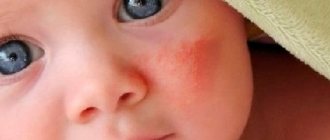
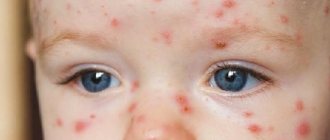
Many parents have encountered such a disease in their children as conjunctivitis. Regardless of the cause, the disease is always accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. It causes discomfort to the child and sometimes causes complications, one of which is visual impairment. Therefore, parents are wondering how to cure conjunctivitis in a child.
But before you begin treatment, you should know the causes of conjunctivitis and what signs are characteristic of different types of the disease.
Causes of conjunctivitis
The outside of a person's eyes is covered by a thin invisible membrane - the conjunctiva. It performs important functions - it protects the eyes from the adverse effects of the environment. The conjunctiva secretes tear fluid, which moistens and lubricates the eyes. In case of contact with mucous membranes
In this article
- Causes of conjunctivitis
- Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in a child
- Treatment of viral conjunctivitis
- Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis in children
- Treatment of conjunctivitis in children 3 years old
- Prevention of conjunctivitis in children
the membrane of bacteria and viruses, the conjunctiva can become inflamed. This process is called conjunctivitis.
According to the etiology of the disease, there are currently three main types of conjunctivitis:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- allergic.
Based on the nature of the disease and pronounced changes in the mucous membrane of the eyes, conjunctivitis is divided into:
- Catarrhal. It is characterized by mucous transparent discharge.
- Purulent. Pus comes out of the eyes.
- Filmy. Thin films are visible on the conjunctiva.
- Follicular. Small pink blisters form on the inner lining of the upper eyelid. They are called follicles.
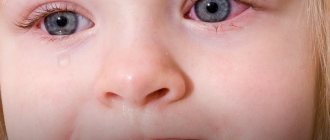
Each type of disease is characterized by certain symptoms, but some types have the same symptoms. Common manifestations are redness and inflammation of the visual organs, possibly active tears and fear of light. In each case, a specific treatment for conjunctivitis is selected. It is impossible to independently determine the type of pathology. The ophthalmologist will make a diagnosis after examination. Conjunctivitis can be treated at home.
Types of conjunctivitis in a month-old baby
The main types of conjunctivitis in infants are:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- allergic.
The difficulty in recognizing conjunctivitis in a child is that the baby is deprived of the opportunity to talk about his feelings. If something is bothering him, parents can only understand it by his behavior. Usually the baby begins to rub his eyes, turn away from the light, and cry for no reason. As the disease progresses, external signs appear. Conjunctivitis will be indicated by redness and swelling of the eyelids, and purulent discharge. During sleep, mucus blinds the eyelids, making it difficult for the child to open his eyes.
As you might guess, bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria, and viral conjunctivitis is caused by viruses. Microorganisms and infectious agents quickly provoke disease, since the immune system of a 1-month-old baby is not able to actively resist infectious attacks.
The most common causative agents of inflammation are the following bacteria: gonococcus, chlamydia, streptococcus, staphylococcus.
This type of conjunctivitis is characterized by purulence from the eyes. Chlamydia and gonococci, which a child can become infected with during childbirth, are very dangerous. They can lead to complete destruction of the cornea and, as a result, loss of vision. Such consequences are unlikely, since parents usually immediately notice the symptoms of the disease and begin treatment.
Viral conjunctivitis in newborns is provoked by pathogens such as adenovirus, herpes virus, enterovirus, etc. But more often, infants catch it from adults with colds. In a baby, conjunctivitis can become one of the concomitant diseases when infected with an acute respiratory virus. ARVI, as is known, is transmitted by airborne droplets, so a newborn is exposed to infection while in the same room with a sick person.
If the cause of conjunctivitis is an allergy, then the first signs appear the very next day after contact with the allergen. Pathology can be caused by children's hygiene products - soap, shampoo, as well as medications. When there are animals in the house, their fur can cause allergies in the newborn.
In infants, internal organs are at the stage of formation, so viruses or bacteria that enter the body can lead to disruption of their functioning.
Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in a child
One of the most common types of conjunctivitis in children is bacterial. This is explained simply. A child learns about the world around him through sensations. Children are drawn to touch objects that are around them. On the street they pick up boxes, candy wrappers and other things from the ground, and then touch their faces with their hands. This way, the mucous membrane gets infected.
A distinctive feature of this type of conjunctivitis is purulent discharge. Typically, symptoms of the disease appear first in one eye, and after a while - in the second. These also include:
- edema;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eye;
- itching, burning;
- fear of bright light.
In different cases, other symptoms may be added to the main symptoms, for example, small pinpoint hemorrhage on the cornea, dry eyes.
Causative agents of conjunctivitis include:
- different types of staphylococci, most often the cause of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus;
- Koch-Wicks wand;
- gonococcus;
- Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- Pneumococcus;
- streptococcus, etc.
Often, parents have no idea how pathogens enter the child’s body. Their spread occurs due to weak immunity, microtraumas, dirt and dust, and foreign objects getting into the eyes. The risk of bacteria entering the mucous membrane increases while wearing contact lenses, but this applies to older children who are allowed to wear contact lenses. Therefore, proper care and hygiene of contact vision correction products are extremely important.
The cause can only be determined in a medical facility. To do this, the doctor will need to take tests, a smear or scraping from the conjunctiva. The procedures are painless and may cause only slight discomfort to the child.
Complex therapy will help to quickly cure conjunctivitis in a child. The main way to combat this type of pathology in children is the use of antibiotics. They are contained in drops and ointments. Only medications prescribed by a doctor should be used in treatment. Self-selection of medications is not allowed. In addition, in addition to the medications themselves, the specialist must prescribe the dosage.
Specialized products for childhood conjunctivitis are not produced. Your ophthalmologist will tell you during your appointment how you can quickly get rid of the first symptoms of bacterial inflammation in your particular case.
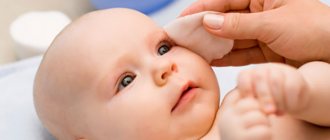
Therapy for an ophthalmological disease does not require hospitalization of the child. After the doctor has made all the necessary appointments, treatment is carried out at home. Before using medications for bacterial conjunctivitis, an eye wash procedure is required.
For these purposes you can use:
- Furacilin solution and other antibacterial and antiseptic pharmaceutical compositions;
- chamomile infusion, calendula, cornflower flowers, diluted aloe juice are also suitable;
- a solution of potassium permanganate, which must be diluted to a pale pink color.
During rinsing, discharge and dried crusts are removed from the child's eyes. After rinsing, you need to apply eye drops. Most often, for the treatment of conjunctivitis in children, doctors prescribe Albucid, Levomycetin, and Vitabact. As a rule, drugs are instilled up to four times a day.
Despite the positive therapeutic effect, children's conjunctivitis is rarely treated with ointments, because most of them have age restrictions. But if the prescription is nevertheless received, the ointments must be stored and applied correctly. As a rule, drugs are kept in the refrigerator. Before use, you need to warm the tube a little in your hands so that the cold product does not cause discomfort to the child. Eyes should be washed with an antibacterial solution. The ointment is placed behind the eyelid. You can use a special stick, or you can do without it. In the second case, you need to make sure that the tip of the tube does not come into contact with your eyes. The product is applied to both eyes, even if symptoms are visible only in one.
If therapy is carried out correctly, in accordance with the doctor’s prescription, then the disease can be defeated after 5-7 days of intensive treatment. When no noticeable improvements are observed after this period, this may mean that the causative agent of the disease has been identified incorrectly or the drugs have been selected incorrectly. In this case, you should undergo a re-examination so that the specialist can adjust the treatment.
Acute bacterial conjunctivitis
Any caring and observant mother can notice the first symptoms of conjunctivitis in a child, but only an ophthalmologist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Today, the most common acute nonspecific catarrhal conjunctivitis, pneumococcal, gonoblennorrhea of newborns, diphtheria conjunctivitis, acute epidemic and diplobacillary conjunctivitis.
These types of conjunctivitis are caused by the following pathogens:
- Staphylococcus aureus and streptococci are the causative agents of acute nonspecific catarrhal conjunctivitis. The first signs of such conjunctivitis in children are eyelashes sticking together after sleep, and the secreted liquid initially has a mucous consistency, but very quickly takes on a purulent appearance. On examination, hyperemia and swelling of the conjunctiva, sclera, transitional folds, and eyelids are noticeable. The mucous membrane becomes swollen, loses transparency, and the pattern of the meibomian glands becomes less noticeable.
- Pneumococcus. Symptoms of pneumococcal conjunctivitis are pronounced and include redness of the mucous membrane of the eyeball (conjunctival injection), in which individual vessels are clearly visible. The transitional fold is swollen; The conjunctiva of the eyelids becomes covered with hemorrhages (hemorrhages) and thin whitish-gray films, under which no bleeding is observed.
- Gonococcus causes gonoblenorrhea in newborns. Infection occurs at the time of birth if the mother is sick with a disease such as gonorrhea. The first signs in newborns appear on the second to fifth day after birth. The symptoms are difficult to miss - the baby’s eyelids become swollen, dense, have a bluish color, and almost do not open. If you press lightly on the eyelid, bloody-purulent fluid flows out from under it. Sometimes the disease initially affects one eye, but if hygiene rules are not followed, it quickly spreads to the other.
- Klebs-Leffler bacillus causes diphtheria conjunctivitis, which affects children from 2 to 10 years old who have not been vaccinated. The diphtheritic form of the disease is the most severe. The first signs of this type of conjunctivitis in children are severe swelling of the eyelids, copious purulent discharge, the appearance of dirty gray films on the entire surface of the conjunctiva, upon separation of which the mucous membrane begins to bleed. With lobar and catarrhal forms, the symptoms are less pronounced. Typically, eye disease is accompanied by damage to the upper respiratory tract.
- Koch-Wicks bacillus causes acute epidemic conjunctivitis. The first symptoms in children are the release of slight mucus, which prevents them from opening their eyes after sleep, then becomes abundant and takes on a purulent appearance. Only a very experienced doctor can determine this type of conjunctivitis, since the symptoms are very similar to diphtheria (appearance of films) and gonoblennorrhea (profuse purulent discharge). The disease may be accompanied by general intoxication of the body.
- Diplobacillus Morax-Axenfeld leads to the appearance of a disease such as diplobacillary (angular) conjunctivitis. The disease is transmitted through contact with an infected person and occurs in a subacute form. Signs of this type of conjunctivitis in children: swelling and hyperemia of the conjunctiva, which is accompanied by hyperemia and swelling of the skin in the corners of the eyes; viscous mucus, which interferes with clear vision, accumulates in the corners of the eyes in the form of waxy crusts.
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis
The type of conjunctivitis caused by a virus is called viral conjunctivitis and is an infectious disease. Its cause is most often adeno- and enteroviruses, transmitted by airborne droplets and household contact, that is, through contact with an infected person and his things. A common cold can trigger viral conjunctivitis. Due to the nature of the disease, sore throat, fever, cough and other signs of ARVI are often added to the general symptoms of eye inflammation. To find out how to treat associated diseases, you should visit your pediatrician.
Compared to bacterial conjunctivitis, with viral conjunctivitis, the baby experiences more severe redness of the eyes and profuse lacrimation. But, as with bacterial, purulent discharge is possible. At first, the symptoms of the disease are visible only in one eye, and after a few hours - in the second.
If there is discharge, the eyes should be rinsed before using the medication. After the procedure, instillation and application of ointments is carried out. In the treatment of viral conjunctivitis, drops are usually used:
- "Aktipol";
- "Oftan";
- "Poludan";
- "Ophthalmoferon" (used even in the treatment of infants).
The ophthalmologist may also prescribe ointments. They are more effective, but many of them cannot be used in the treatment of young children. One of the most common products of this type is Florenal. Acyclovir and Tebrofen are effective in the fight against viral conjunctivitis.
To quickly cure conjunctivitis, it is important to consult a doctor at the first signs of the disease. At the initial stage, it is much easier to fight the disease. In this case, treatment may take only a week.
Increasing the dosage or frequency of use of medications will not contribute to the rapid treatment of the disease, but on the contrary, it can only cause harm.
Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis in children
Unlike the previous two cases, the occurrence of allergic conjunctivitis is difficult to predict. This type of pathology is characterized by a sudden appearance and acute symptoms. Allergic conjunctivitis is characterized by profuse lacrimation, itching and burning, pain and dryness, a feeling of “sand” in the eyes, and fear of light. All symptoms appear immediately in both eyes.
As experts have established, in children the disease is most often caused by a genetic predisposition. Older children suffer from allergic conjunctivitis due to the body's increased sensitivity to various substances. Eye inflammation is often caused by well-known allergens such as dust, pollen, certain foods, chemicals in household cleaning products, animal dander, etc.
The first point in the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis is the elimination of the allergen that caused the disease. Antihistamine drops are used as prescribed by a doctor. In more complex cases, medications are prescribed in tablets.
Cool compresses applied to inflamed eyelids will help relieve the symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis. For severe dryness, the doctor prescribes so-called “artificial tears” - solutions that moisturize the mucous membrane of the eyes.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in children 3 years old
Mothers of 3-year-old children experience conjunctivitis more often than others. This is due to the fact that at this age the child enters an active phase of growth, he begins to attend kindergarten, and more often comes into contact with various pathogens of conjunctivitis. Therefore, it is important for parents to know how to cure conjunctivitis.
In a 3-year-old child, the disease is usually caused by infections, usually bacteria and, less commonly, viruses. Allergic conjunctivitis is associated with a hyperactive reaction of the body to any compounds or substances. The inflammatory process in the conjunctiva in a 3-year-old child may be associated with congenital pathology, since acquired diseases of this nature are absent at this time.
When a diagnosis of conjunctivitis is made at 3 years of age, antimicrobial drops are prescribed. Sometimes systemic antibiotics are required.
Treatment of the child should be carried out under the supervision of an ophthalmologist. The specialist observes how the baby’s body reacts to a particular drug. Standard treatment includes rinsing with antiseptic solutions, using drops and ointments.
For allergic conjunctivitis, Astemizole, Cetirizine, and Fexofenadine are prescribed. Help fight bacterial diseases: Levomycetin, Tetracycline, Erythromycin. The drugs are available in the form of drops and ointments and contain antibiotics. The specialist will tell you the dosage and frequency of use of medications.
For viral conjunctivitis, Poludan, Ophthalmoferon, and Actipol are often prescribed.
A child can develop conjunctivitis at any age. Treatment of children from birth to one year, from one to three years, from three to five has its own characteristics. Each age group requires an individual selection of drugs, treatment regimens and procedures.
Currently, pharmacy chains offer a large selection of drugs for the treatment of inflammation. There is a great temptation in case of the first symptoms of conjunctivitis in a child to go to the pharmacy and choose the necessary medications. This is strictly forbidden. No one enjoys sitting in line and waiting to see a doctor. However, this is the only way to start treatment correctly and complete it quickly.
How quickly do conjunctivitis symptoms appear in infants?
If the causes of bacterial conjunctivitis are associated with disturbances during the birth process or infection of the mother, then the first symptoms may appear a couple of days later when the baby is infected with a gonococcal infection. In the case when the cause of the disease lies in a chlamydial infection, the disease can be diagnosed 5-10 days after the birth of the baby. This is how long the incubation periods of this ophthalmological disease last.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is often called purulent. Many people confuse it with the viral form of the disease. The difference is that with a bacterial infection, only one eye is affected. For viral conjunctivitis - both, but in turn. The bacterial form is quite severe, which frightens parents when diagnosing their baby. With proper treatment, the disease soon goes away. The risk of complications is minimal.
Prevention of conjunctivitis in children
The article noted that very often conjunctivitis appears due to the penetration of bacteria into the body. Maintaining good hygiene will help you avoid illness. Hands should be washed with soap, especially after going outside. In kindergarten and school, the child should be given a clean towel and warned that he should only use it. When visiting the pool, the child must use special swimming goggles.
Like any disease, conjunctivitis is easier to prevent than to treat. Immunity helps young patients resist viruses and bacteria. It is important to support and strengthen it. This is facilitated by an active lifestyle, sports, physical exercise and walks in the fresh air, and eating a variety of foods.