What is hypersalivation?
Increased salivation can be attributed to natural physiological processes between the ages of 2 and 8 months.
Intensive production of excessive amounts of secretion by the salivary glands is called hypersalivation.
The etiology of ptyalism can be pathological or physiological. In newborns, due to underdevelopment of the salivary glands, there is no salivation.
Increased salivation can be attributed to natural physiological processes between the ages of 2 and 8 months.
If signs of hypersalivation appear at an older age, then this indicates the presence of pathological processes in the body.
In medical practice, the following types of hypersalivation are distinguished:
- True. Associated with increased secretion of the salivary glands. Depending on the etiology, it can be bulbar, somatic, medicinal and psychogenic.
- False. Caused by dysfunction of the physiological process of swallowing saliva.
Important! With a severe degree of development of ptyalism, the integrity of the skin may be damaged under the influence of the constituent components of saliva.
Cause: oral diseases (stomatitis, thrush)
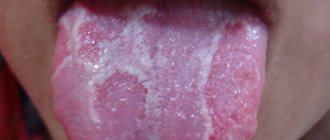
If the baby constantly sucks his fists, and increased salivation is accompanied by an increase in body temperature, a white coating is clearly visible on the tongue, gums and mucous membranes, you should immediately consult a doctor. These symptoms indicate damage to the oral cavity by a fungus of the genus Candida. Factors contributing to the appearance of thrush in children:
- Sugar consumption. The baby can receive it both from baby food (manufacturers often use artificial sweeteners to improve taste) and from breast milk (if the mother’s diet contains refined foods, sweets and preservatives in large quantities).
- Decreased immunity. Thrush in infants often accompanies infectious diseases.
- Poor hygiene. Pathogenic fungi enter the body of a two to three month old baby with dirty nipples and toys, as well as if he puts dirty fingers or fists in his mouth.
- Taking antibiotics. They destroy bacteria that prevent the growth and reproduction of pathogens.
Often children at 2-4 months drool continuously due to stomatitis. With this pathology, blisters and ulcers appear on the oral mucosa. Babies may refuse to eat due to severe pain.
Causes of increased drooling in a child
In medical practice, certain provoking factors for the development of hypersalivation in children of different ages are identified.
Among them, the most common reasons why salivation is increased are:
| Name | Description and age | Additional symptoms |
| Teething | A natural physiological process between the ages of six months and 4 years. Gradual increase in the amount of saliva production. It is characterized by the constant release of transparent saliva of a liquid consistency from the oral cavity. | Hyperthermia of the whole body, increased tearfulness, nervousness, sleep disturbance, constant anxiety and rapid fatigue. The gums are inflamed and red, itchy and painful. |
| Oral diseases | A pathological condition associated with the development of inflammation in the oral cavity at any age in children. The most common diseases include stomatitis and gingivitis. Accompanied by a large amount of saliva with white opaque inclusions. It is also possible that there is blood in the saliva. | With stomatitis, ulcers are observed on the oral mucosa, which at an advanced stage can bleed. Also, the surface of the tongue becomes covered with a whitish coating and severe pain appears. With gingivitis, inflammatory processes are observed in the gum tissue, accompanied by local hyperthermia, swelling and discoloration. |
| Gastrointestinal diseases | They can develop in a child at any age. The most commonly diagnosed pathologies in this case include: pancreatitis, peptic ulcer, enteritis, hepatitis, gastritis. | Large salivation is accompanied by the following symptoms: diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, pain in the abdominal cavity, heartburn, constipation. |
| Nervous system diseases | Abnormal development of the brain and its congenital injuries. Certain forms of cerebral palsy. Also with systematic severe stress or high psycho-emotional overexcitation. These conditions can develop at any age. Therefore, salivation increases regardless of age category. | Increased nervousness and tearfulness of the child. Inconsistency of development with the age of the baby and his lack of correct reactions to a certain stimulus. |
| Fungal infections | Damage to the oral mucosa by pathogenic microorganisms and its inflammation is accompanied by increased hypersalivation. The secreted saliva most often contains white flakes, which are formed during candidiasis and other fungal infections. The risk group includes children of any age category. | The presence of a white coating on the surface of the tongue, lack of appetite, pain when swallowing and chewing food. Constant or periodic feeling of burning and itching in the mouth. |
| Poisoning | Intoxication of the body with toxic substances, potent drugs, heavy metals and concentrated chemicals. Age category of children from 2 years and older. | Vomiting, dizziness, irregular breathing, fainting, diarrhea, watery eyes, dermatological rashes. Formation of ulcers due to chemical burns. |
| Inability to swallow saliva | This pathological process manifests itself in children aged 1 to 4 years. The swallowing reflex is not developed in children with allergies, since due to allergic rhinitis the child uses his mouth for breathing. Therefore, saliva flows out on its own. | Redness of the eyes, difficulty breathing, dermatological rashes, cough. |
| Allergy | Hypersalivation of this etiology develops in children of any age. Increased secretion of saliva (a lot of saliva) is observed when consuming certain foods that are allergens. It can also be skin contact or inhalation of allergens. | Runny nose, rashes in the nasolabial fold area, fever, watery eyes, itching and burning. Increased moodiness and tearfulness. |
| Worm infestations | Excessive secretion of saliva can be caused by the presence of various types of parasites in the child’s body. A special risk group includes children of any age who come into contact with animals, open soil and frequent games in dirty sandboxes. Eating unwashed vegetables and fruits is also dangerous. | Saliva becomes cloudy. Increased anxiety in the child, sudden loss of appetite and body weight, itching in the anal area, nausea, vomiting. |
| Side effects of drugs | When undergoing a therapeutic course using medications, hypersalivation acts as a side effect. | Additional symptoms may include various signs corresponding to the side effects of each group of drugs. |
| Injuries, etc. | Often one of the consequences of a fall is inflammation of the salivary glands, which provokes increased secretion of saliva. Most often, this cause of hypersalivation is observed in children over 6 years of age. | Damage and inflammation of the skin in the area of the grass. Pain on palpation. |
Important! There are many factors that provoke increased salivation in children.
Among them it is also worth highlighting a number of neurological pathologies, diseases of the eyes and ears, as well as diphtheria.
Causes of hypersalivation
- Physiological phenomenon as a variant of the norm.
- Teething process
- Allergic rhinitis in a child with allergies
- Problems with swallowing and anatomical features of the jaw structure
- Oral infections
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract
- Neurological disorders
- Worm infestation
- Poisoning from heavy metals and hazardous chemicals
How to get rid of this?
First of all, you need to determine the causes of excessive salivation. If it is pathological, then you cannot do without the help of a doctor and drug treatment.
If increased salivation is a physiological process, then parents need to alleviate the baby’s condition and support him during the period of hypersalivation:
- The restoration of the baby’s health depends on quick and adequate treatment.
When pathological changes occur in the oral mucosa in a child, it is necessary to consult a specialist. The restoration of the baby’s health depends on quick and adequate treatment.
- To get rid of hypersalivation , the cause of which is stomatitis or gingivitis, dentists prescribe medications that destroy infectious agents and promote rapid regeneration.
- If there is a helminthic infestation or a somatic disease , the symptom of which is increased secretion of the salivary glands, the child should be taken to see a doctor, examined completely and treated with medications that normalize salivation.
- Natural remedies will help improve the condition of the little patient. For stomatitis, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with table salt solution or herbal infusions, and for gingivitis - with sea buckthorn oil.
- You can reduce the secretion of saliva by strengthening the immune forces of the child’s body. For this purpose, they protect children from emotional stress, often take them for walks on the street, give them healthy food enriched with vitamins, and develop them physically by participating in various sports sections.
- Always use a bib. Treat the skin of the face with nourishing creams, and if necessary, dry the skin on the chin with the addition of zinc.
- Using pacifiers will help the baby reflexively swallow saliva when it is released in abundance.
Important! Self-medication of hypersalivation in children is strictly prohibited. Only the help of a qualified specialist will help to correctly establish the etiology of the pathology, on the basis of which appropriate treatment is prescribed.
How to help your baby
Parents will have to come to terms with and go through the period of slobbering toddler. It is unpleasant for the baby to be slobbery, so parents take special care and care for the baby at this time.
It’s not in vain, apparently, that our great-grandmothers invented bibs for babies. Bibs will help now: the fabric absorbs liquid, blouses remain dry, the skin on the neck and chest is also dry.
Sometimes a baby drools so much when lying down that he chokes and simply choke on it. He may experience a cough, even wheezing. To prevent your child from getting into trouble, place him on his side or tummy, or you can put him on a low pillow. So, the drool will flow down and will not harm the baby.
If a baby sucks on a pacifier, he is able to swallow his saliva. When going for a walk, give your baby a pacifier. Using a pacifier is another way to cope with the problem.
Soon the time for teething comes, the baby's gums itch and itch, he constantly chews something to relieve the itching. Help him, massage his gums with your finger. And in the places where the first teeth appear, press lightly. On the doctor's recommendation, buy a special product and lightly lubricate the gums with it, this will calm the baby.
In what cases is it safe, and in what cases is medical assistance necessary?
When teething, children drool heavily; this physiological process does not require any therapeutic measures.
Drooling in this situation is safe and all mommy’s actions boil down to timely replacement of bibs and clothes.
But if such symptoms appear in young children, it is worth visiting your local pediatrician:
- When teething, children drool heavily; this physiological process does not require any therapeutic measures.
Salivation flows heavily and it is difficult for the baby to breathe through his nose. Hyperthermia is noted. We can assume the development of an infection caused by viruses or bacteria.
- Congenital swallowing reflex disorder.
- Abnormal development of muscle tissue of the pharynx or tongue.
- Red eyes, nasal congestion, coughing and sneezing.
- If the tongue has increased in size and constantly falls out of the mouth.
- Saliva has a cloudy color and thick consistency.
- A child at the age of 3 months cannot hold his head up, there is a pulsation of the fontanelle, constant fatigue and moodiness.
Important! Despite the fact that one of the main reasons for increased salivation is the process of teething, doctors recommend not to take risks and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Causes of excess salivation in children
Parents, of course, are concerned when their child is drooling like a river. Why is this happening? Let's list the main reasons:
- Teething. Although the baby's teeth are not yet visible until 6-8 months, the process itself begins very early. This is why, at about 3 months of age, your baby begins to produce excess saliva: the teeth begin to push through the gums.
- Mouth open. A baby may keep his mouth open for quite a long time due to a clogged nose or out of habit. Due to this, he may not swallow saliva, which leads to increased drooling.
- Concentration of attention. The little explorer does not swallow saliva because he is concentrated on some task or interesting subject. This is where the oral fluid flows out.
- Nutrition. Unusually sour food often provokes drooling in the baby.
- Neurological disorders. Facial neuritis (Bell's palsy), cerebral palsy, autism, Down syndrome are diseases that also manifest themselves as excessive salivation in children.
- Side effects of medications. Some medications cause increased muscle tone in the lips, which leads to excess saliva.
- Exposure to toxic substances, including mercury vapor, insect bites.
Non-hazardous circumstances
As you can see, at a certain age, excessive salivation in a child is caused by natural, non-hazardous reasons:
- Insufficient functioning of the glands that are responsible for the production of saliva. In children under one year of age, the process of formation of the salivary glands continues, so a lot of saliva can be produced. The baby does not have time to swallow it, it flows out.
- In a baby up to 2 months, saliva ensures normal swallowing .
- In a three-month-old baby, excessive drooling becomes a harbinger of the appearance of teeth .
- In children who are breastfed, saliva protects the body from germs . It contains maternal antibodies and prevents the development of stomatitis, sore throat, flu and other diseases.
- If a symptom appears in children eating formula, this is a consequence of the normalization of the digestive process . Saliva promotes better absorption of mixtures.
Increased salivation in an infant, and even more so in an older child, can be caused by certain diseases, so it is important to pay attention to other symptoms and go to the pediatrician.
How to prevent irritation from saliva
The most common cause is teething. To prevent itching and irritation, place a diaper at the head of the bed.
It is necessary to lubricate your face with cream at the first sign of irritation from saliva. The following medications can be used:
- Bepanten is a cream for diaper rash and irritation.
- Weleda is an ointment based on natural ingredients. You can learn about Weleda toothpastes from our article.
- Pantestin is a drug that accelerates cell recovery.
If the rash develops gradually, you can use more effective medications to treat skin diseases: Sanosan Baby, Sudocrem and others. They affect the inflammatory process and kill microbes.
It should be noted that current drool is not necessarily the cause of the rash. This can be a sign of one of the serious diseases: measles, chicken pox, rubella and others. You need to consult a pediatrician.
Why does a one-month-old baby drool?
This process is normal for one month of age , because the active work of the salivary glands begins, and the child has not yet learned the swallowing reflex.
The salivary glands develop gradually; if in the first weeks of life they secrete very little fluid, then they gradually develop and the child somehow needs to cope with this.
The baby does not know how to swallow saliva and simply lets it out.
By 4-5 months he will have formed a swallowing reflex, and before that it is better to get bibs.