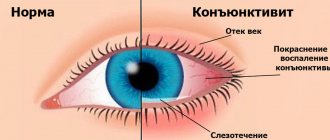
Types of conjunctivitis in children
Conjunctivitis of various etiologies is among the most common ailments in children.
In this article
- Types of conjunctivitis in children
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Bacterial conjunctivitis
- Dacryocystitis
- Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in infants under one year of age
- Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in children
- Prevention of childhood conjunctivitis
The causative agents of the disease spread through household contact and airborne droplets, and infants in the first year of life still have very weak immunity and are not able to sufficiently resist infections. Viral infection can occur when visiting a public place, from parents, while bacteria from dirty hands easily enter the mucous membrane of the eyes. Depending on the cause that caused the development of conjunctivitis in a child under one year old, several types are distinguished.
- Allergic. Eye inflammation develops when the conjunctiva is irritated by various substances. At this age, this most often occurs, for example, when introducing a new type of food. Allergies can also occur to medications, hygiene products, and insect bites.
- Bacterial. The most common type of conjunctivitis in children, which they often become infected with from a sick mother during childbirth (blennorrhea of newborns, chlamydial conjunctivitis), as well as when various microorganisms get into the eyes.
- Viral. It is provoked by various microorganisms, in particular adenoviruses, enteroviruses, etc.
- Dacryocystitis. Occurs due to obstruction of the lacrimal canaliculus. This eye pathology can be treated quite successfully with timely measures taken.
A common symptom for all types of eye inflammation is redness and swelling of the inner lining of the eyelid, but each of them also has its own characteristics. Let's look at the causes and symptoms of various types of conjunctivitis, as well as dacryocystitis in babies under one year old.
Bacterial conjunctivitis in a 7-month-old baby - how to treat it?
The culprits of this type of inflammation are bacteria - staphylococci, gonococci, streptococci, pneumococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other microbes. A child can become infected with gonococcal conjunctivitis from the mother during birth. Signs of this disease appear almost immediately, within a day or two. At 7 months, staphylococcal, streptococcal and pneumococcal conjunctivitis are often diagnosed. They are characterized by the following symptoms:
- severe lacrimation;
- discharge of mucus and pus;
- blepharospasm;
- redness of the eyelids and conjunctiva;
- swelling leading to complete closure of the eyes.
Bacterial infections cause itching, burning and photophobia. The presence of these signs may be indicated by the baby's constant crying. Also, at this age, the child’s temperature rises due to conjunctivitis. There are other symptoms observed with certain types of disease. For example, with pneumococcal inflammation, conjunctival hemorrhages occur. They appear as red dots on the conjunctiva.
Treatment of conjunctivitis of bacterial etiology in a 7-month-old child is carried out using drops and ointments with an antibacterial effect. Antibiotics are used only for severe illness. Moisturizing drops are prescribed to relieve symptoms. Wash the patient's eyes with a solution of Furacilin.
Allergic conjunctivitis
For very young children this phenomenon is quite rare. Typically, allergic inflammation can occur as a reaction to a new product in the diet or to an inappropriate medicine. With an allergy, profuse lacrimation appears, the eyes become red and swollen, the baby begins to worry and rub them. In case of an acute reaction of the body, Quincke's edema, urticaria and other complications may occur. For the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, children under one year of age are prescribed drops that relieve swelling and irritation, for example, Vizin, as well as antihistamines Allergodil, Alezastin, Olopatadine. They help reduce the symptoms of the disease.
Allergic conjunctivitis in 7-month-old children
Eye allergies begin suddenly and develop quickly. The patient experiences uncontrollable lacrimation. This disease also causes unbearable itching. The child will cry and pull his hands to his eyes. First of all, you need to identify the allergen and eliminate contact with it. Symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis are relieved with moisturizing drops based on artificial tears. There are no preservatives in such solutions, so they are suitable even for babies. However, you should not use them without consulting a doctor. You need to make sure that conjunctivitis is a consequence of an allergic reaction and not an infection.
If the disease continues to develop, antihistamines are prescribed. Corticosteroids, which are used to treat very severe inflammation in adults, are not usually prescribed to children at 7 months of age.
Viral conjunctivitis
This disease develops when various viruses enter the body:
- adenoviruses;
- herpes simplex viruses;
- Coxsackie viruses;
- enteroviruses, etc.
Quite often, conjunctivitis occurs against the background of colds - ARVI and influenza. Viral diseases spread very quickly through airborne droplets. Parents should be especially careful during periods of mass epidemics of these diseases and should not visit public places with their children unless absolutely necessary. Here are the symptoms of conjunctivitis in children under one year old that may indicate this disease:
- redness and swelling of the conjunctiva;
- irritation and itching in the eyes, the baby constantly rubs them and shows anxiety;
- profuse lacrimation;
- negative reaction to light;
- enlarged lymph nodes near the ears.
External signs of viral inflammation are quite similar to the manifestations of allergic conjunctivitis. If such symptoms appear, you should promptly visit a doctor or call him at home. Only after diagnosis will the ophthalmologist be able to find out the true cause of the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment. For the treatment of conjunctivitis in children under one year of age, anti-inflammatory drops and ointments approved for use at this age are prescribed. Independent choice of medications can negatively affect the child’s health.
Causes of conjunctivitis
The main cause of conjunctivitis is the entry of pathogenic microflora (bacteria and viruses) into the child’s body, as well as allergic reactions to external irritants.
The most common form of conjunctivitis diagnosed in children is bacterial. In this case, the disease is provoked by streptococcal, pneumococcal, staphylococcal and diphtheria infections. A newborn baby can get the disease when passing through the birth canal of a mother suffering from infectious diseases (chlamydia, gonorrhea, etc.). In older age, bacterial conjunctivitis most often occurs when the mucous membrane of the eye is injured or the eyelids and eyes are touched with dirty hands.
Viral conjunctivitis, as a rule, does not occur on its own, but develops against the background of a general viral infection - influenza, adenoviral and enteroviral infections, chickenpox, herpes, measles, etc. In this case, the development of conjunctivitis occurs due to the penetration of viruses into the mucous membrane eyes through household contact or airborne droplets.
The allergic form of the disease occurs when a child is allergic to certain irritant substances. As a rule, the disease is combined with other manifestations of an allergic reaction - allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, etc. Most often, an allergic reaction is caused by pollen, animal dander, house dust, medications, cosmetics, cleaning products and detergents.
Bacterial conjunctivitis
It develops when pathogenic bacteria enter the body: gonococci, staphylococci, chlamydia, etc. The main symptom of bacterial conjunctivitis is purulent discharge from the eyes, while with allergic and viral inflammation it is clear or mucous. The pus often causes the baby's eyelashes to stick together, especially after sleep. With some forms of bacterial infection, such as chlamydia, the lymph nodes may become enlarged. If you do not promptly treat bacterial conjunctivitis in a child, it can become chronic, and then it will take a lot of time for a complete recovery. In addition, untimely treatment can lead to severe ulceration of the cornea and even loss of vision. To eliminate the symptoms of purulent inflammation, drops and ointments with antibiotics are used - they are prescribed by a doctor in accordance with the age of the child. In addition, it is necessary to wash the eyes several times a day with some antiseptic solution to mechanically remove the pus.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in a one-month-old baby
The doctor will tell you exactly how to treat conjunctivitis in a one-month-old baby. Only a specialist can recommend medications for the treatment of conjunctivitis in a one-month-old baby. After examination by an ophthalmologist and receiving prescriptions, therapy is carried out at home. With the exception of difficult cases when hospitalization of a small patient is required.
Treatment of bacterial and viral conjunctivitis begins with rinsing. You can wipe your baby’s eyes with boiled water or pharmaceutical saline solutions. Infusions of various herbs are also suitable. Chamomile flowers are most often used for these purposes. They are poured with boiling water and allowed to brew for 20-30 minutes. After the solution has cooled, it should be filtered so that small particles of grass do not get into the baby’s eye.
During the day, the eyes are washed 4-5 times and always before each use of medications. There are several rules that should be followed during the procedure:
- both eyes are wiped, even if there are symptoms of the disease in only one;
- a separate cotton pad is used for each eye;
- the solution should not be too cold or hot;
- movements are performed from the outer corner to the inner.
Conjunctivitis in a 1-month-old child is treated with drops and ointments, sometimes tablets and injections are used. Local medications are instilled behind the lower eyelid. Ointments are applied in the same way.
The drugs are instilled in accordance with the doctor's recommendations, usually 1-2 drops in each eye 4-5 times a day. Ointments are usually recommended to be applied before bedtime.
Dacryocystitis
A common disease among children in the first year of life. Its signs appear 6-10 days after birth. If treatment is not treated in time, dacryocystitis can progress to the chronic stage. The cause of this eye pathology is the obstruction of tears through the lacrimal canal, which is clogged with pieces of embryonic tissue. Microorganisms accumulate there, and as a result, purulent inflammation of the eyes develops. Based on its external symptoms, dacryocystitis can be confused with bacterial conjunctivitis, but additional means must also be used to eliminate it. Thus, an important point in the treatment of dacryocystitis is massage of the lacrimal sac, located at the inner edge of the palpebral fissure. It is necessary to remove accumulated pus. This massage is best done after feeding the baby during the day. Place your index finger near the inner corner of the eye and move it towards the baby's nose with a slight but gentle force. It is necessary to make approximately 6-10 such movements. In this case, pus should come out of the lacrimal sac - confirmation that the massage is being carried out correctly. After its completion, you need to rinse the eyes with antiseptic solutions, and then introduce antibiotic drops. These procedures need to be repeated for two weeks - usually during this time it is possible to clean the canal; it is important to do this regularly. If massage does not help, mechanical cleaning of the tubule is prescribed.
Treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis in infants under one year of age
For each type of pathology, their own medications are used. To diagnose the causative agent of the disease, the doctor takes a smear from the conjunctival cavity and then determines its sensitivity to various antibiotics. Only after this does he prescribe antibacterial drugs for the eyes.
"Albucid"
The most common eye drops for children of any age, starting from birth, which effectively eliminate the symptoms of the disease. They contain sulfonamide, an active antimicrobial substance. "Albucid" is also used to treat blenorrhea and purulent ulcers.
"Tobrex"
The active ingredient is tobramycin. This is a strong antibiotic that suppresses protein synthesis in the cells of microorganisms, disrupting their active functioning. Copes with most pathogens of bacterial conjunctivitis. Adverse reactions such as allergies and urinary disorders are possible. In case of such phenomena, you should consult a doctor to change the medicine.
"Vigamox"
The active ingredient is moxifloxacin 0.5%, which belongs to the fluoroquinolones and has an extended bactericidal effect. If there is severe discharge of pus, you can use an additional antibacterial ointment, for example, Erythromycin 1%. It has proven its effectiveness in forms of the disease that are difficult to treat (fungal, gonococcal, diphtheria and others). The ointment should be used after administering all the drops three times a day for 7-10 days, after which see a doctor.
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in children
Viral pathology usually develops against the background of ARVI or influenza. and in both eyes at once. Outbreaks of viral conjunctivitis often develop into epidemics. Antiviral drugs are used to eliminate the symptoms of this disease in children.
"Ophthalmoferon"
Their active ingredients are recombinant interferon 2-alpha and diphenhydramine - thus, antiviral and antihistamine effects are achieved simultaneously. For the treatment of children under one year of age, it is advisable to use Oftalmoferon when the first signs of the disease appear.
"Poludan"
A drug that enhances the synthesis of interferon, which significantly reduces the manifestations of viral eye inflammation in children. The main substances in these drops are polyadenylic and polyuridylic acids. The recommended dose for instillation is 1-2 drops three to four times a day. Already on the third day after starting to use Poludan, improvements in the condition are noticeable, irritation, redness of the eyes, and lacrimation disappear.
"Aktipol"
Antiviral drops that produce interferon in the body, which helps to significantly strengthen its own immune defense. The use of this medicine helps eliminate swelling and redness of the conjunctiva, reduce itching and irritation. "Aktipol" also has a keratoprotective effect, promoting the healing of corneal tissue. Since the product is applied topically, the main active ingredient - aminobenzoic acid - is well absorbed, contributing to a rapid therapeutic effect.
Rules for administering drops and ointments
Before starting procedures, you should wash your hands. Before starting the instillation procedure, you need to wash the baby's eyes with antiseptic solutions to remove any remaining pus. These can be weak solutions of boric acid, furatsilin, etc. Take a separate cotton pad for each eye. When administering drops, make sure that the tip of the bottle dispenser does not touch the mucous membrane and skin around the eyes, so as not to spread the infection. Administer exactly the dose of medication prescribed by your doctor. After completing the procedure, you need to blot the area around the eyes with a clean napkin and wash your hands again. Medicinal drops and ointments are effective means for eliminating the symptoms of conjunctivitis in children. They have a local effect without penetration into the bloodstream. The drugs fight pathogens, performing antibacterial and anti-inflammatory functions. With the correct selection of medicine and following the doctor’s recommendations, the disease can be cured in 7-14 days.
Prevention of childhood conjunctivitis
To prevent bacterial conjunctivitis in children under one year of age, a woman should take care of her health even before the baby is born. She needs to undergo a full examination by a gynecologist and cure sexually transmitted infections, if any. This will help protect the newborn from chlamydial conjunctivitis and blenorrhea. After the birth of a baby, special attention must be paid to the sterility of objects and hygiene products used to care for him. Bacterial infections quickly spread through household contact, as germs easily reach mucous membranes from insufficiently clean hands. It will be useful to ventilate the room, walk with the child more often, and perform water procedures, strengthening his immunity. Always keep the room clean and wet-clean surfaces more often to minimize the risk of infections. During periods of epidemic outbreaks of viral diseases, it is better to maintain a home regime, not visiting public places with your child unnecessarily.
What is the danger of conjunctivitis?
Conjunctivitis in babies under one year of age can be successfully cured with timely consultation with a specialist and initiation of therapy. Self-therapy at home is strictly unacceptable. If conjunctivitis is suspected, a small child should be examined by at least two doctors - a pediatrician and then an ophthalmologist.
If symptoms of conjunctivitis appear in children, you should not use advice gleaned from forums on the Internet. The external manifestations of various ophthalmological diseases can be very similar, and only a specialist will be able to determine the true cause after taking the appropriate tests. Successful treatment of conjunctivitis in a child under one year of age depends on following all the specialist’s recommendations. It will be much more difficult to cope with an advanced disease. In addition, inflammation of bacterial or viral etiology can seriously harm the baby’s vision. In general, this visual ailment is not dangerous. With timely medical care, there is no threat to the visual organs.
Complications
If conjunctivitis is not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner in infants, there is a high risk of the disease becoming chronic and causing frequent relapses. With the adenoviral and herpetic nature of inflammation, damage to the deep structures of the eye occurs.
Possible complications:
- scarring of mucosal tissue;
- keratitis;
- corneal clouding;
- hemorrhage in the eyeball;
- atrophy and erosion of the cornea;
- eyelash loss and abnormal growth;
- ulcers;
- decreased visual acuity;
- dry conjunctiva.