The purpose of the fontanel: what does it mean
After birth, a small soft area on the baby’s head is clearly visible - this is the fontanel, which is hidden under the membrane. As the baby grows, it will stiffen and close.
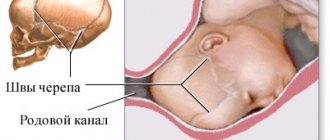
The small fontanelle, also known as the crown, provides elasticity to the newborn’s skull during delivery and allows the baby to safely pass through the birth canal. Because of this elasticity, after childbirth the baby’s head has an elongated and flattened shape, which can initially frighten the mother in labor.
This is a temporary phenomenon, and within a year the head will return to its normal shape.
The fontanel is designed to regulate heat exchange in the brain, soften head impacts, and avoid seizures. When the baby's body temperature rises, thanks to the crown, the necessary cooling of the brain and its membranes occurs.
Normal medical indicators
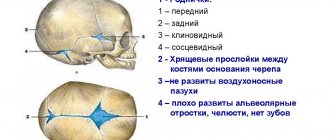
After birth, each person has 6 crowns on the head, however, 4 of them quickly tighten, and the remaining 2 can be clearly visible. They will tighten as the child grows.
At one month of age, the size of the crown is about 30 mm in diameter, but at the same time, a crown within 25-35 mm is considered normal. At 2 months, the fontanel should close by about 5 mm, and by six months it should be about 17 mm in diameter.
As the baby grows, the fontanel decreases and is almost completely overgrown by 12 months. During a preventive examination of a child, a specialist not only measures his height, weight, head and chest, but also examines and feels the fontanel.
How quickly the crown closes depends on individual characteristics, as well as on how much vitamin D and calcium enters the baby’s body. Dr. Komarovsky emphasizes that the period of overgrowth lasts from 3 months to 2 years.
With a lack of these elements, the crown slowly closes, while with a sufficient amount of vitamins, the crown closes in due time.
The bones of the skull develop by enlarging the central region and widening the edges at the sutures. After the crown fuses, the skull stops growing, and increased pressure forms in the head.
Normal fontanelle and head size
Normally, a large fontanelle should be 2 x 3 cm.
During intrauterine development, several fontanelles form on the child’s head in the crown and temples. They manage to close in the first months after birth. Another spring, located on the crown, is delayed by 1-2 years. It is called the anterior one. In outline it resembles a rhombus. By the time the baby is born, the dimensions of the cavity are 2 x 3 cm. It is the anterior spring that raises many questions among parents, especially when it turns out to be too large or small.
The gradual tightening of the fontanelles is one of the signs by which the state of metabolic processes in the body and the growth of bone and brain tissue are judged.
Measure the soft crown of a newborn carefully, without pressing, by feeling the extreme points of the rhombus. First, take measurements from an elongated diagonal connecting the bridge of the nose and the back of the head, and then from a short line running from ear to ear. The data obtained is checked against a table corresponding to the age and size of the fontanel.
It is also important what the circumference of the newborn’s skull is.
However, these values are not the only indicator that the pediatrician relies on when making a diagnosis. The functioning of the central nervous system and the development of the brain are judged by the shape and size of the skull. Head circumference increases by 1.5 cm monthly up to 6 months. So at 1 month it varies between 36.6-37.3 cm, and the size of the fontanel is 25 x 28 mm. By 11 months, the picture of the parameters changes significantly, the girth of the skull approaches 46-46-9 cm, and the fontanelle approaches 5 x 8 mm.
Each child is unique, so deviations from standard figures by 3-4 mm are not considered critical. There is no need to worry when, with a small fontanel, the baby feels well, eats actively, sleeps soundly, and gains weight. But if the newborn is restless, he has developmental disorders against the background of a small spring, we can talk about a serious problem.
The timing of tightening of non-ossified areas on the crown is no less important. In most children, the crown becomes overgrown by 8 months of age. However, if a three-month-old baby has a completely absent anterior fontanelle, this condition is classified as pathological. Here the help of a neurologist is needed.
If a small (posterior) fontanelle in a baby has not closed at 3 months, you should see a doctor, since a slow ossification process can lead to deformation of the skull, impaired hearing and vision, strabismus, and mental disorders.
What does the small size of the crown mean?
The size of the fontanelle is one of the visual indicators of the baby’s health status. In situations where it is less than the permissible norm, this may indicate some diseases, however, only a specialist can establish an accurate diagnosis or refute it after a series of examinations. A small or rapidly growing fontanel may be a characteristic feature of the following diseases:
- Craniosynostosis is a disease of the child’s skeletal system that is not common. It occurs when the crown of the head fuses early, and this provokes an increase in pressure inside the brain, head deformation, hearing or vision impairment. This disease can be either congenital or acquired.
- Rickets slows down the process of fontanel closure. In most cases, this feature is inherited. If the parents also had slow bone healing, then the baby may have the same feature. Rickets often occurs in premature babies, as well as in babies who do not receive vitamin D in the required amount. The baby's skull continues to grow after the membrane has healed. If the fontanel closes quickly and nothing bothers the child, then he is healthy. 400 m.u. is enough for him. vitamin D in 24 hours.
- Abnormal intracranial development. With microcephaly, the child is developmentally delayed and his brain is smaller than it should be. This disease can be caused by congenital rubella or a herpes viral infection. With leukomalacia, there is a softening of the brain tissue, which occurs as a result of congenital diseases, such as syphilis.
- Failure in the process of phosphorus-calcium metabolism and general metabolism.
- Diseases of the nervous system.
Dr. Komarovsky, widely known in pediatrics, says that there are many congenital pathologies that arise as a result of impaired metabolism and absorption of calcium. These disorders lead to convulsions, brittle bones, rapid hardening of the fontanel, physical and mental inadequacy.
If there is a suspicion of rickets, it is necessary to give the child 10,000 IU. per day for 7 days, and after this period return to the usual dosage. In addition, Komarovsky recommends giving the child calcium gluconate and spending as little time as possible in the sun.
Location of fontanelles
The large fontanel is located at the junction of the frontal and parietal bones.
Small - at the junction of the parietal bones with the occipital bone. This is the largest membranous window of a diamond shape. The size of a large fontanelle in a newborn is 20-30 mm. Immediately after birth, its size may temporarily change due to the divergence of the bones. Through the delicate skin, the outline can be seen only with a slight pulsation that occurs when the arterial vessel wall is exposed to it. With age, the membranous tissue becomes harder; the size of the window is determined only with careful palpation.
Sizes as the child grows older
Immediately after the birth of the child, the soft crown begins to gradually be replaced by bone tissue.
It is important to note that in the first year of a child’s development, the brain actively grows, slightly moving the bones of the roof of the skull apart. The replacement process begins from the edges to the middle, the size of the window begins to gradually decrease. The table shows data on how many months a large fontanel in children closes
Over time, its size will become smaller and smaller
The table shows data on how many months the large fontanel in children heals. Over time, its size will become smaller and smaller.
| Dimensions of a large fontanel | |
| Child's age, months. | Average dimensions of a large fontanel, mm |
| 0-1 | 26-28 |
| 1-2 | 22-25 |
| 2-3 | 23-24 |
| 3-4 | 20-21 |
| 4-5 | 16-18 |
| 5-6 | 16-18 |
| 6-7 | 16-16 |
| 7-8 | 14-16 |
| 8-9 | 14-15 |
| 9-10 | 12-14 |
| 11-12 | 5-8 |
The table shows average statistical data, and slight variability in closing dates is allowed. The reduction in the size of the soft crown is determined by individual factors, such as the degree of maturity of the child, the rate of its development, etc. The minimum dimensions are observed by the end of the 1st year of life and amount to 5-8 mm. It is already difficult to determine the smaller size of the window; completely membranous tissue disappears by 1.5 years.
In addition to the size of the fontanel, parents need to take other indicators into account, for example, study the table of the newborn’s weight by month
Late closing - normal or cause for panic
A large fontanel is overgrown by 1 year, maximum - by 1.5 years.
If a large fontanel is not overgrown by one year, do not rush to worry ahead of time. The soft crown has a maximum closure period of 18 months.
It is important to visit a doctor before jumping to any conclusions
The most common causes of delayed closure of the soft crown:
- intrauterine growth retardation is one of the most common causes;
- premature birth – in premature babies the development of the body is slow, especially in the first months after birth;
- dropsy of the brain, or hydrocephalus - this disease provokes an increase in intracranial pressure, which leads to divergence of the bones of the skull, increasing the distance between them;
- congenital or acquired anomalies - rickets, hypothyroidism, achondropalsia, Down syndrome, etc.
In order to determine why a child’s fontanel does not heal for a long time or increases in size, it is necessary to consult a doctor. Without an examination, laboratory or instrumental examination, the cause cannot be determined.
What to do in case of rapid overgrowth
If a newborn's fontanel is small or quickly overgrows, it is necessary to undergo an examination. Possible reasons:
- Craniosynostosis is a disease in which the cranial sutures close prematurely. Craniostenosis is the most common reason why the fontanel quickly overgrows. The disease may be congenital or due to rickets. Complications are prevented through surgery.
- Anomalies of brain development occurring in combination with disruption of ossification processes. They are much less common and treatment is prescribed individually.
The consequences of a small fontanel in a newborn with craniostenosis may be mental development disorders due to injury to the actively growing brain on the bones of the skull roof.
Likely consequences
Every month, starting from the birth of the baby, he must be shown to a pediatrician and other specialists. Preventive examinations will allow you to quickly identify violations and begin the necessary treatment. Failure to contact a specialist in a timely manner can lead to the following undesirable consequences:
- destruction of the skull;
- development of strabismus;
- blindness;
- delay in psychomotor development;
- mental imbalance;
- hearing problems.
Treatment will require surgery, and the sooner the correct diagnosis is made, the higher the likelihood of curing the child. Therefore, it is extremely important to monitor the condition and size of the fontanel, and if there are deviations from the norm, immediately contact a specialist.
Recommendations from experts
The child is given formulas with a minimum amount of calcium and vitamin D.
Starting from 1 month of the child’s life, parents should regularly visit a pediatrician who will take measurements of the head and chest, check the condition of the fontanelle, monitor reflexes, give nutritional advice, etc. If the anterior fontanel is too small , the doctor will refer you for diagnostics to rule out the presence of dangerous diseases. It is also worth considering the following points:
- Avoid adding vitamin D3 and calcium to your baby’s diet. If the child is on artificial nutrition, select the appropriate formula;
- protect the upper part of the baby’s head from injury and drafts;
- For a nursing mother, strictly adhere to the diet, diversify the menu with vitamin and mineral complexes.
Professor Komarovsky says the following about the causes and consequences of a small fontanel in a newborn:
- Vitamin D intake by the mother does not affect the rate of fontanelle closure in an infant;
- Normally, fusion of the cranial bones on the crown occurs from 3 months to 2 years;
- if the crown grows together early, you need to monitor the growth of head circumference monthly;
- with early fusion of springs with a slow rate of enlargement of the skull, it is necessary to exclude the development of microcephaly;
- An anterior fontanelle that is smaller than normal is never the only symptom of a serious illness.
The rate of fusion of the anterior spring is influenced by the type of nutrition, heredity, and structural features of the infant’s skull. Excessively small sizes may indicate the presence of dangerous diseases associated with the brain and central nervous system. Therefore, parents should contact a specialist in a timely manner to avoid serious consequences.
Recommendations for parents
If a child has a small fontanel, but the specialist has not made any diagnosis, then pediatricians advise monitoring the child and his general condition. An alarming signal is the baby crying during sleep, waking up with a loud cry - perhaps he is suffering from headaches due to high blood pressure.
Watch your child as he plays and frolics. The baby's head must be protected from blows, falls and hypothermia, since the small fontanel is not fully capable of performing its functions.
For those children who are bottle-fed, it is necessary to give less milk and select an adapted formula that will contain a smaller amount of vitamin D. After six months, complementary foods in the form of soups, purees and meat should be introduced into the diet.
Protect your child from drafts and damage while at home; at low temperatures, it is advisable to put a cap on the baby’s head.
What does it mean if a newborn has a small fontanel?
04 February 2019
Averyanova Sveta
The baby's fontanelle, or, as people say, the soft crown, plays an important role in the psychophysiological development of the baby. The small size of this non-ossified area of the skull is usually alarming during examination, as it may indicate developmental pathology. Only a specialist can distinguish a physiological feature from a disease; the task of parents is to notice deviations in time and follow the pediatrician’s recommendations.
The size of the fontanel is not the only indicator that the pediatrician will pay attention to. One of the main characteristics of the development of the brain and central nervous system is the shape of the skull and its size. Up to 6 months, head circumference increases by about 1.5 cm every month. For boys and girls, these characteristics are slightly different. (Important! The table can be scrolled left and right)
| Age, months | Head circumference in girls, cm | Head circumference in boys, cm | Size of the fontanel, mm (along the long side of the rhombus) |
| 1 | 36,6 | 37,3 | 30 |
| 2 | 38,4 | 38,6 | 25 |
| 3 | 40 | 40,9 | 22 |
| 4-5 | 40,5 | 41,2 | 18-20 |
| 6 | 42,2 | 44,2 | 17 |
| 7-8 | 43,2-43,3 | 44,8-45,4 | 15-16 |
| 9 | 44 | 46,3 | 14 |
| 10 | 45,6 | 46,6 | 12 |
| 11 | 46 | 46,9 | 8 |
All children are unique, so sizing may vary. If the parameters are 3-4 mm more or less than standard norms, and the baby is healthy and developing normally, there is nothing to worry about. If such an indicator as a small fontanel in a newborn is accompanied by other developmental disorders, it’s time to sound the alarm. After identifying the deviation, the factor that influenced the small size of the soft crown in the newborn is determined.
The time when the non-ossified areas of the crown began to close is also of great importance. If a three-month-old baby has an absence of fontanel, this condition is considered a pathology. In this case, consultation with a neurologist is required.
The size of the fontanelle at birth is influenced by many factors: taking multivitamins and the nature of the mother’s diet during pregnancy, the environment in the place of residence, heredity, and previous diseases. If this phenomenon is due to the individual development of the baby, there is nothing to fear. It’s another matter if the small size of the soft crown is associated with congenital diseases, such as:
- Microcephaly. This diagnosis is made if there is no fontanel in a newborn, and the size of the head is much smaller than normal. The pathology causes disruption of brain formation. The cause of the deviation may be intrauterine infections, radiation, exposure to toxic elements - alcohol, drugs, medications, endocrine disorders in the mother during pregnancy.
- Craniosynostosis.
A disease associated with hereditary pathologies and diseases of the prenatal period. Leads to rapid ossification of the sutures and deformation of the head. Accompanied by neurological disorders, nausea, and possible convulsions. Treatment consists of surgical enlargement of the skull. - Disturbance of metabolic processes in bone tissue. Excess calcium in the blood and its rapid absorption leads to the overgrowth of the fontanelle ahead of schedule.
In addition to a general examination and medical history, diagnosis of the disease includes examination by several specialists: geneticist, neurologist, infectious disease specialist. In addition to medical consultations, infants with a small fontanelle are prescribed laboratory and hardware examinations:
- X-ray of the bone structures of the skull;
- ultrasound scan of the brain;
- computed tomography of the head.
Dangerous diseases, the symptom of which is the small size of the fontanelle, are very rare. The main thing is to find out the cause of the problem in time and take action. Timely diagnosis and treatment will ensure the normal development of the little patient, unless there is severe pathology.
If a child was born without a fontanel or the size of the soft crown is small, he is put under special control in the maternity hospital. Congenital brain defects are usually diagnosed during pregnancy using ultrasound. Such diseases lead to mental retardation and mental retardation. There is no cure for microcephaly; therapy is prescribed to relieve symptoms.
The consequences of craniosynostosis depend on the form of the disease: with monosynostosis, one suture is affected, with polysynostosis – several. Pansynostosis is the early fusion of all cranial sutures. The manifestation and severity of the disease depends on the type of pathology.
Deformation of the skull leads to increased intracranial pressure, malocclusion, strabismus, hearing loss, and respiratory failure. Craniosynostosis is treated surgically; the optimal age for surgery is 6–9 months, since it is at this time that the rate of brain growth is high.
If hypercalcemia is suspected, it is necessary to limit the intake of multivitamin preparations and make adjustments to the menu of the nursing mother or select special baby food. Otherwise, excess calcium can lead to disruption of the functioning of the kidneys, digestive and skeletal systems.
Pediatricians give basic instructions during routine examinations of the child, so they should not be neglected, especially from one month of age until six months, before the sutures of the skull begin to completely close. Here's what to do if a child has a small fontanel, Dr. Komarovsky recommends in his article:
- The main functions of the non-ossified areas of the skull include shock absorption and protection from temperature changes. Therefore, the baby must be protected from injury, overheating and hypothermia.
- The rate at which the fontanel closes is affected by the level of calcium in the baby’s diet, so you need to ensure that its amount does not exceed the permissible limits. You should not prescribe vitamin D to your child on your own or exceed the dose prescribed by your doctor. If a nursing mother takes a complex of vitamins, it is also worth consulting with a specialist.
- In summer, it is advisable to produce vitamin D naturally: by walking in the sun until 12 noon.
- In formula-fed children, it is necessary to control the amount of food eaten.
It is advisable to write down all alarming moments in the child’s behavior and well-being in a separate notebook. At your next visit to the doctor, it will be easier to remember everything that bothered you during the month. Just in case, also keep a list of pharmaceutical medications that were taken before and after the birth of the baby - this will help the pediatrician make a diagnosis faster.
It has been established that uncontrolled intake of multivitamins during pregnancy poses a danger to the newborn. The components of the complex can provoke disturbances in phosphorus-calcium metabolism in a child. Expectant mothers should also not be overly fond of foods high in calcium and follow all the recommendations of the doctor monitoring the course of pregnancy.
The article contains general information and does not replace consultation with a pediatrician.
IMPORTANT ! *when copying article materials, be sure to indicate an active link to the original source: https://razvitie-vospitanie.ru/zdorovie/malenkij_rodnichok_u_novorozhdennogo.html
If you liked the article, please like it and leave your comment below. Your opinion is important to us !
Did you like our content? Subscribe to the channel in Yandex Zen.
Share with friends:
We recommend
What to do when your child often takes deep breaths and yawns
52 443 6
Why do nails on a child's toes or hands peel?
39 223 6
For what reasons does a baby's fontanelle sink?
38 755 9
What to do if your newborn has an unpleasant smell from the navel
35 565 7