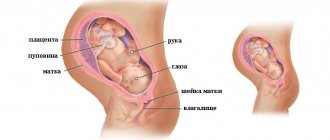
What's important at 38 weeks
The 38th week of pregnancy has arrived - an alarming waiting period for the expectant mother. At this stage, the pregnant woman should be prepared for the fact that she can be taken to the maternity hospital at any moment. If you have not yet packed your bag for the maternity hospital
, now is the time to take care of it. Also collect all the necessary documents: you need to take your passport, medical insurance, exchange card and birth certificate to the maternity hospital. Place all your documents in one folder or file and carry them with you in your purse, especially when traveling.
How you feel
At 38 weeks pregnant, you want to give birth as quickly as possible. The weight, clumsiness and constant ailments are very tiring, and I can’t wait to hold my baby in my arms as quickly as possible.
Before birth, the abdomen must drop down: the fetal head is placed in the pelvic cavity, and the baby assumes its final position. Now the uterus does not interfere with the movement of the diaphragm and does not put so much pressure on the internal organs, so it is easier for you to breathe, and heartburn only bothers you if there are errors in your diet. However, due to the downward displacement of the baby's head, the load on the pelvic bones increases. Therefore, you may experience pain in this area, in the sacrum and in the back of the leg. And pressure on the bladder causes frequent urge to urinate.
By the 37th – 38th week of pregnancy, the mammary glands enlarge even more. A network of small veins shines through the skin, the areolas darken even more noticeably, and “nodules” of the sebaceous glands are clearly visible on them. During this period, the nipples become very sensitive, and if you touch them, the muscles of the uterus contract. It's time to prepare your breasts for feeding your baby. Gently massage your nipples with a rough towel to prevent cracks from forming on them in the future.
Belly size at 38 weeks
The abdominal circumference at the 38th week of pregnancy is approximately 92-98 cm. The fundus of the uterus rises to the costal arches - this is the highest level of the fundus of the uterus.
The belly at 38 weeks of pregnancy can be truly huge: the baby has taken up all the available space and continues to gain weight. It is becoming increasingly difficult for him to move, since the uterus at 38 weeks of pregnancy is squeezing the body from all sides. At this stage, important improvements occur in the little person’s body, the fluff – lanugo and vernix lubrication covering the baby’s skin – partially or completely disappears, facial features become more and more refined
. At 38 weeks of pregnancy, the baby takes its place in the mother’s pelvis and is getting ready to be born.
Photo of a three-dimensional ultrasound at 38 weeks of pregnancy
Interesting Facts
| Options | Indications |
| Time from conception | 36 weeks |
| Period by month | 38 weeks |
| What month | 9 |
| Dimensions and weight of the fetus | 500 mm, 3000 g |
| Uterus dimensions | VDM - 34-37 cm |
| Pregnant weight | Gain from the beginning of pregnancy is 10-15 kg; over the last week 200-300 g |
Your baby is the size of
Leek
500mm Size
3000 g Weight
Most babies are born between 38 and 40 weeks. So the birth is already near. You're probably tired, and the best thing you can do for yourself is to get regular sleep. Don't sacrifice your sleep for other things, go to bed on time. After all, a child can decide to be born at any time. And it is important for you to be fully armed, full of strength and positive energy. Our calendar will tell you what you need to be prepared for in the thirty-eighth week of pregnancy.
What worries a pregnant woman at 38 weeks
During this period, expectant mothers may feel signs of labor
: training contractions, pain in the hip area and sacrum, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of menstrual pain.
Mucous discharge from the vagina at 38 weeks of pregnancy
may also indicate impending labor.
Expectant mothers often worry: how to identify contractions and distinguish them from false ones
? Experts recommend staying calm, because you definitely won’t miss the birth. Real contractions are more noticeable and painful than training contractions; they are repeated periodically, increasing their frequency and intensity. To distinguish false contractions from real ones, change your position: stand up, walk around the room, lie down. If the contractions stop, don’t worry, they are most likely false.
Weight gain at 38 weeks of pregnancy ranges from 8.6 kg (with a BMI of more than 26) to 14.5 kg (with a BMI of less than 19.8). To calculate your individual weight gain at 38 weeks, use the pregnancy weight gain calculator.
Possible problems
Difficulties do not bypass women who are in the last stages of pregnancy. Therefore, expectant mothers need to know what they may encounter and what to do in a particular situation.
- Edema at 38 weeks of pregnancy. In the last weeks, almost all pregnant women swell, even if there were no problems with edema before. And here you need to watch yourself with special care so as not to miss the development of gestosis. Therefore, if you have increased blood pressure and nausea, be sure to consult a doctor. And to slightly correct the appearance of swelling, reduce the amount of salt and liquid you drink during the day (but not too much, because dehydration is also dangerous). It will also be useful to lie down and sit down more often so that your legs are slightly elevated.
- Nausea at 38 weeks of pregnancy can develop for several reasons. For example, if the expectant mother overeats too much, she will not only begin to feel sick, but her stomach may also empty. Another reason is increased blood pressure. Therefore, it is advisable that you have a blood pressure monitor in your home. If you feel sick quite often, it is advisable to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
- Diarrhea at 38 weeks of pregnancy. Some pregnant women experience this phenomenon shortly before giving birth. It is believed that in this way the intestines are cleansed in preparation for childbirth. It is for the same reason that the expectant mother does not feel hungry before giving birth. However, it happens that diarrhea occurs due to an intestinal infection. Then it is accompanied by weakness, nausea, abdominal pain, and the temperature may rise. In this case, you need to contact your doctor. The main thing is to avoid dehydration, which occurs with prolonged intestinal upset.
What does a baby look like at 38 weeks?
At 38 weeks, the baby is about the size of a melon.
At 38 weeks, the Baby’s height is about 47 cm, and his weight is approaching 3 kg. Your Baby is actively preparing for childbirth, namely:
- Baby's lungs are ready to work independently. Thanks to the formation of surfactant, the lungs acquire the ability to expand after birth, and the numerous alveoli - to breathe. Surfactant is also needed so that after the Baby’s first breath, his alveoli, having barely expanded, do not shrink;
- The baby begins to move lower and lower into the pelvic area. The pelvic ring, thanks to relaxin, a special hormone in the mother’s body, has become much softer, and therefore, moving lower and lower, the Baby does not get stuck. This undeniably positive phenomenon also has a downside: When the mother lifts heavy objects or even stands for a long time in public transport, the baby can “ram” the pliable pelvic ring and be born earlier than expected;
- With your help, your baby will also learn one more important skill that he will need during birth - relaxation. Your ability to consciously relax and achieve a state of peace in a short time, almost anywhere, will allow your Baby to learn to quickly calm down in order to rest and gain strength before the next move forward.
Medical observation
At the 38th week of pregnancy, the doctor will listen to the baby’s heart, measure your blood pressure and prescribe a general urine test. If the indicators are normal, there is no reason to worry. But if the pressure is elevated or protein is detected in the urine, there may be a pregnancy complication that requires hospitalization.
Ultrasound at 37–38 weeks of pregnancy is carried out only according to indications - for example, if it is necessary to clarify the location of the fetus in the uterus, assess the degree of maturity of the placenta, the amount of amniotic fluid, or exclude the entanglement of the child in the umbilical cord. During the examination, the doctor will determine the size of the baby, its heart rate, as well as the relationship between the individual parts of the baby’s body.
Useful advice for an expectant mother
Perhaps your attitude towards parenthood is still more emotional than conscious.
That is, you are happy that you will have a Baby, but you have little idea what trials you will have to face after he is born. Or: focused on your current situation, you don’t “think” about what will happen next. This condition is typical for many expectant mothers (and often fathers as well), although it does not in the least hinder the development of parental qualities. Parental qualities:
- this is unconditional love for a child, that is, the ability to accept him as he is;
- this is caring for his physical and mental well-being;
- this is patience and the ability to notice new things in the child’s behavior and appearance;
- this is the desire to understand the child and provide him with care;
- the desire to care for and protect him;
- the ability to rejoice in his small victories and support him in what is not yet going well.
Parenting qualities don't happen overnight. Perhaps you and your partner already have the qualities listed (and many others). But it may also be that it will take a lot of time for them to manifest themselves. If even before birth you begin to treat your Baby as a member of the family, then after birth you will be able to quickly understand his needs and respond in accordance with what the baby needs.
Fetus. Development at 38 weeks
Fetal development at the 38th week of pregnancy
The 38th week of pregnancy has arrived - a period when the baby can be born at any time, and it will be in a timely manner. Urgent (full term) birth can occur from the 38th to the 42nd week of pregnancy. The preliminary date of birth (PDD) is in the middle of this period, exactly at 40 weeks of the obstetric period. According to statistics, only 4% of women in labor give birth exactly on the date of birth, repeated births often occur 1-2 weeks earlier, the first ones often last until 41-42 weeks.
The fetus is already completely ready for life outside the mother, the process of preparation for the last push: childbirth is completed. This is a difficult stage for both the woman and the unborn child, requiring strength and teamwork from them. It is advisable that it takes place at the moment when mother and baby are most ready for it.
At this time, the baby is already becoming quite large. Its weight can range from 2.7 to 4 kg, its body length can be from 47 to 52 cm. The placenta, which provides nutrition to the fetus, has begun to age, so every week the baby gains only about 100 g and grows by 1 cm.
The baby is already very cramped in his mother’s tummy, the amount of amniotic fluid has decreased, almost the entire space of the uterus is occupied by the fetal body. This does not allow him to be as active as before and sets him up for an imminent birth.
By this stage of pregnancy, all internal organs and systems have completed intrauterine development and are ready to immediately begin work after birth. Most of them work regularly at low speed, training and accumulating the necessary elements, others are waiting for their time: the respiratory system is waiting for the first cry of the baby to fill with oxygen, the reproductive system will sleep until the onset of puberty, the immune system is ready to repel the first attack of bacteria and microbes from the outside world that will be encountered during childbirth.
The baby has mastered all the necessary unconditioned reflexes, according to which the neonatologist will assess his condition after birth:
- protective reflex. When a newborn baby bumps his nose into something, his nervous system commands his head to turn to the side;
- support reflex and automatic gait. Of course, the baby will not be able to walk yet, but if he is held in a vertical position, he will pull his legs towards his tummy, but if the legs touch the support, the nervous system will command the body to straighten. If you tilt the baby forward, he will begin to instinctively move his legs;
- grasp reflex. If you press on a newborn's palm, he will clench his fist;
- Perez reflex. When running a finger along the spine from the tailbone to the neck, the newborn will scream and express dissatisfaction;
- Moro reflex. A loud, sharp noise forces the baby to spread his arms to the sides and unclench his fists;
- sucking reflex. Having felt the presence of any object in the mouth, the baby begins to intensively wet it;
- Kussmaul reflex. When the skin near the lips is irritated, the newborn reflexively turns its head in search of the chest;
- hand-mouth reflex . When you simultaneously press the baby's palms, he opens his mouth.
These reflexes are a major contribution to adaptation to the new world; they play an important role during the first months of life, after which they are gradually replaced by conscious reflexes. Their appearance is the result of the development of the nervous system: the main command and analytical center of the body.
At this time, the nervous system has completed the stage of intrauterine development, but does not stop improving. Cells of the brain and peripheral nervous system continue to be covered with myelin (a substance that improves the conduction of nerve impulses and protects neurons from damage).
Every minute, numerous nerve connections are formed in the baby’s head, and this process will continue for many years. The cerebral cortex does not stop changing. New grooves are formed across its entire surface, which merge into convolutions. The baby is actively preparing to explore the world around him. To do this, he has the most important points for receiving information: sense organs.
At this stage, the baby's vision is very imperfect. It can only distinguish between light and dark, further development of visual perception will occur after birth during the first years of life.
The baby’s hearing, on the contrary, is perfectly developed. The baby can recognize his mother's voice, her heartbeat and other sounds that he often hears. Immediately after birth, the baby will be a little disoriented. A huge amount of noise surrounding him will merge into a single concert. Only over time will the baby learn to isolate individual sounds from the cacophony, and even later, associate them with a specific object or event.
The taste and smell of the fruit are well developed at this stage. They are interconnected, so when the belly feels the taste of amniotic fluid (they change depending on what the mother eats), his sense of smell remembers this information. Now he distinguishes between sweet and bitter, sour and spicy.
An extensive network of nerve endings is spread throughout the baby’s body, allowing him to receive information about surrounding objects by touch and respond to touch. So, if the hand feels a touch, the fingers will instantly try to grab the irritant, and the leg will push away.
The role of the nervous system in the life of every person cannot be overestimated; it opens up the possibilities of cognition and learning, controls the processes of adaptation to changes in external factors, monitors the work of the whole body as a whole, etc.
At this stage of pregnancy, the nervous system is already involved in all processes in the fetal body. It is she who sends signals to the main glands: the pituitary gland, pancreas, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus and adrenal glands, stimulating them to produce the necessary hormones necessary to start or inhibit all processes in the body.
Immediately after birth, the baby will have to learn to eat in a new way (eat breast milk or formula), so now the digestive and urinary systems are trained to perform their duties.
Every day, the baby swallows amniotic fluid, which is successfully processed in the stomach into useful and unnecessary substances. Sugars and other necessary elements are sent to the bloodstream, from where they are distributed throughout the body. Unnecessary fluid is removed from the body by the kidneys through the urinary system; solid particles (epithelial cells, particles of vernix, etc.) remain in the intestines, where they are stored in the large intestine using peristalsis. After birth, all these elements will leave the body in the form of original feces (meconium). It will be black or dark green.
By the 38th week of pregnancy, the respiratory system is in a state of full readiness, awaiting birth. The lungs, bronchi, trachea and upper respiratory tract are ready for active activity and are fully mature.
Sexual development of the fetus at this stage is also completed. In girls, the labia minora are closed by the labia majora, the genital slit is closed. In boys, the testicles have either descended into the scrotum or are in close proximity. Both options are normal; sometimes prolapse occurs in the first months of life without concomitant pathology.
Externally, the fetus completely corresponds to a newborn child: a proportionate plump body, pinkish skin with a small number of folds, a small amount of original fluff (it will disappear in the first days of life), a sufficient amount of subcutaneous fat. The skeleton is formed and consists of 270 bones. This is more than that of an ordinary adult, but it is necessary that the child can be safely born and grow until the age of 25, when the process of bone fusion is completely completed.
All of the above achievements of the little man are important and necessary for a normal life. Immediately after birth, the baby will undergo its first exam. The neonatologist will evaluate him on the Apgar scale and give him the first points.
What is the Apgar score?
At 1 and 5 minutes of life outside the mother, the baby is assessed by a neonatologist using a special table that indicates his condition. A total of 5 characteristics are studied, each of which can receive a maximum of 2 points:
- color of the skin;
- pulse;
- grimaces;
- muscle tone;
- reflexes.
By adding up the data on these indicators, the doctor receives a result from 0 to 10 points. Both estimates (1 minute of life and 5 minutes of life) are included in the documents that the mother will receive upon discharge. A score of 7 to 10 points is considered good. The assessment is necessary to decide on the necessary medical procedures and diagnose possible complications or pathologies.
This first exam of the baby is very important, because it sums up intrauterine development. And at the 38th week, the fetus can already pass it perfectly, because everything is ready.
Position of the fetus in the uterus
95% of babies at this stage are in a head down position (cephalic presentation). This is the most favorable position for birth, as the largest part of the body (the head) appears first. If there are no medical contraindications, childbirth takes place naturally.
In the case of a pedunculated or longitudinal position of the fetus (about 5% of all pregnancies), a medical commission is most often convened to determine the possibility of a natural birth or a cesarean section.
Movements
At the 38th week of pregnancy, the fetus is quite large and takes up almost all the free space in the uterus. It is already very difficult for him to twist and turn, so the movements become less frequent. Normally, the expectant mother should feel about 10 movements in 12 hours. In a calm position, 1 movement in 30 minutes.
An overly active or, on the contrary, calm baby is a reason to seek medical help.
Tests and studies during pregnancy
Visiting a doctor monitoring pregnancy: once a week.
Weighing, measuring blood pressure, measuring the height of the uterine fundus, listening to the fetal heartbeat. General urine test - before each visit to the doctor. Indicates the quality of kidney function.
Dopplerography (a study that allows you to evaluate blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, placenta and main vessels of the child) - 33-34 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation, according to indications . The study allows you to find out whether the child is getting enough oxygen and nutrients.
Cardiotocography (CTG, synchronous recording of fetal heartbeats and uterine contractions) - 33-34 weeks after the first day of the last menstruation, according to indications. The child’s condition is assessed and intrauterine hypoxia is excluded.
Necessary studies and analyzes
OAM and UAC are already familiar tests for any pregnant woman. A general urine test shows whether there is an inflammatory process in the woman’s urinary tract or gestosis. A complete blood count is necessary to assess the amount of hemoglobin. This is important, because indirectly this parameter indicates whether the pregnant woman and her baby have enough iron. A lack of iron in the body is fraught with the development of iron deficiency anemia.
If there are certain indications, the expectant mother will be prescribed additional tests and examinations. For example, fetal cardiotocography will show how the child’s heart functions and whether he is developing hypoxia.
Good to know
A treacherous loop. Umbilical cord entanglement
Childbirth: when to go to the maternity hospital and how will I give birth? Contraction Guide
When to go to the maternity hospital? In an ambulance or on your own?
Secret language. What do doctors talk about during childbirth?
How can you tell when labor is starting?
How do you know when you're about to give birth? Harbingers: 9 signs of impending birth
All texts for pages about mother and baby were kindly provided by RAMA Publishing - these are chapters from the book by Svetlana Klaas “Your Favorite Little Man from Conception to Birth”, reviewer Irina Nikolaevna Kononova, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor of the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Ural State Medical Academy (Ekaterinburg).
Mother. Sensations and changes in the body, preparing for childbirth
Condition of the mother at the 38th week of pregnancy
At the 38th week, most women begin to feel better than in previous weeks. Several factors contribute to this:
- the stomach begins to sink lower, giving the stomach and lungs more freedom. It becomes easier to breathe and eat. These changes are not observed in all women; in some, uterine prolapse may begin later, and in some cases before the birth itself; less often, the uterus does not change its location at all before the baby is born;
- from the 38th week the main period of gestation is completed, the expectant mother is less worried about maintaining the pregnancy, because if the baby is born, he will be capable of normal life activities;
- appetite decreases. By eating less and not feeling the constant desire to chew, the parent is less likely to experience discomfort from the gastrointestinal tract, although nausea and stool upset may appear immediately before childbirth;
- the amount of energy increases. The desire to prepare everything for the arrival of the baby comes with redoubled force, the expectant mother feels an emotional uplift and a surge of strength. But against the backdrop of a large belly and the difficulties associated with it, fatigue quickly sets in and fatigue sets in.
At the 38th week, the female body still experiences discomfort from the enlarged uterus, which contains a fairly large baby. Periodically, unpleasant sensations are felt:
- in back. The spine is under severe stress, responding with pain after a long walk or work;
- in the legs. Cramps and pain may appear or continue to cause discomfort. Quite often, it is at this time that varicose veins appear. It is recommended to carefully monitor the condition of your legs, consult a gynecologist in a timely manner about the need to wear compression garments or use medications and cosmetics;
- lower abdomen. Unpleasant sensations can be caused by gradual separation of the bones, pressure on the bladder and intestines. If a pregnant woman experiences periodic pain in this area, it is worth contacting a gynecologist for advice. When the abdominal prolapse begins, the pressure on the bladder and pelvis increases. The number of trips to the toilet increases, and there is a feeling of a constant desire to pee. This is normal if urination is not accompanied by pain or pain. In this case, you need to contact a gynecologist, having first passed a urine test;
- in the chest. Those expectant mothers whose belly has not begun to descend continue to experience discomfort in the lungs, stomach, and diaphragm. Also, in some cases, discomfort is caused by the preparation of the breast for lactation: it swells, becomes covered with a network of blood vessels, and colostrum is released.
At the 38th week, the expectant mother increasingly thinks about the issue of impending birth. Some women are worried that they will not be able to understand in a timely manner that the process has begun, others worry that it will be too painful, and still others think about possible complications and difficulties.
If there is insufficient awareness and preparation for what is coming, a pregnant woman may experience severe stress, which will not benefit either the mother or the fetus. It is recommended that if you have questions related to the approaching birth, you should remain calm and positive, and dispel fears with knowledge: consult a gynecologist, read the information below.
Harbingers of childbirth
Childbirth is a complex natural process that requires a lot of strength from the female body. In order for it to proceed correctly, nature has provided for a number of changes that occur in the female body shortly before day X. In some cases, changes begin in advance, 1-2 weeks, in others - immediately before childbirth: 1-2 days.
It is quite difficult to guess when a particular woman will start giving birth, judging by the harbingers, so the expectant mother should not panic when she discovers this or that sign; it is better to carefully consider the procedure.
At the 38th week, a woman may notice the appearance of precursors of labor:
- prolapse of the abdomen. In preparation for childbirth, the female body adjusts, the uterus moves lower into the pelvic area, reducing pressure on the lungs and stomach, but increasing pressure on the pelvic organs;
- increased frequency of urination. The uterus puts more pressure on the bladder, increasing discomfort and making trips to the toilet more frequent;
- increased frequency of training contractions . Non-painful contractions become more frequent at week 38 and may cause inconvenience. If they do not occur with the same frequency and do not cause pain, this is a normal phenomenon, training before childbirth;
- decreased appetite. During the birth of a new life, it is important for the body not to be distracted by extraneous processes. Hormonal levels reduce a woman’s desire to eat so that the digestive system is not overloaded with work, taking a lot of energy;
- a sharp decrease in weight up to 1.5 kg. Excess fluid leaves the body, the amount of food intake decreases - this leads to a decrease in body weight;
- increased bowel movements, diarrhea. Usually these precursors appear immediately before childbirth, 1-2 days. If a woman notices the appearance of causeless stool disorder, it is recommended to strengthen control over her well-being in the coming days;
- “Nesting syndrome” is a popular name for the behavior of women before childbirth. Many expectant mothers have a strong desire to clean up the whole house in order to prepare it for the baby;
- shortening of the cervix. This harbinger can only be seen by a gynecologist or obstetrician during an examination. For the fetus to be born, the cervix needs to shorten and open. During the first birth, most often, there is a slow shortening at first, followed by an opening. The second and subsequent births are characterized by the simultaneous occurrence of both processes.
These signs are called precursors of childbirth; depending on the characteristics of a particular woman, they can appear both 2 weeks before day X and immediately at the beginning of the birth process. Any option is considered normal.
Childbirth, when to go to the hospital
How to understand that contractions have begun
Childbirth at the 38th week occurs quite often, especially in multiparous women. The expectant mother should understand what signs should help her get to the emergency room of the maternity hospital as quickly as possible:
- constant abdominal pain that does not go away at rest, gradually intensifying;
- increased training contractions, the appearance of pain. The abdomen turns to stone at regular intervals;
- the baby is quiet, does not knock at rest or on the left side for 60 minutes;
- aching, persistent pain in the back (lower part). The pain can be localized to one point or spread to the entire lower body. If the discomfort does not subside while lying down, you need to go to the maternity hospital;
- a feeling of pressure in the thighs with pain, aching pain in the pubis. It may seem to a woman that the pelvic bones are actively moving in different directions;
- vomiting, intestinal cramps, diarrhea or frequent bowel movements along with other signs of labor are a signal to immediately go to the maternity hospital;
- rupture of amniotic fluid. A woman may feel a pop in the area of the uterus, after which a noticeable amount of fluid flows out of the vagina. From this moment on, the woman should not perform any hygiene procedures and immediately call an ambulance or go to the maternity hospital by car, while trying not to sit, but to lie down.
Having noted the appearance of one or more signs of labor, the best decision would be to go to the maternity hospital, where an obstetrician-gynecologist will examine you in the emergency room and refer you to the maternity ward or pregnancy pathology department to identify the cause of what is happening.
What is the difference between training contractions and real ones?
Quite often, at the 38th week, primiparous women are worried about the question: “How to distinguish training contractions from real ones?” In some cases, training movements of the uterus bring a woman not only discomfort, but also pain, so a pregnant woman may be afraid to miss an important time. We would like to reassure you that it is almost impossible to confuse real contractions and training ones. There are several signs that will help you calm down and clearly understand what exactly is happening:
- periodicity. Training contractions do not have a specific rhythm of occurrence; approximately the same period of time passes between real contractions, which is constantly decreasing. When giving birth for the first time, you can go to the maternity hospital when the interval between contractions reaches 15 minutes with the duration of abdominal tone up to 2 minutes; for repeated births (especially after a short period of time after the previous birth: up to 5 years), it is worth going from the very beginning of labor;
- abdominal tension. During training contractions, only part of the abdomen tenses: top, bottom, during childbirth - the entire surface of the abdomen becomes stone, this is accompanied by painful sensations;
- the ability to influence unpleasant sensations. During a training contraction, you can reduce its intensity: rest, drink water, take a walk; during childbirth, the intensity of the pain increases, the duration of the contraction increases and cannot be manipulated to reduce sensations, the woman should try to breathe through the contraction correctly, but the pain will not go away completely.
What to do if labor begins at 38 weeks
If a woman realizes that labor has begun, she needs to call an ambulance or go to the maternity hospital by car, taking the necessary things with her. First of all, she must have a complete set of documents in her hands:
- maternity passport (+copy);
- compulsory medical insurance/voluntary medical insurance policy (+ copy);
- exchange card issued in hand at the antenatal clinic;
- insurance certificate of the state pension fund;
- birth certificate (if already received in consultation);
- referral to the maternity hospital (if any);
- agreement with the maternity hospital or doctor (if any).
With your documents, take a bag with permitted items to the delivery room. Please note that different maternity hospitals may have their own prohibitions on personal belongings of women in labor. It is advisable to collect a package with things for childbirth in advance, guided by the rules of the selected maternity hospital.
If a woman’s water has not broken, the intensity of contractions is low: about 4-5 per hour, then the pubic area can be shaved. At 38 weeks, it can be very difficult to do this on your own, so it’s a good idea to ask your loved ones for help.
In maternity hospitals there is no single decision on this issue; in some, shaving is not considered mandatory, according to new research; in others, they are guided by the need for hair removal during surgical interventions.
It is advisable to choose clothes for a trip to the maternity hospital according to the principle of “what is easier to take off and fold.” In the emergency room, the woman will be completely undressed, so as not to waste time changing clothes and folding clothes, it is better to take care of a small amount in advance. It’s good if someone close to you comes to the maternity hospital with the woman in labor, who can take unnecessary things home.
Features of fetal development
At this time, the child turns out to be completely ready for life outside the mother’s belly. All organ systems function fully. If a woman continues to bear the fetus, then no significant changes in its development will occur. The baby will simply continue to grow in length and gain weight. At this time, the baby weighs 3 kg or more, and his height is on average 50 cm. Every day his body weight increases by another 30 g.
The baby's skin became pink and smooth. Lanugo and vernix have almost completely disappeared.
The baby's first stool (meconium), which is dead skin cells, has formed in the baby's intestines. As a rule, it comes out after the baby is born. However, there are situations when the baby has bowel movements while still in the womb. In this case, the amniotic fluid becomes greenish in color, and the baby itself will be covered in green mucus at birth.
If a woman is carrying a male child, by this time his testicles have already descended into the scrotum. This is a very important point, so after the baby is born, the doctor will definitely check this fact.
Visiting an obstetrician-gynecologist
Visiting a doctor at the 38th week of pregnancy
At the 38th week of pregnancy, a scheduled appointment with a gynecologist is possible. On the eve of the meeting, it is necessary to undergo tests, directions for which were issued at the previous appointment:
- general blood analysis;
- general urine analysis;
- blood test for antibodies (for women with negative Rh factor);
- biochemical blood test (for medical reasons);
- blood sugar test (for medical reasons).
Also, before the meeting, it is necessary to do a fetal cardiotocography (CTG), and transfer the results to the doctor.
At the appointment, the gynecologist will conduct the usual tests:
- will measure general indicators of a woman’s health: body temperature, blood pressure, heart rate;
- weigh the pregnant woman and calculate the weight gained since registration:
- use a soft meter to measure the volume of the abdomen and the height of the fundus of the uterus;
- listen to the fetal heartbeat using a stethoscope.
Having assessed the test results, CTG, and data obtained as a result of the examination, the doctor will draw a conclusion about the current condition of the expectant mother and baby. He may suggest a chair-based examination to assess the condition of the cervix.
At the end of the appointment, based on the data received, the doctor can set a date for the next meeting or issue a referral for hospitalization, if there are medical indications.
Ultrasound
At the 38th week of pregnancy, a routine ultrasound is not performed. An additional ultrasound examination is possible if there is a suspicion of pathology or to decide on the option of delivery (natural birth or cesarean section).
If desired, a woman can have an ultrasound scan for a fee to ensure that the pregnancy is progressing well.
Uterus and belly
At the 38th week of pregnancy, the uterus may be at a height of 35-36 cm from the symphysis pubis if the abdomen has begun to descend, or at 36-38 cm if the process of abdominal descent is not observed. The fundus of the uterus is located at a height of about 16 cm from the navel.
Women who have begun the process of abdominal prolapse note a change in its shape. The navel, which previously looked up, may now be directed straight or slightly downward. The shape of the abdomen depends on the position of the fetus: if the baby is upside down, then most often the stomach resembles the shape of a drop; if the baby is legs down, a strong prolapse is possible in one or several parts of the abdomen.
At the 38th week of pregnancy, there remains a risk of stretch marks; the skin of the abdomen is very stretched, so you should continue to constantly monitor its condition and lubricate it with the cream recommended by the gynecologist for stretch marks.
Discharge, bleeding, menstruation
Normally, at the 38th week of pregnancy, there may be more discharge than a week ago and small clots of mucus may appear. In this case, the bulk of the discharge should be light or milky in color, smooth in consistency, and practically odorless.
A change in the color of the discharge to green, yellow or gray (with a strong unpleasant odor) is a signal for an urgent consultation with a gynecologist. This indicates the presence of a vaginal infection (most often thrush). There is very little time before the birth; it is necessary to try to protect the fetus as much as possible while passing along the paths. While the baby is in the womb, he is safe, but infection can occur during birth. It is advisable to carry out treatment as early as possible to reduce the risk of infection.
If a woman notices the appearance of red, brown or pink discharge, she should immediately seek advice from the nearest maternity hospital. Red, pink or brown discharge may indicate the onset of labor or the presence of pregnancy pathology. Both options require the woman to be under medical supervision.