Back to list Previous article Next article
09.07.2014
Tags:
breastfeeding, breastfeeding, microflora
( 2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Breastfeeding is very important!
Breast milk has been and remains the best nutrition for a newborn. No milk formula, even the highest quality, can fully replace it. Because it is with breast milk that your baby receives the full amount of nutrients, microelements and vitamins necessary for the full growth and development of this particular child. Moreover, in the form and proportions determined by Mother Nature herself. However, in some cases and depending on a number of circumstances, the quality indicators of human milk may change, and not for the better. This, of course, can cause harm to the baby, who will simply be “malnourished,” that is, not receive enough components that are extremely necessary for his growing body.
What determines the quality of breast milk?
There are many stereotypes and even superstitions about this. Often, nursing mothers hear from more “experienced” relatives and friends that in order to increase the fat content of milk, you need to eat more, consume more dairy products with a high percentage of fat, and lean on sweets and nuts. It is believed that consuming large quantities of a wide variety of high-calorie foods (fatty meat or sausages) can give lactation an additional “impulse” of quality. In everyday life you can often hear the expression “poor milk” , which characterizes milk that supposedly has low fat content and for this reason cannot be a complete nutrition for the baby (sometimes they say “blue milk”, in fact it is “foremilk”, which contains more water and immune factors, in contrast to the “back” – more fatty and high-calorie). There are also warnings: do not eat garlic and onions, which will supposedly give the milk a bitter taste and the child will refuse it. Breastfeeding mothers are also strongly advised to refrain from smoking, drinking alcohol, taking uncontrolled medications and... not getting carried away with coffee, since caffeine easily penetrates into milk.
Of the above tips and prohibitions, perhaps the most indisputable are the last ones - about the dangers of cigarettes, alcohol, coffee and medications . All other recommendations - in relation to the same sausages that are supposedly “nutritious” - are far-fetched. One comedian, by the way, noted that “not a single animal was harmed during the production of sausages.” Of course, he exaggerated, but there is a lot of truth in these words. It is well known that various ingredients are added to sausages that have nothing to do with real meat. In particular, preservatives and dyes, flavor enhancers and thickeners, etc., etc. Now imagine that this explosive mixture first enters the woman’s body, and then, having penetrated into the milk, into the child’s body. So is it worth consuming such products to improve lactation rates? The answer, I think, is obvious...
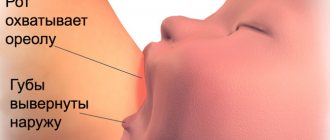
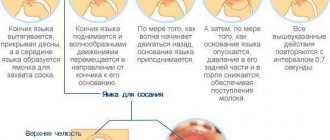
In fact, completely different factors influence the quality of breast milk . They have nothing to do with food (more precisely, they do, but indirectly - read about this below), and even more so to the amount of food eaten by the mother. Lactation occurs regardless of the quantity and quality of food a woman eats. Even if, hypothetically, she stops eating altogether, the process of producing breast milk will not stop. If the mother’s nutrition affects anything, it is, first of all, her own health. What stimulates breast milk production? It turns out that they are hormones, the production of which is especially activated when the baby suckles, stimulating the nipples. The nutritional value of milk - that is, its quality indicators - completely depends on the state of the woman’s body, her health, and hormonal levels. Culinary preferences have absolutely nothing to do with it.
The quality and quantity of breast milk is influenced, among other things, by the timing of lactation (it is known that in the first two to three days after birth, highly nutritious colostrum is produced, then transitional milk, and only then mature milk), as well as the state of the microflora and the functions of food digestion in the body nursing mother. We will talk about the last factor in more detail today.
How to help the body recover
“Previously, there was an opinion that if you have a rotavirus infection, you should not consume dairy products,” says Elena Kolganova. — Now scientists have revised their opinion on this matter: if a child is breastfed or formula-fed, then nothing needs to be changed. For adult children, it is advisable to remove fresh fruits and vegetables, as they enhance peristalsis and fermentation processes in the intestines.”
If a child has a temperature above 38.5 ºС, you can give him antipyretics, and in case of severe pain - antispasmodics. You should not give painkillers - this will mask the symptoms and it will be difficult for the doctor to make a diagnosis. You should not rinse your child’s stomach - this will increase vomiting and lead to extreme dehydration - loss of consciousness, convulsions.
“Treatment of uncomplicated rotavirus infection is symptomatic: the main thing is to drink plenty of fluids. Vomiting and loose stools usually go away on their own. However, taking probiotics can speed up the recovery process; their administration is safe and quite effective,” says Daria Zakharova.
It is always easier to prevent a disease than to treat it - observe the rules of personal hygiene and teach your children to do the same, wash fruits and vegetables and do not drink tap water.
Microflora is disrupted - lactation suffers
A woman’s culinary preferences, as we said above, really have nothing to do with the nutritional value of breast milk. However, its quality indicators can be seriously affected by the state of the gastrointestinal tract of a nursing mother: how well food is digested and absorbed, whether she has gastrointestinal diseases and whether she suffers from dysbiosis . Serious microflora disturbances occur as a result of a variety of ailments, the treatment of which requires the use of antibacterial drugs. The same often occurs directly in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - for example, ulcers, colitis and others. And, of course, a woman’s nutrition - this factor has a constant impact on the state of the microflora. Insufficient content of prebiotics (fiber) and an excess of refined foods and clearly harmful substances (chemical additives) lead to catastrophic delayed consequences.
Let us briefly recall that the natural microbial flora of the intestine is a collection of a wide variety of microorganisms. It is estimated that there are from several hundred thousand to one million microbes per milligram of intestinal contents. The vast majority of colon bacteria—approximately 90%—are bifidobacteria . The rest are lactic acid bacteria (lactobacillus), E. coli and others. These microorganisms are beneficial and actively participate in the processes of digestion, production of vitamins, and also suppress the development of so-called opportunistic microflora, that is, pathogenic bacteria. All this is very important for maintaining the health of every person, including nursing mothers. Judge for yourself: if the intestines and the beneficial protozoa contained in them function “like a clock,” then the process of producing breast milk occurs according to all the laws of nature: it is fully saturated with all necessary nutrients.
However, a completely different picture is observed in nursing mothers suffering from dysbacteriosis. With this diagnosis, the “balance of power” in the intestinal tract changes radically. The first violin is no longer played by bifidobacteria and lactobacilli , but by the same opportunistic microflora that produces toxins. As a result, the processes of absorption of nutrients are disrupted - there are few useful ones, but there is an excess of harmful ones. Digestion itself is also upset, dyspepsia occurs, and the synthesis of vitamins decreases. Ultimately, local inflammatory reactions are observed, the body’s defenses (immunity) weaken, against which various infections are possible. And most importantly, since today we are talking about the relationship between the state of the microflora and breastfeeding : with such an obvious imbalance of the microflora, the absorption of beneficial substances is disrupted or even reduced to a catastrophic level, and harmful substances are increased. All this is fraught with problems not only for the health of the nursing mother, but also for her newborn child. Because harmful substances get into the milk that the baby eats. And it turns out that his diet begins to contain unsafe toxins and carcinogens that can cause irreparable harm to his just-forming body.
Decreased wall immunity. How to fight?
Why is it that dysbiosis disrupts or significantly decreases the absorption of beneficial substances, while potentially dangerous substances, on the contrary, increase? The reason is a decrease or complete absence of parietal immunity in the intestine. To restore it to its previous level, a nursing mother needs to completely reconsider her diet, consuming more healthy foods: protein and lactic acid products, fruits, vegetables, etc. However, in a number of advanced cases this is clearly not enough and experts prescribe special preparations - probiotics containing live cultures of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. They are produced by manufacturers in dry (lyophilized) and liquid form. Normoflorins are the most famous in our country and neighboring countries . Why, you ask? The fact is that during the production of liquid probiotics there is no loss and weakening of the active properties of beneficial microorganisms, while during drying these processes take place. For this reason, the effect of using dry probiotics does not appear immediately. Plus, it is less pronounced and short-lasting. , experts recommend liquid forms of probiotics for women suffering from dysbiosis during lactation Thanks to their rapid action, the balance of intestinal microflora and, accordingly, all digestive functions are just as quickly restored, including one of the most important - the absorption of all useful components of food.
Back to list Previous article Next article
First aid
Regardless of the cause of diarrhea in a nursing mother, treatment should begin immediately. This will be emergency first aid before seeing a doctor. The first thing a nursing mother should do after giving birth is to exclude from her diet all fatty, spicy, salty and pickled foods, as well as sweets, desserts, milk and fermented milk products. In this condition, she needs a strict diet. Then you need to start taking enterosorbents, you can use activated carbon and Enterosgel, and you need to do this right away.
It should be remembered that the main danger of diarrhea of any etiology is dehydration. Once excreted in the stool, it is significantly diluted with water from the small intestine. Therefore, it is recommended that a nursing mother try to ensure a normal drinking regime. The best solution is to use pharmaceutical rehydration solutions like Regidron etc. You can make your own using warm water, baking soda, sugar and salt. These solutions also restore the salt balance in the body and help to quickly recover from diarrhea, which needs to be treated as soon as possible.
Activated carbon is a sorbent recommended for diarrhea (after cleansing the stomach).
Food poisoning is a common cause of diarrhea in nursing mothers. The algorithm for what to do before the doctor arrives to tell you specifically how to treat diarrhea should be as follows:
- Rinse the stomach with a weak solution of manganese or plain boiled water.
- Try to ensure bed rest, leaving the baby with the family.
- Drink as much water or rehydration solution as possible (ideally at least 1.5 liters per day).
- Avoid food for 12 hours and eat only breadcrumbs and black tea to satisfy your hunger.
- Take activated charcoal or another approved sorbent while breastfeeding.
Diarrhea during breastfeeding, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fever and other unpleasant symptoms, should consult a doctor immediately. Regardless of whether you plan to take medications that are prohibited or simply undesirable during lactation, this is strictly prohibited. They can negatively affect the child.