What causes stridor?
This question often arises for parents. After all, before treatment, it is always important to identify the main cause of the development of a pathological symptom.
Predisposing features of the respiratory tract in children
Of course, stridor breathing is more likely to be observed in young children. Because the anatomy of the upper respiratory tract is imperfect and there are some peculiarities. The larynx in children has a small opening. But the main mechanism for the development of stridor breathing is the appearance of turbulent air flows after it passes through the narrowed lumen of the larynx.
But it is important to note that not all children have pathological stridor. The situation worsens with abnormalities in the development of the upper respiratory tract. If there is weakness in the cartilaginous elements of the larynx, then sagging of such cartilages can cause a mechanical obstruction and the appearance of stridor breathing. This pathology is detected in premature infants with rickets.
Etiological factor
As mentioned above, stridor is a manifestation of a particular disease. The cause of pathological noise when breathing can be congenital malformations of the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract, and cardiovascular system.
Often, stridor develops during acute infectious diseases and disappears after complete recovery. Allergic reactions accompanied by swelling of the larynx can also manifest as stridor breathing.
Benign and malignant neoplasms of the larynx act as a causative factor for stridor more often in adults. A pathological symptom may appear due to traumatic injury to the larynx or aspiration of a foreign body. It is also possible that the larynx may be compressed from the outside, that is, by a tumor of the esophagus or inflammation of the thyroid tissue.
Congenital stridor in an infant - whistling and noise when breathing
Often after the birth of a child or in the first or second months of life, the child whistles, sniffs, mutters or grumbles while breathing. This worries parents - we will try to understand the reasons for these phenomena.
The anatomy of the upper respiratory tract in infants, as well as other body systems, has certain characteristics.
Children's larynx has little free space, and the nasal passages are narrow and tender, with a small nose and air often cannot pass freely, and all the obstacles make the child grumble and murmur. Finally, the main mechanism for the development of various sounds or breath sounds is the creation of turbulent air currents after passing through the constricted larynx.
In most cases, the cause of grunting and sniffing noises during breathing is the development of crusts in the baby's nose, but another reason for all these noises in a child is also considered - congenital stridor.
Grunting and sleeping of a child can also be caused by congenital anomalies of the nasal passages or curvature of the nasal septum, the onset of rhinitis, congenital eustachitis or labyrinth.
In order to minimize the baby’s breathing difficulties, parents need to:
- humidify the air in the room using ventilation and carry out wet cleaning in the children's room at least 1-2 times a day;
- clean the baby’s nose daily with cotton swabs;
- If necessary, if nasal breathing is very difficult, wash your nose with saline solution.
If your child's nose is blocked frequently and for a long time, you should contact your pediatrician to find out the cause.
What is congenital stridor
- Congenital stridor, or noisy and rough breathing, occurs immediately after the baby is born, but sometimes this congenital abnormality can occur later.
- The sounds of a child's breathing may vary in character and timbre.
- The sound of the murmur depends on the original cause of the stridor - usually it is a congenital feature associated with soft laryngeal cartilage when the nasal passages are too narrow, which is congenital stridor.
But it could also be congenital stridor:
- vocal fold paralysis;
- benign neoplasms of the larynx;
- laryngeal papillomatosis;
- laryngeal cysts;
- Choan artesia;
- partial laryngeal paralysis;
- struma congenita, often associated with hypothyroidism
The pathology is recognized and corrected by an otolaryngologist, neurologist, pediatrician, gastroenterologist and pulmonologist.
- It is important to note that abnormal sound levels may vary depending on the situation.
- When you sleep in a warm, moderately humid room while walking, your breathing can be almost silent.
- Conversely, increased noise is noticeable during crying, coughing, sucking and swallowing.
Most often, there is no neonatal period. However, children under one year of age may be underweight and therefore have poor development, swallowing problems, and voice changes.
It should be noted, however, that stridor in children is often mild and does not affect the child’s development, nutrition and sleep.
Particular attention should be paid to infants when they become infected. Catarrhal symptoms that appear during the disease provoke an acute attack of stridor. The baby's condition worsens greatly, shortness of breath develops, the skin turns blue when breathing, and at the height of breathing there is an attraction of the elastic parts of the chest (intercostal spaces, jugular fossa, epigastric region).
Severe disease can lead to suffocation, which is life-threatening, often leads to detailed results and requires immediate medical attention and hospital stay in a children's clinic.
As the child matures, the cartilage hardens and the cavity expands, the pathology begins to disappear and the child is no longer bothered.
If the symptoms of the pathology have not subsided by the 6th month of the child’s life and have not disappeared completely by the age of 2, a comprehensive examination is prescribed to identify the organic causes of noisy breathing.
Congenital stridor
Congenital stridor occurs immediately after the birth of a child. The leading manifestation is noisy, rough breathing. Congenital pathology may appear later, but this is rare. The mechanism of occurrence of pathological noise is the same and indicates the appearance of turbulence in air flows passing through the narrow lumen of the larynx.
Causes of congenital stridor
The main causes of congenital stridor are anomalies in the development of the larynx. Children born prematurely have softening of the cartilage of the larynx, trachea, and bronchi. Such malformations of the respiratory system form mechanical obstacles to the passage of air.
The walls of the respiratory organs cannot fully perform their function and bend inward. Insufficient muscular support of the respiratory system can also contribute to the appearance of stridor. Less commonly, congenital pathology can be observed in various tumors. Malformations of the respiratory system include choanal atresia, paresis and paralysis of the vocal cords.
Stiffness is one of the symptoms of a genetic disease. This pathology is detected immediately after birth based on multiple developmental defects, phenotypic characteristics, and the results of genetic testing.
Manifestations of congenital stridor
Congenital stridor in newborns manifests itself in the first days after birth and can then intensify. The noise that a child experiences when breathing can vary in character and timbre. The sonority of the noise depends on the original cause of the stridor. It is important to note that the level of pathological sound may vary depending on the environment.
When sleeping in a warm, moderately humid room, breathing may be almost silent. The opposite picture is observed with crying, coughing, sucking and swallowing. The neonatal period is often uneventful. Children under one year of age may have poor weight gain and, therefore, lag behind in physical development; swallowing problems and voice changes may also occur. But it is worth noting that more often stridor in children occurs in a mild form and does not affect the development, eating and sleep of the child.
The situation is more severe when an infection occurs. Catarrhal symptoms that appear during the disease provoke an acute attack of stridor. The child's condition is worsening, shortness of breath is observed, the skin turns blue when breathing, at the height of inspiration one can notice retraction of the pliable places of the chest (intercostal spaces, jugular fossa, epigastric region). A severe course of the disease can lead to an attack of suffocation, which is a life-threatening condition, often leads to a detailed outcome and requires immediate medical attention. Congenital stridor can cause the development of serious diseases: bronchial asthma, pneumonia, tracheitis and bronchitis.
Treatment approaches
Before starting treatment, it is important to identify the cause of the pathological symptom. In the case of mild stridor, you can adopt observational tactics, not forgetting the constant monitoring of an otolaryngologist. After all, after 6 months of life, the situation, as a rule, improves, and by 3 years this symptom disappears completely.
If a child has mechanical obstacles to air flow in the form of benign tumors, then surgical removal is indicated. Surgical intervention is also possible for pathology of the cartilaginous skeleton of the respiratory tract. Situations with a layer of infections require special attention; then, during attacks of stridor, immediate hospitalization is required to prevent a life-threatening condition.
Treatment
Depending on the cause of stridor, specialists choose treatment tactics. If the cartilage tissue of the larynx is soft, then no special drugs are prescribed; the symptoms disappear on their own during the first year of life.
All other cases of the disease require surgical and medical treatment. Surgery and further therapy for sick children are carried out in the departments of thoracic surgery, otolaryngology, oncology, cardiac surgery, endocrinology, and toxicology.
The main goal of therapy is to restore airway patency and eliminate the causes of pathology.
Acute stridor, accompanied by hysteria and panic in the child, requires emergency medical care. The patient is immediately hospitalized. In the hospital, he is undressed and provided with fresh air. To stop the child from hysteria, experts use distracting procedures: mustard plasters on the shins, a warm bath, or, in extreme cases, ammonia. After the attack of hysteria is relieved, doctors move on to drug therapy.
Drug treatment
- Decongestant therapy - Sorbitol, Mannitol, Reogluman, Furosemide.
- Hormonal therapy - Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone.
- Treatment with humoral immunomodulators - interferons and monoclonal antibodies.
- Bronchodilators that reduce spasms - Eufillin, Salbutamol.
- Inhalations with bronchodilators, hormonal drugs, adrenaline and ephedrine help expand the patient's airways.
- Injections of novocaine, vitamins B.
Surgery
The choice of operation is determined by the immediate cause of stridor.
- Laryngeal hemangioma is removed with a carbon dioxide laser.
- For vocal cord paralysis, a tracheotomy is performed.
- Laryngeal cysts are treated by aspiration of its contents and excision of the walls with a laser.
- Stridor caused by laryngeal papillomatosis is treated by removing papillomas with microinstruments. To prevent relapse of the disease, long-term and continuous administration of interferon drugs is required.
- Severe respiratory disturbances during tracheomalacia that do not disappear spontaneously are eliminated by tracheotomy.
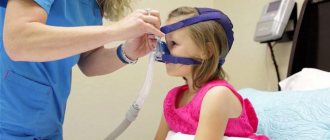
- With the development of a critical condition and acute attacks, intubation with artificial ventilation is performed.
Acquired stridor in children. Causes
Acquired stridor has other causes. In young children, the development of a pathological symptom is most typical after aspiration of a foreign body. Today, bronchial asthma in children is quite common. It is allergic swelling of the airways that leads to the appearance of stridor breathing.
Complications after acute tonsillitis - retropharyngeal abscess, epiglottitis act as a mechanical obstacle to the passage of air. Enlargement of the thyroid gland and tumor-like formations of the esophagus, larynx, bronchi or trachea are also causes of the development of stridor. Cicatricial narrowing of the respiratory gap in the larynx can occur after prolonged intubation.
Congenital stridor in newborns: what is it?
When a baby is born, young parents often encounter a problem such as stridor in newborns. This disease can cause panic in adults, especially when accompanied by anxiety symptoms . What kind of disease is this, how can you help your child cope with it?
Description of the disease
Stridor is a pathological process that develops in the form of obstruction of the respiratory system, accompanied by noisy wheezing. Many doctors do not consider it a disease, but just a symptom of a pathological process developing in the respiratory system.
Stridorous breathing is a loud noise that appears in the baby when inhaling or exhaling . It occurs as a result of minor physiological injuries or serious diseases for which treatment must be carried out.
This pathology can be detected if a child, for example, has soft laryngeal cartilages, and their consistency resembles plasticine.
When you inhale, they close, and due to the influence of bronchial pressure in the upper respiratory tract, the air begins to vibrate.
Most parents worry about the possible consequences that may arise as a result of this pathology, but, according to doctors, stridor will have absolutely no effect on the further condition of the voice.
Stages of the pathological process
The stage of the disease is determined by the degree of its complexity.
Compensated
This is a milder type of illness for which treatment is not necessary. In children under one year of age, the pathology will go away without outside help .
Border-compensated
This stage occurs as a borderline state between the previous stage of the disease and the next. At this time , it is necessary to constantly monitor the child’s condition in order to prevent the development of the pathological process .
Decompensated
This is a stage of the disease during which mandatory treatment is required, sometimes even surgically.
Critical
This is the most dangerous stage. It is characterized by severe respiratory distress, which requires resuscitative actions. The only way to save the baby is through surgery .
Forms of stridor
Characteristic clinical symptoms
The main clinical symptom is a loud breathing noise that can be heard at a distance. The nature of the noise can determine the level of damage to the respiratory tract. As a rule, the volume of stridor indicates the degree of narrowing of the respiratory gap. The louder the noise, the narrower the gap. But suddenly weakened noise is often an unfavorable indicator and indicates complete airway obstruction.
It is also important to pay attention to the timbre of the noise. For example, a high frequency of stridor indicates a lesion at the level of the vocal cords. A low timbre indicates a lesion above the ligaments, that is, in the upper part of the larynx. The average pitch of the murmur indicates involvement below the vocal cords.
Experts identify forms of noise that are also important in finding the cause of the development of this symptom. Inspiratory noise occurs during inspiration and has a low pitch. Expiratory stridor, on the contrary, is observed during exhalation and is characterized by an average frequency of noise. And the last, two-phase, develops during inhalation and exhalation and has a high pitch.
Examination of children with stridor
Diagnosis of children with this symptom is extremely important, since treatment should be carried out in the direction of the underlying disease. Before the examination, the specialist must carefully collect anamnesis, find out the onset of pathological noise, and determine the form of stridor. After all, congenital and acquired noise has different causes. It is important to determine the duration and severity of this symptom. The doctor determines what additional symptoms may occur during stridor breathing. In children, it is always important to assess physical and neuropsychic development, as well as learn about the peculiarities of the perinatal history.
Basic diagnostic methods
- Physical examination. It is necessary to conduct an external examination of the patient and record any deviations. During palpation, it is important to identify possible formations in the face and neck. It is important to evaluate other vital signs: frequency and depth of breathing, heart rate.
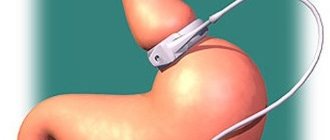
- Instrumental diagnostic methods. The “gold standard” in diagnosing stridor is fibrorhinopharyngolaryngoscopy. This method can be used without the use of general anesthesia, which is certainly an advantage. If necessary, local anesthesia and vasoconstrictor drugs can be used. The instrument is inserted into the nasal cavity and advanced further, assessing all the structural elements of the respiratory system. This method can be performed even on premature babies, since the fiberscope has several sizes. Using this method, you can visually determine the cause of stridor breathing. If necessary, other diagnostic methods may be prescribed, such as x-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging of the larynx. After consultation with other specialists, additional methods may be prescribed.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is carried out, first of all, with true and false croup. Also with laryngitis, lymphogranulomatosis, abscesses of retro- and paratonsillar tissue. Fibrorhinopharyngolaryngoscopy allows you to make the correct diagnosis with high accuracy.
1.General information
Stridorous is called heavy, labored, noisy breathing with a hissing and/or whistling sound; Many other acoustic effects are also possible (gurgling, gurgling, wheezing, etc.), which even for a non-specialist can instantly distinguish pathological breathing from normal breathing. The fundamental, physical cause of stridor (stridor breathing) is a change in the nature of the air flow in the respiratory tract: from laminar (uniform, smooth) it becomes turbulent, i.e. vortex. Obviously, given the anatomical complexity of the human airway, stridor can be caused by many specific factors - unfavorable, abnormal or pathological.
Strictly speaking, wheezing at birth is not a disease in itself. However, in such cases, consultation with a pediatric otolaryngologist and other specialists is mandatory, since abnormal breathing may be based on one or another obstruction (blocking the lumen) of the airways, or structural features of the latter. The International Classification of Diseases (heading “Congenital anomalies [malformations] of the respiratory system) provides the diagnosis “Congenital stridor of the larynx.” This condition occurs in the general population with a frequency of over 4%; If we consider all cases of stridor breathing in newborns, then the share of congenital stridor of the larynx accounts for more than 40% (according to other sources, up to 60-70%). Almost always (98%) congenital stridor is accompanied by chronic hypoxia, i.e. oxygen starvation - which explains the need for diagnosis and, at a minimum, observation by a specialist - however, in most children, hypoxia is compensated, transient and, thus, does not require intervention.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Treatment of stridor
Treatment of stridor breathing depends on the initial cause of the pathological symptom.
Stridor can go away without a trace by 2–3 years.
Children whose stridor is mild should be regularly monitored by a pediatrician, otolaryngologist and pulmonologist. Doctors evaluate the patient’s condition over time, and as it worsens, therapeutic measures can be taken. In most cases, children with stridor are treated with watchful waiting.
Drug therapy and its possibilities
Medicines are used if stridor occurs as a result of allergic edema. In this situation, hormonal drugs - glucocorticosteroids (Prednisolone, Pulmicort) can be prescribed. Hormone replacement drugs are also prescribed for thyroid diseases.
Surgery
Surgical therapy is also indicated for the treatment of the underlying disease. Surgical intervention is used for aspiration of a foreign body, softening of laryngeal cartilage, and neoplasms in the laryngeal area. In emergency cases, when there is a risk of developing acute respiratory failure, patients are prescribed oxygen. In case of complete obstruction of the airways, tracheotomy (dissection of the tracheal cartilage) is indicated, followed by placement of an endotracheal tube and artificial ventilation of the lungs.
Prevention of stridor
A child with this pathological symptom should be constantly monitored by specialists. Parents should create a favorable environment at home so as not to provoke an increase in pathological noise when breathing. It is important to monitor the child’s psychological state and correct it in time. Up to 3 years of age, it is necessary to prevent acute viral and bacterial infections that can cause suffocation in a child.
Stridor in newborns (congenital) - symptoms of pathological noisy breathing in children under one year old
Sometimes the long-awaited birth of a child is overshadowed by a terrible diagnosis - congenital stridor, heard from the mouth of a neonatologist in the maternity hospital. Any mother worries about her baby, especially in matters related to health. Is stridor really a serious phenomenon or should parents calm down and just follow the doctor’s recommendations?
In most cases, stridor is just a baby's noisy breathing and does not pose any health risks.
Stridor in babies - what is it?
Stridor in newborn babies manifests itself as loud breathing, hissing, or whistling. It happens that symptoms in infants appear during the first two months of life, and parents urgently need to show the child to the doctor, since stridor can be a sign of serious illness and threaten life.