To make an appointment with a doctor
Calling a pediatrician to your home
Our doctors
Our prices
January 27, 2021
Author of the article: Stanislav Vladimirovich Synebogov
Otorhinolaryngologist of the highest category, Candidate of Medical Sciences, member of the European Rhinological Society (European Rhinologic Society)
Experience: 25 years
+ Make an appointment
Ear problems are common in childhood. Parents may notice that children do not respond to calls to them, have difficulty understanding speech, and complain of pain in the ears. But don't panic right away. In most cases, the cause is not pathology, but an ordinary cerumen plug in a child. What is she? And how to recognize it?
Causes
The causes of wax plugs in children can be very different. Violation of the ear's natural cleansing of wax secretions usually occurs due to increased production of secretions. The glands work more actively. This is possible against the background:
- foreign body entry;
- otitis;
- frequent mechanical cleaning of ears with cotton swabs;
- anatomical features of the auditory organs;
- decreased ventilation of the auditory canal due to frequent wearing of a hearing aid;
- too dry air.
Prevention
Carrying out regular preventative measures will minimize the likelihood of wax plugs. It is necessary to keep the ear canals clean and regularly remove secretions. Cotton swabs should not be used. Such household items can compact wax and clog the ear canal, damage the upper layers of the epidermis and cause inflammation.
Cosmetic cotton swabs are most often used after water procedures: washing hair, washing in the shower, taking a bath. A cotton swab is not able to dry the ears, but warm boric alcohol accelerates the evaporation of water. It is enough to drop 4-5 drops of the product into each passage, then lower your head and dry your ears with a towel, napkin or cotton sponge, wrapping the material around your little finger.
A cosmetic cotton swab can be used for delicate cleaning; you can wipe only the outer part of the ear canal, without going deeper than 4 mm. The vestibule should be cleaned using gentle circular movements.
If you suspect an ear plug, the right decision would be to visit the hospital. Specialists from the Diamed medical institution will perform an otoscopy, assess the condition of the canal, and, if necessary, remove the ear plug. Such procedures are safe, performed in a comfortable environment, and do not cause complications.
What types of ear plugs can there be?
How to remove wax plug from a child? First you need to determine its type, size and consistency. Secretion accumulations can be:
- plasticine-like;
- hard and dry;
- pasty.
In the first case, the deposits resemble plasticine. They are viscous, sticky, brown in color. Solid deposits are usually dense and dirty gray or almost black in color. The pasty secretion is quite soft. It can be pale or deep yellow in color.
At the first stages of its formation, deposits may be loose. It's easy to deal with them. But if there are no symptoms or they are simply ignored, then the plug thickens, sinks lower, becomes hard, sometimes even rocky.
In rare cases, deposits consist of keratinized scales of the ear epidermis. They are white in color, hard and quite dangerous, as they can lead to the formation of bedsores in the bone region.
There can be so much wax masses that they begin to leave the inner space of the ear and penetrate into its outer part.
How to make an appointment to remove wax plugs in a child’s ear?
You can get an appointment with a specialist at the Energo clinic at a time that is most convenient for you. Contact us by phone, let us know when you plan to visit the otolaryngologist, after which the consultant will fill out your appointment. Upon request, you will be informed about current promotions and discounts, and will be advised on the cost of the service.
Before conducting a diagnostic examination and removing wax from a child, you will be asked to fill out a consent form for these manipulations. Filling it out will take no more than a couple of minutes.
Symptoms of wax plug in a child
For a long time, the ear plug does not manifest itself in any way. The accumulation of secretion is gradually compacted. Symptoms of wax impaction in a child begin to manifest themselves only when the ear canal becomes 75% blocked. Then the baby may begin to complain about:
- sensation of noise and ringing in the ears;
- itching;
- congestion;
- pain.
There is also a decrease in auditory perception, in which the normal tone of speech or the moderate sound of a television is not perceived. The baby asks to turn it up louder and often repeats questions addressed to him.
Some young patients say they hear their own voice. This phenomenon is scientifically called autophony.
This process usually starts through a previous trip to the pool or taking a bath. Fluid enters the ear. The cork swells and begins to exert pressure. A wax plug in a child's ear puts pressure on the eardrum. The classic symptoms include sore throat, cough, dizziness, and nausea.
How do wax plugs occur?
The sticky mass of sulfur forms a lump of varying density from epidermal scales and dust, which is gradually brought out when talking and chewing. There are sulfur plugs:
- soft;
- dense;
- dry;
Their plasticity depends on the time of their existence.
Earwax can form in children's ears even in the first months of life. Their formation can be caused even by too zealous treatment of the child’s ears - in response to the removal of wax from the ears, even more is produced compensatoryly to protect the ear canals. Another reason for the formation of plugs lies in the use of cotton swabs to clean the ears - they cannot penetrate deeply and simply compact the accumulated wax.
When to see a doctor
If the child’s wax plug inside the ear is deep, then even parents without special equipment can notice it. When examining the ear canal, a dark brown or black spot may be detected. In such situations, taking initiative is too dangerous. Don't run for a cotton swab and clean your baby's ears. This can only aggravate the situation and even deprive you of your hearing. In addition, the instructions for cotton swabs, including those for children, state that they are used only for cleaning the nasal passages and the outer part of the ear. Do not use sticks for internal passage.
What you really should do is see a doctor. You need to make an appointment immediately if your baby experiences pain.
Earwax removal by a pediatrician
Surprisingly, there is no single effective way to remove wax. The main thing is to regularly keep your ears clean, namely, keep the auricle clean.
Pediatricians choose one of three methods for removing plugs:
- Using drugs to remove wax plugs in the ears - these can be water-based drops (with the addition of hydrogen peroxide, acetic acid, saline) or oil-based (any type of oil).
- Removing wax plugs of various sizes from a child using an ear syringe is a popular procedure that should only be performed in a doctor's office. The pediatrician uses a manual or electronic irrigator to flush out the wax.
- Manual removal is another common method in which the pediatrician removes the wax themselves using a metal or plastic curette or other instrument. Manual removal is great if the doctor is unable to use drops, such as when a child has a perforated eardrum.
The wax plug is easily removed using suction or aspiration - but you should not try this procedure at home. It's always better to consult a specialist. An experienced doctor will delicately remove excess wax from the baby.
In some cases, doctors combine methods: the otolaryngologist, before manually removing the wax, drops drops into the ear to soften it.
Diagnostics
An otolaryngologist (ENT) diagnoses problems with children's ears. If a child has an ear plug, it can be identified directly during an examination by a specialist.
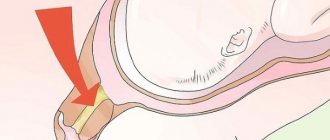
Otoscopy is performed as a diagnostic test. The cerumen plug itself in a child looks like a gray-brown mass that blocks the ear canal and eardrum. The consistency of the contents is determined using a button probe.
If necessary, audiometry is also done, which helps determine the quality of the baby’s hearing. It often occurs when there is a traffic jam.
During diagnosis, it is important to differentiate ear plugs from:
- a foreign object accidentally entering the ear;
- cholesteatomas;
- hearing loss;
- otomycosis.
This is necessary, since the signs of cerumen plug in a child are also characteristic of these diseases.
Removing wax plug
Do not try to remove a dense, dry cork using sharp objects - needles, toothpicks, matches, tweezers. By chance you can:
- push it even deeper;
- puncture the eardrum, which will lead to permanent hearing loss;
- To soften the dry plug, hydrogen peroxide heated to 37C is introduced into the ear several times. The resulting foam bubbles will at some point push the sulfur plug out;
- The heated furacillin is drawn into a large syringe (20 ml), a cannula is inserted without a needle into the ear canal and the plug is washed out of the ear with a stream under the pressure of the piston;
- If liquid is used to dissolve plugs, then the child should be placed on the side opposite the stuffy ear, the solution should be dripped into the ear canal and the child should be left in this position for 15 minutes, then he turns over to the other side so that the loosened plug flows out of the ear;
Liquids must be heated so that the child does not experience sharp pain in the area of the eardrum. The washed ear should be covered with a cotton ball for several minutes.
Treatment
How to remove an ear plug from a child? For this you need the help of a doctor. He will determine the depth of the accumulation of gland secretion, its consistency and location. This is done with a stethoscope with a flexible probe. The otolaryngologist must also first make sure that there is no pressure on the eardrum or bedsores in the ears. Only after this a choice is made in favor of a suitable treatment method.
How to remove a child's ear plug? Of course, you cannot use pins, needles, hairpins or other sharp objects for this. The professional doctor will:
- rinsing the ear canal;
- dissolution of solid accumulations of sulfur;
- will give useful recommendations so that the situation does not repeat itself in the future.
For sulfur plugs in a child's ear, rinsing is done with a solution of furatsilin or potassium permanganate. The temperature of the liquid should correspond to the baby's body temperature. The liquid is injected into a large disposable syringe, the head is tilted and a pressurized jet is applied into the ear canal. The cork will gradually wash out. The child must be held tightly, as sudden movements of the head can lead to mechanical damage to the ear.
If the child’s ear plug is dry and hard, then before the procedure it is necessary to inject several drops of hydrogen peroxide into the ear for 2-3 days. It will soften the deposits, making them softer and paste-like.
Their use is allowed only if there are no current or previous problems with the eardrum.
For otitis media or hearing loss, attempts are made to treat ear plugs in children by carefully removing them with tweezers or a probe.
Symptoms of earwax formation
The peculiarity of this pathology is its asymptomatic course in the initial stages of development.
In extremely rare cases, the process is accompanied by mild pain, which many parents mistake for minor inflammation. In most cases, blockage appears unexpectedly after water enters the ear cavity, which increases the volume of the cerumen plug several times, and the child develops specific symptoms:
- noise in ears;
- feeling of stuffiness;
- slight dizziness;
- decreased hearing acuity;
- sensation of a foreign object in the ear.
A characteristic sign of blockage of the ear canal is autophony. This is a condition in which a child hears the echo of his own voice in the affected ear when speaking.
In some cases, an additional symptom of ear plugs in children is pain in the head or in the damaged ear. The pressure of the sulfur substance on the eardrum can provoke slight nausea, coughing and migraine attacks. In advanced cases, otitis media, bedsores and myringitis (inflammation of the eardrum) may develop.
The following signs will allow you to suspect that a cerumen plug has appeared in the ear of a small child who is not yet able to speak:
- the baby is worried, touches the sore ear, tries to scratch or pick it;
- the child does not immediately respond to the parents’ voice or sound stimuli;
- the baby shudders if he is touched, but he does not see the person approaching.
If the ear plug has formed shallowly, parents can see it themselves during examination.
Forecast and prevention of sulfur plugs in a child
Once the plug is removed, all symptoms should disappear. After a few hours, the doctor will re-examine the baby to make sure that all accumulations of sulfur have been removed.
In order not to encounter such a nuisance and not cause problems for your baby, it is recommended:
- maintain normal air humidity in the house - 50-65% (use wet towels, bowls of water during heating periods or air humidifiers);
- do regular cleaning of the ear canals not with cotton swabs, but with cotton swabs made with your own hands;
- try to visit an otolaryngologist at least 1-2 times a year for monitoring (especially if there have already been episodes of disorders associated with the ears);
- with the doctor's permission, use drops for prevention that will clean the ear canal and prevent otitis.
With timely measures taken, the prognosis is good. The doctor will remove the plug, and the child will immediately stop experiencing pain, discomfort, and will feel a complete restoration of hearing function.
If you ignore the problem or try to solve it at home, it can get worse and cause complications. These include: suppuration, bedsores, otitis media, sinusitis, mechanical injuries, hearing loss.
To prevent this, you need to regularly undergo examinations by an otolaryngologist. Remember that young children are not always good at understanding their own feelings. Check the ear canals, do not give them to small children under the age of three, and do not neglect the rules of personal hygiene.
If the problem has already affected you, this does not mean that now you need to clean your ears every day. It is necessary to remove the secretion as it accumulates. Too frequent cleaning will destroy the natural microflora, which effectively copes with penetrating pathogenic microorganisms. Your doctor will tell you about other individual recommendations after the procedure.
Diagnosis of blockage of the ear canals
The main diagnostic method is otoscopy - a visual examination of the ear canals using a special funnel and reflector. During the examination, the otolaryngologist assesses the patency of the ear canals, identifies the type of blockage and the size of the plug.
Also, during the examination, the doctor can determine the presence of:
- neoplasm in the ear cavity;
- foreign object;
- inflammatory processes.
The density of sulfur accumulation is assessed using a special probe. Additionally, you may need microotoscopy - examination of the eardrum using a microscope.
How to make an appointment with a specialist
If you need to remove a wax plug from a child’s ear, find out the cause of pain and lumbago, get advice, and undergo a diagnosis of hearing problems, you can contact JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg). Modern equipment, experience and knowledge will help to detect the disease in time and eliminate it.
To make an appointment, call the contact number +7 (495) 995-00-33. If the child is suffering from acute pain, the baby is capricious, or the temperature is rising, then dial the ambulance number +7 (495) 229-00-03. Calls are accepted 24 hours a day.
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is located near the Mayakovskaya metro station (5 minutes on foot) at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, 10.
Signs of ear plug formation
Sulfur plugs often form completely unnoticeably. When pain or uncharacteristic sound effects appear, many suspect otitis media, although such pathological symptoms often indicate the formation of sulfur accumulation.
Most often, sulfur plugs make themselves felt after swimming. The development of pathological processes can be suspected by the following symptoms:
- pain, itching;
- unusual noise, crackling;
- feeling of fullness;
- you can hear your own echo in your head;
- discomfort when chewing food;
- distortion of sounds or hearing loss.
Situations where cerumen plug has formed next to the eardrum are the most dangerous. The patient may experience weakness, cough, dizziness and nausea, but there are no typical symptoms of colds.
It is necessary to visit an otolaryngologist as soon as possible. You should not use folk remedies or try to solve the problem yourself. Inadequate treatment can negatively affect your health. It is important to carry out therapy correctly and in a timely manner.
Medical offers to make an appointment with an otolaryngologist (ENT) of the highest category. A full range of diagnostics and treatment of ENT diseases in Tula. Tel. for recording.