No teeth at one year of age
Why does a child’s teeth not grow after a year of life?
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Unsuitable climate.
- Poor quality of food and water.
- Diseases and infections.
- Vitamin and calcium deficiency.
To dispel or confirm suspicions, you need to take your baby for examination to a therapist and dentist. To determine the causes of delayed jaw development, blood tests, urine tests, ultrasound examinations of organs, and testing of thyroid function may be necessary. To exclude edentia (lack of teeth) from the diagnostic field, fluoroscopy is performed.
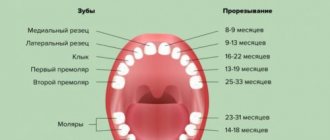
How many teeth should a child have before 1 year of age?
Initial signs of teething, as a rule, appear at six months of age: active salivation, inflammation of the gums, refusal to eat. During this period, the lower incisors begin to break through, which is accompanied by swelling, diathesis, tearfulness, drowsiness, runny nose, cough, fever and even vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. Symptoms disappear 3-7 days after the exacerbation.
Eight- and nine-month-old babies grow up to six teeth. As a rule, the lower incisors are already fully formed, and the upper ones are just beginning to develop. The child learns to chew and bite food independently.
At 10-11 months, as a rule, the incisors of both rows are already formed in the mouth, and adjacent teeth are also breaking through. At this time, after eating food, it is recommended to give the baby water. To avoid caries, you should not accustom him to sweets. Maintain hygiene and cleanliness of the pacifier and spoon from which you feed your baby. If a child’s lower front tooth does not grow at this age, there is no need to panic - experts define this situation as standard and not requiring intervention. To get rid of false suspicions, you can go for a medical examination. Our VTV clinic is always happy to help with any dental problem.
Permanent teeth
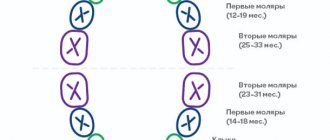
The change in the primary bite begins in children aged 5-6 years. By this time, the roots of baby teeth begin to dissolve and tooth mobility appears.
- At this age (5-6 years), the lower front incisors are the first to be replaced. In parallel with them, at about 6 years of age, the first permanent chewing teeth appear. Often their appearance is not even noticed, since they erupt behind the milk teeth.
- At 6-7 years old, the upper front incisors are replaced
- At 7-9 years of age, the baby teeth will fall out and be replaced by permanent lateral incisors.
- At the age of 9-11 years , the fourth and fifth milk teeth (molars) will be replaced by the 1st and 2nd premolars.
- The last ones, at the age of 11-13 years, will be replaced by permanent teeth - fangs.
- By the age of 12-13, all baby teeth will be replaced by permanent ones and the child’s mouth now has 24 teeth. Oral hygiene often suffers at this age. This is due to adolescence. Carise especially often affects the fissures (grooves) of the sixth teeth - molars. The process happens very quickly and often develops into pulpitis! Therefore, it is important to pay attention to caries prevention. A good way to protect the fragile enamel of permanent teeth is by sealing fissures and maintaining some professional hygiene. and, of course, following some rules.
- At 13-14 years of age, the second molars (seventh teeth) will erupt.
- And already at the age of 18, and sometimes later, wisdom teeth appear.
In order to keep your teeth healthy and straight, we recommend that you come for a preventive examination to the dentist every 6 months and visit the orthodontist at the ages of 6, 12 and 18 years.
Over 1 year old
At one year of age, children, as a rule, already have eight full milk teeth in their mouths. This age limit is the optimal time to visit the dentist. The doctor will evaluate the condition of the oral cavity and help prevent problems.
At the age of 1.5-2 years, a child can have from 4 to 14 teeth. We must begin to accustom him to oral hygiene, showing him how cleaning is done by example. By the age of 2.5 years, children, as a rule, acquire two dozen milk teeth, which serve them until the age of 5-6 years. A visit to the dentist or orthodontist may be necessary if:
- premature development of the jaws, which is facilitated by endocrine dysfunction;
- growth retardation, often caused by rickets, digestive problems, infections and genetic inheritance;
- incorrect position of the incisors, indicating deeper bone disorders.
Until the age of six, the number of teeth remains the same - about 20. At this time, you need to continue to develop in the child a love of oral hygiene, wean him from finger sucking and nail biting.
The first replacement of baby teeth with molars begins at 6-8 years of age. By the age of 14-15, the jaws are completely renewed.
Baby teeth in children
The replacement of baby teeth with permanent teeth in children occurs at the age of 6–7 years. However, there are some deviations from this norm. Let's try to figure out how the change occurs, which teeth are changed and what parents should pay attention to during this process.
A little about anatomy
An interesting fact is that baby teeth begin to form at the earliest stages of gestation. But they usually erupt when the baby reaches six months of age. The question of how many baby teeth children should have is asked by many mothers. Their set differs significantly from the regular ones. For example, if an adult should have 32 teeth, then small children have only 20 milk teeth. Loss begins after the permanent teeth have formed. Basically, this process begins with the lower incisors and takes 6–8 years.
In what order do teeth change?
Over time, the baby grows, and so does his jaw. That is why permanent molars (molars) will appear first - they were absent earlier, because there was simply no room for them.
Next, a complete change of teeth occurs in approximately the same pattern as the growth of baby teeth in children. First of all, the lower incisors sway and fall out painlessly, then the upper ones, after them comes the turn of the premolars (the first pair falls out in children by the age of 10, the second by the age of 12). The last ones to fall out are the fangs; they become loose only by the age of 13. By age 14, a child should already have permanent second molars. After 18 years, third teeth begin to erupt; people call them wisdom teeth.
Many mothers are interested in the question of how many baby teeth fall out in children. They are all completely replaced by permanent ones, that is, 20 teeth must fall out.
How to care and when you may need medical help
If a child complains of severe pain, you note that the gums look inflamed, there is redness, and the enamel is too sensitive - this is a reason to contact a pediatric dentist. In addition, parents should provide the baby with a balanced diet with a sufficient amount of minerals and elements (in particular calcium).
After a tooth falls out, there may be a wound that bleeds (5-10 minutes). To avoid bleeding, you need to make a sterile cotton swab and wrap it with gauze, then give it to your child to bite on. If the bleeding cannot be stopped for a long time, you will have to contact your pediatrician and get tested, as there may be a problem with blood clotting.
Precautionary measures
All teeth require constant care. For example, the enamel of baby teeth is fragile, and if proper monitoring is not carried out, there is a high risk of developing such an unpleasant phenomenon as caries. Then you won’t be able to postpone visiting the doctor. Therefore, the main task of the parent is to choose the correct toothpaste and ensure that the child brushes his teeth regularly.
Many children neglect this action or rush to finish the procedure as quickly as possible. It is necessary to explain to your child that brushing their teeth is a fundamental factor due to which they will be healthy for many years.
When children's baby teeth change, many kids try to loosen them on their own, and especially brave ones even pull them out. Also, the child often touches the cutting tooth with his hands. In these cases, it is necessary to explain to him that performing these actions may ultimately lead to an infection being introduced into the oral cavity, causing the gums to become inflamed. If a growing tooth causes discomfort and pain, a consultation with a dentist is required.
What to do to ensure that your child’s teeth develop normally
Before and during pregnancy:
- Maintain dental health.
- Eat well and varied.
- Eat more foods high in calcium.
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Walk in the fresh air more often to maintain a healthy level of hemoglobin in the blood.
- Treat in strict accordance with medical recommendations.
After childbirth:
- provide the child with a rich and balanced diet;
- monitor the baby’s hygiene;
- walk in the fresh air to harden the child’s body;
- prevent infection and diseases of internal organs;
- Consult a doctor in a timely manner in case of painful syndromes.
If a new tooth does not grow in place of a baby tooth
The loss of baby teeth, as well as their appearance, does not occur simultaneously, but in accordance with the development of the jaws and the growth of permanent replacement. The concept of a protracted renewal is quite relative, because for some the radical will show itself in a week, and for others in a month or two. And in the second case, we are not always talking about deviation.
Often baby teeth are “pushed out” by molars, which almost immediately make their way out, but if a child’s tooth falls out and a new one does not grow and is not visible, you need to wait a few weeks.
Reasons to see a doctor:
- lack of replacement 2-3 months after the loss of a baby tooth;
- swelling and redness of the gums, pain without signs of germination of a molar;
- sequential loss of other teeth without the appearance of new ones.
Reasons why a child’s tooth does not grow for a long time:
- Infectious diseases, including past ones.
- Lack of calcium in the body.
- Oral diseases.
- Mechanical injuries.
A child’s tooth has fallen out and is not growing, but the situation does not correspond to the reasons indicated? Perhaps the delay is provoked by poor ecology, incorrect or poor-quality diet, stressful situations, or even genetic preconditions.
Symptoms of pathology
The main symptom is the presence of teeth beyond the natural set. They can have different positions, shapes and numbers. The process of teething of abnormal teeth is often accompanied by pain, fever, and inflammation of areas of the oral cavity. If measures are not taken in a timely manner, complications may develop:
- redness and swelling at the site of the impacted tooth;
- problems with chewing food and digestion;
- injuries to the mucous tissues of the oral cavity;
- violation of the position of the main teeth (dystopia) and the formation of malocclusion;
- various speech defects - mainly problems with the pronunciation of hissing sounds;
- loosening of adjacent normal teeth;
- deformation of the jaw bones.
In young children and adults, the pathology has its own nuances. They are associated with age-related characteristics of the body and affect the subsequent development of maxillofacial structures. Statistics on the spread of pathology in children and adults:
- 60% of cases are children and adolescents during the period of replacement of milk teeth with permanent ones;
- 35% of cases are adults;
- 5% of cases are small children during the period of growth of baby teeth.
Reference! Supernumerary teeth, as a rule, have a standard structure, sometimes with a smaller crown size. Less common are deformed formations of a teardrop-shaped, lumpy, chisel-shaped form.
Pathological causes of delay
If a child’s teeth have fallen out and new molars do not grow for a long time, the reasons for the delay should be sought in pathologies:
- Retention is a complete or partial delay in eruption. Partial retention is observed when the crown of a molar tooth appears in the socket of a milk tooth, but growth stops there. Often the cause is early loss of a baby tooth, accidental or surgical. That is, a replacement for him has not yet been formed.
- Adentia – absence of teeth. This rare problem is common in older people, but can also occur in children. As a rule, it is triggered by taking strong medications during pregnancy.
Orthodontic treatment
Depending on the situation, it is used after tooth extraction or instead of it. In children, it is used to stimulate the loss of baby teeth and eliminate false hyperdontia, as well as to facilitate and accelerate the eruption of a normal set. In addition, orthodontic treatment with the installation of braces, mouth guards, dental plates or other auxiliary structures can straighten crooked teeth and return them to their proper place.
Before prescribing treatment, the dentist carefully evaluates the condition of the complete and supernumerary structures and, depending on the overall picture and prognosis for the future, can use both formations or leave the strongest and most durable tooth (not necessarily complete).
Recommendations for avoiding delay
- After tooth loss, you should not eat or drink hot drinks for several hours.
- The plug that forms in the hole cannot be removed to avoid infection. It will disappear on its own.
- It is not advisable to eat solid food for the first time after the loss.
- If you experience pain, redness, swelling or other signs of exacerbation, you should immediately contact your dentist. Remember, our specialists are always ready to help and answer your questions by phone.