How the fetus develops
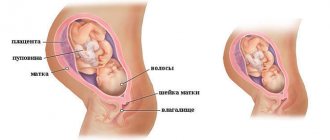
In the second trimester, the fetus continues to develop individual organs and systems. By week 18, its weight reaches approximately 300 g. During this period, the child may hiccup, yawn, and fingerprint patterns appear on his fingers. At 20-21 weeks, when you feel the first movements, the baby already skillfully controls his movements and understands where individual parts of the body are located. From about 23 weeks, subcutaneous fat begins to be deposited. Over the next 4 weeks, the weight of the fetus almost doubles and by the end of the second trimester it is 800-900 g.
There are several more interesting facts related to fetal development in the second trimester:
- Hairline. Around the 15th week, the first hairs begin to sprout on the baby’s skin, and at the 22nd week, eyelashes and eyebrows appear. At the same time, its body is covered with embryonic fluff - lanugo. Lanugo has an important function: it retains the waxy lubricant that is secreted by the skin and protects it from the effects of acidic amniotic fluid.
- Digestive system. By mid-pregnancy, the fetus learns to suck and swallow. By swallowing amniotic fluid, it even tastes the foods you eat. The liquid that enters the body is processed by the baby’s kidneys - every 40-50 minutes he excretes urine.
- Sense organs. The fetal ears move from the side of the neck to the correct position. Starting from the 22nd week, the baby can already see and hear. His eyes open.
- Heart. After 17 weeks, the baby’s heart stops beating spontaneously - its contractions are now controlled by the brain. From week 20, the fetal heartbeat can be heard through the abdomen with a stethoscope.
- Brain.
By week 24, the number of cells in the brain reaches its maximum. The child develops his own sleep-wake cycle. He dreams.
| Babies born at 6 months have approximately an 85% chance of survival. They cannot breathe on their own yet, so they are connected to a ventilator. During the nursing process, such newborns are prescribed special therapy that stimulates the maturation of lung tissue. |
How to choose a maternity hospital?
Choosing the hospital where a woman is going to give birth is an important issue. It should be a place that provides good, professional care, comfort and a sense of security. Therefore, it is worth choosing a hospital for childbirth in advance. After visiting the most suitable facility, the following details should be discussed:
- Ask how much individual obstetric care costs, what medical interventions are available and how much they cost, whether family births are practiced, and whether showers/baths are available during labor. If possible, ask to see the delivery room and postpartum room.
- Determine whether the hospital is prepared for complications during childbirth - whether it has the necessary equipment to provide immediate care to the newborn and the woman in labor.
The conversation with the midwife and the overall impression that the expectant mother experiences after visiting the maternity and postpartum rooms often determine the final choice.
In the second trimester, psychological comfort sets in; you are accustomed to the idea that you will soon become a mother; plans are made for the future, when your beloved child will play a key role. To find out how your pregnancy and baby will develop further, read the article about the third trimester of pregnancy. We have also prepared a short checklist for you on what you need to do in the second trimester:
You can download this checklist from this link.
Possible complications
=> Gestational diabetes.
This is a special type of diabetes that can develop in a woman at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy. During this period, the hormones that the placenta begins to produce suppress the production of the pancreatic hormone, insulin. To maintain normal blood sugar levels, the pancreas has to work twice as hard. If it fails, insulin deficiency occurs and, as a result, diabetes.
Those most susceptible to developing this disease are:
- overweight women (BMI over 30),
- who have previously given birth to a large child (weighing more than 4.5 kg),
- having direct relatives with diabetes,
- pregnant women over 35 years old.
Gestational diabetes is manifested by increased thirst, frequent urination and weakness. To confirm the diagnosis, the woman is given a glucose tolerance test.
Diabetes in pregnant women is fraught with the development of neurological and respiratory disorders in the child after birth, so this disease must be taken seriously. A strict diet is recommended for pregnant women. For severe diabetes, insulin therapy is used.
After giving birth, gestational diabetes goes away on its own, but women remain at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
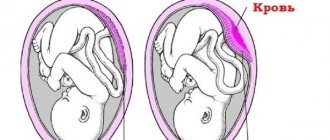
=> Placenta previa.
Usually the placenta forms in the fundus or on the walls of the uterus, but sometimes it is located in its lower part. In this case, they talk about its presentation. With this diagnosis, the placenta completely or partially blocks the baby’s birth path. If the exit from the uterus is partially blocked, the placenta can still move to the correct position towards the end of pregnancy. Then the baby will be born naturally, without a caesarean section.
The most common symptom of placenta previa is bleeding. The reason for their occurrence lies in the low elasticity of the placental tissues, which do not have time to stretch following the rapidly growing lower part of the uterus. In some places, the placenta detaches, which is accompanied by damage to blood vessels.
Bleeding begins suddenly and almost always for no apparent reason. They often occur at night. Once it appears, bleeding occurs again and again. Moreover, you can never predict what they will be next time in terms of strength and duration.
Bleeding is life-threatening for mother and baby, so it can only be treated in a hospital setting.
=>
Frozen pregnancy .
This is a complication of the first or second trimesters of pregnancy, in which the fetus stops developing and dies. In this case, spontaneous abortion may not occur. For some time, the uterus continues to grow, and human chorionic gonadotropin, the hormone responsible for maintaining pregnancy, continues to be detected in the woman’s blood.
As the functions of the placenta fade, the mother’s subjective signs of pregnancy disappear - nausea, drowsiness, breast swelling. In the second trimester, a characteristic symptom of fading pregnancy is the cessation of fetal movements.
The cause of the condition may be:
- genetic disorders in the fetus,
- maternal infections (eg rubella, toxoplasmosis),
- autoimmune disorders (diseases in which a woman’s body produces antibodies that attack her own cells and the cells of the fetus),
- exposure to negative external factors (radiation, vibration),
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol, drugs).
Most often, frozen pregnancy is diagnosed during a routine ultrasound (at 11-12 weeks of the first or 18-21 weeks of the second trimester). The dead fetus is removed from the uterine cavity. It is recommended to plan your next pregnancy no earlier than six months later.
=> Anemia.
In the second trimester, iron reserves in the mother's body are actively used up, which can lead to iron deficiency. As a result, the level of hemoglobin in the blood of a pregnant woman drops below 100 g/l. This condition is called anemia.
Anemia can be suspected by a feeling of weakness, tinnitus, dizziness, headaches, and dry skin. Although with a mild course of the disease, the mother’s well-being often remains normal.
Anemia threatens the development of placental insufficiency, leading to fetal starvation, and late miscarriage. Childbirth may be complicated by bleeding. To treat anemia in pregnant women, iron supplements are prescribed.
Second trimester of pregnancy
What vitamins should I take?
The second trimester of pregnancy is traditionally called the “golden period of pregnancy.” After all, usually by this time the toxicosis has subsided, and the belly is not yet so large as to cause discomfort in the expectant mother. This period marks the development of the baby’s basic systems and organs. For this process to go well, the pregnant woman must follow all the recommendations of the gynecologist and take certain micronutrients. In the second trimester, it is minerals that come to the fore, the deficiency of which can jeopardize the pregnancy itself.
Entering the second period of pregnancy, the expectant mother should pay attention to the following vitamins and minerals:
- Iodine;
- Iron;
- Calcium.
These micronutrients can be obtained from the diet by selecting it correctly, or taken additionally in the form of tablets if the results of a biochemical blood test show their deficiency.
Iodine is usually prescribed to women at the planning stage of pregnancy, since this element is important in the functioning of the thyroid gland. Then, when pregnancy occurs, it is responsible for the metabolism and proper development of the child. This is why it is so important not to stop taking iodine supplements in the second trimester. Iodine should be taken throughout pregnancy and lactation. Its deficiency will provoke the growth of goiter and disorders of the immune system. It has been proven that 250 mg of iodine every day contributes to the birth of children with a high IQ.
The most common complication of the second trimester of pregnancy is iron deficiency anemia. It causes a decrease in the protective function of the body, increased tone of the uterus, weakness, drowsiness, disruption of placental blood flow and even fetal hypoxia. Laboratory anemia is diagnosed using a general blood test, so before visiting a gynecologist it is necessary to regularly conduct this study. If the hemoglobin level drops below 110 g/l, the doctor recommends following a special diet and prescribes iron supplements in tablets or syrup. This element is best absorbed in the afternoon along with folic acid or vitamin C.
In the 2nd trimester, the pregnant woman’s need for calcium increases, since the child needs it for the formation of the skeleton, as well as the nervous, genitourinary and endocrine systems. The daily norm of this element is 1500 mg. Calcium deficiency leads to fetal growth retardation, cramps and muscle pain in a pregnant woman. It is also believed that calcium deficiency during pregnancy affects the development of rickets in the newborn. This is due to the fact that it is in the prenatal period that the bone apparatus and milk teeth are formed. However, an overdose of calcium can create additional stress on a pregnant woman’s kidneys, so it is important to calculate the exact amount of calcium in your diet with your gynecologist. This micronutrient is best absorbed together with vitamin D and in the evening.
Tone
Increased uterine tone - every second woman hears this diagnosis throughout almost the entire duration of pregnancy. Is it dangerous and what should be done with such a diagnosis?
Tone can appear in any of the three trimesters of pregnancy and is characterized by tension and involuntary contraction of the muscles of the uterine walls. At this time, the woman feels pain similar to pain during her period (the lower abdomen begins to ache and pull). In rare cases, a pregnant woman does not feel any discomfort. With this option, it will be possible to detect increased tone during an ultrasound examination.
Symptoms and causes of increased tone
When uterine tone occurs, the pregnant woman experiences pain, as with the onset of menstruation, often this is accompanied by peculiar contractions, and it seems that the stomach begins to “turn to stone.” It is especially dangerous if such contractions are accompanied by bloody discharge from the vagina.
The greatest danger is the occurrence of hypertension in the first trimester. Usually during this period, this condition is associated with a disruption in the production of the hormone progesterone and requires observation and treatment, otherwise there is a risk of losing the child.
In the 2nd trimester, tone may appear more often (from about 20 weeks), but this happens without pain. This condition is called training contractions. If the tone is accompanied by prolonged pain with a long duration, this can provoke hypoxia in the child.
Any of the following reasons can provoke tension in the uterus: Rh conflict (if the pregnant woman has a negative Rh and the fetus has a positive Rh), toxicosis, thyroid diseases (hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism), sex, viral diseases (influenza, ARVI), physical activity increased complexity, stressful situations, sedentary lifestyle.
Treatment methods for tone
If the above symptoms occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. If the doctor does not detect any serious changes, then special medications will be prescribed - antispasmodics, magnesium and vitamin B6 (no-spa, Magnelis B6). Hormonal drugs - utrozhestan or duphaston are prescribed for disturbances in the production of the hormone progesterone. In more serious cases, hospitalization will be prescribed.
Taking any medications without a doctor's prescription during pregnancy can cause negative consequences - both for the pregnant woman and for her unborn child, so entrust the treatment to a specialist.
When tone occurs, it is important to balance work and rest, not to be nervous, do light exercise and try to spend more time in the fresh air. Be sure to eliminate nicotine and alcohol. And most importantly, fully comply with all recommendations prescribed by your doctor.
Possible problems
What problems can a pregnant woman expect from the fourteenth to the twenty-sixth week of pregnancy?
There are several of them:
- Breast enlargement and/or nipple irritability;
- False Braxton Hicks contractions in the lower abdomen and groin;
- A growing belly and active weight gain, as a result;
- Heartburn due to increased acidity in the gastrointestinal tract;
- Changes in skin pigmentation are possible;
- Stretch marks on the skin, sometimes accompanied by itching;
- Snoring is possible as a result of swelling of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx;
- Softness of the gums, sometimes accompanied by bleeding;
- Dizziness as a result of changes in blood pressure;
- Leg cramps;
- Dyspnea;
- Vaginal discharge;
- Urinary tract infections.
The body of the expectant mother is being rebuilt and changing - all these ailments are physiologically determined. However, it is not a fact that the whole range of problems will necessarily accompany the second trimester of pregnancy. These are possible (hypothetical) difficulties. For many pregnant girls, little on this list bothers them in the 2nd trimester. Don't forget that your positive attitude is very important!
What not to do in the 2nd trimester?
It is not recommended for expectant mothers from 14 to 26 weeks of pregnancy:
- Tobacco smoking and alcohol consumption;
- Experience stress, irritation, overwork;
- Wear tight, restrictive clothing;
- Lift objects weighing more than three kilograms;
- Steam in a high temperature bath for more than 15 minutes;
- Take medications without a doctor's prescription.
Sex in the 2nd trimester
During normal pregnancy, sex in the second trimester is not contraindicated. However, young spouses should avoid “extreme” positions when making love. The partner must be attentive and careful, not forgetting about the “interesting” position of the partner.
Many expectant fathers, observing their spouse's growing belly, do not initiate sex for fear of harming the fetus. However, this is more myth than reality. If your desires are mutual, if the chosen position is comfortable for the expectant mother, mutual joy from sex will only strengthen your relationship without any harm to the unborn child.
Colds and other ailments
A pregnant girl can take any medications only after agreeing with her doctors. For example, during a routine examination at the antenatal clinic with your gynecologist. Many medications are contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women, as they can adversely affect the health of the fetus and lactation, respectively.
Therefore, in order not to take additional medications, it is important for the expectant mother to try not to get sick. For example, avoid colds or acute respiratory viral infections. In this regard, it is important to strengthen your immune system in advance - at the stage of preparation for pregnancy (the development of immunity is promoted by: taking multivitamins, hardening, regular walks and physical exercise).
During flu epidemics (February-March), try not to visit public places with high concentrations of people to reduce the risk of infection. Avoid hypothermia or overheating, regularly ventilate the room in which you are located.
Stay positive and don't get overwhelmed. Remember that very soon you will give life to a new person. Let the thought of this miracle help you smile more often and rejoice during the happiest time in every woman’s life!
Medical examinations and tests
If the pregnancy is progressing normally, from 13 to 20 weeks it is enough to visit the antenatal clinic once a month. After 20 weeks, the doctor recommends visiting more frequently - once every 2-3 weeks. This is due to the fact that in the second half of pregnancy the load on the female body increases, so the expectant mother and baby need closer monitoring.
At each appointment, the doctor will:
- check blood pressure,
- measure the distance between the pubic bone and the fundus of the uterus and the abdominal circumference (this will allow you to judge the growth of the fetus and assume polyhydramnios or oligohydramnios),
- after 20 weeks - listen to the fetal heartbeat using a stethoscope,
- inspect your arms and legs for swelling,
- palpate the abdomen to determine the position of the fetal head and back.
Tests and studies that will need to be performed in the second trimester:
- General urine analysis. It is given before each visit to the gynecologist. Allows you to diagnose urinary tract infections and kidney disorders (pyelonephritis).
- General blood analysis. Detects anemia, inflammatory processes in the body, assesses the condition of the kidneys and liver. If the test shows an increase in blood sugar, the woman is given a glucose tolerance test to diagnose diabetes.
- Ultrasound.
It is carried out between 18 and 21 weeks of pregnancy. It is at this time that the fetal organs become clearly visible, and the doctor can identify malformations of its development. With a successful combination of circumstances, an ultrasound in the second trimester can determine the sex of the child.
If a woman registers for pregnancy after 14 weeks, she is also offered to take a “triple test” to assess the risk of genetic abnormalities in the fetus (this is the name given to a blood test for a complex of substances that are produced in the second trimester).
If you did biochemical screening in the first trimester and it showed normal results, you do not need to take the “triple test”.
Feelings of the expectant mother
The belly will become noticeably rounder, and already in the middle of the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, your position will become noticeable to everyone around you. Nausea, weakness and dizziness characteristic of the first trimester stop. We hope you feel full of strength and energy.
At this stage, the gynecologist will be able to palpate the uterus through the anterior abdominal wall. If at the beginning of the trimester its bottom is located 13 cm from the pubic joint, then by the end it rises by an average of 26 cm. Due to the pressure it exerts on neighboring organs, you may feel heaviness in the abdomen, heartburn, and shortness of breath.
Constipation during this period of pregnancy occurs due to eating disorders. Another factor is progesterone, which relaxes smooth muscles. Therefore, do not forget about fiber-rich foods and drinking regime.
Vaginal discharge
Normally they should be colorless or whitish, odorless or slightly sour. Consult a gynecologist if they suddenly acquire:
- yellow-purulent or greenish tint;
- curdled consistency;
- Strong smell.
These are possible symptoms of thrush or infectious diseases. In the second trimester of pregnancy, many medications are allowed to be taken, so it is easier to cope with the problem.
How to distinguish discharge from amniotic fluid?
The waters are completely transparent and liquid and are absorbed into the laundry. Leakage of amniotic fluid is a condition that requires immediate treatment at the hospital. Therefore, if you suspect rupture of the membranes, consult a gynecologist.
What to do in the second trimester
- Review your wardrobe. You will need not only special clothes for pregnant women, but also comfortable shoes. Avoid high-heeled shoes - they increase the risk of falls and create additional stress on your feet.
- Stop sleeping on your stomach. Starting from 4 months, the most comfortable and safe sleeping position is on the left side with a pillow between the legs. This position improves blood supply to the placenta and nutrition of the fetus.
- Increase your caloric intake. In the second trimester, you will need to consume 300-350 more calories per day (about the same number of calories contained in 2 glasses of milk or a bowl of oatmeal). Additional intake of vitamins during this period is usually not required. But if you think that your diet is not balanced enough, consult your doctor - he will recommend suitable multivitamin complexes.
- Buy things for the child. Buy the essentials while you can. In the third trimester, shopping will be tiring for you.
- Choose a maternity hospital.
Choose one or two options in case of premature birth.
Nutrition for pregnant women: features of the second trimester
According to WHO nutrition standards, the energy value of a pregnant woman's diet in the second trimester should be increased by 360 kcal/day. The main source of energy in the diet should be grain products, especially whole grain flour, cereals, and bread.
It is also worth increasing your consumption of vegetables and fruits, which are the main source of vitamins and minerals. In the second trimester of pregnancy, it is recommended to consume about 400 grams of vegetables and fruits per day.
Protein plays an important role in the diet of pregnant women; in the second trimester, their need is much higher. At the same time, half of the total daily amount of protein should be covered by animals, the main sources of which are milk and its products, as well as lean animal meat (for example, poultry, fish). Meat products also contain iron, which protects against anemia.
It is important to include omega-3 in the diet, which is necessary for both mother and child. Omega-3 reduces the risk of miscarriage and premature birth, plays a key role in the proper development of the fetal nervous system, and protects neurons from the development of inflammatory changes.
How to keep weight under control?
When visiting a gynecologist, a woman is asked to familiarize herself with tables with weight gain norms by month (or week). The doctor will help you calculate the rate of gain if there is an initial weight deficit, and in this case it is permissible to gain up to 14 kg. On the contrary, for those who were initially overweight, the increase should be limited to 7-8 kg. Too low increases are harmful to the child’s health, since without the mother’s fat tissue he will not be able to fully develop (fat tissue is needed for the normal development of the baby)!
After the birth of a baby, women who have had optimal weight gain experience best breastfeeding, since there is an ideal hormonal background for milk production. Trying to lose weight during pregnancy is prohibited, since the baby will not receive the nutrients it needs. Weight control is also important to prevent the development of hidden edema. Therefore, you need to eat right, not overeat, if necessary, use infusions of diuretic herbs, and take fasting days on the doctor’s recommendation.
What is uterine hypertonicity?
Hypertonicity is the contraction of the uterus during pregnancy. This condition can occur at any time.
Signs:
- abdominal tension, it becomes “like a stone”;
- additional negative sensations – pain and heaviness in the lower back or back.
Of course, this condition often frightens a woman. Only a doctor can determine whether there is a threat of premature birth. The specialist conducts an examination, questions the patient, clarifying the nature of the tone, its duration, intensity and frequency. If required, an unscheduled ultrasound is prescribed.
Braxton-Hicks contractions in the second trimester
These are the so-called training contractions. The sensations during them are the same as with hypertonicity. But there is a cardinal difference - duration.
Features of training bouts:
- duration from several seconds to several minutes;
- quick cessation after changing body position or taking a shower;
- frequency - sometimes up to 10 times per day.
Before childbirth, such matchups can occur even more often. Thus, the body prepares for childbirth.
Thrush and how to deal with it?
By the end of the second trimester, thrush (candidiasis) occurs in a huge number of pregnant women. It directly depends on the state of immunity, and in a woman it is greatly reduced so that the body does not “decide” to reject a foreign body - the fetus. Reduced immunity is fertile ground for the active proliferation of Candida fungi, which provoke an inflammatory disease. Another factor that increases the risk of developing thrush is a change in hormonal levels, which affects the change in pH in the genitals.
Treating candidiasis is a complex process, and the trouble is that there are no effective medications that can be used during pregnancy. And it must be treated, even if it does not occur without symptoms. It is especially important to get rid of thrush before childbirth, because the baby, when passing through the birth canal, can be infected with pathogenic fungi. All medications are prescribed only by a doctor, and it is better not for the expectant mother to use folk remedies !
How much weight can a woman gain during pregnancy?
Doctors “allow” a woman to ideally gain 10-13 kg of weight during pregnancy. In the first three months, body weight increases by 2 kg, then weight increases by 1.5-2 kilos per month. The first trimester is characterized by low fetal weight gain, while from the second trimester of gestation the baby grows rapidly, as does the uterus itself, the volume of amniotic fluid, and fatty tissue. The woman’s total blood volume also increases, and all the numbers added together form such a large weight gain.
Of the 10-13 kg increase, adipose tissue normally accounts for up to 4 kg, no more. Consumption of fatty, high-calorie foods during pregnancy causes an increase in the proportion of adipose tissue and the development of obesity, which threatens problems for the baby . For the pregnant woman herself, obesity is also fraught with various troubles:
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Pain in the back/lower back, development of osteochondrosis;
- Varicose veins;
- Arterial hypertension.
What should you pay attention to?
At any stage of pregnancy, a woman needs to protect herself from infections. A slight increase in body temperature is not a sign of pathology, but occurs due to hormonal changes, but if it is accompanied by a cough and other symptoms of ARVI, you should consult a doctor. Today there are many medications approved for use by expectant mothers, but you should not self-medicate - you should be monitored by a doctor.
It is important to pay attention to proper nutrition.
- You should eat food often, in small portions - this will reduce the load on the digestive tract.
- The diet must be balanced (contain all necessary nutrients, vitamins and microelements), the products must be natural (without harmful dyes, stabilizers, preservatives). Pregnant women should also not eat fast food.
- Alcoholic drinks (including beer) are contraindicated - alcohol is toxic to the child and negatively affects the health of the pregnant woman. Many people are concerned about whether a pregnant woman can drink kvass. The opinions of experts are mixed. The alcohol content in kvass is low, so if the drink is made from natural ingredients according to ancient recipes, then it can be consumed. Of course, you should avoid kvass, which contains more chemicals than natural ingredients.
Anemia during pregnancy - how to treat?
Most often, anemia occurs due to an increase in plasma volume. There is an increase in the amount of the liquid component of the blood, but the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin remains the same. But sometimes real anemia occurs due to poor nutrition, impaired absorption of iron in the intestines, or frequent bleeding (threat of interruption, hemorrhoidal bleeding).
If hemoglobin decreases sharply, the fetus will suffer from hypoxia. Diagnosis is made by blood test. Be sure to prescribe medications containing iron. Anemia can be prevented by taking prenatal vitamins that contain iron and eating a balanced diet.