Chickenpox - in common parlance, chickenpox is considered more a childhood than an adult disease, which you need to get over once and forget forever, as immunity to this disease is developed. Parents whose children have not yet been ill should be aware of this disease in order to provide the sick child with proper care.
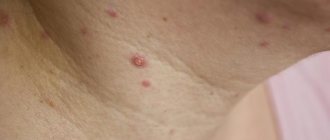
The main sign by which chickenpox is recognized is blisters filled with clear liquid. The rash usually begins from the lower extremities, and within a few hours moves to the top of the head. Most often the disease is accompanied by high fever. It must be remembered that the bubbles that appear on the child’s skin should under no circumstances be squeezed out - scars may remain. Chickenpox is not always accompanied by large rashes; one patient may have from 10 to 50 abscesses, while another child may be covered with them from head to toe. The rash covers not only the skin, but can also form on the mucous membrane of the eyes, on the genitals and even in the mouth. The incubation period for chickenpox is 1 to 3 weeks and is transmitted by airborne droplets over a distance of up to 100 meters. This means that if your child, who was not sick, was in the same room with a chickenpox carrier, know that yours is next.
Chickenpox can be diagnosed by symptoms, without tests or examinations. A child with chickenpox needs home treatment. During the period of rashes, baths should be avoided. Nowadays, just like many decades ago, bubbles are smeared with brilliant green for the purpose of disinfection and drying. As a rule, children from 2 years old experience discomfort on the skin, accompanied by burning and itching. To alleviate the condition, the child is given allergy medications that help reduce itching. Make sure that the child does not scratch the abscesses, this will eliminate the possibility of infection under the skin. In some cases, when an infection occurs, children are prescribed an antibiotic that fights bacteria, but does not affect the course of chickenpox, since it is not effective for viral infections.
Prevention and treatment of chickenpox in children
In recent years, a vaccine has become available that prevents chickenpox infection. The vaccination is effective even after contact with a sick person, the main thing is to have it done within 72 hours. Children are vaccinated against chickenpox from 1 year of age. Immunity lasts for up to 20 years.
It is worth remembering that any disease must be diagnosed correctly and on time. Doctors at our clinic will help you understand the disease and prescribe effective treatment for chickenpox in children . You can make an appointment on this page.
Chickenpox in a child: a reminder for parents
Chickenpox is a viral disease caused by one of the varieties of the herpes virus, namely the varicella-zoster virus. This virus enters a child’s body through airborne droplets – that is, a child can become infected from a sick child. Moreover, patients with chickenpox are contagious in the active phase of the pathology, which occurs two days before the appearance of the rash.
Chickenpox is the popular name for the disease. In medical practice, the pathology is called chickenpox. This disease has characteristic signs and a mild course in childhood, so if a child has had chickenpox, this is good, because then he develops immunity. If a person did not get this disease in childhood, he can become infected with the virus in adulthood, but in this case the disease will be much more severe, and, possibly, severe complications will even develop against its background. That's why doctors say that having chickenpox as a child is normal and even beneficial.
How long does chickenpox last?
How long does chickenpox last? For any organism, this question is individual, but there are limits beyond which this period does not go. Chickenpox lasts for different periods of time in both children and adults.
The entire period should be divided into stages.
The first stage is incubation. How long is the incubation period for chickenpox?
The average duration of the period is from 1 to 3 weeks.
The countdown starts from the moment of infection until the appearance of symptoms of the disease. In children they appear on average at 8-10 days, but in adults usually by the end of the third week. After this, a prodromal period begins, during which a person begins to experience headache, weakness, fever, aching joints, and lack of appetite. This is very similar to a common cold. It usually lasts a couple of days, after which the first pimples appear. Chickenpox rashes
also last differently for everyone. The average time period is from 3 to 10 days. The rashes appear immediately after the prodromal period, and are renewed every two to three days, replacing each other. During the entire period of rashes, they replace each other 3-4 times. Therefore, pimples, vesicles, papules, and crusts can usually be found on the skin. A person is especially contagious during the period of rashes, since they tend to open and thus release the infectious agent in large quantities.
It turns out that
chickenpox in children
last
on average from 10 to 14
days
.
In adults,
chickenpox often lasts
about three weeks.
How long does fever last for chickenpox in children?
This question is also individual, however, if you try, you can prevent the temperature from rising above 39 degrees for 3-5 days.
However, if a person’s immunity is weakened, or the disease is advanced, one can suffer from fever for two weeks. If a person has a fever, they should call 911 immediately. To reduce the temperature to a normal level, complex therapy is needed. Treatment should only be prescribed by a doctor. This is especially true for adults, since their disease is more severe and can cause serious complications. How long does the chickenpox quarantine last?
Doctors believe that the disease is dangerous for 4 to 13 days.
For this reason, the institution in which the outbreak of the disease was detected is closed for two weeks. How long does sick leave last for chickenpox?
If a child is sick, it is better not to go to the clinic, but to call a doctor at home, since in a medical facility the baby can infect other children. If the diagnosis is confirmed, the doctor prescribes a sick leave for one of the parents for a period of 5 to 10 days, in extreme cases up to 15 days. If an adult falls ill, the average length of his stay on sick leave is 10-14 days. However, if complications arise, the period can be extended to three weeks or more. This is explained by the fact that chickenpox is more difficult for an adult to tolerate than a child. ', '~DETAIL_TEXT' => ' Chickenpox is an infectious disease that first manifests itself with standard respiratory symptoms, and a little later with characteristic rashes on the skin and mucous membranes. This disease is considered a childhood disease, but it also happens to adults who were not infected in childhood. You can become infected from a sick person from the end of the incubation period to the end of the active phase.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of chickenpox are typical. These include:
- increase in body temperature to subfebrile levels (less often to febrile);
- the appearance of papulovesicular rashes throughout the body;
- symptoms of general malaise (weakness, drowsiness, etc.).
Symptoms appear after the incubation period has passed, which usually lasts 5-7 days, but can sometimes last two weeks. The rashes characteristic of this disease appear first on the face and then spread throughout the body - appearing on the arms, chest and back, and lower extremities.
At first, the rashes appear as small blisters that itch and itch. Then the bubbles burst and a weeping surface forms underneath. At the final stage, the blisters become covered with a crust, which should never be torn off, as scars may remain.
Contagious period of chickenpox (in general)
It is not surprising that it is adults who worry when chickenpox is contagious, because at an older age severe forms of the disease and its complications are possible. What is important is the total number of days during which an infected person is dangerous to healthy individuals.
So, the patient is contagious:
- at the end of the incubation period (one day before the rash appears);
- during the active period of the disease, the duration of which is from 2 to 9 days;
- 5 days from the moment the last pimple appeared.
Thus, the period of infectiousness of chickenpox ranges from 8 to 15 days. If the disease lasts from 9 days, then the person poses a danger for a longer period of time.
Most adults are immune to chickenpox, so the risk of catching it at an older age is low. The disease lasts the longest in people over 12 years of age (moderate and severe forms predominate).
Treatment
If pathology is diagnosed, then treatment of chickenpox in children should be symptomatic. Young patients are given antipyretics if the temperature exceeds 38.5. Medicines that reduce itching are also prescribed, for example, antihistamines such as diazolin, suprastin and some others (as prescribed by a doctor).
In addition, the blisters are lubricated with a solution of brilliant green, due to which they dry out, itch less and heal faster. It would be correct to use drugs that enhance immunity to treat chickenpox. But in adult patients, chickenpox, a type of herpes virus, is treated with Acyclovir.
Causes and features of pathogen transmission
The disease spreads quickly and easily indoors, since the causative agent, the herpes virus, can be transmitted through coughing, sneezing, i.e. by air. A greater number of chickenpox cases occur in preschool children. Children staying in the same group room of a kindergarten get sick faster, although the virus is able to penetrate with air flow into neighboring rooms. Less commonly, the pathogen is transmitted through toys or third parties, since it is unstable in the external environment.
The peak of the disease occurs in spring/autumn, together with the peak of colds. The pathogen is transmitted by the bloodstream to the epithelial layers of the skin, where it begins to actively multiply. There are subjective signs of the onset of the disease: irritability, tearfulness of the child, the appearance of a common rash similar to hives. Due to the mobility of the virus in the blood, internal organs may be affected. The mucous membrane is an excellent “soil” for the virus; as a result, small hemorrhages form at the site of the papules. Immunity after the disease is stable (except for early infection by the virus).
Adults who did not have chickenpox as children may not get sick at all if they have a strong immune system. But when infected, adults become seriously ill, with a high rise in body temperature, and subsequently scars and visible dents form in place of the papules.
Features of the pathogen:
- papular fluid contains DNA;
- the virus is deactivated at a temperature of 45 to 50 degrees. It is enough to soak the patient’s clothes in hot water for half an hour to destroy the virus. Disinfectants should not be used when processing children's clothing; they can cause increased itching and rashes;
- the virus is not destroyed by freezing; after defrosting, the pathogen is still active. But it does not tolerate sunlight well, so when disinfecting a room, you can use ultraviolet lamps;
- the pathogen can be transmitted through the placenta from a sick pregnant woman to the fetus, as a result of which there may be damage to the fetus that does not threaten its life;
- in exceptional cases, chickenpox is contracted twice, if the first time occurred before the age of one year, when the child’s own immunity is not yet “working.”
Symptoms of the disease
On average, up to two weeks after the virus enters the body, the child feels normal. Then the body temperature rises sharply and quickly, and at the same time rashes appear on the head under the hair, cheeks, near the lips, and on the mucous membranes of the mouth. Due to the rash, the child becomes restless, the unpleasant tingling sensations in the papules a little later turn into severe itching, and the baby’s condition worsens.
Development of chickenpox
Initially, only a rash is visible on the skin, similar in appearance to miliaria. Then characteristic small spots become visible, in place of which bubbles with transparent contents - vesicles - form. There is always a small border around the bubble - a hyperemic halo. After a few hours, the liquid in the bubble becomes cloudy, and even later the bubble bursts and the liquid begins to flow out of it. If the vesicle is not touched, then after two or three days it begins to dry out. A dense crust forms from the center to the edges of the bubble, and after the crust has completely dried, the skin remains pink, but without scars, smooth to the touch. If a child actively scratches the rash, indentations may form, as after a BCG vaccination.
The bubbles do not appear all at once, but several days apart, so quarantine for chickenpox lasts up to three weeks. During this time, rashes in different stages of development may be visible on the skin - from spots to crusts. To treat chickenpox, doctors still recommend using a solution of brilliant green, which disinfects and dries watery blisters. Yes, it is ugly, the child will walk around with spots, but it is effective in preventing suppuration from scratching and the rapid healing of wounds.
If the course of the disease is severe, with a large amount of rash, the child is prescribed medications that lower the temperature and antihistamines. Acyclovir is effective only if used in a timely manner; if the disease is protracted, it should not be used. Sometimes doctors prescribe immunostimulants, for example, cycloferon liniment - it successfully replaces brilliant green. The drug facilitates the course of the disease and prevents the development of purulent infection when the blisters are scratched.
Features of the pathogen
Chickenpox develops as a result of a virus called Varicella Zoster entering the body. This is a type of herpes simplex that has its own DNA and lipid membrane. Due to its significant size, the varicella is visible under a conventional light microscope. Therefore, there are no problems with diagnostics even without special analysis.
Like herpes, once it enters the human body, the chickenpox pathogen remains there forever. It is found in the nerve cells of the spinal cord in an inactive state and can manifest itself when the immune system is significantly weakened.
If this happens, the person gets sick again with chickenpox or another form - herpes zoster. This rarely happens due to the active production of antibodies during illness; it is enough to get sick once to form lifelong immunity.
Chickenpox in adults is uncommon; according to statistics, 75% of people acquire immunity in childhood. If a person is unlucky enough to fall into this number, then the probability of getting sick is high.
This is explained by the extreme contagiousness and pathogenicity of the virus, close to 100%.
The lifespan of varicella zoster in the external environment is no more than 15 minutes. The exact time depends on the microclimate parameters. At high temperatures and under ultraviolet rays, the virus dies faster. This time is enough for chickenpox to spread over a distance of 20–30 meters, infecting nearby people and passers-by.