Relationship between the number of moles and the risk of melanoma
There is a lot of research on this issue. If you start reviewing everything, you will end up with a long and boring article that you will not be interested in reading, and I will not be interested in writing.
I have selected some of the largest studies that will help us form our own opinion on this issue.
However, before considering research data, let’s move from the folk concept of “mole” to the medical concept of “nevus”.
Types of moles
The most harmless moles are pigmented ones, they are called lentigo.
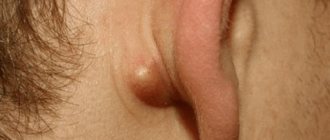
They look almost like freckles and are very easy to confuse. Such moles are formed due to the accumulation of melanocytes under the skin, cells responsible for pigmentation. All other types of birthmarks can cause trouble for their owner. These are epidermal-dermal nevi - moles that can rise above the surface of the skin, usually located on the palms, feet or in the groin area. Intradermal nevi are convex, often covered with hair. Dysplastic nevi are irregularly shaped tubercles with unclear boundaries; they can be more than a centimeter in size.
One of the most dangerous is a giant nevus. This is a congenital spot that can cover large areas of the skin. It is usually removed early, since it looks scary, and the risk that it will degenerate into a malignant formation is quite high.
What is a mole and what moles are important?
Already at this stage, interesting things become clear. Not every brown formation on the skin fits the definition of a “mole” and will be counted.
In 1990, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) clearly defined the concept of a “nevus” (pigmented nevus) for epidemiological studies of this type.
Brown or black pigment spots or nodules (papules), which stand out quite well in a darker color against the background of the surrounding skin. Lesions to be counted should not show signs of freckles, solar lentigines, seborrheic keratosis, café-au-lait spots, or other non-melanocytic lesions.
The conclusions from this definition are both pleasant and not so pleasant:
1) What you previously thought was a mole may not be, and your risk of melanoma will be lower than you thought.
2) You will not be able to independently count the number of nevi on the skin. This can only be done by a doctor - a dermatologist or dermato-oncologist. I will say more, in some cases, without a dermatoscope, even an experienced specialist will not always be able to distinguish solar lentigo from a pigmented nevus.
Causes of moles
Over time, there are more nevi on the surface of the skin.
According to recent research, there are 3 main reasons for the appearance of new moles in children:
- Genetic predisposition. If parents have many dark spots on their body, then the child will most likely encounter them.
- Ultra-violet rays. Exposure to the sun increases the risk of malignant degeneration of nevi, so on sunny days it is better to walk in shaded places, use creams with an SPF factor, and do not forget about a hat.
- Hormonal background. Many neoplasms occur during puberty, when hormonal changes occur. The number of nevi may increase during pregnancy, menopause, and during serious stress and illness.
How many moles is that? And which ones?
I will give 2 of the largest and most recent studies that I was able to find. Both works represent a meta-analysis, i.e. a synthesis of data from several clinical studies. In my opinion, this type of research is often more credible than a single study.
1. Study by Italian authors from 2005
Meta-analysis of risk factors for cutaneous melanoma: I. Common and atypical naevi.
The results of 46 individual studies are summarized.
Everything is the same, but in words: the risk of melanoma increases in direct proportion to the number of nevi, both ordinary and atypical. The minimum risk of developing melanoma is in a person with 15 or fewer nevi on the skin, no nevi on the hands, and no atypical nevi.
The maximum risk is for a person with more than 100 regular nevi, 15 nevi on the hands and 5 atypical nevi.
2. American study from 2010
Catherine M. Olsen, Heidi J. Carroll and David C. Whiteman
Estimating the Attributable Fraction for Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Nevi and Melanoma
The results of 49 studies were summarized.
The results are consistent with previous research.
The risk of melanoma increases with the number of common and/or atypical nevi on the skin.
In contrast to the previous study, it was noted that 42% of patients with melanoma had 25 or more common nevi and/or 1 or more atypical nevus.
The authors consider these patients to be a high-risk group and recommend more careful monitoring and training in self-diagnosis methods.
Unfortunately, neither in the first nor in the second study the authors make specific recommendations on the frequency and format of observation of patients at risk. We will try to formulate answers to these questions a little later.
Is the appearance of a large number of nevi dangerous?
A baby has many moles on his body or face - this does not mean that he has melanoma. Evenly colored brownish spots are not a cause for concern.
The indication for contacting a dermatologist is the modification of formations. You should visit a doctor if you have the following signs of degeneration:
- itching, burning, peeling;
- a sharp increase in size of the formation;
- color change;
- asymmetry, uneven edges;
- change in shape (it was flat, it became convex);
- change in structure;
- hair loss from a mole;
- injury.
What to do if there are a lot of moles on the body?
From the first study , we found that the likelihood of developing melanoma increases in direct proportion to the number of regular and/or dysplastic (atypical) nevi.
A second meta-analysis suggests that people with 25 or more common nevi and/or 1 or more atypical nevi are at risk for developing melanoma.
I think that after reading the previous paragraph, all readers were most likely divided into 3 groups:
- “I have a lot of moles and definitely more than 25, I’ll get melanoma! Oh God!"
- “I have less than 25 moles and I can now relax 100% about melanoma.”
- We ran to count the moles and realized that they couldn’t cope without a doctor.
It seems to me that there is no need to divide everything into black and white. Unfortunately, anyone can get melanoma. And those who have more than 25 moles, and those who have fewer, and even those who have only one or two moles. No one is 100% insured, it’s just that the probability is different for everyone. It is important to understand that the number of moles is just one of 17 risk factors for melanoma. I think that you shouldn’t draw any fatal conclusions and panic just because you have a lot of moles.
A mole hurts: what to do in this case?
Children almost never have moles: they begin to appear on the body only closer to puberty. It is at this moment that hormonal changes begin in the body. By the way, due to surges of hormones, moles may become larger while you are expecting a baby: don’t worry if you find a couple of new spots. Take a closer look at them: moles that are symmetrical with flat edges should not be a cause for concern.
However, every suspicious nevus needs to be monitored. The thing is that moles are, in fact, a cluster of pigmented melanocytes. And under specific conditions, they can transform into melanoma cells - one of the most terrible malignant tumors, which tends to recur and “grow” into other organs.
How to be monitored if you have many moles?
In my practice, if a person does not have risk factors for developing melanoma, I recommend being seen by an oncologist for an examination with a dermatoscope annually in May at Melanoma Diagnosis Day. In addition to this, conduct a complete self-examination of the entire skin once every six months; you can examine a mole in a hard-to-reach place using two mirrors.
If a person has one or more risk factors, he or she should visit a dermato-oncologist for dermatoscopy once every 6 months and conduct a self-examination once every 3 months.
For those who have many moles (25, 50 or 100 - it doesn’t matter) and it seems difficult to monitor them, there is a type of dynamic monitoring called digital mapping of nevi.
Here's an example of how this happens in Germany:
This type of observation, according to the European Society of Clinical Oncology (ESMO), is considered the most adequate for patients with a large number of nevi:
According to data as of October 2021, such devices are available in Russia, Moscow and Yekaterinburg, the price for an examination can reach 10 thousand rubles.
Update December 2021.
I am proud to announce that I am now conducting a similar examination in St. Petersburg.
The mechanism of the appearance of moles in a child
Moles are formed during the period of intrauterine development; they may not form immediately. As a rule, age spots appear in babies under 1 year of age.
The formation mechanism depends on the individual characteristics of the organism and the type of spot.
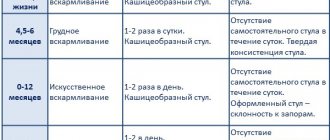
| Type of education | Peculiarities |
| Red spots immediately after childbirth | They arise due to pressure on the baby’s skull. They disappear on their own during the first year of a child’s life. |
| Flat nevi of burgundy color | The result of vascular pathology. |
| Flat brown nevi | The spot may have different shades of brown. Does not require removal in the absence of alarming symptoms. |
| Strawberry hemangioma | A bright red spot, soft on palpation. Congenital pathology manifests itself in the first month of a baby’s life. In the absence of indications, removal is not recommended. |
| Cavernous hemangioma | Formations in the form of blood vessels with blurred boundaries. Spots that appear during puberty. Destruction is not required, they go away on their own. |
Summary, or Briefly about the main thing
A large number of moles - 25, 50 or 100 - is not a reason to panic, but just one of 17 risk factors for developing melanoma. In such a situation, you should see an oncologist with dermatoscopy at least once every six months or more often, if your doctor thinks so. Self-examination of the entire skin using two mirrors is carried out once a month.
According to research, the optimal way to monitor a large number of moles is digital nevus mapping.
Other articles:
- Removing moles with a radio knife: why is it safe
- Options for incomplete mole removal: is there any danger?
- Histology of a mole: stages of research and frequently asked questions
- Radio wave removal of papillomas
Melanoma: when can it develop?
On average, in 5-20% of cases, fairly large moles, whose size exceeds the “bar” of 2 cm, transform into malignant tumors. Doctors say that you need to be careful with these, especially if they are in places of contact with shoes/clothing: they say , trauma to the nevus - a cut, bruise, abrasion - or constant rubbing of it can lead to the development of a tumor over time.
In fact, there is a lot to debate about this issue. For some patients whose moles have already transformed into melanomas and begun to bleed, it often seems that the blood appeared precisely because of the damage. They immediately go to the doctor, and a consultation with an oncologist in Kaluga shows that the patient has cancer. It is important to understand here that it was not the injury that led to the disease, but the disease that caused the bleeding.
On the other hand, some moles can actually grow after damage. But histological studies show that such a mole is not always melanoma. Theoretically, tissue repair processes occur in the area of damage, and this is always associated with the presence of a mixture of biologically active substances that stimulate cell growth and division. Cancer cells can also grow on such a “cocktail,” but so far there is no practical evidence of an increase in the risk of developing melanoma due to trauma to a mole. So, if you accidentally cut a mole, there is no need to panic.
Yes, and run to the oncologist with a request to remove the unfortunate tumor too. But dynamic monitoring will not hurt - you need to visit a doctor from time to time. You definitely need to go to an oncologist if a mole is peeling, characteristic ulcers have appeared on it, it is bleeding, there is discomfort - tingling, itching with a burning sensation.
If you have decided to remove it, discuss it with your oncologist. Firstly, it is very important not to simply remove the mole, but to conduct a subsequent histological examination: doctors must make sure that the nevus does not contain dangerous cells. It is not so easy to determine “by eye” what kind of mole is in front of them: there are also clinically atypical melanomas, hiding under the mask of completely harmless spots, which are very difficult to recognize at the stage of a simple initial examination. So detailed research never hurts.
Possible complications and precautions
The main feature of a progressive pathological process is that the tumor grows rapidly in a short period of time (over the course of a month). When a white mark forms around a birthmark, do not be alarmed; this is a sign of Setton’s nevus. It occurs as a consequence of sunburn and disappears on its own after some time. A dangerous signal is the growth of moles throughout the body. This phenomenon requires specialist supervision.
Precautions to be taken:
- Limit children's exposure to the sun between 11 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- Protect your skin from ultraviolet rays with sunscreens and lotions.
- In hot weather, wear a hat and walk with your baby in the shade.
- If the tumor is injured, it is necessary to treat it with hydrogen peroxide and immediately contact a specialist.
Treating stains using folk remedies at home is prohibited due to the risk of complications.
Inspection of suspicious elements should be carried out at an early stage to avoid undesirable consequences.
Reasons for the rapid growth of a mole
A child’s mole has grown larger – a situation that makes parents worry.
Congenital marks have a specific classification:
- hemangioma;
- spots with a light orange color (stork bite);
- saturated wine stain (fire stain).
Hemangioma is a vascular formation that appears some time after birth.
The size of the nevus immediately increases rapidly. By the age of ten, the element becomes pale and disappears without a trace.
A stork bite is a pigmented cell cluster that occurs on the eyelids, back of the head, and in the bridge of the nose. It looks like a large speck, rich pink in color.
Common are bright red nevi on the scalp, which increase in size as the child grows and disappear with age.
Acquired moles are divided into:
- intradermal;
- epidermal;
- combined.
The first two varieties resemble peas, and the combined type is a smooth formation at the same level as the skin in the form of a brown speck.
The reasons for the increase in nevi are the following factors:
- Prolonged exposure to sunlight.
- Hormonal changes.
- Mechanical damage to the skin surface (impact, rubbing, scratch, cut, insect bite).
- Viral infection.
Genetic predisposition contributes to the enlargement of a mole. The more birthmarks mom and dad have, the higher the risk of their formation in the baby.
According to statistics, fair-skinned, premature babies have a higher risk of developing nevi than dark-skinned babies. Girls are more susceptible to the appearance of congenital formations.
Dangerous accompanying symptoms
Any spots on the baby's body should be controlled by parents. Periodic examination allows you to notice the first signs of transformation of moles into melanoma:
- Asymmetry: in its natural form, a nevus is an even geometric figure, an oval or a circle, the halves are symmetrical in relation to each other. The growth of one part of the spot is an important symptom for examination.
- A healthy mark has smooth edges, while a pathological mark has blurred borders with jagged sides.
- Change in color: uniform color and color is normal, the presence of inclusions or a change in tone is a sign of deformation of the spot.
- If the diameter exceeds 6 mm, you should visit a doctor.
- Hair loss in the affected area.
If one of the above symptoms is detected, you must seek help from a medical facility to avoid dangerous consequences.

![shutterstock_1111315238 [converted].jpg](https://dou10ugansk.ru/wp-content/uploads/shutterstock_1111315238-preobrazovannyj-jpg-330x140.jpg)