When we talk about herpes, we most often mean human herpes simplex viruses type 1 and 2. The same ones that cause us trouble with regular “colds” on the lips. However, today scientists know much more than two types of herpes virus infection. They vary in both contagiousness and prevalence among people. For example, diseases caused by human herpes virus type 6 (HHV-6) are as common as infections caused by herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2; it is also sometimes mistakenly called human herpes simplex virus type 6. It must be said that in the modern world, perhaps, there is not a single community, tribe or other society where this type of herpes has not been discovered. However, most people do not even suspect that they are carriers of this type of virus. We will talk about the features of herpes virus type 6, its manifestations and risks for children in this article.
- Symptoms of herpes type 6 in children
- Features of therapy
- Prevention
Herpes type 6 belongs to the group of viruses with which humanity has coexisted for thousands of years, but knows little about them. Until recently, herpes was almost not studied, since these microorganisms were not considered dangerous to human health, unlike the flu or the coronavirus currently raging in the world. However, herpes can also cause a lot of trouble for a person. The discovery of herpes type 6, which we will consider in this article, occurred relatively recently and, in some way, by accident. In 1986, American biochemists in Nevada studied the blood of AIDS patients. Doctors were interested in infections that were in the blood of patients and could be dangerous for patients. An unknown virus was discovered in some of the biomaterial. After two years of research, they were classified as herpesviruses. They were sometimes called herpes simplex virus type 6, but this is not an accurate wording. The virus was actively studied, but very often showed a different clinical picture of the disease. Scientists were perplexed: there is one virus, but its manifestations vary. And only in the 21st century, or more precisely in 2021, with the development of technical diagnostic methods, it was decided to divide type 6 herpes into two types. It was noted that with a similar structure, subtypes of herpes type 6 differ in a number of characteristics. So the first type of herpes type 6, or HHV-6A, is the cause of various disorders in the nervous system of adult patients, but the second subtype (HHV-6B) is a factor in the appearance of infantile roseola.
Symptoms of herpes type 6 in a child
Herpes virus type 6 in children mainly manifests itself as roseola infantum, which was often previously mistaken for another infectious disease, rubella. They are indeed very similar in symptomsii.
What are the main symptoms of childhood herpes type 6?
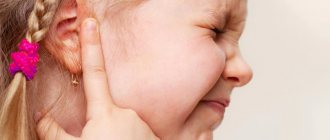
It should be noted that those at risk are primarily babies over 4 months old. At this age, an active child may suddenly, seemingly without reason, develop a fever and last up to five days. Then profuse rashes appear all over the baby's body. This rash, although it occupies a significant part of the child’s skin, is usually not accompanied by itching and does not cause much concern to the little patient. Parents are more afraid of this virus than their children. It is not always possible to diagnose the cause of rashes and fever. Sometimes, a herpes infection can be mistaken for measles, enterovirus infection or allergies. Moreover, when a rash appears, the child becomes lethargic, capricious, and may lose appetite. You can also observe enlargement of the lymph nodes in the baby. The rash lasts from several hours to several days. Pediatricians always recommend that if such young children have a fever, immediately contact a specialist. By the way, often herpes can occur without any rash at all. An accurate diagnosis can only be made after a series of tests.
Manifestations of the disease depending on the type of herpes virus
Herpes simplex virus type 1
The most common variant of herpetic infection, which occurs with frequent relapses. Causes the development of so-called “colds” on the lips and/or stomatitis.
Skin lesions
Usually the skin around the lips and wings of the nose is involved, less often - the cheeks, forehead, ears, external genitalia and other areas.
Within one or two days or simultaneously with the rash, swelling, redness, burning and itching of the skin appears. Then painful reddish tubercles appear, turning into small bubbles with transparent contents. After 3–5 days, the blisters open, and in their place crusts form, falling off after a few days.
Sometimes weakness, fever, headache occur, and appetite decreases. On days 3–5 of illness, nearby lymph nodes usually become enlarged.
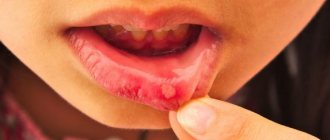
Damage to the oral mucosa (stomatitis)
Children aged 6 months to 3 years are most often affected. The disease begins acutely with an increase in body temperature to 39–40°C and a disturbance in general well-being (moody, lethargy, drowsiness).
Bubbles with transparent contents appear on the red and swollen oral mucosa, which quickly open to form erosions. Due to pain and damage to the mucous membrane, the child has difficulty swallowing (drooling occurs) and refuses to eat.
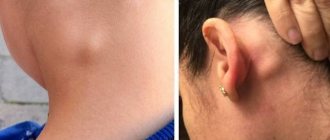
A few days after the onset of the disease, the lymph nodes in the neck become enlarged.
Herpes simplex virus type 2
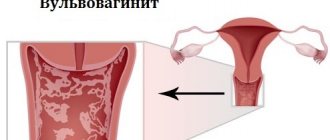
Affects the external genitalia. Manifestations of the disease and rash are similar to herpes simplex virus type 1. Almost always the disease occurs with a disturbance in general well-being.
The rashes are located:
* In girls - on the labia minora and majora, inner thighs, vaginal mucosa or in the perineum.
* In boys - on the foreskin, scrotum, in the urethra and further spread to the mucous membrane of the bladder.
Herpes virus type 3 - varicella-zoster
Causes development:
* Chickenpox is a childhood infection that occurs during primary infection. Body temperature rises. A rash appears on the skin and mucous membranes in the form of bubbles with transparent contents without any specific favorite place. Recovery occurs in 10–14 days.
* Shingles is the result of a relapse of the disease. Painful and itchy characteristic herpetic rashes appear on one side of the body along the nerve affected by the virus. Body temperature often rises and general well-being is disturbed.
Read more about chickenpox and herpes zoster.
The fourth type is Epstein-Barr virus
Primary infection may not manifest itself at all, or the symptoms may resemble a cold.
With weakened immunity, infectious mononucleosis develops:
* The virus first affects the oral mucosa - a sore throat develops.
Symptoms of intoxication occur weakness, poor appetite, fever.
* The pathogen spreads throughout the body, rushing to the lymph nodes, liver and spleen (the places of reproduction of B-lymphocytes) - leading to their increase.
* Possible disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract (diarrhea, vomiting) and the occurrence of jaundice (due to liver damage).
Infectious mononucleosis: take care of the liver and spleen!
The fifth type is cytomegalovirus
A child can become infected in utero from the mother if she suffered an acute infection during pregnancy. There are usually no external manifestations after birth. However, serious consequences develop: hearing loss, decreased intelligence, speech impairment and others. The severity depends on the period at which the infection occurred.
Acquired infection: from the mother - at the time of birth or in the first days of life, later - from peers or adults. The disease occurs asymptomatically or in the form of ARVI (with weakened immunity), sometimes the lymph nodes become enlarged.
The same cytomegalovirus.
Types six and seven - roseola infantum
Infantile roseola develops. The first to appear is high fever , which lasts for three days.
After body temperature normalizes, a pink-red rash The rash does not itch, and after a few days it disappears without a trace. The disease is usually mild and leaves no consequences.
A mysterious childhood disease - roseola rosea or the “sixth disease”.
Complications that may be associated with herpes type 6
Unfortunately, HHV-6B is not always limited to fever and rash during the initial infection. More serious consequences are also possible:
- meningoencephalitis;
- myocarditis;
- fulminant hepatitis;
- thrombocytopenic purpura;
- mononucleosis-like syndrome;
- various pneumonias.
In addition, at a high temperature, and it can suddenly exceed 40 degrees, there is a risk of seizures and febrile convulsions. Convulsions suffered at this age can subsequently provoke epilepsyiv.
Herpesvirus in children and its types
A child can be infected with the human herpes virus (HHV) from birth, but the symptoms of this pathology appear much later, when his immunity weakens. To date, medicine has carefully studied 5 varieties of this infectious disease:
- HSV-1 is herpes simplex virus type 1. It manifests itself as a cold on the lips, a blistering rash on the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose.
- HSV-2 is genital herpes, transmitted sexually, to children - in the womb or during the birth canal. It appears as a rash on the genital mucosa.
- HHV-3 causes chickenpox and shingles.
- HHV-4 - Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). It causes the development of serious diseases; it can cause viral hepatitis, meningitis, and cancer.
- HHV-5 is a cytomegalovirus. Causes cytomegaly. The salivary glands and lymph nodes undergo pathological changes, and in severe cases, internal organs (liver, kidneys, lungs).
Herpes type 6, just like types 7 and 8, still raises many questions among scientists. But herpes of this type still remains the most studied. It is divided into two groups - 6A and 6B. The first can provoke nerve disease in a small child, and also cause multiple sclerosis in the future (a little proven fact). The second causes fever and skin rash in childhood (sudden exanthema, roseola).
Features of therapy for herpes virus type 6 in children
As in the case of HSV 1 and HSV 2, today there are no drugs that can completely rid a person of herpes virus type 6. As a rule, having had type 6 herpes, a child acquires immunity and the ability to suppress the activity of the virus. However, the virus continues to exist in the human body.
During the period of illness, the doctor prescribes symptomatic treatment, which reduces discomfort for the child and eases the course of the disease.
Complex therapy includes antipyretic drugs, which are prescribed if the temperature of a small patient rises above 38.5 degrees, and antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs. Considering the age of the child, and most often we are talking about children aged 4 months to three years, before using any drugs you should carefully read the instructions. For example, popular antiviral drugs from the acyclovir group, according to the instructions, have age restrictions and are not recommended for children under three years of age. (acyclovir tablets are approved for children from 1 year of age). Drugs that are approved for use from the first day of life include VIFERON Suppositories. The suppository contains human recombinant interferon alpha-2b, as well as vitamins C and E. This medicine helps the child’s body cope with the infection more quickly. The course of treatment is five days, VIFERON Suppositories in a dosage of 150,000 IU are used once every 12 hours.
But rashes on the baby’s skin can be treated with VIFERON Gel. The product is applied three to five times a day. This drug can also be used at a very early age.
Treatment of herpes in children
It is impossible to eliminate the herpes virus from the body, so the goal of treatment is to reduce its activity , eliminate symptoms by activating the immune system, achieve stable remission and prevent complications.
The most effective medicine against most manifestations of the herpes virus in children is the substance acyclovir. Treatment uses both oral and local medications. Source: I.F. Barinsky, L.M. Alimbarova, A.A. Lazarenko, F.R. Makhmudov, O.V. Sergeev Vaccines as a means of specific immunocorrection for herpetic infections // Questions of Virology, 2014, pp. 5-11
A comprehensive treatment regimen for acute herpetic infection includes:
- antiviral-antiherpetic drugs - tablets, injections and ointments - based on acyclovir;
- surface antiseptics for the prevention of secondary bacterial infections;
- immune stimulants – herbal and interferon derivatives;
- multivitamins and vitamins in therapeutic doses;
- antipruritic antihistamines;
- antipyretics;
- hepatoprotectors – in case of severe intoxication;
- diet therapy with sufficient amounts of protein and exclusion of foods that are sources of arginine.
In severe general condition, bed rest is recommended. Only a doctor can decide how to treat herpes in a child.
Health care
Treatment of a dangerous virus should begin with a visit to a qualified specialist. This is especially true for parents of children under one year of age. A child can be treated both conservatively and with folk remedies.
Treatment of herpes type six is based on an integrated approach. The doctor treats the virus with:
- Drug treatment (prescription of antiviral drugs); vitamin therapy;
- Symptomatic treatment (relevant for reducing temperature);
- proper care.
- Treatment of children is carried out:
Drug therapy
Antiviral drugs (gevisos, acyclovir, vectavir) used to treat aphthae;
- Immunostimulating drugs (immunoglobulins, Cytotex), especially when treating children under 1 year of age;
- Interferon preparations (Rebif, Reafferon), the main purpose of which is to stop the spread of infection in the blood;
- Antipyretic suppositories and mixtures (liquid treatment is recommended for children under 1 year of age, and mixtures and syrups for older children).
- You can get rid of unpleasant symptoms not only with traditional treatment. You can also cure a sick child using ancient folk recipes. Remember that treatment must be carried out under close medical supervision.
Grandmother's wisdom
Treatment is carried out using:
fir oil (indispensable in the treatment of flaking and itching);
- earwax (this remedy allows you to quickly heal ulcers);
- alcohol compresses (this type of treatment is suitable for the sixth type of disease);
- table salt (this product is used to treat wounds).
- Treatment with folk remedies has virtually no contraindications. However, it should be remembered that it is not recommended to treat children under one year of age in this way, as there is a risk of developing an allergic reaction.
Treatment of pathology consists in proper compliance with hygiene requirements. To cure herpes quickly, it is important to pay attention to preventive measures.