There are many reasons for this:
- Baby regimen: feeding strictly at a certain time, and not at the request of the child in the first 1-2 months of life, when lactation is established
- Mistakes in attaching a baby to the breast
- Cracked nipples due to improper feeding technique
- Breast injuries
- Sleeping on your stomach
- Physical overexertion
- Anxious state
- Overwork
Despite the common causes of lactostasis, according to statistics, only 3% of women are not capable of full breastfeeding. It follows that the remaining 97% can have productive lactation and feed the baby as much as they decide.
Manifestations of lactostasis
Swelling appears at the site of congestion in the chest. The skin over it turns red and becomes hot to the touch. You can feel the area of compaction under your fingers. The woman experiences discomfort, and often severe pain, and her body temperature rises.
Compresses for lactostasis
Lactostasis is stagnation of milk in the breast. It may be accompanied by soreness and lumps in the mammary gland, local redness of the skin, and in some cases, an increase in body temperature.
The main causes of lactostasis include:
- ineffective breast emptying;
- long breaks between feedings;
- blocked ducts;
- chest injuries and bruises;
- chest compression during sleep;
- wearing tight underwear;
- stress and severe fatigue of the mother.
How to help yourself if there is congestion in the chest?
In order to cope with milk stagnation, it is necessary to ensure good and frequent emptying of the breast, as well as reduce swelling of the breast tissue.
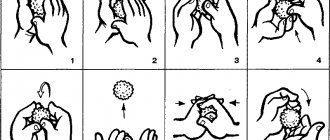
The child will help you cope well with the first task. Place your baby on the affected breast as often as possible. Ensure proper latching to ensure the most efficient emptying of the breast. If feeding is impossible for some reason, or there is no relief in the breast after the baby is attached, it is necessary to express the breast regularly.
You can reduce swelling with lymphatic drainage massage and a properly selected compress.
What compress to make for lactostasis?
You can find a huge number of different recommendations on this issue. Most of them can be divided into several groups:
- Warming compresses.
These include honey and alcohol compresses using camphor oil. They provoke tissue heating, which can further increase swelling in the area of congestion, and components such as honey can also cause an allergic reaction and irritation of the skin of the chest.
- Compresses with unproven effectiveness.
Salt compresses, cakes with cottage cheese, compresses made from chamomile infusion, using onions, beets, soda, aloe have no proven effectiveness, and therefore you should not rely only on their effect.
Please note that no compress should be left under cling film. This leads to tissue heating and increases the risk of increased inflammation.
- Cold compresses.
Of all the types of compresses used for lactostasis, a cold compress is considered the safest and most effective. It is recommended by doctors and lactation consultants. It helps relieve swelling in the area of pain and reduce the development of the inflammatory process. Frozen berries, ice, or a bottle of cold water can serve as a cold compress. Cold can be applied to the chest through a layer of fabric for 10-15 minutes.
Separately, you can consider the common advice about using cabbage leaves as a compress. Despite the fact that this method has no proven effectiveness, many note the positive effect of cabbage on swelling. If you want to use cabbage leaves during lactostasis, wash and cool them, mash them before applying to the breast so that the cabbage releases juice, and keep in the compaction area until the leaf warms up.
It is important to remember that with lactostasis, the whole range of measures is important, including regular effective emptying of the breast and the fight against edema. Compresses can help cope with stagnation, but cannot be the only therapeutic measure.
With proper action, lactostasis goes away within a few days. But if you cannot cope with milk stagnation on your own, immediately seek help from a doctor or a lactation consultant. Take care of yourself and your health!
Natalia Pankova, lactation consultant
Treatment of lactostasis at home
Breast lactostasis in a nursing mother and its treatment at home is an important task, which competent specialists and recommendations will help you cope with:
1. Stimulation of milk flow: putting the baby to the breast at least once every 2 hours, or pumping as often. Little by little, excess milk will be mechanically eliminated, reducing pressure in the mammary gland and alleviating the woman’s condition. You can express yourself manually, or you can purchase an assistant for this purpose - a breast pump.
Types of devices:
- A pump/breast pump with a bulb is the simplest and most affordable device from a financial point of view. However, frequent use can quickly lead to the formation of cracks, so such breast pumps are more likely for one-time use than for regular use. In addition, due to the constant mechanical squeezing of the pump, the hand gets tired quite quickly, without expressing the entire required volume of milk.
- A piston breast pump is a next generation device. He expresses milk and massages the breasts, thereby preventing lactostasis and other troubles. It does not make noise (which is very important if the mother expresses at night or near a sleeping baby) and is very productive, allowing you to collect at least 200 ml of milk in 10 minutes. An electric device allows you to save time first of all. He expresses both breasts at the same time without the slightest physical effort on the part of the woman. The nozzles have an anatomical shape, the breast pump imitates the sucking of a child and prevents the formation of cracked nipples and stagnation of milk.
2. Taking a warm shower or even a bath, especially before feeding. Can be combined with a gentle massage of the breast using circular movements. Or you can grab your breast with your palms, one from below, the other from above, and use gentle, gentle movements to massage the lump towards the nipple.
3. A timely consultation with a competent doctor or lactation specialist is required (to exclude mastitis as the cause of increased temperature, pain and lumpiness in the mammary gland), who will assess the condition of the breast and give recommendations on the correct feeding technique, if treatment is necessary, including selection special ointments allowed during breastfeeding.
4. A time-tested traditional medicine recipe, according to which compresses from lightly beaten cabbage leaves help with lactastasis.
Tiunova Elena
K.M.N., pediatrician of the highest category, nutritionist
“The use of warm (warming) compresses on the mammary gland is not recommended!
Stagnation of milk in nursing women, or lactostasis
5004 10 February
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Milk stagnation: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Lactostasis is a condition of women during lactation associated with stagnation of milk due to a violation of its evacuation from the mammary glands. It is most often diagnosed in primiparous women aged 21 to 35 years in the first weeks and months after childbirth. The mammary glands increase in volume, their lobules become dense. These phenomena lead to swelling, engorgement and soreness of the glands. According to the clinical observations of a number of researchers, skin hyperemia during lactostasis is often associated not with inflammatory phenomena, but with mechanical damage to the skin of the mammary gland with fingers during rough expression. Unfortunately, lactostasis is considered the main reason for refusing breastfeeding.
The consequence of lactostasis in the absence of timely treatment can be an inflammatory disease of the mammary gland - mastitis.
Types of lactostasis
Lactostasis can be unilateral or bilateral. The formation of lactostasis is facilitated by a congenital anomaly with the presence of narrow and tortuous milk ducts in a woman, as well as a history of mastopathy (more common in women over 35 years of age).
The consequence of lactostasis can be non-infectious mastitis - blockage of one or more milk ducts. This blockage causes the formation of a “milk plug” due to irregular or insufficient emptying of the breast or improper attachment of the child, when not all lobules of the mammary gland are in a physiological position, which leads to compression of the milk ducts.
In the absence of proper treatment, chronic blockage of the milk ducts leads to the development of an inflammatory process in the mammary gland - infectious mastitis.
Infectious mastitis has 2 types: parenchymal (when the functional tissue of the mammary gland is affected) and interstitial (the damage extends to the integumentary tissue). The disease is characterized by an increase in body temperature to 39–40°C, redness and a local increase in temperature of the mammary gland, and purulent discharge from the nipples may be observed.
Possible causes of milk stagnation
In the early postpartum period, lactostasis is associated with an inconsistency between the process of milk production and milk output. Until the 7-8th day after birth, the endocrine mechanism of lactation regulation predominates, when in response to a drop in serum progesterone and estrogen after childbirth, the levels of prolactin and oxytocin, which are rightfully considered the “conductors” of lactation, increase. Disruption of the process of milk excretion and the formation of milk stagnation, as a rule, is caused by improper attachment of the baby to the breast, infrequent feedings, cracked and sore nipples, sluggish sucking of the baby or lack of breastfeeding due to the health of the mother or newborn. Under these conditions, the epithelium of the milk ducts is damaged, and the preconditions are created for the development of an infectious process.
A week after birth, the autocrine type of lactation begins, when milk is produced “on demand.” During this period, the cause of lactostasis is technical errors in breastfeeding, leading to ineffective sucking and, accordingly, stagnation of milk or cessation of its secretion.
Correct expression of breast milk is considered a key way to prevent and combat lactostasis and mastitis.
In addition, there are factors that increase the risk of developing milk stagnation. These include:
- flat nipple;
- sagging breasts;
- narrowed milk ducts;
- wearing tight underwear;
- sleeping on your stomach;
- hypothermia of the chest;
- stressful situations.
Which doctors to contact if milk stagnation
In the maternity hospital, a consultation is carried out by a doctor - an obstetrician-gynecologist. If lactostasis develops after discharge, you should contact a gynecologist at your place of residence for further examination and subsequent consultation with a mammologist or gynecologist-endocrinologist. If the development of infectious mastitis is suspected, an immediate consultation with a surgeon is recommended to decide on surgical intervention.
Diagnostics and examinations for lactostasis
- To identify the cause of milk stagnation, diagnosis should begin with an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands.
Lactostasis - symptoms, types.
Clinically, lactostasis in a nursing mother looks like a local bumpy compaction in the mammary gland without redness. It is accompanied by a painful feeling of fullness and a violation of the outflow of milk (breast milk is not released from one or more ducts at all or comes in droplets). The simple form of lactostasis does not produce a temperature reaction.
Since the metabolism in the lactating gland is significantly increased, the inflammatory reaction with continued stagnation of milk develops very quickly. First, swelling occurs, and the tuberosity of the tissue underneath is masked. The stagnant area becomes even and smooth to the touch. Locally, redness may occur and the temperature of the skin above the seal may increase. When the body temperature rises and a flu-like syndrome appears, it can be assumed that lactostasis has turned into mastitis. The rate of inflammation development depends on the health status of the nursing woman. For some it takes 3 days, for others several hours. According to WHO recommendations, lactostasis is given 24 hours to resolve on its own, then you need to consult a doctor.
A rise in temperature is a very important diagnostic sign for lactostasis. Therefore, it is necessary to measure body temperature correctly! Measurements are taken in the armpit on the healthy side or in the elbow bend if the process is bilateral, and best of all with an infrared thermometer in the forehead area.