A little about tuberculosis
Tuberculosis has been and remains a dangerous infectious disease. Koch's bacillus, or Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent of the disease, is so aggressive and resistant to the external environment that it can remain viable for several months in dry sputum, on various surfaces.
Mycobacterium is easily transmitted by airborne droplets (coughing, sneezing) and through household contact. Penetrating into the body, the microbe affects various organ systems, but most often these are the chest organs. However, not in all cases tuberculosis is active - approximately a third of the planet’s inhabitants are “owners” of a latent form of the disease, that is, the microbe is present in their body, but the immune system successfully copes with it. Such people do not suffer from tuberculosis (the possibility of activation of the pathology is no more than 10%) and do not pose a danger to others. If the immune system is weakened (HIV, diabetes, chronic disorders, poor nutrition, stress, and so on), the likelihood of developing the disease increases sharply.
ON A NOTE! According to statistics, the incidence of tuberculosis in Russia has decreased in recent years. However, many experts are skeptical about such data, rightly believing that not all cases of infection and mortality were taken into account. Since the times of the USSR, there has been an opinion that only socially disadvantaged people can get tuberculosis. In fact, mycobacterium does not select a person by status. In addition, this attitude towards the disease leads to a situation where “prosperous” people, having fallen ill, try to hide this fact from others, including doctors and relatives.
Another reason for the lack of statistical recording is the stereotype associated with the symptoms of tuberculosis. It is believed that the patient must certainly choke from coughing, spit phlegm with blood, and so on. But such symptoms indicate an already advanced stage, when the disease is difficult to treat. And at the early stage of infection, a person may only feel fatigue, loss of strength, a slight increase in temperature in the evening and other signs that easily fall into the category of “you just need to rest.” As a result, there is no need to see a doctor, tuberculosis progresses and spreads.
Treatment of the disease is long-term and requires taking medications from different groups for several months. In the absence of timely and adequate therapy, the result is death. In addition, tuberculosis is dangerous due to its complications on the brain, bone tissue and others.
Why is Mantoux needed at 1 year old?
Norma Mantoux at 1 year
Not all parents understand why a baby of this age is given an injection and made to suffer. Many also seriously believe that tuberculin tests are the same as vaccination, which means that the child can become infected with a dangerous disease.
In fact, tuberculin contains only killed bacteria of the human and bovine tuberculosis strain, so the risk of infection is reduced to almost zero. But it is pointless to perform tuberculin tests before the age of one year. As many years of medical practice have shown, at this age the results of the Mantoux test in children at this age often turn out to be false. This is due to the intensive formation of immunity, including to tuberculosis, after the BCG vaccination given in the first days after the birth of the baby. This is why it is necessary to get the first Mantoux vaccination at 1 year of age.
Sometimes tests are postponed if, for some reason, BCG vaccination in the maternity hospital was postponed and performed 1-2 months later. In this case, Mantu is given at about a year and a half - the timing depends on how much the anti-tuberculosis vaccination was delayed and for what reasons. This method is considered safe and does not threaten children's lives. Mantoux is needed more often at 1 year of age if the baby has had contact with people infected with tuberculosis or there is a suspicion that there has been a health-threatening contact.
Mantoux – vaccination or test?
Vaccination against tuberculosis - BCG. The vaccine is named after the names of the scientists who created it in capital letters: Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG). The vaccine contains live but inactivated bovine mycobacteria. The first vaccination is given to newborns in the maternity hospital, usually on the 4th day of the child’s life.
Many people do not understand why vaccination is done so early, where can a baby encounter this infection? In fact, the situation with tuberculosis in our country is unfavorable, and not all tuberculosis patients know about their disease. They don’t even suspect that they are contagious and lead a normal life. TB doctors know that the earlier a child is infected, the greater the likelihood of the infection turning into a disease. And the sooner he is vaccinated, the faster the baby will develop immunity and he will be protected. There is even a grotesque poem on this topic, the author of which, unfortunately, is unknown:
“When they come to ask for permission for a child to have BCG done,
And this will be after the birth, but before discharge, Don’t allow it - there are no tuberculosis patients in your family, So that you don’t get infected from others - do your shopping on the Internet, Walk away from all passers-by, visit your girlfriends don't drive, Let your husband quit his job. Warn your relatives that you don’t want to see them anymore for ten years. Kindergarten and school are flying by and warm greetings to the university. Let the child grow up at home, under his mother’s skirt - All wild, unlearned, without life goals or ideas. Old age will creep up unnoticed. He won’t give you water - he’ll go out into the street to get it and get lost there. Alas."
So, in response to vaccination, the body produces protective antibodies - immunity is formed. Immune memory weakens over time, so revaccination is required (repeated administration of the vaccine at seven and 14 years). BCG does not provide 100% protection against tuberculosis, but in case of infection it significantly reduces the risk of complications and death, promotes a milder course of the disease and a faster recovery.
Mantoux allows you to:
- determine the body’s sensitivity to mycobacteria;
- identify the hidden form of the disease;
- assess the risk of developing the disease in the future.
In other words, using the test, you can not only detect tuberculosis in a timely manner, but also predict the immune response to infection.
What's included
The drug contains a complex mixture of mycobacterial proteins - tuberculin. It is pre-cleaned and treated with special solutions. It does not pose a danger to human health and is not a cause of tuberculosis.
FROM THE HISTORY. Tuberculin was discovered by the German microbiologist R. Koch in 1890 for the treatment of tuberculosis. The crude composition led to numerous and severe toxic effects, recovery did not occur, so it was perceived critically by society. But as tuberculin was further used in animals, the diagnostic properties of the drug were discovered. In 1907, a scientist from Austria, K. Pirke, proposed using tuberculin diagnostics for people using a skin test. And in 1908, C. Mantoux (France) developed a method of intradermal administration, which is used in diagnostic practice to this day. The purified preparation was adopted by WHO as an international standard in 1952.
What is Diaskintest
"Diaskintest" is a domestically produced drug intended for the diagnosis of tuberculosis. It is administered in the same way as Mantoux - intradermally into the forearm area. Diaskintest was introduced into Russian clinical practice in 2009.
As in the case of Mantoux, a conclusion about the presence/absence of a disease is made based on the body’s reaction. The formation of a compaction of a certain size at the injection site indicates infection with Koch's bacillus. Diaskintest has high specificity and sensitivity: it can detect the causative agent of tuberculosis in 96% of cases. For comparison, Mantoux gives a positive reaction to vaccine mycobacteria (BCG) and other non-tuberculosis strains of microorganisms.
ATTENTION! Diaskintest is not an alternative to Mantoux! This is a clarifying method for diagnosing tuberculosis. It can also serve as an assessment of disease activity during treatment and the effectiveness of the therapy.
Diaskintest is suitable for people of any age. A negative result will show with very high confidence that the person is not infected with mycobacteria.
For the differential diagnosis of tuberculosis and other diseases, a test with the drug Diaskintest is carried out in combination with a clinical, laboratory and x-ray examination in an anti-tuberculosis institution.
What does the drug contain?
The drug "Diaskintest" is a product of genetic engineering. This is a protein obtained artificially. It includes two antigens - compounds foreign to our body, which are characteristic specifically of the causative agent of tuberculosis. Therefore, the drug causes a reaction only if there are mycobacterium tuberculosis in the body. Like Mantoux, Diaskintest does not contain mycobacteria in any form and does not contribute to infection.
What are the complications of Mantoux at 1 year?
Different children tolerate Mantu in different ways per year, each child has its own characteristics of the body. Lack of appetite, lethargy, drowsiness - parents often turn to the pediatrician with just such complaints, fearing that these are signs of a positive Mantoux reaction. Some babies have a fever after the Mantoux test. But this is more likely a reaction to stress after visiting a noisy street, a hospital, the actions of doctors and an unpleasant injection, rather than possible complications and deviations.
The most unpleasant consequences of Mantoux is obtaining a false positive result, since in this case a healthy child will be sent for repeated tests many times and may be prescribed fluorography, which is very harmful at this age. It’s even worse if the baby is prescribed anti-tuberculosis treatment using serious antibacterial drugs, when in fact he is completely healthy. Therefore, from the very beginning, parents should take the first Mantoux test seriously and adhere to all the doctor’s recommendations in order to get a reliable result the first time.
Comparison of Mantoux and Diaskintest
Immunodiagnosis using Mantoux is carried out for children vaccinated against tuberculosis from 12 months of age until they reach the age of 18 years. An intradermal allergy test with tuberculin (Mantoux test) is performed once a year, regardless of the results of previous tests up to and including 7 years of age.
Diaskintest is performed once a year, regardless of the results of previous tests from 8 years of age to 17 years of age inclusive.
For those not vaccinated against tuberculosis, a Mantoux test is performed 2 times a year, starting from the age of 6 months.
Below is a comparative table of the Mantoux and Diaskintest tests.
| Mantoux | Diaskintest | |
| Place and method of drug administration | Forearm, intradermal | Forearm, intradermal |
| Compound | Proteins from killed mycobacteria extract | Recombinant protein obtained by genetic engineering |
| Indications | • Routine diagnosis of tuberculosis • Detection of the latent form of the disease • Disease risk assessment | • Identification of the causative agent of tuberculosis • Clarification of the diagnosis in case of doubtful Mantoux • Evaluation of treatment effectiveness |
| Contraindications | Eat | Eat |
| Side effects | Possible | Possible |
| Does it show a hidden form of the disease? | Yes | Yes |
| Is there a reaction to BCG? | Yes | No |
| Is there a reaction to other strains of mycobacteria? | Yes | No |
| Does it make it possible to determine the strength of immunity? | Yes | No |
| Test result | • Negative • Doubtful • Positive | • Negative • Doubtful • Positive |
| On what basis is the conclusion made? | Presence/absence, size of papules (seals, “bumps”) | Presence/absence, size of papules (seals, “bumps”) |
| Is it suitable for children | Yes (source: SanPin 3.1.2.3114-13 clause 5.1: “...from 12 months to 18 years”) | Yes (source: Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 124n dated March 21, 2021: “use in children over 7 years of age and adolescents”, for ages under 7 years - according to indications) |
| Is it suitable for adults | According to indications | According to indications |
| Test frequency | For children – once a year annually. Adults - as needed | According to the doctor's indications |
| Risk of contracting tuberculosis | No | No |
If the result is positive or questionable, in both cases additional examination is required. This may be a laboratory test of blood, sputum or smear, chest x-ray, CT, MRI and other methods.
News
An immunological test, which is designed to detect tuberculosis infection in the body, is called the Mantoux test. A tuberculin preparation, consisting of two dead bacteria, is injected subcutaneously and, as a rule, causes some kind of inflammation on the surface of the skin, based on the condition of which doctors decipher the results of the procedure.
The inflammatory focus occurs as a result of the connection of closely located lymphocytes - blood cells that form cellular immunity - with tuberculin bacteria artificially introduced into the body. The reaction provokes the awakening of those cells for which the causative agent of the disease is already familiar.
If there are a large number of them, then the inflammatory process on the skin occurs more intensely, and a wide compaction forms in response to the injection. For a doctor, this phenomenon indicates the possible presence of a tuberculosis bacillus in the body. In this case, the specialist prescribes additional studies to make a more accurate diagnosis.
WHY DOES IT NEED TO BE MADE MANTU TO A CHILD EVERY YEAR?
An intradermal test is performed on children starting from 1 year of age, once a year, mainly at the same time. Regardless of the results of the previous test, the next one must be performed.
This diagnostic method is not used for babies under one year of age, since in infancy it cannot give reliable results. The immune system is not yet sufficiently developed, and the “button” can give a negative result in the wrong direction.
WHY DO THEY MAKE MANTU FOR CHILDREN?
Many people mistakenly believe that the Mantoux vaccine is a vaccination. In fact, this is not true. It is more correct to call the procedure an allergy test; a tuberculin preparation reveals whether the child’s body is “familiar” with the causative agent of tuberculosis – Koch’s bacillus.
Tuberculin diagnostics is designed to identify tuberculosis bacteria in the body and determine the possibility of vaccination and revaccination with BCG - vaccination against this disease to form stable immunity.
The first vaccination against tuberculosis - BCG - is given almost immediately after birth, and based on the Mantoux results, children who need revaccination are selected. It is performed at 7 and 14 years of age, and when living in areas with high epidemiological rates of tuberculosis infection, also at 12 and 16 years of age.
Using the information that the Mantoux reaction shows, it is determined how a child’s immunity to the disease is formed after vaccination, whether his body is able to resist the pathogens of the common and rather dangerous disease tuberculosis, to track the individual dynamics of the results for the possibility of early diagnosis of the disease, to determine the epidemiological indicators of the population for tuberculosis .
Therefore, parents who are afraid to carry out this procedure with their children should not worry. Mantoux is only a mandatory means of monitoring the behavior of the immune system in relation to Koch's bacillus. The test allows you to detect danger in time and promptly take preventive or therapeutic measures to eliminate tuberculosis.
FEATURES OF THE TUBERCULIN TEST PROCEDURE
Tuberculin diagnostics are carried out regularly, in preschool institutions, as a mass tuberculin diagnostic event, and for those who do not attend kindergartens - in a children's clinic, under the subsequent supervision of a local doctor.
The nurse uses a special tuberculin syringe to inject the drug into the inner surface of the arm, between the wrist and the crook. The patient should be in a sitting position at this time. The drug contains 0.1 ml of a solution of two purified tuberculin units.
At the injection site, redness and a papule form - a kind of bulge on the surface of the skin, which is called a “button”. The results are assessed on the third day after the procedure. During this period, the “button” should not be smeared with anything, covered with a band-aid, wrapped in a bandage, wet with water, allowed to sweat excessively, rubbed, or heated.
In case of accidental contact with moisture, the skin should be lightly blotted with a towel. The injection site may be itchy, but you should ensure that your child does not scratch the area to avoid an excessive allergic reaction.
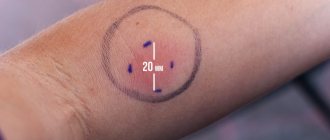
Only with proper care does the Mantoux test give a reliable result, so it is very important for parents to ensure that their child follows these rules. When summing up the results of the procedure, it is very important to measure the size of the “button”, and not the total diameter of the redness of the inflammatory focus. The papule has a denser structure compared to the surrounding area of skin and rises slightly above it.
Diagnosis of tuberculosis based on the Pirquet test is not made based on the results of one sample. Only by assessing the dynamics, performing the procedure regularly with a long break, and also by connecting related factors, can reliable conclusions be drawn.
It is worth mentioning separately that the result of this method may be false positive. This can happen if we make a “button”, and it gives a positive reaction in the absence of a pathogen in the body.
This often happens due to the fact that a person may be a carrier of non-tuberculous mycobacterium, as well as an increased tendency to develop allergies or any recent infection. In such situations, the doctor prescribes additional studies and analyzes related factors to identify the origin of bacteria in the body.
Parents should not worry about the Mantoux test when performed on a child, as it provides additional information for the doctor.
Positive result
– is not a reason for immediate treatment for tuberculosis. However, some factors may indicate increased danger:
- The test gave a positive result, unlike the previous one;
- The diameter of the inflammatory focus increased by any value, if the previous one was more than 12 mm;
- The size of the inflammation increased by more than 6 mm, with the previous size of the “button” being up to 12 mm;
- Hyperergic reaction - a papule measuring more than 17 mm and a pustular wound at the injection site;
- Every year, mantu grafting shows results of over 12 mm;
- In children over 7 years old, the “button” does not decrease in size.
These factors relate to the diagnosis of children who were vaccinated with BCG in the maternity hospital. In those who were not vaccinated at birth, any positive Mantoux reaction to tuberculosis may indicate the presence of the causative agent of this disease in the body. Unvaccinated
For children, the test needs to be done more often - once every six months.
If the doctor decides to refer the patient to a TB specialist, do not immediately panic! Unfavorable test results only give rise to a more extensive diagnosis, which will be carried out by a highly specialized specialist. A comprehensive examination includes a CBC, urine test, FG, extended Pirquet test, sputum culture, and possible examination of family members.
DO ALL PEOPLE NEED TO DO MANTU: EXISTING CONTRAINDICATIONS TO THE PROCEDURE
The decision to perform a Mantoux test is made by the doctor. It is given to all children in the absence of clear contraindications:
• Presence of severe skin diseases; • Epilepsy; • Chronic diseases in the acute stage; • Asthma, especially accompanied by allergies; • High temperature, ARVI ; • Infectious processes; • Aggravated manifestations of allergies.
When carrying out routine vaccination, the Mantoux test can be performed only 1 month after any vaccination or before it, immediately after assessing the condition of the “button”.