Causes of the disease
Vitamin D enters the baby’s body in two ways:
- It is synthesized in the skin under the influence of sunlight (ultraviolet radiation). Further biotransformation takes place in the liver and kidneys.
- With food. In this regard, artificial formula is more nutritious than breastfeeding.
Lack of sunlight and poor nutrition (including mothers) are the main reasons for the development of rickets in infants.
The following factors may increase the risk of developing the disease:
- not getting enough sunbathing;
- high birth weight;
- prematurity;
- refusal of breastfeeding and use of unbalanced formulas;
- rapid weight gain;
- digestive disorders;
- congenital diseases of the liver, kidneys, and endocrine system;
- taking anticonvulsants;
- low physical activity;
- hereditary metabolic disorders.
Causes and prevention of rickets in infants
Metabolic disorders with a decrease in the level of vitamin D and its active metabolites in the child’s body are a polyetiological pathological condition that develops due to the influence of several common factors:
- Incorrect feeding of a child - up to the age of six months for a baby, the only source of all necessary compounds, vitamins, and minerals is mother's milk, so he should not be breastfed. If, for objective reasons, a woman cannot feed her child with breast milk, he is transferred to artificial feeding. It is important to use only specially adapted milk formula. Feeding with cow's or goat's milk is not allowed.
- Insufficient skin insolation - when exposed to sunlight, namely the ultraviolet spectrum of light, endogenous (own) vitamin D is synthesized in cells, which in the liver is converted into an active form responsible for regulating the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus salts.
- Inflammatory or somatic pathology of the structures of the gastrointestinal tract, accompanied by impaired absorption of vitamin D from food.
- Impairment of the functional state of the liver or kidneys, which may be of congenital or acquired origin. In this case, the conversion of vitamin D into its active metabolites, which are directly involved in the regulation of the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus salts, is disrupted.
- Long-term systematic use of drugs of the pharmacological group anticonvulsants.
Knowledge of the provoking factors that lead to the development of rickets in infants allows us to select optimal measures aimed at preventing the development of metabolic disorders:
- Breastfeeding or using an adapted milk formula.
- Walking in the fresh air – even in winter, you should take a walk outside with your baby. Exposure to a small amount of sunlight on the facial skin promotes the synthesis of endogenous vitamin D.
- Timely detection and treatment of pathological conditions of the gastrointestinal tract, liver or kidneys that affect the level of vitamin D in the child’s body.
- Limiting the duration and dosage of taking anticonvulsants.
If necessary, for children born in winter, the doctor prescribes preventive medications containing age-appropriate amounts of vitamin D and mineral salts of calcium and phosphorus. Taking simple preventive measures will make it possible to avoid negative consequences for the child’s health associated with metabolic disorders, as well as bone deformation.
Watch in this video how to do massage and gymnastics for a child who has had rickets:
They are also prescribed with caution to children receiving adapted milk formulas that already contain vitamin D.
Clinical manifestations
Due to insufficient mineral metabolism, the development of bone tissue is disrupted. In addition, other systems also suffer: nervous, endocrine, muscular, etc.
Pathology has stages, its manifestations can vary greatly in intensity.
Stages of rickets in infants:
- initial stage;
- height;
- recovery (convalescence);
- residual effects.
The severity of rickets is determined by the severity of symptoms.
It is important to recognize rickets when the first symptoms appear. These include:
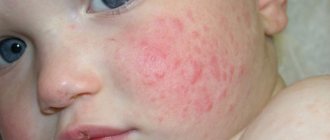
- thickenings on the ribs at the transition points between bone tissue and cartilaginous tissue - “rachitic rosary” (see photo);
- increased sweating;
- the baby is restless, there may be twitching of legs and arms during sleep;
- the edges of the large and small fontanelles soften;
- sweat and urine acquire a peculiar sourish odor.
The very first manifestations may occur at 2–3 months of life.
Damage to the skeletal system
The specificity of rickets is such that the bone apparatus undergoes the greatest changes. Even if there is a sufficient amount of calcium and phosphorus in the diet, if there is a lack of vitamin D, they will not be absorbed normally.
Damage to the skeletal system is manifested in the following:
- the edges of the fontanel and the sutures of the bones of the skull soften;
- the shape of the skull changes, it is sloping in the occipital region;
- the frontal and parietal regions protrude;
- fontanelles do not close for a long time;
- deformation of the chest is noted: “cobbler’s chest” - depression in the lower part of the sternum or “keeled (chicken)” chest - protrusion of the sternum;
- bone growths—“rosary beads”—appear on the ribs;
- rachitic kyphosis (curvature of the spine) develops;
- on the legs and hands, thickenings appear on the epiphyses of long bones - “rachitic bracelets”, on the phalanges of the fingers - “strings of pearls”;
If you ignore the problem and do not treat rickets, the symptoms will increase. There is a change in the pelvic bones, it flattens and decreases in size. The bones of the legs are curved in an O-shape or X-shape. Flat feet appear.
Teeth appear late, they are susceptible to caries, and the bite is disturbed.
Defeat of other systems
Calcium deficiency inevitably affects other systems of the baby.
The muscles and central nervous system suffer the most.
The muscles become flabby and lose tone. The tendons are not strong, the joints become loose. When a child sits down, he prefers to cross his legs and support his torso with his arms. The rectus abdominis muscles are hypotonic, can diverge, and a characteristic “frog belly” appears.
Neurological changes affect almost everything. Behavior changes, tearfulness and anxiety increase. Sweating of the skin increases, especially at the point of contact of the scalp with the pillow. Increased skin sensitivity (hyperesthesia). The baby begins to cry and be capricious when touched, although this has not been noticed before.
Doctor's advice
Walking is very important for a baby, especially under the age of one year. 20 minutes of exposure to the sun (not at noon, so as not to get sunburned, but in the morning or evening) will significantly increase the level of vitamin D. You must remember that the sun's rays penetrate through fabrics, clothes, and clouds, so you should not expose your child to the scorching sun for a long time, It is enough for him to sleep in the stroller outside even in cloudy weather.
Victoria Druzhikina Neurologist, Therapist
Deep progression of the pathology leads to general lethargy, lethargy, and apathy. Conditioned reflexes are poorly formed in sick children.
How is rickets treated?
To cure rickets, you will need a set of measures:
- taking vitamin D, and, if necessary, calcium and phosphorus;
- elimination of the cause of the disorder;
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- physiotherapy.
Vitamin D intake
The norm of vitamin D for the treatment of the disease is 600-700 IU/day. A doctor should prescribe the dosage, and he will also monitor the intake of medications.
The opinion of a pediatrician, candidate of sciences, Dr. Komarovsky, is interesting. He claims that a dose of vitamin D exceeding 500 IU/day is a real crime for the attending physician.
Komarovsky claims that a lower norm can cure the disease. Instead of vitamin in some cases, he recommends taking drops such as Aquadetrim. Dosage regimen: 1 drop of aqueous solution per day.
READ ALSO: analogues of the drug "Aquadetrim" for infants
Gymnastics and massage
Gymnastics for sick children consists of the following blocks:
- Passive exercises are manipulations that parents perform on the child’s body. Crossing the upper and lower limbs, their flexion and extension.
- Active exercises. The baby performs these movements himself. Parents help him by moving toys and making hand gestures.
- Reflex movements. The child performs them in response to blows and touches from his parents at certain points on his body.
The massage begins with calm, sliding strokes. This helps reduce the child’s anxiety and normalize the tone of the central nervous system. Next, rubbing is performed - more intense movements, the purpose of which is to work with the deep layers of the skin. The result will be an acceleration of metabolic processes.
The next stage is kneading the muscles. Gently massaging the arms and legs accelerates blood flow and promotes the removal of metabolic products from the body. Finally, the massage therapist begins vibration - small tapping on the body. Vibration without stopping removes excess muscle tone, tapping intermittently strengthens it.
Diagnostics
An accurate diagnosis can only be made using laboratory tests:
- Biochemical analysis of blood and urine will help determine the content of phosphorus, calcium and alkaline phosphatase.
- Urinalysis - Sulkovich's test shows the amount of calcium excreted from the body.
- Diagnostic radiography and bone ultrasound may be prescribed.
Interpretation of test results allows you to accurately determine the cause and source of negative phenomena.
If you suspect rickets in your baby, be sure to consult a pediatrician. Some residual effects of the disease may remain with the child for life.
Treatment
There are two therapeutic approaches: specific treatment and nonspecific. The ideal option is their combination – complex treatment:
- balanced diet;
- walk outdoors;
- gymnastics, massage, water treatments;
- symptomatic treatment of other diseases;
- prescribing medications containing vitamin D and calcium.
It happens that rickets appears for other reasons not related to calcium and vitamins. For example, in case of impaired absorption of calcium in the gastrointestinal tract, pathology of the parathyroid glands or pituitary gland. These forms of rickets are much more difficult to treat.
Preventive measures
Prevention of rickets in an infant should begin in the last months of pregnancy and should only be carried out under the supervision of a specialist.
A pregnant woman needs to eat well, walk in nature, and take vitamins in recommended doses.
It is important for the baby to provide rational feeding, going for walks, exercise and massage.
All children under three years of age are prescribed vitamin D in prophylactic doses depending on age, type of feeding and region of residence.
Victoria Druzhikina
Neurologist, Therapist
For information on the symptoms and treatment of rickets in infants, watch the video “Doctor Komarovsky’s School”:
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://sevgb6.ru/doc/klinicheskie-rekomendacii/raxit.pdf
Rate how useful this article was
5 Voted by 1 person, average rating 5
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Severity of rickets
Depending on the severity of the clinical manifestations of rickets in infants, 3 degrees of the disease are distinguished.
- Mild course of rickets, rickets of the 1st degree. In infants, grade 1 rickets is quite mild, and no disturbances in psychomotor development are observed. Damage to bone and muscle tissue is mild and reversible with proper treatment.
- Moderate rickets, 2nd degree rickets. The manifestations of rickets are quite pronounced; weakness of the muscles and ligaments attracts attention. The child's static functions are disrupted, the spine is deformed, the stomach becomes large and round, and the abdominal muscles diverge. On the part of the heart, weakness, muffled heart sounds, increased heart rate, and anemia are noted. Possible digestive and respiratory problems. Such children lag behind in physical and mental development.
- Severe rickets, rickets of the 3rd degree. It is characterized by severe violations of all organs and systems. The nervous system is significantly affected, the child is lethargic, inhibited, and does not react to others.
The patient's skeletal system is deformed, the muscles are extremely flaccid. The child loses the ability to move and forgets acquired skills. The functioning of the heart, respiratory and digestive systems is seriously impaired, and severe anemia develops.