Home | About us | Delivery | Advertisers | Login | Registration
- Medicines
- dietary supplementsVitamins
- Categories from A to Z
- Brands from A to Z
- Products from A to Z
- Medical equipment
- beauty
- Child
- Care
- Honey products appointments
- Herbs and herbal teas
- Medical nutrition
- Journey
- Making medicinesStock
Pharmacy online is the best pharmacy in Almaty, delivering medicines to Almaty. An online pharmacy or online pharmacy provides the following types of services: delivery of medicines, medicines to your home. Online pharmacy Almaty or online pharmacy Almaty delivers medicines to your home, as well as home delivery of medicines in Almaty.
my basket
Apteka84.kz is an online pharmacy that offers its customers medicines, medicinal and decorative cosmetics, dietary supplements, vitamins, baby food, intimate products for adults, medical equipment and thousands of other medical and cosmetic products at low prices. All data presented on the Apteka84.kz website is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical care. Apteka84.kz strongly recommends that you carefully read the instructions for use contained in each package of medicines and other products. If you currently have any symptoms of the disease, you should seek help from a doctor. You should always tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the medicines you take. If you feel you need further help, please consult your local pharmacist or contact our GP online or by telephone.
© 2021 Pharmacy 84.
Instructions for use
Azithromycin is a semisynthetic antibiotic with a bacteriostatic mechanism of action. Accumulating in the human body, it begins to act bactericidal, that is, destroy the cells of bacteria that cause the disease. The drug is available in several forms and in various dosages:
- tablets of 250 and 500 mg;
- capsules of 250 and 500 mg;
- suspension of 100 and 200 mg per 5 ml;
- injection .
for the treatment of children under 12 years of age . It is available in powder form for home preparation. Each package contains a bottle of medicinal powder, a plastic syringe for administering medication to patients with difficulty swallowing and children who cannot drink solid medications, a 5 ml measuring spoon and instructions for using Azithromycin suspension for children.
The pediatrician prescribes Azithromycin for children for sore throat, tonsillitis, bronchitis, pneumonia and a number of other common diseases . The dosage is chosen based on the child’s weight. Children weighing over 45 kg are prescribed capsules or tablets with a dosage of 250 mg, and up to 45 kg - syrup.
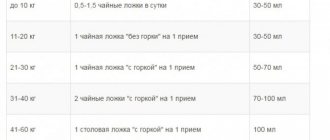
Dosage of the drug according to the patient's weight.
| Weight (in kg) | Dosage in solution 100 mg per 5 ml (in ml) | Dosage in solution 200 mg per 5 ml (in ml) |
| 5 | 2,5 | – |
| 6 | 3 | – |
| 7 | 3,5 | – |
| 8 | 4 | – |
| 9 | 4,5 | – |
| 10-12 | 10 | – |
| 12-24 | – | 5 |
| 25-34 | – | 7,5 |
| 35-44 | – | 10 |
| 45 or more | – | 12,5 |
In case of a serious illness, the doctor increases the dosage and chooses a different regimen for taking the medicine (stepwise, longer and with larger doses of the medicine). Duration of therapy is from 3 to 5 days.
How to take the drug. The suspension for children, like other forms, is taken once a day 1 hour before meals or 2 hours after. It is better to take the medicine at the same time. If an appointment is missed, doctors recommend resuming the missed appointment and repeating it after 24 hours.
- To prepare the syrup, boiled water at room temperature is poured into a bottle with powder up to the mark indicated on the bottle and the solution is shaken.
- It is recommended to use the suspension within 5 days from the date of preparation.
- prepared preparation before each use .
- After use, the spoon or syringe is washed and wiped dry.
- The drug is washed down with water, rinsing the mouth from any remaining medication.
- For the correct dosage and ease of administration, children under 3 years of age are administered the drug with a special measuring syringe.
Interaction with other drugs and other types of interactions
Azithromycin should be administered cautiously to patients with other drugs that may prolong the QT interval.
Antacids. When studying the effect of concomitant use of antacids on the pharmacokinetics of azithromycin, overall no changes in bioavailability were observed, although peak plasma concentrations of azithromycin decreased by 25%. Azithromycin and antacids should not be taken at the same time.
Cetirizine. In healthy volunteers, when azithromycin was co-administered for 5 days with cetirizine 20 mg at steady state, no pharmacokinetic interaction phenomena or significant changes in the QT interval were observed.
Carbamazepine. In a pharmacokinetic interaction study in healthy volunteers, azithromycin did not show a significant effect on plasma levels of carbamazepine or its active metabolites.
Cyclosporine. In a pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers receiving an oral dose of azithromycin 500 mg/day for 3 days followed by a single oral dose of cyclosporine 10 mg/kg, a significant increase in the Cmax and AUC0-5 of cyclosporine was demonstrated. Therefore, caution should be exercised when using these drugs together. If concomitant use of these drugs is necessary, monitor cyclosporine levels and adjust the dose accordingly.
Oral anticoagulants such as coumarin. In a pharmacokinetic interaction study, azithromycin did not alter the anticoagulant effect of a single 15 mg dose of warfarin administered to healthy volunteers. In the post-marketing period, there have been reports of potentiation of the anticoagulant effect after simultaneous use of azithromycin and coumarin-type oral anticoagulants. Although a causal relationship has not been established, frequent monitoring of prothrombin time should be considered when prescribing azithromycin to patients receiving coumarin-type oral anticoagulants.
Digoxin and colchicine. Concomitant use of macrolide antibiotics, including azithromycin, and P-glycoprotein substrates, such as digoxin and colchicine, has been reported to result in increased serum levels of P-glycoprotein substrate. Therefore, when azithromycin and digoxin are used concomitantly, the possibility of increased digoxin concentrations should be taken into account and drug serum levels should be monitored.
Methylprednisolone. In a pharmacokinetic interaction study in healthy volunteers, azithromycin did not show a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of methylprednisolone.
Terfenadine. Pharmacokinetic studies have not reported interactions between azithromycin and terfenadine. In some cases, the possibility of such an interaction cannot be completely excluded, but there is no specific data on the presence of such an interaction.
Theophylline. Azithromycin did not affect the pharmacokinetics of theophylline when azithromycin and theophylline were administered concomitantly to healthy volunteers. The combined use of theophylline and other macrolide antibiotics has sometimes resulted in increased serum theophylline levels.
Zidovudine. Single doses of 1000 mg and multiple doses of 1200 mg or 600 mg of azithromycin had little effect on the plasma pharmacokinetics or urinary excretion of zidovudine or its glucuronide metabolites. However, azithromycin administration increased the concentrations of phosphorylated zidovudine, a clinically active metabolite, in mononuclear cells in the peripheral circulation. The clinical significance of these findings is unclear, but may be useful for patients.
Macrolide antibiotics can enhance the effect of theophylline, terfenadine, warfarin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, triazolam, digoxin, ergotamine and cyclosporine. Azithromycin has no significant interaction with the hepatic cytochrome P450 system. It is believed that the drug does not have the pharmacokinetic drug interactions characteristic of erythromycin and other macrolides. Azithromycin does not cause induction or inactivation of hepatic cytochrome P450 due to the cytochrome metabolite complex.
Ergot. Given the theoretical possibility of ergotism, simultaneous administration of azithromycin with ergot derivatives is not recommended.
Pharmacokinetic studies have been conducted on the use of azithromycin and the following drugs, the metabolism of which largely occurs with the participation of cytochrome P450.
Didanosine. When daily doses of 1200 mg of azithromycin were coadministered with 400 mg of didanosine per day in six HIV-positive volunteers, there was no effect on the steady-state pharmacokinetics of didanosine compared with placebo.
Rifabutin. The simultaneous use of azithromycin and rifabutin did not affect the plasma concentrations of these drugs. Neutropenia has been observed in patients taking azithromycin and rifabutin concomitantly. Although neutropenia has been associated with the use of rifabutin, a causal relationship with concomitant use with azithromycin has not been established.
Atorvastatin. Concomitant use of atorvastatin (10 mg per day) and azithromycin (500 mg per day) did not cause changes in atorvastatin plasma concentrations (based on the HMG CoA reductase inhibition assay). However, post-marketing cases of rhabdomyolysis have been reported in patients taking azithromycin with statins. Cimetidine. In a pharmacokinetic study of the effect of a single dose of cimetidine on the pharmacokinetics of azithromycin, taken 2 hours before dosing with azithromycin, no changes in the pharmacokinetics of azithromycin were observed.
Efavirenz. Concomitant use of a single dose of azithromycin 600 mg and efavirenz 400 mg daily for 7 days did not cause any clinically significant pharmacokinetic interaction.
Fluconazole. Concomitant use of a single dose of azithromycin 1200 mg does not change the pharmacokinetics of a single dose of fluconazole 800 mg. The total exposure and half-life of azithromycin did not change with simultaneous use of fluconazole, but a clinically insignificant decrease in Cmax (18%) of azithromycin was observed.
Indinavir. The simultaneous use of a single dose of azithromycin 1200 mg does not cause a statistically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of indinavir, which is taken at a dose of 800 mg 3 times a day for 5 days.
Midazolam. In healthy volunteers, simultaneous use of azithromycin 500 mg per day for 3 days did not cause clinically significant changes in the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam, which was administered as a single dose of 15 mg.
Nelfinavir. The simultaneous use of azithromycin (1200 mg) and nelfinavir in equilibrium concentrations (750 mg 3 times a day) causes an increase in the concentration of azithromycin. No clinically significant side effects were observed; therefore, there is no need for dose adjustment.
Sildenafil. In normal healthy male volunteers, there was no evidence of an effect of azithromycin (500 mg daily for 3 days) on the AUC and Cmax of sildenafil or its main circulating metabolite.
Terfenadine. Pharmacokinetic studies have not reported interactions between azithromycin and terfenadine. In some cases, the possibility of such an interaction cannot be completely excluded, but there is no specific data on the presence of such an interaction. Triazolam. Co-administration of azithromycin 500 mg on day 1 and 250 mg on day 2 with 0.125 mg triazolam in healthy volunteers did not significantly affect all pharmacokinetic parameters of triazolam compared with triazolam and placebo. Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. Co-administration of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole double strength (160 mg/800 mg) for 7 days with azithromycin 1200 mg on the seventh day did not have a significant effect on the maximum concentrations, total exposure or urinary excretion of trimethoprim or sulfamethoxazole. Azithromycin serum concentrations were consistent with those observed in other studies.