crohn's disease,
- tumor processes in the liver, pancreas, papilla of Vater, gall bladder.
Any of these conditions requires examination, both laboratory and instrumental, as well as consultation with doctors.
Changes in stool can also be of a nutritional nature, for example, when consuming large amounts of rice or potatoes. Treatment with antidiarrheals, antacids, and X-ray examination using barium sulfate also affects the color of stool.
When to sound the alarm
The following signs should alert you and force you to consult a doctor as soon as possible, as they indicate disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract:
- pain in the abdomen in any area, especially after eating;
- yellow skin color;
- increased body temperature;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- change in urine color;
- loss of body weight;
- decreased appetite;
- bloating;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- deterioration of condition.
The appearance of these symptoms along with the presence of gray feces indicates the development of severe digestive pathologies.
If the consistency of stool has changed (they have become solid or, conversely, liquid), this indicates the addition of inflammatory pathologies of the intestines, stomach, liver, and pancreas. These diseases should never be ignored.
Untreated inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract can lead to the development of oncological processes.
Causes of dark green stool
Vegetarians very often experience stool disorders.
Why does the stool turn dark green? In this case, changes in the shade of feces are caused by the plant pigment chlorophyll. It is found in spinach, arugula, parsley, dill, Brussels sprouts, green beans and other leafy vegetables. A large amount of fiber provokes similar symptoms as a result of accelerated transport through the intestinal tract. Another reason for the appearance of dark green stool is metabolic disorders. The fact is that the bile pigment biliverdin, during rapid evacuation, does not have time to complete the complete decay process. As a result, the substances preceding it can be found in feces instead of brown stercobelin. Therefore, with diarrhea, as well as when using laxatives, stool becomes green in color.
Antibacterial medications can even cause dark green diarrhea. The state of dysbacteriosis with the development of fermentation and rotting processes of eaten food products causes similar symptoms.
Conditions accompanied by fever for more than a day, pain in different parts of the abdomen, nausea and vomiting require special attention. These may be signs of serious intestinal infections such as dysentery.
With pancreatitis, all characteristics of stool may change. Liquid stool becomes yellow-green in color (sometimes light yellow), with a shiny surface. These stools have a strong stench and are very difficult to wash off.
When examining the coprogram, dietary fiber and fatty inclusions are detected. With pancreatitis, a large amount of fat in the stool appears due to a deficiency of the enzyme lipase, which breaks down fats. An additional contribution is made by an incorrect diet with a large amount of fatty, fried, smoked foods.
The most important diagnostic criteria for pancreatitis are biochemical indicators (lipase, amylase, trypsin), as well as instrumental studies such as ultrasound, computed tomography, radioisotope scanning, echography.
Gray color of stool
With the start of taking medications such as bismuth preparations containing iron, activated carbon, aspirin, ibuprofen or products with dark pigment, the appearance of gray stool is natural.
This condition does not require discontinuation of medications or additional treatment; there is nothing to worry about. But feces with a putrid odor and a dark gray hue indicate significant disturbances in the digestive processes. This may be nonspecific ulcerative colitis or putrefactive dyspepsia. With pancreatitis, inflammatory foci of glandular tissue become swollen. As a result, the lumen of the bile ducts passing through the pancreas is significantly reduced. Gray stools are formed due to insufficient flow of bile into the intestines.
Norms and pathologies of feces in infants
In newborns, feces differ significantly in consistency and color from adults. Original feces (meconium) are black, odorless, with a smearing consistency and similar to machine oil. All meconium is expelled within a few days after birth, and the stool takes on a different consistency and color.
Newborn chair
When breastfeeding, what the baby leaves in the diaper is largely determined by the mother's nutrition. Poop can have different shades: brown, yellow, orange, mustard, sandy, even greenish, this is the norm in the absence of other impurities and symptoms.
In artificial babies, the color of stool is usually yellow or brownish, sometimes it can even be blackish (when using iron-containing mixtures or diluting them incorrectly), the color rarely changes (only when changing the mixture).
Babies' stool color may vary
The consistency of normal stool is similar to porridge and has a milky or sour curd smell (in infants). Newborns poop after each breastfeeding (artificial babies poop less frequently, since the formula takes longer to digest); in children by the age of 10 months, the frequency of bowel movements decreases to 1-2 times a day. If their number is significantly less, the baby’s stool is hard, this indicates a problem of constipation, which can be solved by proper nutrition of mother and baby.
Note! If lumps of undigested food appear in the feces, do not be alarmed right away - this often occurs due to the immaturity of the baby’s digestive system.
Gray stool occurs in a child when he is transferred from the breast to formula or when he changes from one brand of artificial nutrition to another. The silvery tint of poop appears when the baby is fed with slightly diluted cow's milk - this amount of protein is clearly too much for the baby's body. If a child takes certain medications (such as Ibuprofen, Agumentin, Paracetamol), his stool may also turn gray, which will change when the medications are discontinued. If a nursing mother has a large amount of dairy and plant foods on her menu, the baby will poop light gray feces.
If foam, mucus, or, even worse, streaks of blood become noticeable in children's stool, or if it itself turns reddish and acquires a very unpleasant putrefactive odor, this is already a pathology indicating disturbances in the digestive system.
Recommendations
If you notice any changes in your stool, do not despair. You need to calmly figure everything out, and if necessary, resort to additional diagnostic methods (laboratory, instrumental studies) and the help of qualified specialists. They will be able to make a definitive diagnosis and prescribe effective treatment if necessary.
Children's problems are perceived with the greatest trepidation, but fortunately, most often they are not serious. They consist of irrational nutrition, and for healing you just need to choose the right diet. And in good condition, just observation is enough, and after a few days the stool will recover on its own.
Proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle are the main components of the well-being of the entire digestive system.
When do you need a doctor?
If the baby does not show signs of anxiety, eats well, cries little, his temperature is normal, there is no mucus or blood clots in the feces, observation for several days is enough, as well as an analysis of the feeding mother’s nutrition (or wait until the baby is “artificial” "adapts to the new mixture).
If the color of the “children's surprise” does not acquire the usual shade, lumps of mucus, foam or blood appear in it, the child develops rashes, the stomach swells, the temperature rises, sleep and appetite are disturbed, he becomes lethargic, burps heavily, cries, and at the same time tightens his legs to the tummy, this indicates the onset of pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract, liver or pancreas and the need to urgently visit a pediatrician.
If there are problems with the gastrointestinal tract, the baby cries and pulls his legs towards his stomach
After conducting research, the doctor will prescribe adequate treatment (special diet, medications with enzymes, etc.), after which the color of the child’s stool should return to normal.
An infant is very vulnerable due to the immaturity of the digestive system, so parents should closely monitor any changes in his condition. One of the best indicators of a baby's health is the color of its stool, which can vary. Thus, gray stool is not always a pathology, but may indicate the presence of dysfunction in the body. If nothing bothers the child, it is worth observing him - perhaps this is just a reaction to a new food, formula or product in the mother's diet.