What's happening to mom
In the fourth week, external signs of pregnancy are not yet obvious. But the body is already actively restructuring. A woman may not be aware of her situation at this time, since the symptoms resemble the precursors of menstruation. By the end of the fourth week, pharmacy tests can already determine pregnancy.
Feel.
In the fourth week, signs of pregnancy become clearer. Increased production of progesterone provokes constipation and bloating. Frequent urge to urinate also causes discomfort. Early toxicosis may appear. Physiological sensations and emotional mood change:
- Mood swings.
A sharp change in mood from euphoria to apathy, causeless tearfulness, and sensitivity to words and reactions appear. Sometimes unreasonable fears appear. - Drowsiness and fatigue.
The body retains energy for restructuring, so even after rest and full sleep, the desire to sleep does not go away. - Changes in taste.
Habitual food can be disgusting or tasteless. At the same time, new unexpected addictions may appear. - Odor intolerance.
The urge to vomit from the aroma of your favorite perfume or the smell of familiar dishes is already a reason to buy a pregnancy test and check your suspicions. - Appetite.
A change in appetite can either increase or manifest as a complete refusal of food. - Chest pain.
In the fourth week, the mammary glands enlarge, causing pain. Nipples become especially sensitive. - Stomach ache.
The uterus stretches and increases in size, which can cause pain.
Changes in the body.
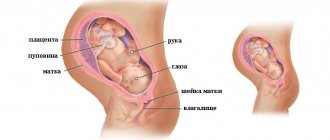
In the fourth week, active production of hormones and restructuring of the entire body continues. The fetus is already attached to the wall of the uterus and receives all the necessary nutrients from it. The formation of the placenta begins, which will take on the burden of fetal development from the twelfth week of pregnancy until the birth itself. Blood circulation in the mammary glands increases, the breasts prepare for the upcoming lactation.
External changes.
Significant visible changes occur in the breasts in the fourth week. Breast volume increases (sometimes by a size) within a week. A vascular network appears. The halo darkens and pigmentation may appear in other areas of the skin. The volume of the abdomen does not change and does not outwardly indicate an “interesting position.”
What happens to the embryo
In the fourth week, intensive cell division slows down, the division of the germinal disc begins, the formation of the child’s internal organs and external germinal organs.
Structure of the embryo.
The germinal disc is divided into germ layers (special layers of cells), which during development are transformed into certain groups of organs, systems and tissues of the child.
- The outer layer of cells (ectoderm). The cells of the outer germ layer form skin, hair, nails, teeth, eyes, nose and ears. The neural tube of the spinal cord and the entire nervous system of the fetus are formed from these same cells.
- The middle layer of cells (mesoderm). The cells of the middle layer are responsible for the development of the heart, blood vessels and circulatory system, the formation of muscle tissue, the formation of the kidneys, gonads and skeleton of the child.
- Inner layer of cells (endoderm). The organs of the respiratory and digestive systems, liver, lungs and bladder will be formed from the cells of the inner layer.
Extraembryonic organs.
In the fourth week of pregnancy, the amnion, chorion and yolk sac are formed. In the process of further transformation, the amnion will become an amniotic sac containing amniotic fluid. The bladder protects the embryo from damage and prevents the fetal tissue from drying out. At the same time, the umbilical cord is formed. The chorion transforms into the placenta. The cells of the placenta, with the help of chorionic villi, are embedded in the inner lining of the uterus. By the end of the week, the placenta begins to provide the fetus with oxygen, water, maternal antibodies and remove waste products. Starting from the twelfth week, the placenta will function as an independent organ. The yolk sac provides the embryo with a nutritional supply and begins to produce red blood cells.
It is important to note that the male genes of the embryo are responsible for the formation of extraembryonic organs.
What can be seen on an ultrasound
At 4 weeks of pregnancy, a tiny fertilized egg (blastocyst) will appear on the monitor in the form of a small anechoic round formation up to 5 mm in the uterine cavity.
A detailed examination allows you to see the yolk sac in the form of a ring-shaped hyperechoic formation up to 3 mm in diameter. It is he who, during the development process, will be the supplier of nutrients to the growing fetus. In the uterus, the doctor observes diffuse dilatation of blood vessels. This is a physiological response to the progressive increase in the embryo's needs for nutrients and oxygen.
The ovary contains a functioning corpus luteum, which produces the pregnancy hormone progesterone. Duplex mapping shows a decrease in the resistance index in the arterial vessels of the corpus luteum. There is an increase in the size of the uterus and the intensity of the echostructure.
Surveys
There are several ways to confirm pregnancy:
- Pharmacy test. He can already show two stripes, but a more accurate result is obtained closer to the end of the fourth week.
- Lack of menstruation. If your period does not start on the estimated date, you should wait another day or two to make sure there is a delay.
- Ultrasound. During the examination, you can already see the embryo (a point in the uterine cavity).
- Analysis. To reliably determine pregnancy, you can donate blood for hCG. The concentration of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) increases during pregnancy. A blood test will help confirm successful conception.
If pregnancy is confirmed, you can go to the antenatal clinic for an appointment with a gynecologist.
Ultrasound
of the fetus.
In the fourth week of pregnancy, indications for ultrasound examination may include:
- suspected ectopic pregnancy in the woman's history;
- acute pain in the lower abdomen or side;
- bloody issues;
- possibility of multiple pregnancy.
An ultrasound examination at an early stage can accurately show the site of attachment of the egg and promptly recognize an ectopic pregnancy. If symptoms are missed, the growing egg can rupture the fallopian tube, which is very dangerous. During a normal pregnancy, an ultrasound is not necessary. By the end of the fourth week, it is possible to determine only the fact of attachment of the fertilized egg to the wall of the uterus. The embryo is still too small, and it will not be possible to diagnose the child’s development. The baby's size at the fourth week is about 1 mm and weighs 0.5 g.
Laboratory diagnostics.
At the initial appointment, the gynecologist will collect the necessary data, conduct an external examination, and prescribe a number of tests. For up to 12 weeks, the following is prescribed:
- general urine analysis;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- blood test for glucose;
- testing for HIV and viral hepatitis B and C;
- hCG analysis;
- blood clotting test;
- smears for flora and cytology;
- testing for TORCH and infections.
A complete list of necessary tests is issued by the doctor after registration.
Ultrasound at the 5th obstetric week of pregnancy
There are standard timings for performing ultrasound screening during pregnancy. For the first trimester it is 10-13 weeks, for the second – 20-24, for the third – 32-34 weeks. But in some cases, ultrasound diagnostics can be performed not only during these periods, but also earlier. Quite often, women are prescribed an ultrasound at 5 weeks of pregnancy. This is the period when the embryo can already be visualized and its heart begins to beat.
Why is an ultrasound performed at 5 weeks of pregnancy?
Ultrasound at the 5th obstetric week of pregnancy is performed for the purpose of:
- Confirm pregnancy. At 5 weeks, the pregnancy test should already show two lines, although rare errors do occur. To 100% confirm pregnancy, ultrasound screening can be performed.
- Confirm correct attachment of the fertilized egg. It must be fixed in the uterus, otherwise (for example, when the fertilized egg is fixed in the fallopian tube), an ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed.
- Assess the vital activity of the embryo in the fertilized egg.
- Detect multiple pregnancies.
- To refute the possibility that the increased level of hCG to which the pregnancy test reacted is not a consequence of a pathology of the female reproductive system.
- Identify threats of miscarriage.
As a rule, at such an early stage, ultrasound is prescribed for those women who:
- Previously had a caesarean section. In this case, you need to look at how the chorion (which will later become the placenta) is attached. Close attachment to a uterine scar or attachment directly to a scar can become a serious threat of miscarriage.
- Previously suffered miscarriages.
- Previously had a frozen or ectopic pregnancy.
- We became pregnant through the IVF procedure.
Alarming symptoms
During pregnancy, a number of problems may arise with the adaptation of the embryo in the womb, which lead to rejection of the fetus from the walls of the uterus. In the early stages, it is also important not to miss an ectopic pregnancy.
If the pregnancy proceeds normally, then menstruation will not begin. In the case where the zygote is not implanted into the endometrium (uterine lining) due to defects in conception, hormonal imbalances or complications, menstruation will come. In such cases, they do not talk about miscarriage. In most cases, the fact of conception goes unnoticed. Bleeding becomes a cause for concern if pregnancy is confirmed.
Discharge.
Normally, discharge during pregnancy should remain light, homogeneous, odorless (a slight sour odor is allowed), as before conception. Only their number can change. If the discharge has a strong unpleasant odor, becomes abundant, changes color and consistency, you should consult a doctor. The cause of such changes may be sexually transmitted infections.
Brown discharge.
Scanty brown discharge may be the result of an egg attaching to the endometrium. The body creates a special protective plug from mucous secretions. It closes the cervical canal of the uterus and serves to protect the fetus from infections and bacteria. The plug normally comes out before childbirth.
Bloody issues.
Bloody discharge during a confirmed pregnancy is always an alarming sign. Red or scarlet discharge may indicate bleeding. The reasons for this may be the threat of miscarriage, problems with the placenta, or injury to the mucous membrane. Prolonged, scanty discharge accompanied by pain may be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy.
"Period".
If pregnancy is established, menstruation cannot occur. Bloody discharge is a sign of complications:
- The body rejects the nonviable fetus.
- Hormonal disbalance. Lack of progesterone or high levels of androgens.
- Frozen pregnancy. Infectious diseases in the first weeks can provoke fetal death.
Stomach ache.
In the fourth week of pregnancy, abdominal pain may be associated with changes in the female body. The uterus begins to grow and stretch the ligaments, this provokes nagging pain in the lower abdomen. A malfunction of the digestive system can cause bloating, constipation and discomfort. Such pain is not a pathology. Increasing acute pain is a possible symptom of a threatened miscarriage, ectopic or frozen pregnancy.
Temperature.
In the first months of pregnancy, a woman's temperature may rise slightly. This is explained by the body’s reaction to the changes taking place and the increased production of hormones. A temperature of 38 degrees or higher may indicate a cold or viral disease. Self-medication during pregnancy is unacceptable. If necessary, the doctor will select approved medications that will not harm the baby.
Signs and sensations
What happens in the 4th week of pregnancy? Despite the serious “restructuring” in the body, some women may not experience any special sensations. Some expectant mothers note an uplift in mood and a surge of strength. But there are also those who, under the influence of growing progesterone, develop toxicosis, decrease their ability to work and brain activity, and manifest emotional instability.
The rate at which your figure changes depends not only on your build, but also on your physical fitness. If your abdominal muscles are strong, they will keep your stomach flat for a long time, and in the 4th week of pregnancy you will remain slim and fit - up to 8-12 weeks.
Having abs and good muscle tone reduces the likelihood of stretch marks, but does not guarantee their absence. The problem of skin stretching is related to its elasticity, rate of weight gain and other factors.
At a later stage, when the baby in the womb puts more pressure on your internal organs, you can provide abdominal support with the help of a special bandage. It continues to be worn after childbirth by cesarean section, as well as to speed up the restoration of the figure.
Breast size continues to increase in the 4th week of pregnancy, while soreness may begin to decrease, unless we are talking about implants. What to do if you had breast surgery before pregnancy? What complications to expect? Will I be able to breastfeed my baby? In most cases, mammoplasty does not cause problems. The combined or axillary method of implant placement does not interfere with full lactation. After the birth of a child, it is better to “develop” the breasts not with your hands, but with the help of a breast pump. At the end of feeding the baby, the shape of the breast is usually completely restored. If the nipple-areolar complex was affected during implantation, breastfeeding is impossible, which the surgeon warns the woman about before surgery.
The uterus at 4 weeks of pregnancy looks like a small apple and gradually enlarges, putting pressure on other pelvic organs. Frequent urination is possible, vaginal discharge is more abundant, normally transparent, without a strong odor. If bloody inclusions appear, consult a doctor.
Already in the early stages, the formation of edema is possible. In this case, consultation with a specialist is also necessary. You cannot limit the amount of fluid you consume on your own. Lack of water can lead to stagnation of bile, the formation of stones (with cholelithiasis), and constipation.
Nutritional Features
Proper nutrition during pregnancy provides mother and baby with all the necessary microelements and vitamins. A balanced menu, taking into account the costs of bearing a baby, will help a woman maintain her figure and give everything the new body needs. In the fourth week of pregnancy, the embryo develops internal organs and systems and begins to receive all vital substances from the mother. Now a woman’s nutrition means caring for her baby. The diet should contain foods high in important microelements and vitamins:
- Iron.
To maintain hemoglobin at a normal level, a sufficient amount of this element is necessary. Hemoglobin carries oxygen to tissues, and a decrease in its concentration in the blood leads to fetal hypoxia (oxygen starvation). Iron is found in red meat, fish, eggs (yolk). - Protein.
It is necessary for the growth and development of the fetus. Protein is the building material of embryonic cells. It is found in fish, meat, nuts, and seeds. - Fats.
These substances are also involved in the construction of cells and are a source of energy. It is important to combine animal and vegetable fats in your diet. - Calcium.
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes a change in bone tissue with a decrease in its mineral density. To compensate for these losses, you need to consume enough calcium. It is also necessary to take into account the formation of the baby’s skeleton. Calcium can be obtained from dairy products, almonds, and leafy greens. - Complex carbohydrates.
Complex carbohydrates include whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. Carbohydrates maintain energy balance. If the body does not have enough energy, proteins necessary for the development of the fetus go into the “furnace”. - Alimentary fiber.
Fiber is needed to normalize intestinal motility. Eating enough vegetables, herbs and fruits will ensure normal functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. - Water.
It is important to drink enough clean water. - Vitamins.
Now there is a large selection of ready-made vitamin complexes for pregnant women. Your gynecologist will help you choose the right one.
While maintaining correct eating habits, you should exclude or limit some foods while pregnant:
- Alcohol.
Any alcoholic drinks must be avoided for the entire duration of pregnancy. This is especially important in the first trimester, when the embryo is actively developing and the nervous system and brain are forming. - Canned food.
For long-term storage, a large number of preservatives, stabilizers and other chemical products are used. - Salt.
It is advisable to reduce the consumption of salty foods as much as possible. Salt retains water, puts additional stress on the kidneys and leads to swelling.
What will an ultrasound show at 5 weeks of pregnancy?
An ultrasound in the fifth week of pregnancy will show a fertilized egg with an embryo inside (with a normal, standard course of pregnancy). Also, based on the scan results, it will be possible to judge the attachment of the chorion and the location of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. If the fertilized egg has not reached the uterus and is fixed, for example, in the fallopian tube, an ultrasound will show this, and the woman will be diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy.
An ultrasound at the 5th week will show the baby’s heart and will allow you to evaluate the frequency of its beating. Already at such a short period of time, it will be possible to suspect possible pathologies of the fetal heart, although it is difficult to make an unambiguous conclusion about the presence/absence of a heart defect.
An ultrasound will show how actively the fetal neural tube, which will later become the baby’s bone marrow, is developing.
Embryo movements
To assess the viability of the fetus and its well-being in the womb, its heart rate is assessed.
Norms and decoding
There are several main parameters of fetal development that are taken into account when interpreting ultrasound results:
- embryo size – standard value is about 4 mm;
- yolk sac size – standard value 4-5 mm;
- the size of the fertilized egg - according to the norm, it should be approximately 1 cm;
- Heart rate is normal from 70 to 100 beats/min.
Ultrasound can also be used to estimate the weight of the embryo - it should be approximately 4 g.
Ultrasound results are not the only information that should be taken into account when making a diagnosis. It is also important to evaluate blood tests, urine tests, and the results of other additional studies.