Causes (etiology) of diabetes in infants:
Unfortunately, at the moment there is no information about the exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis, but several risk factors for its development can be identified:
- colonization of the skin by yeast fungi of the genus Malassezia;
- increased secretion of sebaceous secretions (oily skin);
- immunodeficiency conditions (HIV, patients after transplantations, etc.);
- heredity (history of the disease in close relatives);
- unfavorable climate (spring-autumn exacerbations are typical).
Treatment
Since the crusts adhere very tightly to the skin, under no circumstances should they be removed mechanically - this can severely damage the baby’s delicate skin and leave large scars.
Before removing crusts on a baby’s eyebrows, a couple of hours before bathing, they should be lubricated with warmed baby oil, burdock oil or Vaseline. When the baby is in the bath, you should wash the eyebrows with baby shampoo and try to remove the crusts with a soft washcloth or toothbrush. After bathing, it is advisable to wipe the eyebrows with any disinfectant and apply an antiseptic cream. Usually 2-3 such procedures are enough to remove dried formations.
If such measures do not help, you need to consult a pediatrician who will prescribe a special ointment. There are special solutions designed to lubricate seborrheic areas and help exfoliate crusts.
In breastfed babies, crusts may occur as a reaction to some of the mother's foods. So, if they continue to actively grow, the mother should stop eating fatty and smoked foods and reduce the presence of salty and sweet foods in the menu to a minimum.
If the cause of crusts on the eyebrows of a baby is exudative diathesis, the nursing mother should avoid foods containing trophallergens. It is advisable to increase the amount of vegetables and fruits mother consumes - healthy
For bottle-fed babies, it is advisable to replace milk with fermented milk products - acidophilus, kefir, etc.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis
Childhood diabetes is characterized by gradual development and diffuse rashes in certain places - most often on the scalp (including along the hairline), on the face (in the area of the nasolabial folds and along the eyebrows), and also under the diaper.
Based on skin manifestations, seborrheic dermatitis is divided into several types:
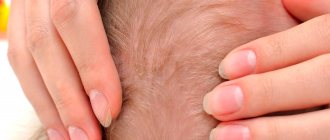
- Oily type - the appearance of oily crusts on the scalp, and the appearance of acne on the face is also possible.
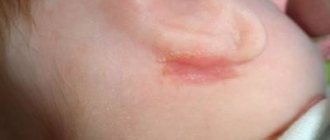
- Dry type - the appearance of dandruff on the head, as well as cracks in the area behind the ear.
- Mixed type - manifestations of both types are observed.
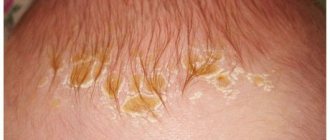
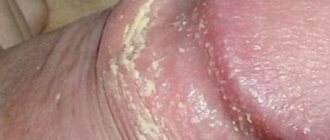
In infants, DM often develops in the oily type - in the form of a lesion on the scalp, covered with a thick yellow crust (gneiss, “baby cap” or “milk crust”) and the appearance of yellow flaky scales of characteristic localization (see above). In addition, another type of rash can also be detected on the skin of the face - clearly defined pink-red plaques covered with whitish scales. The same rash can be observed in the diaper area.
Dermatologist Anna #a_medclinic_Bolshakova talks about newborn acne. ⠀ The popular name “infant bloom”, “hormonal rash”, “newborn acne” or dermatologically transient neonatal pustular melanosis is a variant of the physiological norm. One of the reasons is considered to be fluctuations in hormonal levels, which affect the activity of the baby’s still imperfect sebaceous glands (due to an increased concentration of estrogen from the mother). ⠀ Usually, “newborn bloom” begins to appear in the second or third week of life, and passes without a trace by the 3rd month. ⠀ Small red elements (pustules) with whitish or white-yellow spots, similar to pustules, appear on the baby’s skin. The rashes may merge into groups.
They are absolutely sterile! That is, they have nothing to do with bacterial pustules.
The predominant localization of the rash is the face (cheeks, forehead, eyelids, chin); it can also be found on the neck, behind the ears, and upper torso, and in boys also on the genitals. ⠀ In contrast to allergic and pseudo-allergic appearances of newborn acne:
- do not bother the child (no itching, sleep or appetite disturbances)
- characterized by “white tips” in the center
- never peels off
- rashes do not merge into weeping lesions!
That is: if the rash spreads throughout the body, bothers the child, merges into weeping lesions or peels off - this is no longer neonatal acne. ⠀ “Hormonal rash” must be distinguished from prickly heat. ⠀ Since flowering of newborns is, in fact, a completely normal phenomenon, in most cases no specific therapy is necessary. By 2-2.5 months of the baby’s life, the rashes disappear on their own, and not even the slightest trace remains in their place. Treatment is required only for very severe types of hormonal rash. In such situations, the help of a dermatologist or endocrinologist is required.
You should never squeeze white spots on your baby's skin, as such actions can lead to infectious complications and cause scars. There is also no need to treat pustules with alcohol solutions and other antiseptics (potassium permanganate, furatsilin, etc.).
Proper care for the delicate skin of a newborn involves only ensuring its dryness and cleanliness. The use of fat-based ointments is also contraindicated for newborn acne, since they create an airtight film on the baby’s skin, which only worsens the situation. ⠀
Differential diagnosis of diabetes and other dermatological diseases
Diagnosis of seborrheic dermatitis is based on the clinical picture and includes assessment of the nature of the rash (color, shape, and other properties), its location and symmetry. Sometimes it is necessary to use microbiological diagnostics if there is a suspicion of an initially infectious nature of the rash or the addition of a secondary bacterial/fungal infection.
The difficulty in diagnosing seborrheic dermatitis lies in making a correct differential diagnosis with other clinically similar dermatological diseases, because psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, and rosacea (rosacea).
Treatment and care for seborrheic crusts in children
Seborrheic dermatitis may resolve without treatment, but relapses are common after periods without clinical manifestations. If treatment is still necessary, then to correctly prescribe it, you need to contact a specialist - a pediatric dermatologist.
Often the basis of treatment is the selection of special medicinal cosmetics: shampoos, lotions and creams that can gently cleanse the scalp of crusts and remove excess sebaceous secretions from the facial skin. In addition, for children it is important to select products that can relieve itching, because... additional scratching of the rash can lead to secondary infections.
For treatment, products are used that contain the following components:
- keratolytics (eg salicylic and lactic acids) - to soften the top layer of skin;
- antifungal agents - when mycoses are attached;
- local corticosteroids - to relieve inflammation;
- in severe cases, phototherapy and the use of isotretinoin to reduce seborrhea are justified.
Skin care for children with diabetes should be regular (daily) to improve the course of the disease and speed up recovery. Children's cosmetics for skin care with diabetes are classified as medicinal products and therefore are selected only by a specialist (pediatric dermatologist). Care includes the following procedures:
- Applying baby cosmetic oil before washing your hair to soften seborrheic crusts.
- Wash your hair with a special shampoo using gentle massaging movements to avoid skin trauma.
- Daily treatment of rashes on the face, along the hairline and in the area behind the ear with a special cream or lotion.
- Thoroughly dry the skin after hygiene procedures to prevent the appearance of a damp environment favorable for the development of microorganisms.
How to remove milk crusts quickly and comfortably?
Authors : Ulyanova Alexandra
As an advertisement
What are “milk crusts”?
Seborrheic dermatitis, gneiss or simply “milk crusts” are white or yellowish sebaceous scales that appear on areas of the skin rich in sebaceous glands: scalp, ears, face, upper third of the chest and back, inner thighs. They usually appear in the first 10 weeks of life.1
Why does my child have scabs?
This problem occurs in about 70% of children and usually goes away in a few weeks or months.
This is usually due to excessive activity of the sebaceous glands due to the presence of maternal hormones in the child’s body. 1 Therefore, you should not worry that your baby was so unlucky.
Do they need to be removed?
This is not dangerous for the baby, but the skin must be cleaned of crusts to prevent infection. In addition, the appearance of the crusts is not very attractive!
What if there are only a few crusts?
If there are very few crusts, they are small and loose, then washing your hair daily with a special foam shampoo for newborns will be sufficient. This foam contains climbazole and salicylic acid in a concentration approved for use in children's shampoos, which limit the growth of bacteria and help soften milk crusts.
How to remove crusts using oil?
To get rid of milk crusts, they traditionally use this method: the crusts are softened with warm boiled vegetable oil and combed out with a comb. If there are a lot of crusts, then it becomes almost a military operation. Heat the sunflower oil, make sure it is not too hot, apply it to the baby's head and put a cap on top. This procedure, of course, stains your hands, diapers, and clothes with oil. After a few hours, wash the head and start combing, being careful not to scratch the baby’s skin or damage the hair follicles with the comb. This procedure must be repeated regularly, as crusts may reappear over time. Agree, this procedure is not pleasant!
Is it possible to remove crusts quickly and without combing?
Fortunately, science is moving forward, and there are modern and safe ways to get rid of milk crusts.
Mustela scalp cream for “milky crusts” will help cope with the problem in an average of one week. And you don't have to comb it out with a comb!
Applying the cream is more convenient and easier than regular oil: it is non-sticky with a milky texture, and has a thin applicator nose. Hands, clothes and towels - everything remains clean.
How does milk crust cream work?
The cream acts not only on the crusts themselves, but also on the cause of their occurrence, regulating the production of sebum. The cream contains effective softening components, such as borage oil, which also has moisturizing properties.
Apply the cream to the crusts, massaging lightly, leave overnight and rinse off the next day. The crusts will come off easily during washing. The cream works faster and more efficiently - on average, within seven days the crusts disappear completely. 2
For better results, after applying the cream, it is better to wash your head with Mustela foam shampoo for newborns and use it instead of regular shampoo to minimize the risk of crusts. The texture of the foam is very delicate and consists of 99% ingredients of natural origin.
When should you see a doctor?
If crusts appear, as well as if the skin condition worsens, redness or itching appears, you should consult a pediatrician.
Clinical recommendations “Seborrheic dermatitis in children.” Union of Pediatricians of Russia, 2021 https://www.pediatr-russia.ru/sites/default/files/file/kr_sebder.pdf
According to the results of a test involving 60 children who used the cream for 2 weeks, 63% of respondents completely disappeared milk crusts on average within 6.6 days, the remaining 37% showed an improvement in their condition. Clinical studies Cleanreal D1516/TC091/1042F4
published 05/04/2019 14:11 updated 05/04/2019