Hypertonicity in a child is an excessive overstrain of the flexor muscles. It is due to the fact that for a long time the muscles of an unborn child are in constant tension: in the uterine cavity, the arms are clenched into fists, and the legs are pressed to the body, and the chin is to the chest. In the womb, fetal movements are limited and not varied. It is more comfortable for newborns to maintain the fetal position, this way they feel more protected and calm.
The tension in the muscles of the baby's head and neck in the mother's belly is quite strong, so after birth the head is slightly tilted back, and the limbs are bent and pressed close to the body. In nine cases out of ten, children in the first months of life experience muscle tone, which goes away on its own. As the child grows and adapts to living conditions outside the womb, the muscles relax and voluntary movements appear. However, in some infants the state of tone persists even after 3 months, which may indicate deviations from the norm and the need for treatment. Most often this is due to the fact that during intrauterine development or during childbirth (immediately after it) the child’s nervous system was damaged. The central nervous system is not able to fully transmit impulses to the muscles for their proper functioning due to damage to the neurons of the brain.
Do not be afraid of this diagnosis, since the child’s nervous system is not fully formed, and its condition can be influenced. The main thing is to pay attention to the baby’s well-being and behavior in time, consider the deviation and seek help from a specialist.
Doctors distinguish the following types of hypertension:
- general, that is, the whole organism;
- only upper or lower extremities;
- according to hemitype, that is, the tone of the limbs on one side: right or left.
How to recognize hypertension in newborns
It is important to monitor the child’s behavior and state of health in order to identify deviations and solve the problem in a timely manner. Parents should monitor their baby and consult a doctor if the following symptoms occur:
- from the first days a newborn holds his head, and does not “drop” it back;
- When you move your arms or legs to the sides, you feel resistance. When trying again, the child becomes unhappy, cries, and the tension increases;
- frequent, profuse regurgitation after feedings with general poor appetite, colic;
- restless and short sleep, in which a tense posture remains: arms and legs are pressed tightly to the body, the head is pulled back, nervous twitching is possible;
- throwing back the head and arching the body, tremor of the chin and limbs when crying;
- increased excitability of the child, painful reaction even to minor sound and light stimuli;
- Taking the child by the arms and placing him on a flat surface, slightly tilting him forward, you can observe that he will reflexively begin to walk. In this case, the baby puts his foot on his full foot, and does not walk on tiptoe.
Self-control: normal muscle tone
Up to 1 month Lying on his back, the baby assumes the “fetal position”: arms are bent and pressed to the chest, fingers clenched into a fist, legs apart at the knees, skin folds are symmetrical. Lying on his stomach, the baby turns his head to the side, placing his arms under his chest. At the same time, he bends his legs and imitates crawling movements.
From 1 to 3 months, the baby can stretch his arms forward and bring them to his eyes or mouth. Closer to three months of age, he begins to reach for a toy - for play and development. If you put a rattle in his open palm, he holds it tightly. He lifts and holds his head well while lying on his stomach, turns his head in different directions.
From 3 to 6 months In the supine position, the baby’s arms and legs are half bent, palms open. The child purposefully reaches out to the toy and takes it. Closer to 4 months, the baby learns to roll over from his stomach to his back, and closer to 6 months - to sit up and crawl. By six months, the child rests on open palms, rising with outstretched arms.
From 6 to 9 months The child moves actively, rolls over from his stomach to his back and back. Sits down, crawls and makes the first attempts to stand up.
From 9 to 12 months, the baby crawls, stands up and tries to walk, first with support, and then independently.
Why does hypertension occur in infants?
The causes of hypertension in infants are caused by the action of unfavorable factors during intrauterine development, during childbirth, or in the first days after birth.
During pregnancy, the fetus may suffer due to the following factors:
- hypoxia - a long period of oxygen starvation;
- acute infectious diseases suffered by the mother or her chronic diseases;
- general intoxication of the mother’s body;
- bad habits of women: smoking, drinking alcohol, taking drugs;
- early/late toxicosis, threat of miscarriage, uterine tone;
- Rh conflict between mother and child.
Difficult, rapid or, conversely, protracted labor can also cause increased muscle tone in babies. Various birth injuries, umbilical cord entanglements, lack of oxygen (hypoxia) - all this can lead to disruption of the newborn’s nervous system and cause abnormalities and illness.
Hypertonicity at 4-5 months in a child and massage
In newborn children, the nervous system is still far from developed, this is due to postpartum stress. Therefore, in children in the first months of life, we can often observe increased muscle tone and more often in the direction of hypertonicity, i.e. increased excitability. In such children, symptoms such as trembling of the upper and lower extremities, flinching at sharp sounds, and trembling of the chin can be noted. From the moment of birth until the baby is 3-4 months old, these symptoms are a physiological manifestation of the adaptation period. But if parents observe hypertension in a child at 4 or 5 months, then they should not delay a visit to a neurologist, but should immediately show the baby to a specialist, because this condition is a sign of perinatal encephalopathy. Hypertonicity at 4.5 months in a baby is manifested by symptoms such as increased excitability, restless sleep, trembling of the chin, trembling of the limbs, posture during sleep with the head thrown back, etc. In order to remove all the symptoms of increased muscle tone in such children, the proper functioning of the nervous system should be restored.
Hypertonicity at 4.5 months can be treated quite well with complex treatment, and properly selected therapy can completely eliminate all symptoms of the disease. Otherwise, hypertension in a child at 4-5 months can lead to serious disorders and problems at an older age. For example, impaired coordination of movements, impaired speech abilities, impaired motor activity in the upper and lower extremities.
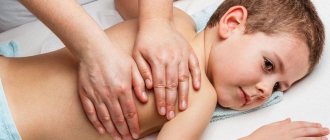
For hypertension, one of the leading treatment methods is massage. Massage for a child with hypertonicity for 4 months is performed by a specially trained massage therapist who is proficient in massage techniques. During a procedure such as a massage for a 4-month-old child with hypertonicity, it is important to remember that a prerequisite for a massage is a calm state and positive emotions of the baby; otherwise, the situation is further aggravated and muscle tone increases. A gentle approach to the baby is important here, because... he is still at that age when he does not understand that he needs to endure unpleasant massage movements for his own good. Massage for a 4-month-old child with hypertonicity is performed in the morning, before feeding, with warm hands, preferably at home and in a familiar environment. The duration of one session is on average 10 minutes.
This special massage is aimed at developing the extensor muscles during massage movements and relieving muscle tone, especially in the upper and lower extremities. As an introduction, before starting the massage, light stroking movements are performed and preferably in the following sequence: arms, legs, place the baby on the tummy, then move to the back, and turning back onto the tummy, rub the feet. Turning on the right and left sides, perform reflex extension of the spine and ends by laying the baby on the tummy and performing reflex crawling. Then they move on to deeper massage movements, which are aimed separately at relaxing the whole body and relaxing the limbs. The direction of the massage movement is from the shoulders to the fingers and from the feet to the groin area. When performing a massage on a 4.5-month-old child with hypertonicity, remember that even a light load should be balanced. To relax the baby’s entire body, take the baby’s armpits and gently swing them in different directions - left, right, this exercise is called a “swing”.
The next “cradle” exercise is performed in this way: the baby is laid on his back, and the massage therapist puts his hands under the head and back and begins to swing to the sides - top, bottom, right, left. Afterwards, the hands are moved under the lower back and buttocks and again perform a rocking movement. This exercise trains the upper and lower torso. Relaxation of the limbs is carried out using the piston rubbing method, when the baby’s arm or leg is placed between your palms and moved up and down. To relieve muscle tone in the hip joint, rubbing begins from the feet to the knees, mentally drawing a figure eight on the foot and lightly stroking the knee area. Such exercises are performed 4-5 times. When training the hands, the massage therapist allows the baby to clasp his thumb with his palm, and with the other hand he strokes in the direction from the wrist to the shoulder. The number of such movements is 4-5 times. During the massage, the fetal position deserves special attention, because... Everyone, without exception, likes it. The massage therapist clasps the baby’s feet and palms with one hand, and with the other, supporting the head, rocks the baby. For infants, this exercise is a kind of relaxation.
The final exercise is in the form of moderate pressure on the toes and heels, because The nerve endings in this area are responsible for the functioning of the body as a whole.
Hypertonicity at 4.5 months is not a death sentence; by performing a therapeutic massage and surrounding your baby with love and affection, you will forget about this problem forever.
How to treat hypertension in infants
Hypertonicity in infants is very common. When examining a child, a pediatrician and neurologist can easily identify it. In some cases, the increased tone goes away on its own by 3–4 months. In addition to the main symptoms, doctors rely on the following reflexes of the child, which, with normal development, should disappear by the 3rd month of life:
- step reflex. With the body in a vertical position, the baby begins walking movements on a flat surface;
- support reflex. On the floor, the child places his foot on the entire foot, and not on the toe;
- symmetry/asymmetry reflex. When the baby lies on his back and presses his chin to his chest, his legs extend and his arms bend. When tilting the head to the left, the left limbs bend; when tilting to the right, vice versa;
- tonic reflex. In the position on the stomach, the arms and legs are bent; in the position on the back, they are straightened.
In addition to pediatrics and neuropathology, osteopathy is widely popular and effective in treating tone in children. This is the main alternative to traditional treatment: massages, physiotherapy, aromatherapy, therapeutic exercises, drug treatment, which in most cases only relieves symptoms. The main task of the osteopath in this case is to find the cause of abnormalities in infants and eliminate hypertonicity.
The doctor collects a detailed medical history and asks how the pregnancy and childbirth proceeded. For osteopathy, the human body is a single whole, all its organs and systems are inextricably linked with each other. The specialist has very sensitive fingers, and all the manipulations he performs are extremely soft and gentle.
Disorders of the nervous system, which causes muscle tone in infants, are treated by an osteopath with a special massage. These procedures do not cause pain or discomfort in children, therefore they are absolutely safe. The positive effect will be noticeable after the first sessions. The child experiences an improvement not only in muscle tone, but also in appetite, sleep, and digestive processes. The osteopathic doctor triggers the necessary mechanisms in the baby’s body, aimed at correcting the functioning of the brain centers and metabolic processes between them.
Parents should listen to the doctor’s recommendations, but self-medication is unacceptable, since the osteopathic doctor performs extremely delicate and gentle manipulations with the child, requiring certain knowledge, skills and qualifications. The duration of therapy is different for each patient, so return visits to the clinic may be repeated after one to two weeks.
Symptoms of hypertonicity and hypotonicity of muscles in infants
Increased muscle tone (hypertonicity) in infants can occur due to damage to the nervous system or brain due to:
- birth injuries;
- hemorrhages;
- hypoxia (lack of oxygen) during childbirth;
- meningitis;
- increased excitability in a child.
Symptoms of hypertension:
- great body tension, tightness;
- inability to relax during sleep (fists clenched, arms near the chest, legs near the stomach);
- holding the head immediately after birth due to hypertonicity of the neck muscles;
- restless sleep, colic;
- frequent tremor (shaking) of the chin;
- excessive regurgitation;
- when placing the baby on his feet, he tucks his fingers and tries to stand on his “tiptoes”;
- if you pull a child by the arms, he does not straighten them, but tries to rise with his whole body;
- possible curvature of the neck (if a cervical injury occurred during childbirth);
- the child later begins to crawl, sit and walk.
Hypotonia (decreased muscle tone) in a newborn most often occurs in premature babies and in children with brain problems, as well as with endocrine pathologies and infection:
- when infected in the womb;
- during birth trauma;
- due to intracranial hematoma.
Symptoms of hypotension:
- lethargic and constantly sleepy state of the baby;
- low mobility, poor appetite and slow weight gain;
- the baby does not hold his head up for a long time, his arms and legs are extended along the body;
- the tummy has a flattened shape;
- when spreading the hips, no muscle resistance is felt;
- if you lay the baby on his tummy, he does not try to bend his arms and raise his head, but lowers his face to the surface;
- in severe forms: impaired sucking, swallowing, breathing.
Dystonia (asymmetric tone) of muscles in an infant occurs if the muscles experience uneven tone: some of them are in decreased tone, others are in increased tone.
Symptoms of dystonia:
- the baby takes unnatural positions;
- the child falls on his side, and his body arches;
- skin folds are unevenly located;
- the child’s posture develops with complications: scoliosis, clubfoot, and curvature of the neck may occur;
- psychomotor development is impaired;
- in severe forms - cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy).
Why is hypertension dangerous?
As mentioned earlier, infant hypertonicity can be caused by disorders of the nervous system. It is obvious that such deviations will worsen and develop if measures are not taken. At first, motor disturbances in the baby will be noticeable, and subsequently deviations in fine and gross motor skills, coordination, and speech will appear. Possible problems with gait and posture, developmental delay. All of the above suggests that the problem of increased tone in infants requires special control, primarily from parents. Timely detection of disorders, their causes, as well as subsequent proper treatment is the key to the health and normal development of a little person.