Children, due to their characteristics, are more often susceptible to various diseases. The child’s immune system has not yet learned to fight pathogens. The friendly bacteria that the child inherits from the mother protect the body from strangers carrying the disease. However, the child is defenseless against many microbes. They can cause various diseases. Often the urinary organs are affected. Cloudy urine is often a symptom of kidney and bladder disease.
- The mechanism of urine turbidity in children
Doctor Komarovsky about cystitis - video
- Reasons for changes in urine - table
Causes of cloudy urine - photo gallery
- Doctor Komarovsky about urine analysis - video
- Pharmacological agents
Drugs used for urinary tract diseases - table
- Methods of surgery on the urinary tract - table
Prerequisites for the development of inflammation in the kidney
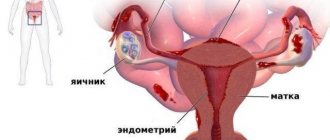
The system of organs that form urine begins to operate even before the baby is born. In nine months, the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra are formed in the mother’s womb. The kidneys are the main link in this chain. It is here that the blood passing through the small vessels of the glomeruli is cleansed of waste and toxins. Urine acquires its final composition as it passes through narrow, winding tubes called the renal tubules.
Nephrons consist of glomeruli and tubules
From the renal tubules, urine enters the cups and then the pelvis, a small cavity surrounded by muscles. They help move urine further into the ureter. This is a winding tube, the wall of which also contains muscles. A special membrane, the mucous membrane, comes into contact with urine. Its cells are able to withstand the influence of an aggressive environment. Two ureters carry urine into the bladder. Here it accumulates for some time, after which it is excreted through the urethra.
After birth, a child's kidneys need to mature. The glomeruli become larger, the tubules become wider, and the ureters become less tortuous. Over time, the bladder can hold more urine. These features lead to the fact that children suffer from kidney and urinary tract diseases more often than adults. Infants—newborns and infants—are especially susceptible to adverse factors.
Urine passes through several organs on its way
The composition of urine is a reflection of all stages of its formation and progression. Cloudy urine indicates trouble in this orderly and well-functioning system. You should pay attention to this sign in a timely manner, since the disease is a serious problem for the entire body.
How to recognize
After collecting urine, a change in color or the presence of sediment is alarming.
Normally, children have light-colored urine, while newborns have transparent urine. It is odorless and has a uniform consistency. The color of this liquid is affected by food, medications, diseases and other factors. Changes in color and consistency may be temporary and do not require treatment. Sometimes this is a symptom of pathology. Pathology can be noticed during urination or in the form of sediment formation. After collecting the analysis, when the container is standing, inclusions can be found at the bottom. It is white, yellow or another color.
White flakes indicate the presence of kidney and urinary system diseases. Most often, they indicate an inflammatory process, as a result of which mucus and epithelial cells become deposited. The urine may be dark in color.
The mechanism of urine turbidity in children
The composition of urine in children differs from that in adults. The bulk of urine is water. It contains some substances that the body sent for disposal. No other elements should be present; normal urine is always clear. In newborns it is almost colorless, in older children it is straw yellow. Turbidity in urine is caused by protein, leukocytes, red blood cells, mucus, and salts.
There is normally no protein in urine. It appears in cloudy urine due to inflammation. It is inevitably accompanied by the formation of inflammatory fluid - exudate. This is what causes cloudy urine. A much more serious problem is a large amount of protein in the urine. A destroyed filter in the glomeruli allows large proteins from the blood into the urine.
The kidney filter is normally impermeable to proteins.
Another reason for cloudy urine is white blood cells. These white cells are found in large numbers in the blood. They are an integral part of the immune system, protecting the body from bacteria and viruses. In favorable conditions they are found only in the blood. The appearance of a focus of inflammation is a signal for leukocytes to begin fighting the infection. With the blood flow they penetrate to the site of action. The presence of leukocytes in the urine is a direct evidence of inflammation. The infection can penetrate the kidneys, bladder, and urethra.
Doctor Komarovsky about cystitis - video
Red blood cells also make the urine cloudy. They have nothing to do with immunity. Their role is one - to carry oxygen. Their appearance in urine indicates serious problems. The first option is that somewhere in the urinary system, an inflammatory focus has destroyed a small vessel, and now blood flows from it in small portions. The second reason is that red blood cells leak into the urine through the glomerular filter.
The most common source of bleeding is the arcuate veins
Mucus is a product of the inflammatory process. Its appearance in the urine causes turbidity. If there is a lot of mucus, it creates sediment in the form of flakes. Turbidity is caused by salts - phosphates, oxalates, urates. They are formed from phosphoric, oxalic or uric acid. A small amount of salts is held in suspension. Otherwise, the salts precipitate and group into stones.
Salts in urine are one of the reasons for cloudiness
Physiological reasons
What does sediment in a child’s urine indicate? First of all, pay attention to the condition of fresh urine and the general well-being of the child.
Urine becomes cloudy after contact with air and settling. These are normal processes that occur in any sample over time. Urine also oxidizes. A few hours after it gets into a pot or a special jar, it darkens and acquires a more pungent odor.
If parents notice that sediment or plaque has formed in the pot over time, but the urine is clear and nothing bothers the child, there is nothing wrong with that. Salts are excreted with urine, which can be deposited at the bottom of the pot if the container is poorly washed. Your child's toilet should be cleaned and disinfected regularly.
There is a rule: to assess the condition of urine, no more than 1.5 hours should pass from the moment of urination to the examination. Long-term storage of biological fluid, even in a cold place, distorts its physicochemical properties.
Physiological causes of sediment in urine:
- If the sample is fresh and the parent finds sediment in the urine, the child’s cause may be related to insufficient drinking regime.
- Hot weather, profuse sweating, and improperly selected clothing can also cause cloudiness in a baby’s urine due to an increase in salt concentration.
- Stress and physical activity can cause short-term increases in protein excretion in the urine, which also causes turbidity. After replenishing the body with water and rest, these conditions go away on their own.
- Contamination of a freshly collected sample for analysis occurs when it is improperly collected from the surface of the child’s external genitalia after insufficient hygiene.
- The baby urinates much less frequently than loose stool. Physiological adjustments to the functioning of all body systems are underway. With the introduction of complementary foods, the composition and properties of the baby's secretions also change.
- Cloudy urine in a 2-year-old child may be associated with the addition of new foods to the diet. Plums, figs, grapes, gooseberries, sorrel, and legumes can reliably cause temporary turbidity in urine.
- In a 3-year-old child, cloudy urine may be observed periodically when the urine becomes acidic. For example, when overeating meat food. The acid reaction is accompanied by desquamation of epithelial cells from the mucous membrane of the urinary organs and an increase in the turbidity of the biological fluid.
Often cloudy urine in a 3-year-old child (the reasons are related specifically to eating behavior) causes unnecessary worry among parents. Dried drinks, soda with dyes, insufficient regular drinking water - all this can disrupt the excretory function of the kidneys with an increase in the concentration of salts in urine.
Causes of cloudy urine
There are a number of mechanisms for clouding urine. Each of them underlies at least several diseases of the urinary organs. They are accompanied by various symptoms, a set of which can suggest a specific cause for the appearance of cloudy urine.
Reasons for changes in urine - table
| Urinary tract diseases | Cause of illness | Mechanism of the disease | Associated symptoms |
| Pyelonephritis | Pathogenic microbes and viruses | Inflammation of the renal cups and pelvis |
|
| Glomerulonephritis | Immune aggression | Damage to glomeruli by immune cells |
|
| Cystitis | Microbes and viruses | Inflammation of the bladder wall |
|
| Urethritis | Microbes and viruses | Inflammation of the urethra |
|
| Urolithiasis disease | Increased amount of salts in urine | Precipitation of oxalates, urates, phosphates |
|
| Kidney tumor | Formation of malignant cells | Spread of malignant cells |
|
| Hydronephrosis | Blockage of urine flow from the kidney | Expansion of the calyces and renal pelvis |
|
| Polycystic kidney disease | Wrong gene | Formation of fluid-filled cavities in the kidneys |
|
| Interstitial nephritis | Allergic reaction | Inflammation of cells between the glomeruli and tubules |
|
Causes of cloudy urine - photo gallery
Pyelonephritis occurs under the influence of pathogenic microbes
Glomerulonephritis - a disease of the glomeruli
Cystitis - inflammation of the bladder wall
Wilms tumor is the most common neoplasm in children
Hydronephrosis occurs due to an obstruction in the flow of urine
Polycystic disease is a hereditary kidney disease
Kidney stones are formed from salts - urates, oxalates, phosphates
Symptoms and treatment
The main signs accompanying urinary tract infections:
- cloudy urine;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen, lumbar region;
- pain during urination;
- temperature increase;
- fever, chills;
- foreign impurities appear in the urine: blood, sediment, “flakes”, pus;
- the whites of the eyes and skin tone change from the usual to yellow;
- urine acquires an unpleasant odor;
- the child is restless, whiny;
- appetite decreases, sleep deteriorates;
- vomiting develops;
- bowel dysfunction (diarrhea);
- weakness appears, the child is lethargic.
it is enough to normalize the drinking regime; you will have to change your diet (give up processed foods, sweet soda, items with preservatives and dyes);
an important point is the use of vitamin-mineral complexes according to the norms for a certain age; If cloudy urine occurs while taking antibiotics, then at the end of the course of therapy it is important to take probiotics and drink enough fluid to remove excess accumulated drugs from the body.
Therapy for pathological processes depends on the diagnosis made by a nephrologist or urologist. During treatment, advice from an experienced pediatrician and gastroenterologist is important if a urinary tract infection has developed due to the penetration of E. coli, opportunistic bacteria inhabiting the gastrointestinal tract.
The main groups of drugs for stopping the inflammatory process:
- antibiotics. Ampiox, Carbenicillin, Ampicillin, and drugs from the cephalosporin group are suitable for children. At an early age, potent compounds - aminoglycosides - are not prescribed;
- (diuretic drugs). Furosemide, Diacarb, Hypothiazide, Veroshpiron. Natural diuretics: watermelon, cranberry juice, lingonberry leaf tea, dill water;
- general strengthening compounds, vitamin and mineral complexes;
- preparations that dissolve salts. (dragées from 6 years), (from 12 years), (syrup - from 1 year, capsules and drops - from 7 years);
- antispasmodics. Fennel fruit oil, dill water, M-anticholinergic agent priphinia bromide, mint tea, Platiphylline;
- analgesics. Paracetamol, Panadol, Ibuprofen, Nurofen.
How to prevent cloudy urine in a child? Doctors recommend studying the list of factors that provoke negative processes in the kidneys and bladder.
Preventive measures:
drinking clean water according to the norms for a certain age; proper nutrition, avoidance of harmful products containing synthetic dyes; reasonable consumption of meat dishes, sour fruits, sorrel. Drinking milk with a high percentage of fat content is not beneficial; the child’s diet should be appropriate for his age; careful hygiene of the external genitalia, especially in girls; refusal to swim in polluted waters; taking antibiotics only as prescribed by a pediatrician or specialist; after the course, using drugs with lactobacilli to restore intestinal microflora; prevention of hypothermia; treatment of inflammatory diseases: through lymph and blood, harmful bacteria spread throughout the body, penetrate the bladder, kidneys; timely visits to doctors if there is a change in the child’s behavior, weakness, chills, or a change in the color of urine
It is important to notice signs of intoxication in time and prevent the spread of infection.
When the urine becomes cloudy in children, you should not panic, but rather deal with the causes of the deviation.
It is important to remember what the child ate and drank the day before, what medications he took, and whether he suffered an infectious disease. All parents’ questions will be answered by a urologist or nephrologist, with whom you should make an appointment
If additional signs are observed that confirm the development of a pathological process in the body, then you should not postpone a visit to a specialist: pathologies of the bladder and kidneys in advanced stages are difficult to treat, and relapses are possible.
Children's doctor Komarovsky will talk about urine analysis and the features of treating urinary tract infections in the following video:
A urine test can at the right time indicate the presence of pathologies developing in the body. Everyone understands that urine produced in the body under normal conditions should be a transparent yellow liquid without impurities.
Signs of normal urine:
- yellow;
- no turbidity;
- transparency;
- there is no protein, glucose, ketone bodies, casts, bilirubin, hemoglobin, salts, bacteria;
- single erythrocytes, leukocytes and epithelial cells are present;
- There are no white flakes.
Treatment methods for diseases accompanied by cloudy urine
A pediatric nephrologist treats urinary tract diseases. The disease is affected from several sides - with the help of medications, physiotherapy methods, and, if necessary, surgical interventions are used.
Pharmacological agents
Medicines are a doctor’s faithful assistant in the fight against diseases of the urinary system. They effectively influence microbes, inflammation, blood flow speed in blood vessels, metabolism in kidney cells, and normalize blood pressure. Combinations of drugs are selected by a specialist depending on the cause of the disease.
Drugs used for urinary tract diseases - table
| Pharmacological group | For what diseases is it used? | Examples of drugs |
| Antibiotics |
|
|
| Antiviral drugs |
|
|
| Antipyretic (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory, painkillers) drugs |
|
|
| Diuretics | Glomerulonephritis |
|
| Hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs, including those that suppress immunity | Glomerulonephritis |
|
| Uroantiseptics |
|
|
| Herbal uroantiseptics |
|
|
| Blood thinners | Glomerulonephritis |
|
| Antihypertensive drugs |
|
|
| Vascular and metabolic drugs |
|
|
| Antitumor drugs, including immunosuppressants |
|
|
Drugs for the treatment of urinary tract diseases - photo gallery
Cycloferon helps in the fight against viruses
Lasix stimulates urine production
Prednisolone is a hormonal drug
Levofloxacin kills pathogenic bacteria
Cyston - herbal antiseptic
Trental improves blood movement through blood vessels
Nurofen is an analgesic and antipyretic drug
Cefotaxime is an effective antimicrobial agent
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy will help the youngest patients cope with inflammation. In addition, these methods are allowed from the first days of life and have virtually no side effects:
- electrophoresis using current will deliver drugs to the inflammatory focus;
- laser therapy will help the inflamed organ recover;
- magnetic therapy eliminates inflammation;
- Ultrasound therapy will help the inflammatory lesion heal without scars.
Operations
Surgeries are used in special cases when the kidney is significantly altered by disease and is unable to perform its job. In addition, the high risk of blockage of urine flow and urinary tract infection are also reasons for surgical intervention.
Methods of surgery on the urinary tract - table
| Type of disease | Operation name | Operation technique |
| Kidney tumor |
|
|
| Hydronephrosis |
|
|
| Urolithiasis disease |
|
|
Types of surgeries on the urinary tract - photo gallery
Nephrectomy is rarely used in children
Pyeloplasty is a way to eliminate the cause of hydronephrosis
The stent facilitates the flow of urine from the kidney
Nephrostomy serves to drain urine from the kidney
Kidney resection involves removing part of an organ
A child has cloudy urine: what could it be and what diseases provoke the appearance of such a symptom?
The table below lists diseases that are often the main cause of changes in the physical characteristics of urine. Each illness is accompanied by the appearance of a number of other unpleasant symptoms that help identify the disease.
| No. | Name of the disease | Symptoms | Treatment |
| 1. | Acute respiratory diseases | An increase in body temperature provokes the appearance of cloudy urine with sediment. | Treatment is aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms, increasing the body's protective properties and immunity. After symptomatic therapy, urine becomes normal. |
| 2. | Inflammatory processes in the organs of the genitourinary system | Increased body temperature, cutting or dull pain in the kidneys, bladder or vagina, depending on where the problem is located. | Due to the inflammatory process in urine, the number of red blood cells and white blood cells increases. They cause changes in its color and density. Treatment is aimed at eliminating inflammation and improving organ function. |
| 3. | Diseases of the liver and biliary tract | With hepatitis, in addition to cloudy urine, appetite deteriorates, nausea and vomiting appear. Parenchymal jaundice is accompanied by yellowing first of the mucous membranes and then of the skin. | If the urine becomes cloudy and dark, like beer, this may be an indicator of a high content of hemoglobin breakdown products in the urine. Since these substances should not be in the urine, you should immediately go to the doctor for examination. |
| 4. | Acute appendicitis | Pain in the lower abdominal cavity, fever, cloudy urine. | If you have these symptoms, you should immediately call an ambulance or go to a medical facility yourself for emergency surgical care. An attack of acute appendicitis is an extremely, extremely dangerous condition, so you cannot hesitate in such a situation. |
| 5. | Diabetes | Acetonemia, glucose starvation of cells. | Special ketone bodies are formed in the blood, which are responsible for changes in the color and smell of urine. To keep acetone levels under control, parents are advised to purchase special tests that are very easy to use at home. |
| 6. | Pyelonephritis | An increase in body temperature, pain when urinating, the presence of white flakes in the urine, the urine becomes cloudy and acquires a greenish tint. | Treatment is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process in the kidneys and tubular system. In case of severe pain, additional medications are prescribed to reduce pain. |
In a 2-year-old child, cloudy urine may be detected due to congenital anomalies in the structure of the kidneys that were not immediately identified. Due to its structure, urine stagnates in the bladder. Sometimes a phenomenon occurs such as urine being thrown into the ureters. Because of this, a large number of bacteria and leukocytes from the affected kidney tubules enter the urine.
If there is blood in the urine, you can judge about liver problems
Complications and prognosis
The appearance of cloudy urine is only part of the problem. Usually the disease affects the body more deeply and widely. Therefore, the prognosis of treatment depends entirely on the nature of the underlying disease. Pyelonephritis and cystitis can be completely cured. Glomerulonephritis often becomes chronic. In case of hydronephrosis, it is possible to preserve a functioning kidney. The prognosis for treatment of a kidney tumor depends on its type. For example, Wilms tumor is curable in 90–95% of cases. Each disease has its own complications, but the most dangerous is chronic renal failure - poisoning of the body with toxins that are retained in the blood due to the low rate of filtration in diseased kidneys.
Diagnosis of pathologies that contribute to clouding of children's urine
The primary diagnosis of pathology associated with cloudy children's urine includes a general urine test, in which a laboratory technician examines its color and the presence of sediment. This study allows you to identify the following diseases in an infant:
Additional methods for examining cloudy urine include:
- urine test or Nechiporenko test, necessary for a detailed study of the formed elements of urine;
- analysis according to Zimnitsky;
- biochemical laboratory blood test;
- Ultrasound of the bladder and kidneys.
Before taking a urine test, parents need to make sure that the container is sterile and the child is well washed. Otherwise, the research results may be unreliable. Urine collection from infants is carried out using a special urinal, which is attached to the baby's genitals. Urine collected from a potty or diaper is not suitable for analysis.