What it is?
A frozen pregnancy is a pregnancy that initially complied with all medical standards, but at a certain period suddenly stopped developing. The cessation of progress in the development of the fetus leads to its death, but it remains in the uterine cavity. For this reason, this pathology is called a failed miscarriage.
In fact, at the very beginning everything happens, as in a normal pregnancy - the egg is fertilized, enters the uterus and is implanted for further development, but at one moment it stops. This pathology also includes “empty ovum” syndrome. It represents the development of membranes in which there is no embryo. With this syndrome, a pregnancy test is positive, as well as an hCG test.
What are the developmental anomalies of the fertilized egg?
Problems with the fertilized egg can arise on the way to the uterus. If the speed of movement of an egg through the fallopian tubes is too high, then its membranes do not have time to fully mature and such an egg is not able to attach to the wall of the uterus. Then a miscarriage occurs.
The fertilized egg may attach low. When the egg is low, there is no particular threat to either the fetus or the mother, but in this case, cervical pregnancy often develops. But with a cervical pregnancy, you should hurry up and terminate it, since there is already a direct threat to the mother: in the future you will have to perform a hysterectomy, that is, remove the uterus.
A false ovum can be detected during an ectopic pregnancy. There is no embryo in this egg; there is only an accumulation of glandular secretion from the fallopian tubes or blood. If a specialist does not see the embryo in the first or second week, then there is nothing to worry about - it should not be visible there. And if there is a truly false fertilized egg, it makes no sense to continue the pregnancy.
Quite often, during echoscopy, a fertilized egg is detected that is deformed. What is the reason for the deformation? This defect develops with increased tone of the uterus, and there are plenty of reasons for hypertonicity: stress, infections of the woman’s genital organs, imbalance of sex hormones.
A small fertilized egg can be a diagnostic sign of a frozen pregnancy. However, it should be borne in mind that this anomaly is determined taking into account the relationship between the size of the egg and the gestational age, so you need to be sure that the exact period is determined correctly.
Sometimes a specialist sees during an ultrasound session that the fertilized egg is larger than the embryo. This may indicate a frozen pregnancy. BUT in this case, you should also keep in mind that the gestational age may not be accurate, the egg simply did not have time to grow and is not visible on the device now. In this case, it is advisable to repeat the echoscopy in the seventh week.
Normally, the fertilized egg has a round shape. An elongated ovum indicates a possible loss of the embryo, that is, a frozen pregnancy. In this case, too, you should not rush to have an abortion. If the contraction of the embryonic heart is visible, it is worth observing the dynamics of its further development. Of course, echoscopy will have to be done repeatedly and quite often.
Dangerous timing: when can it happen?
Fetal development can stop at any time up to 28 weeks (in rare cases, cessation of development can occur later), but the greatest likelihood of such a pathology occurs in the first trimester. There are also several periods with the highest risks of frozen pregnancy, these include the following periods:
- 3-4 weeks;
- 8-10 week;
- 16-18 weeks.
It is these periods that most often become critical for pregnancy.
Causes of missed abortion?
Even doctors are not always able to find out with certainty why a frozen pregnancy occurred. In modern medicine, there are a number of reasons that can cause this pathology. They are all divided into several large groups:
- Genetic pathologies. It is these reasons that most often provoke the arrest of fetal development. Pathological genes or the presence of an extra chromosome in the embryo can cause the development of many defects that are incompatible with life, which leads to termination of pregnancy. Often genetic pathologies cause pregnancy to stop developing in the eighth to tenth week.
- Infections. A frozen pregnancy can also often occur due to the presence of infectious diseases, since during the period of bearing a child, a woman experiences a fairly serious decline in immune defense. TORCH infections, which include rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes and toxoplasmosis, are considered especially dangerous during this period. The greatest danger to the fetus is the mother’s first “meeting” with the infection while she is already pregnant. Therefore, when registering, pregnant women are strongly recommended to undergo screening for these types of infections. Even seemingly simple and common diseases such as influenza or ARVI can cause pathology, especially in the early stages, when vital organs are forming in the fetus. The infection can affect the fetus directly, causing various types of abnormalities, or it can affect the membranes, resulting in a significant lack of oxygen or nutrients to the fetus.
- Hormonal disorders. Hormonal balance is extremely important for normal childbearing. Therefore, with a lack of progesterone or an excess of male hormones (androgens), the likelihood of miscarriage significantly increases. It is recommended to treat any hormonal imbalances before pregnancy.
- Antiphospholipid syndrome. Because of them, the formation of placental vessels may decrease or become blocked, which leads to disruption of the fetus receiving the necessary nutrition.
- Teratozoospermia. This cause of missed pregnancy is associated with pathologies in the man’s seminal fluid. With teratozoospermia, sperm have an abnormal structure, so fertilization with such a cell leads to abnormal development of the embryo.
- Lifestyle. The presence of bad habits, as well as lifestyle during pregnancy (and the planning period) can also negatively affect the development of the embryo, causing it to die. Drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking, stress, occupational hazards, daily routine, sedentary lifestyle, unbalanced diet - all these are considered negative factors for pregnancy.
- Other factors. Fading of pregnancy can also occur due to a sharp change in climate or a history of abortions (especially if there were several of them).
In some cases, several reasons may be detected at once that could lead to the miscarriage of pregnancy.
Vacuum aspiration of the ovum
To terminate pregnancy in the early stages, up to five weeks, and obtain material from the uterine cavity, vacuum aspiration of the fertilized egg is performed. There are the following indications for its implementation:
- pathological development or fading of pregnancy,
- the presence of contraindications to continuing pregnancy,
- termination of pregnancy at the request of the woman if menstruation is delayed for no more than 21 days,
- after a previous abortion if there are remains of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity,
- for the purpose of myometrial biopsy,
- accumulation of blood or fluid in the uterine cavity,
- abortion is involuntary.
Either minimal manual vacuum aspiration or machine aspiration is used.
This procedure is not considered an operation; it is performed using local anesthesia or under general anesthesia. It lasts about five minutes and results in significantly less blood loss. After vacuum aspiration of the fertilized egg, an echoscopy of the uterus should be performed to make sure that there is no fertilized egg left in its cavity. If an ultrasound reveals remains of the fertilized egg in the uterus, then curettage will be performed.
Pathology of the ovum can only be detected during echoscopy. However, one should not make a diagnosis or make a decision to terminate a pregnancy based solely on ultrasound results. Only echoscopic observation of a pregnant woman over time and comparison of ultrasound data with the results of other studies will help the doctor make the correct diagnosis and choose reasonable pregnancy management tactics.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of a frozen pregnancy are the same in any trimester. The main signs that may indicate such a pathology are:
- vaginal discharge with blood;
- general weakness, chills, increased body temperature;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- cessation of swelling and soreness of the mammary glands;
- sudden disappearance of toxicosis manifestations;
- absence of fetal movements (with pathology in the second trimester).
Despite the existence of characteristic symptoms of the pathology, often the cessation of fetal development goes unnoticed, since the basal temperature can remain within 37 degrees, and the hCG level remains high for several more weeks. In this case, the woman learns about the problem only at her next doctor’s appointment or routine ultrasound.
Basics of ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy
SonoAce Ultrasound Magazine
Contains current clinical information on ultrasonography and is aimed at ultrasound doctors, published since 1996.
Introduction
Despite its high cost and unknown complications, the use of ultrasound in obstetrics is justified for the following reasons: (a) At least 50% of those women who confidently state that they know their pregnancy dates are off by at least two weeks, and the timing the onset of labor can be critical for the survival of the child, (b) 90% of fetal anomalies occur without a family history. Even with a clinically normal pregnancy, gross fetal anomalies can occur. It is rare that obvious risk factors can be found in expectant mothers. (c) Neither clinical examination nor heredity provide reliable information about multiple pregnancies. (d) In a significant number of cases with low-lying placenta, there are no symptoms until bleeding begins.
Indications for ultrasound in the first trimester
The main indications for ultrasound in the first trimester of pregnancy are doubts about the gestational age, lack of sufficient clinical data on the normal course of pregnancy. When conducting research, the following approaches can be used:
- Assessment and registration of the condition of the fetal sac and embryo (confirmation of the presence of pregnancy), accurate determination of the gestational age and location - uterine or ectopic pregnancy. The fetal sac is a cavity ring-shaped formation corresponding to the chorionic cavity, and occupies the bottom or middle part of the uterine cavity. Its border is a wide ring of echo signals (trophoblastic ring). An eccentrically located fetal sac indicates the presence of a bicornuate uterus, pregnancy in a rudimentary uterine horn, or an impending miscarriage. The shape of the membranes depends on the degree of filling of the mother's bladder. In addition, it is necessary to exclude hydatidiform mole, pseudopregnancy due to mass formations of the pelvic organs or hormonally active ovarian tumors.
- Real-time confirmation of embryonic cardiac activity (amplification may be required to detect weak pulsations).
- Confirmation of multiple pregnancy.
- Detection of space-occupying formations of the uterus and appendages (it is necessary to exclude the presence of fibroids and ovarian tumors, which may interfere with the normal course of pregnancy or childbirth).
Fetal biometry in early pregnancy
Transabdominal ultrasound
Table 1.
Fetal biometry by week (early pregnancy).
| Fetal biometrics | weeks |
| Fetal sac | 3-5 |
| Placenta | 4-5 |
| Cardiac activity | 5-7 |
| Embryo and yolk sac | — |
| Detection of the double decidual sac | 5 |
| Double bubble symptom | 6-7 |
| Head | 9 |
| Ventricles | 11 |
The first sign of intrauterine pregnancy is the presence of a fetal sac; its internal diameter of 5 mm corresponds to the period of 5 weeks of pregnancy by menstruation. A rupture of the trophoblastic ring indicates a pathology during pregnancy. Implantation hemorrhage separates the layers of the decidua capsularis and decidua vera. It appears as a triangular anechoic zone on the outside of the amniotic sac, along the fundus or internal borders of the membranes. Hemorrhage occurs in half of all pregnancies and in most of them the hematoma resolves by 15 weeks. The chorionic cavity becomes the amniotic cavity after the fusion of the amnion and chorion. This can be simulated by an empty amniotic sac during twins or a hematoma behind the membranes.
The yolk sac, which is the earliest source of hematopoiesis, appears as a closed ring or two parallel lines floating inside the chorionic cavity. By seven weeks it is 4-5 mm in size and disappears by 11 weeks - the period during which congenital anomalies can occur.
Transvaginal ultrasound
Transvaginal ultrasound makes it possible to establish the indicated signs (Table 1) 1 week earlier, since in this case high-frequency sensors are used to visualize the pelvic organs.
Table 2:
Fetal biometry - the probability of detecting the chorionic cavity, yolk sac, embryo.
Scheme:
Fetal biometry in early pregnancy. YM - yolk sac, PM - fetal sac.
Notes
- Thickening of the choriodecidua by 4 weeks is the first ultrasound sign of intrauterine pregnancy.
- The double vesicle phenomenon is formed by the amniotic sac-embryo-yolk sac complex.
- A distinct pulsation near the yolk sac may appear even before the embryo becomes visible.
Pathology
Bleeding with or without uterine hypertonicity may be associated with miscarriage, cervical erosion, polyp, ectopic pregnancy, or hydatidiform mole.
Spontaneous miscarriage
- termination of pregnancy, regardless of the reason, before 20 weeks. It occurs in 10% of pregnancies, most often between 5 and 12 weeks.
Threatened miscarriage
— signs are the detection during repeated studies of a decrease in the motor activity of the embryo, slowing of cardiovascular pulsations, small sizes of the fetal sac compared to the size of the embryo, uneven contours of the fetal sac and an area of retrochorionic hemorrhage.
Inevitable miscarriage
is established in the presence of premature rupture of the membranes due to dilatation of the cervix. Various patterns may be identified: a normal gestational sac, separation of the membranes from the uterine wall, an atypical position of the membranes, the appearance of a liquid-liquid interface, which indicates bleeding into the cavity of the gestational sac, cervical dilatation, or the location of the ovum in the cervix or vagina.
Incomplete miscarriage.
Its signs are an empty or ill-defined amniotic sac, an enlarged uterus, and the presence of an undifferentiated, highly echogenic mass in the cavity.
Accomplished miscarriage.
The uterus is enlarged, without signs of the presence of a fetal sac, embryo or placenta in its cavity; pronounced central echo signals may be due to a decidual reaction. The use of ultrasound can help avoid surgery.
Destruction of the fertilized egg.
In this condition, there is no embryo in the fetal sac. A repeat study is required up to 7 weeks. The sac appears disproportionately small or large compared to the size of the uterus. The membranes are poorly defined or irregularly shaped. The yolk sac symptom has diagnostic value in the destruction of the fertilized egg. In 50% of cases, chromosomal abnormalities are observed.
Failed miscarriage.
In this case, the embryo is retained in the uterine cavity after its death. Sometimes it is difficult to visualize a dead embryo due to inflammation of the chorionic villi, which leads to hydropic changes in the placenta. The embryo may be small, swollen, or deformed due to maceration.
Ectopic pregnancy
occurs when a blastocyst implants outside the uterine cavity, in 90% of cases - in the fallopian tube (ampulla or isthmus). Other possible sites are the abdomen, ovary, or cervix. Predisposing factors for the development of ectopic pregnancy include inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs, the use of intrauterine contraceptives, surgical interventions on the abdominal organs, pelvis or fallopian tubes, and infertility. Clinical symptoms: absence of regular menstruation, positive pregnancy test, abdominal pain, bleeding from the vagina, detection of a mass formation in the appendage area, human chorionic gonadotropin more than 6500 mTU/ml and the hCG level does not double every few days. Before making a final diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy, it is important to ensure that there is no fetal sac in the uterine cavity, since in 1:30,000 cases a combination of intrauterine and ectopic pregnancy is possible.
With an ectopic sac, false membranes may be found in the uterine cavity. False membranes are easily distinguished by their central location in the uterine cavity, the absence of a double ring and signs of the presence of an embryo in the membranes. Rupture during an ectopic pregnancy leads to hemoperitoneum. Early ultrasound diagnosis allows surgical removal of an ectopically located embryo in a short time before life-threatening complications arise.
If the fetal sac is centrally positioned, pregnancy is possible in one of the horns of a bicornuate uterus. An abdominal ectopic pregnancy is possible if the sac or embryo is visualized outside the uterine body. Implantation occurs on the intestine or omentum. Retroversion and abnormal development of the uterus should be excluded. Volumetric formations of a mixed structure can be visible during ovarian or cervical pregnancy. With chronic rupture of the fetal sac in the pelvic cavity, dense masses may be detected due to the organization of blood clots in the hematoma. In ectopic pregnancy, the differential diagnosis is made with a corpus luteum cyst, endometriotic cyst, hydropyosalpinx and loops of the small intestine.
Rice. 1.
Pregnancy in a bicornuate uterus.
Rice. 2.
Fetal sac with yolk sac. There is no fetal pole.
Summary of changes on ultrasound
- An echo-free uterine cavity and the absence of an intrauterine sac do not exclude the presence of a normal intrauterine pregnancy at a very early stage.
- False membranes.
- Uterine adnexa: the presence of a living ectopic embryo, ectopic membranes with or without a yolk sac, or a dead embryo, mass formation of the adnexa, as well as the absence of any data from the adnexa.
- Fallopian tube rings: a dense rim with a hypoechoic center - the fallopian tubes are dilated, spindle-shaped, and contain echogenic fluid (blood).
- Cul-de-sac (shells): no fluid, small to moderate amount of fluid, no echogenic fluid.
Embryo death
Based on clinical data, embryonic death is often difficult to determine, so ultrasound confirmation is necessary. In order to make a reliable guess, it is necessary to use the following criteria: altered membranes, the absence of an embryo when the size of the fetal egg is more than 16 mm in diameter, or the absence of a yolk sac when the membranes are more than 8 mm in diameter (when performing a transabdominal ultrasound: 25 mm - without an embryo and 20 mm - without yolk sac); mild decidual reaction; uneven contours, low location or absence of the double decidual sac.
Ultrasound picture in the early stages: the yolk sac and embryo are absent - an empty fetal sac, with dynamic observation - there is no enlargement of the membranes, no fetal pole is formed. Beginning - mid-first trimester - absence of fetal heartbeat, shriveled amniotic sac or yolk sac.
Trophoblastic disease
Bubble skid:
complete (classic) - vesicular degeneration of placental villi, trophoblastic hyperplasia, absence of a normal embryo; partial hydatidiform mole - there is a slow change in the functioning capillaries of the villi, which affects only some of the villi associated with the changed embryo or fetal membranes.
Invasive mole
- invasion occurs by direct spread or through the veins - the source of dysplasia is located outside the uterus.
Choriocarcinoma
- proceeds very aggressively.
Trophoblastic tumor of the placenta
- very malignant, originates from the intermediate cells of the placental site.
Ultrasound picture: an enlarged uterus is filled with a group of echo-dense vesicles, increased echogenicity is associated with hemorrhages into the cavity of the vesicles, in the depths of the myometrium there is a distinct area with a hypoechoic center and a dense rim of invasion.
Conclusions and practical advice
- It is necessary to examine the fetal sac: position, size and shape to exclude normal intrauterine pregnancy; document the presence of a trophoblastic ring. Check the contents of the membranes and determine the position of the yolk sac.
- Assess the integrity of the meninges and myometrium to exclude bleeding and identify the fetal pole and heartbeats.
- Perform an adnexal examination to rule out polycystic ovarian disease.
- Conduct dynamic studies at critical times, as well as when detecting deviations from the norm in the first trimester.
Ultrasound is mandatory and indispensable in the diagnosis and management of women in early pregnancy.
Literature
- Hagan-Ansert SL. Textbook of Diagnostic Ultrasonography, New Dehli, BE Publications, 1989, pp. 106-440.
- Palmer PES. Manual of Diagnostic Ultrasound, Geneva, WHO, 1995, pp. 221-245.
- Carter]. An Atlas of TVS, Philadelphia, J. B. Lippincott.
- Sutton D. Textbook of Radiology & Medical imaging, London, Churchill Livingstone, 1992, pp. 1175-1183.
- Robinson HP. The use of Diagnostic Ultrasound in Obstetric Practice, RACOG Bulletin.
SonoAce Ultrasound Magazine
Contains current clinical information on ultrasonography and is aimed at ultrasound doctors, published since 1996.
How to recover after a frozen pregnancy?
If such a pathology occurs, it is imperative to remove the dead embryo from the uterine cavity, if this does not happen naturally. To do this, a cleaning is carried out, with the help of which all particles of the membranes are removed from the uterus. Both curettage and vacuum can be used. If freezing occurs in a very early stage, doctors may suggest a medical abortion, which is somewhat more gentle for the woman, including psychologically.
Doctors recommend abstaining from another pregnancy for six months (as recommended by the World Health Organization). This time is enough for the body to recover after the incident. Therefore, during this time, women are recommended to take oral contraceptives, which minimize the likelihood of conception and also help normalize hormonal levels.
During recovery, it is also recommended to lead the healthiest and most active lifestyle possible, take care of a balanced diet and take vitamin complexes. A woman definitely needs psychological support, and if she suffered a particularly difficult incident, she may need the help of specialists - a psychologist or psychiatrist. This will help you get back to normal and prepare for your next pregnancy.
When does the fertilized egg appear?
After the sperm penetrates into the egg in the abdominal cavity, they merge and form a fertilized egg. Initially, it is a group of cells that move towards the uterus and continue to divide along the way. They travel this path in ten days and by the time the egg reaches the uterus, there are 32 of them! Then the elements of the fertilized egg are formed: membranes, placenta and umbilical cord. It is covered with an upper layer called the chorion, with the help of which it feeds on life-giving substances and receives oxygen and is attached to the wall of the uterus. Of course, the main element of the fertilized egg is the embryo. In the last weeks of pregnancy, the fertilized egg weighs about five kilograms and completely fills the uterine cavity.
What tests should I take after?
Before becoming pregnant after a frozen pregnancy, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of a recurrence of what happened. Treatment must be appropriate to the problem that caused the pathology. Therefore, it is extremely important to undergo a full examination, which will help determine the reason for the fading of fetal development. Based on the results of the examination, doctors prescribe treatment in accordance with the detected diseases.
It is recommended to undergo examination after the woman’s menstrual cycle has returned (usually this takes about 30 days after cleansing). But both spouses should get tested. A full examination includes:
- genetic examination of spouses;
- tests for TORCH infections;
- study of hormonal levels;
- blood coagulogram;
- Gynecological ultrasound;
- spermogram;
- immunogram.
Such an examination is usually sufficient to determine the causes of frozen pregnancy both in the early and late stages. The attending physician may prescribe additional tests if necessary. All these examinations can be completed at the IVF and infertility treatment clinic of Academician V.I. Grishchenko.
A frozen pregnancy is not a death sentence - in 90% of cases, after the occurrence of such a pathology, spouses in the near future become happy parents of healthy babies. The main thing is to undergo a full examination and eliminate the cause of the pathology. And if necessary, you can undergo the procedure of artificial insemination (IVF).
Answers to frequently asked and discussed questions on the forums:
✅ Can an ultrasound mistakenly show a frozen pregnancy?
An erroneous diagnosis of “non-developing pregnancy” occurs in the early stages. In our clinic, in order to avoid such mistakes, ultrasounds at 5-6 weeks are performed by at least two specialists. If there are no clear criteria for a non-developing pregnancy, then the patient is recommended to undergo a repeat examination after 3-7 days. And on repeated examination it may turn out that the frozen pregnancy turned out to be normal.
✅ Is it possible to do without cleaning during a frozen pregnancy?
If a frozen pregnancy tends to resolve itself, then it can come out on its own, and then curettage (cleaning) is not required. As soon as the discharge ends, it is necessary to check with an ultrasound that there are no elements of the fertilized egg left in the uterine cavity. If the pregnancy has frozen early and there are no signs that it is going to resolve itself, i.e. there is no bleeding, then it is advisable to do a curettage.
✅ Frozen pregnancy - cleaning or pills?
Medical methods of abortion are indicated for women who have already had pregnancies in the past and had natural births. But it is more correct to do curettage or vacuum, if time permits. Because sometimes, after medical terminations of pregnancy, you also have to do a curettage, but this time due to complications. Because the contents of the uterine cavity do not always come out completely, and inflammation is added, and this is a big trauma for the uterus and it is better to prevent this. Therefore, it is better to do moderate curettage on time, without severe trauma and without complications, than to do it as a forced measure. And most importantly, the products of curettage can be sent for genetic research to identify the reasons for the fading of fetal development.
✅ Can there be a frozen pregnancy without symptoms?
It happens that the pregnancy stops, and the patient knows absolutely nothing about it, and this is discovered at a later stage, when she is informed that the fertilized egg does not match in size, that the pregnancy stopped earlier, but, unfortunately, this cannot be suspected in advance absolutely impossible. The first signs of an undeveloped pregnancy can appear 2-3 weeks after the incident. This is bloody discharge or nagging pain in the lower abdomen. If you experience these symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor.
✅ How long does it take to have a miscarriage during a frozen pregnancy?
If a woman decides to wait for spontaneous expulsion of an undeveloped pregnancy, what happens?
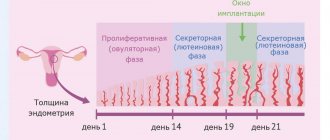
The endometrium tries to reject the frozen fertilized egg, but the inflammatory processes occurring in this endometrium slow down this process, and the process can last from several days to several weeks. Which negatively affects the endometrium and contributes to the development of the inflammatory process of “endometritis”. It happens that the fertilized egg does not come out completely, leaving some part in the uterine cavity, from which a placental polyp is often formed, preventing the onset of a subsequent pregnancy. ONLINE CONSULTATION
Causes of deformation of the ovum
At 10-14 weeks of pregnancy, a woman undergoes an ultrasound examination, which allows the doctor to take measurements of the ovum to determine the exact gestational age. Sometimes during the examination a deformed fertilized egg is discovered. The main cause of this pathology is considered to be an increase in uterine tone.
Why does the uterus become toned? Doctors identify several reasons:
- Psychological. The nervous situation in the family and at work, personal fears associated with the course of pregnancy cause stress in a woman. There is general tension in the body, which also affects the condition of the uterus.
- Infectious. Diseases of an infectious nature provoke an inflammatory process that negatively affects the muscle tissue of the uterus and leads to an increase in its tone.
- Intimate life. Violent sexual intercourse during pregnancy actively affects the reproductive organ, causing it to overstrain.
- Hormonal imbalance. Improper hormone production can lead to endometrial growth. Filling the uterine cavity, it negatively affects the surrounding structures, which is how an irregularly shaped fertilized egg is formed.
- Physical activity. Passion for physical exercise provokes tension in the muscle tissue of the uterus and tones it.
During pregnancy, the uterus has heightened sensitivity to any irritants. Even a simple palpation of the abdomen or a short jog can tone it down. However, these are temporary phenomena and are not considered serious disorders. A cause for concern is the frequent manifestation of increased uterine tone and an elongated outline of the egg. With such signs, the doctor is forced to constantly monitor the condition of the organ and the course of pregnancy.