Have you been in your children's room lately? Surely, our mothers still keep marks on the wall, door frame or somewhere else that indicate how we grew up. Do you remember how terrible the phrase of your grandmother or mother was that if you don’t eat porridge, you will never grow up. But we ourselves became parents, and those horror stories are a thing of the past. Now we are coming up with new ones in order to make children sleep, eat well, so that they also grow and develop well.
Today I invite you to touch upon the issue of child growth indicators. Namely, let's talk about how much they should grow over a given period of time, what this indicator depends on and how it can be influenced.
What does growth depend on?
To begin with, I propose to look at what indicators are the norm in this matter. So, the most active increase in the growth of infants is observed in the first year of life. It is during this period that children grow by 25 or even more centimeters. During the 2nd year of life, the indicators decrease and an increase in the previous indicator by 8-12 centimeters is considered the norm. Next, children should gain 4-6 centimeters annually.
If you notice that the baby has grown less than 4 centimeters in the 3rd year of life, then this is a reason to contact an endocrinologist. In this case, you shouldn’t rely on chance and expect that it will catch up with everyone at a certain age. Of course, this could happen, but what if it doesn’t? If you miss this moment and do not contact specialists in time, then changing anything in adolescence will be extremely difficult, almost impossible. In most cases, doctors diagnose constitutional growth retardation. That is, these children experience a late onset of puberty. However, this diagnosis or problem does not require any additional manipulations; such children will catch up with their peers a little later, closer to 16-18 years. But at the same time, in some cases, additional studies may be prescribed to help identify growth hormone deficiency. This problem may be the result of heredity or problems in the endocrine system. Previously, children with low levels of this hormone were doomed; boys did not grow above 140 cm, and girls - 130 cm. However, now, thanks to modern medicine, the problem can be solved.
So, we have looked at what norms are acceptable and are not considered a reason for worry. Now let's talk about the factors that influence the increase in the indicator. So, the growth indicators of a baby, first of all, depend on heredity. As you yourself understand, if the baby’s mom and dad are short, then you shouldn’t expect the baby to grow 2 meters. Of course, there is a chance that he will take the genes of his grandparents or even great-grandmothers, but it is very low. Heredity is indeed very significant, but at the same time it is not the only thing that affects the growth of the baby.
Other factors include: proper nutrition, daily routine, rest and even the atmosphere in the family. As for the last fact, there are several interesting points. Short children occur not only in dysfunctional families, but also in families where children do not experience true love. Despite the fact that parents can take care of, feed, clothe the baby, buy expensive toys, but not feel true love for their child. This condition is called psycho-emotional stunting. As a result, growth growth in a baby who does not experience parental warmth and love is significantly slower. Well, let's further discuss in more detail other factors that are responsible for the normal increase in these indicators.
The effect of vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency on the risk of developing type 1 diabetes in children
According to modern concepts, vitamin D traditionally belongs to the group of fat-soluble vitamins; it is not actually a vitamin in the classical sense of the term, since it is not biologically active. Due to two-stage metabolization in the body, it is converted into an active hormonal form - 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D and has a variety of biological effects due to interaction with specific receptors localized in the nuclei of cells of many tissues and organs. In this regard, the active metabolite of vitamin D behaves like a true hormone, which is why it is called D-hormone. Moreover, following historical tradition, in the scientific literature it is called vitamin D [1].
Currently, an increasing number of studies indicate the role of vitamin D deficiency in the development of chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system, diabetes, and cancer. In most cases, the basis of the evidence base comes from epidemiological studies in adults. The effect of vitamin D deficiency on the development of chronic pathology in children and adolescents has been much less studied [2]. It is known that more sun exposure during childhood and early adolescence is associated with a reduced risk of developing multiple sclerosis [3].
Vitamin D deficiency increases the risk of developing autoimmune diseases, which include type 1 diabetes. In the pathogenesis of the development of the disease, the leading link is the destruction of beta cells by T-helper type 1 autoantibodies. In vitro, calcitriol (vitamin D) inhibits T cell proliferation and reduces the production of cytokines, T helper type 1 cells, IL-2 and IFN-γ, and consequently reduces the autoimmune inflammatory response [4, 6].
Purpose of the study: to study the content of the transport form of vitamin D - hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) in the blood serum of children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus and to assess the risk of developing the disease depending on the supply of it to the body in children.
Materials and research methods
The study included 44 children diagnosed with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus - 17 people under 7 years of age and 27 people from 7 to 16 years of age. Among the children with type 1 diabetes there were 18 boys and 26 girls. The control group of 40 people (25 boys and 15 girls) consisted of 15 people under 7 years of age and 25 people from 7 to 16 years of age. Patients with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus included in the study did not have significant differences in gender compared to the control group.
The level of vitamin D was assessed by the content in the blood serum of the transport form of the vitamin - 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D). Interpretation of the results of determining the level of (25(OH)D) was carried out in accordance with the recommendations of the International Society of Endocrinology (2011) and the recommendation of the European consensus: severe deficiency - level (25(OH)D) less than 10 ng/ml, deficiency - from 10–20 ng/ml, deficiency - 21–29 ng/ml, values > 30 ng/ml were considered normal [5].
Based on the results of the study, a database was generated in the MS Excel 2010 spreadsheet package, on the basis of which statistical data processing was carried out using statistical application packages using the statistical software package Microsoft OfficeExcel 2010, Statistica 6.0 (StatSoft, USA), IBM SPSS Statistics 20. The research results were processed by methods of descriptive and variation statistics (O. Yu. Rebrova, 2002). Descriptive analyzes were performed for all children included in the study. If the distribution of a characteristic was taken to be close to normal, then the arithmetic mean (M) and the standard error of the mean (m) were calculated.
For a comparative analysis of qualitative indicators in two groups of patients for one characteristic, the χ2 test and Fisher’s exact test were used (for small sample sizes). For comparative analysis of quantitative data, the nonparametric Mann–Whitney test (U) and the Kruskal–Wallis rank test (H test) were used.
The risk of developing the disease was assessed by determining the quantitative value (OR) with the calculation of its 95% confidence interval (CI) and calculating the significance of pairwise comparisons between groups (Fisher's test). When OR = 1, there was no connection between the compared factors (traits), when OR < 1, there was a negative connection, and when OR > 1, there was a positive connection between characteristics.
Results and its discussion
The results of determining the level of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D in the blood in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus and in healthy children are presented in Fig. 1.
A study of the level of vitamin D in the blood serum showed its low level in the vast majority of children both with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus and in the comparison group (95% and 72.5%, respectively), which indicates an insufficient supply of vitamin D in the population in general, which may be due to the peculiarity of the location of Krasnoyarsk in a zone of low insolation and the small number of sunny days throughout the year. At the same time, in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus, deficiency of vitamin D is significantly more common - in 59% and in 36% - insufficiency of vitamin D compared to the comparison group (12.5% and 60%, respectively), which indicates a more pronounced hypovitaminosis of vitamin D in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. The lowest values of vitamin D level in the blood serum were determined in preschool children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus - 19.75 ± 3.28 compared to healthy children of the same age, whose vitamin D level was 53.2 ± 9.94 . In schoolchildren, the difference in vitamin D levels was less significant: 21.82 ± 2.08 in children with diabetes mellitus and 31.28 ± 3.33 in healthy ones (Fig. 1).
Thus, it can be assumed that a deficiency in serum 25(OH)D may serve as one of the risk factors for the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus.
To test the effect of vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency in the blood on the risk of developing type 1 diabetes, the OR estimate was used - odds ratio (OR), to assess the significance of which a 95% confidence interval (95% CI) was used. Vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency were taken as a risk factor, and the development of type 1 diabetes mellitus was taken as an outcome.
In children with vitamin D deficiency, the risk of developing type 1 diabetes was 3.6 (OR), in children with vitamin D deficiency this figure was 5.9 (OR), therefore, the lower the concentration of vitamin D in the blood, the higher the risk of developing the disease diabetes mellitus type 1.
AA Ginde, JM Mansbach, CA Camargo (2009) in their study showed that while the peak incidence of viral infections, especially in the pediatric population, usually occurs in the winter months, when skin synthesis of vitamin D is insufficient, in individuals with levels 25(OH)D below 10 ng/ml increases the risk of developing an upper respiratory tract infection, regardless of the season.
An analysis of the incidence of onset of type 1 diabetes mellitus depending on the time of year found that most often children with newly diagnosed cases were admitted to the hospital in the spring, when, presumably, the level of serum 25(OH)D was minimal (Fig. 2).
Determination of the blood serum level of 25(OH)D in children with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus depending on the time of year and the onset of the disease showed that the majority of children with this diagnosis generally had a deficiency and insufficiency of its content in the blood without significant differences in depending on the season (Fig. 3).
The majority of children admitted to the hospital with the first symptoms of type 1 diabetes mellitus have metabolic decompensation and are admitted in a state of diabetic ketoacidosis of varying severity. The children included in our study are no exception. In Fig. 4 clearly shows that 81.8% of children were admitted with symptoms of ketoacidosis.
A study of the severity and severity of clinical manifestations of ketoacidosis depending on the body’s supply of vitamin D showed that the lower the concentration of vitamin D, the more severe the degree of ketoacidosis. Children with severe ketoacidosis (pH < 7) were 100% vitamin D deficient. With moderate acidosis (pH 7.0–7.15), vitamin D deficiency in the blood serum was 3 times more likely to be detected compared with deficiency (71, 1% and 21.4% respectively). In mild ketoacidosis, there was a predominance of children with vitamin D deficiency in the blood serum, with no significant differences in the comparison groups.
Conclusion
Thus, a study of the level of 25(OH)D in the blood serum showed the presence of insufficiency and deficiency of vitamin D in 84.5% of the examined children, while the frequency of detection of hypovitaminosis D in children with newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus significantly prevailed over the group of healthy children. The data obtained indicate the undesirable consequences of the lack of specific prevention of hypovitaminosis D in older age groups in increasing the risk of developing type 1 diabetes in individuals predisposed to it. When assessing the odds ratio, a relationship was revealed: the lower the concentration of 25(OH)D, the higher the risk of developing type 1 diabetes. The presence of deficiency and insufficiency of vitamin D not only contributes to the development of the disease, but also aggravates its course, which is consistent with literature data. For example, in a study by JD McNally, K. Leis, it was shown that 25(OH)D levels were lower in children with bronchiolitis or pneumonia admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit than in healthy control children or children with pneumonia. not requiring therapy in intensive care conditions [7]. Our study showed an association between the severity of clinical symptoms and the severity of ketoacidosis and low serum vitamin D25(OH)D levels, highlighting the need to adequately provide vitamin D to a growing child and prevent deficiency.
Literature
- Schwartz G. Ya. Vitamin D deficiency and its pharmacological correction // Russian Medical Journal. 2009; 17(7):477–486.
- Zakharova I.N., Yablochkova S.V., Dmitrieva Yu.A. Known and unknown effects of vitamin D // Issues of modern pediatrics. 2013; 12 (2): 20–25.
- Van der Mei IA, Ponsonby AL, Dwyer T. Past exposure to sun, skin phenotype, and risk of multiple sclerosis: case-control study // BMJ. 2003; 327:316.
- Holick MF Vitamin D: Physiology, Molecular Biology, and Clinical Applications. R. 867–881.
- Zakharova I. N., Maltsev S. V., Borovik T. E. Vitamin D deficiency in children of different ages in Russia // Pediatrics. 2014; 93 (2): 75–80.
- Ginde AA, Mansbach JM, Camargo CA, Jr. Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and upper respiratory tract infection in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey // Arch. Intern. Med. 2009; 169(4):384–390.
- McNally J. D., Leis K., Matheson LA, Karuananyake C., Sankaran K., Rosenberg AM Vitamin D deficiency in young children with severe acute lower respiratory infection // Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2009; 44(10):981–988.
N. Yu. Grishkevich*, 1, Candidate of Medical Sciences N. A. Ilyenkova*, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor E. P. Shitkovskaya*, Candidate of Medical Sciences S. I. Dmitriev** G. Yu. Strelnikov**
* FSBEI HE Krasnoyarsk State Medical University named after. prof. V. F. Voino-Yasenetsky Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, Krasnoyarsk ** Krasnoyarsk City Clinical Hospital No. 20 named after. I. S. Berzona, Krasnoyarsk
1 Contact information
DOI: 10.26295/OS.2019.12.59.002
The influence of vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency on the risk of developing type 1 diabetes mellitus in children / N. Yu. Grishkevich, N. A. Ilyenkova, E. P. Shitkovskaya, S. I. Dmitriev, G. Yu. Strelnikov For citation: Attending physician No. 6/2019; Page numbers in issue: 12-15 Tags: adolescents, children, vitamin D deficiency, autoimmune diseases
Proper nutrition
Children's diet should be balanced and rich in various vitamins and minerals. For example, their daily diet should include meat or fish, since this group of products is rich in protein. At the same time, he should eat several fresh vegetables and fruits every day. Carrots are considered especially healthy due to their beta-carotene content. However, it is worth remembering that in order for it to be better absorbed, you need to eat carrots with sour cream or butter. By the way, dairy products should also be present in the baby’s daily diet. After all, they are rich in calcium, and this is the basis for building a strong skeletal system.
Movement
There is a long-proven fact in medicine that children who spend more time outdoors grow many times faster. However, in addition to daily walks, the baby may be recommended to attend sports clubs. But when choosing a direction, give preference not to strength sports and wrestling, but to volleyball, basketball, and tennis. If you look at statistics, you can see one of a thousand short basketball players, which cannot be said about boxers.
Rest
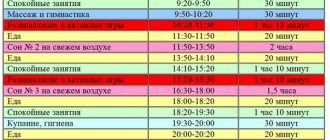
Remember how our grandmothers told us: “If you want to grow big, you need to eat porridge and sleep well.” No matter how funny it may sound, it is still true. It is believed that 70% of growth hormone is produced at night. That is, as you yourself understand, if the baby goes to bed late, sleeps poorly and wakes up often, then he will also grow poorly. What to do in such cases? The answer is very simple, set a daily routine for the baby, come up with a rule for the whole family: we go to bed no later than 21:00. Direct all your efforts to ensure that your little one falls asleep on time. This doesn’t require much: turn off the TV in advance, walks with friends and guests should end in the evening, no later than 20:00. Before going to bed, be sure to bathe your baby in comfortable, slightly cool water. If he demands, then feed him before bed, read a book or play some calm game. Such an evening will definitely bear fruit and give you and your baby a sound sleep, and as a result, good health.
Vitamins for growth and their description
When a child begins to lag behind his peers in growth, this most often frightens young parents. However, we have already figured out that in order for children to grow well, their daily routine must include: a balanced diet, rest, walks and/or sports. Let's find out in more detail which vitamins can be effective for the height growth of a 5-year-old child. To be fair, it is worth noting that these vitamins are contained in simple foods that we eat every day, and therefore they will be an effective means of accelerating the growth of older children, for example, 10-12 years old. And consuming them at a more mature age will help maintain the condition of the skin of the hands, face, hair, nails, skeletal system, and the entire body as a whole, in ideal condition. Let's find out which vitamins are considered most essential for our body:
- Vitamin A . We all know about its ability to maintain visual acuity and eye health. In addition, vitamin A is often used in cosmetology, as it helps to nourish and moisturize the skin. As for the process of increasing the “height” of the baby, then this vitamin has its own role. It occupies one of the most important positions in the formation of tissues and the production of growth hormone, and is also involved in the process of bone hardening.
- B vitamins . The following vitamins can influence the increase in the indicator: B1, B2, B6, B9, B12. A large number of vitamins of this group are found in: greens, nuts, legumes, grains, eggs, cheese, meat.
- Vitamin D takes an active part in the formation of bone cells. Promotes better and faster absorption of calcium. We get most of this vitamin from exposure to sunlight. However, our body can get this vitamin from certain foods, such as milk, egg yolks and fish oil.
- Calcium is the basis of the human skeletal system. In addition, its deficiency affects the growth rate of children. Be sure to include in your daily menu foods that are rich in calcium, for example: dairy and fermented milk, greens, etc.
- Iodine is the main element of the thyroid gland. The hormones it produces contribute to normal growth and development of the body.
Eating foods that contain all of these vitamins will help you keep up with your height growth goals. However, there is no need to suffer from day to day and measure out how much you need to eat of those other foods in order to replenish your daily supply of useful microelements. Modern pharmaceuticals offer a wide selection of all kinds of drugs, which already include the necessary dosage of certain groups of vitamins that will help accelerate the growth of the child. Let's look further at the most popular of them.
Vitamin A – retinol.
Discovery history and interesting facts:
As mentioned above, it was one of the first to open. This happened in 1913 by scientists observing two groups of mice. After a series of studies, they came to the conclusion that butter and the yolk of a chicken egg contain, in addition to protein, fat, lactose, starch and salt, some substance necessary for life. During their experiments, it was shown that mice receiving the above ingredients suffered from eye inflammation and diarrhea. And their condition was noticeably alleviated when natural butter, cod liver oil or chicken egg yolk were added to the diet.
Role in the body:
- retinol has a beneficial effect on vision - it ensures physiologically normal activity of the visual analyzer, participates in the synthesis of visual pigment in the retina, and in the perception of light by the eye;
- is a powerful antioxidant (slows down the aging process) - participates in redox processes, regulation of cell membranes;
— in the baby’s body, vitamin A promotes the growth of bone, cartilage and muscle tissue, the formation of subcutaneous fatty tissue;
- necessary for the normal functioning of the immune system - increases the barrier function of mucous membranes, increases the phagocytic activity of leukocytes.
The unit of measurement for the amount of vitamin A is IU (international units). 1 IU = 0.3 mcg
Daily requirement: children under 1 year – 0.5 mg (1650 IU); children from 1 year to 6 years – 1 mg (3300 IU); children over 7 years of age and adults 1.5 mg (5000 IU).
Simple vitamins (preparations and their descriptions)
Simple vitamins, like any other medicine, can be prescribed by a pediatrician, based on the age and condition of the baby’s body. For example, before the age of 1 year, doctors do not prescribe multicomponent vitamins, since for an infant this can be a very heavy load on the kidneys. However, the pediatrician’s only recommendation may be that infants take vitamin D. It is prescribed as a preventive measure for the development of rickets.
Older children are recommended to consume whole complexes that can replenish the daily requirement of microelements and minerals in the body. Such drugs can be divided into 2 subgroups:
- Simple - they contain exclusively calcium for children and vitamin D3, these include: “Complivit Calcium D3”, “Nycomed Calcium D3”, etc.
- Complex - they contain a wide variety of vitamins and minerals. Let's take a closer look at this group below.
Vitamin B5 – pantothenic acid.
Discovery history and interesting facts:
It got its name from the Greek word, which translated means “omnipresent”. And this is true, vitamin B5 is found in every tissue, in every cell of a living organism. Pantothenic acid performs important functions for the normal functioning of physiological processes. Pantothenic acid was first isolated in 1933 by scientists at the University of Texas at Austin. Using brewer's yeast as a model organism, they isolated a previously unknown nutrient. The essential function of pantothenic acid was determined in 1953 with the discovery of coenzyme A (coenzyme A or CoA). Vitamin B5 is a substrate for the body's production of CoA, without which our cells cannot feed and function properly. Therefore, sufficient presence of pantothenic acid in the body is a prerequisite for maintaining normal life functions.
Role in the body:
— as a structural component of CoA, vitamin B5 is involved in the metabolism of macronutrients: proteins, fats, carbohydrates, cholesterol and fatty acids;
- participates in the biosynthesis of hormones - steroid and sex hormones, growth hormone;
- actively participates in the formation of erythrocyte hemoglobin, histamine synthesis and antibody production;
— vitamin B5 is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters of the nervous system, especially important for the conversion of choline into acetylcholine.
Daily requirement: children under 1 year – 2 mg; adults – from 5 to 10 mg.
Vitamin complexes
The modern pharmaceutical market also boasts a huge selection of vitamins, the purpose of taking which is not only to increase growth, but also to strengthen the immune system and, in general, to maintain a small body.
The most popular complexes include:
- "Vitrum Calcium D3" is approved for use from 12 years of age.
- "Calcemin" is approved for children from 5 years of age.
- “Calcium D3 Classic” – from 3 years.
- "Multitabs Baby" is approved for use up to 1 year.
- “Multi-Tabs Baby Calcium+” – from 2 to 7 years.
- "Revital Calcium D3" - for children from 12 years old.
- "Unicap U" is allowed from 2-4 years.
Vitamin E – tocopherol.
Discovery history and interesting facts:
The year of discovery of vitamin E is considered to be 1922, when scientists Evans and Bishop published a report on their research into the causes of infertility in experimental animals. They concluded that such a disorder occurs in the body in the absence of a certain substance in the diet, which was called vitamin E.
When this vitamin was deficient in the diet of laboratory rats, males experienced a decrease in testosterone production, and females were unable to bear fruit. When their diet was enriched with foods rich in this substance (oil, oats and wheat), these disorders disappeared and fertility was restored.
In 1936, a substance was isolated that had the properties of vitamin E. Researchers named it “tocopherol” - from the Greek “tos” - childbirth, “phero” - to give birth and “ol” - the chemical designation of alcohol, which in terms of the chemical composition of vitamin E is.
Role in the body:
- first of all, tocopherol is a powerful antioxidant - it prevents the degradation of polyunsaturated fatty acids, protects cells from damage by free radicals - inhibits cell aging, improves their trophism;
— strengthens the walls of blood vessels, prevents the formation of blood clots;
- has a beneficial effect on reproductive function;
- considered the vitamin of youth and beauty - will improve the appearance of skin, hair and nails.
Daily requirement: children under 1 year – 5IU; adults – 10 IU.
Video
I suggest you watch a short video, an excerpt from a television program, which tells what causes stunted growth in children, and what parents should do when they notice such a problem in their child.
Surely, each of us has a first aid kit at home, but it’s unlikely that anything in there can be used for children. This is why many doctors recommend collecting a first aid kit for a newborn. In the first months after birth, these may be drugs that fight pain in the abdomen, for example: dill water for newborns or the drug Bobotik. In the future, the list of medications that should be kept at home will grow. So, for example, any first aid kit should contain antiseptic and antibacterial agents, a drug that lowers the temperature, etc. In addition, in addition to medicines, the first aid kit should include vitamin complexes that help babies develop correctly and according to standards.
Today we have discussed with you why some children may not catch up with their peers in height, and what needs to be done in this case. Of course, it is worth noting that it is under no circumstances recommended to self-medicate. If you have any suspicions, seek advice from a specialist, and your local pediatrician will be able to prescribe you the most appropriate option for both treatment and preventive measures, based on the general condition of the baby and its developmental characteristics.
Well, now it's your turn to share information. Tell us in the comments on the site if your child was lagging behind his peers in terms of growth, at what age it was diagnosed and what treatment was prescribed.