February 28, 2019
Averyanova Sveta
An umbilical hernia in newborns is very frightening for parents, especially if the protrusion is gigantic in size. Moms and dads think with horror about going to the surgeon and the upcoming operation. In fact, there are several conservative methods for treating the defect. This is a special massage and gymnastics.
How to cure an umbilical hernia in newborns without surgery, what massage techniques and exercises to use most effectively, you will learn from our article.
Causes of umbilical hernia
Congenital or acquired protrusion of the navel in children is provoked by the following factors:
- Prematurity. The connective tissue does not have time to mature, which is why 3 out of 10 premature and low birth weight babies have this congenital disease.
- Genetic predisposition. In children with such a history, weakness of the fibers of the umbilical ring is observed.
- Pathologies of peritoneal development. The wall of the abdominal cavity changes.
- Rickets. Due to the acquired disease, the tone of the peritoneal muscles decreases.
- Frequent hysterical crying. During a tantrum or prolonged crying, an infant overexerts the abdominal muscles, causing tissue rupture.
- Difficulties in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. A hernia is provoked by severe colic, increased flatulence, and chronic constipation.
It is impossible to leave an umbilical hernia in a baby without attention. Treatment is carried out in two ways: conservative and surgical. Surgical intervention is indicated for children over 3 years of age with a bulge of more than 2 cm. If the hernia is small and does not bother the child, it is recommended to use conservative methods of therapy.
This is a newborn's navel massage for a hernia and gymnastics.
On a note! In addition to massaging and exercise therapy, it is useful to swim in the pool and place the baby on the stomach. The doctor may apply a bandage to the bulge to hold it in place. These methods are also conservative and are allowed for very young children.
How to cure an umbilical hernia in a child?
Except for cases where pathology provokes the development of complications, it is not customary to treat a hernia either with medication or surgery. To eliminate it, the following conservative methods are used:
- massage;
- bandage;
- plasters.
As for the bandage and special patch, can they be purchased at any pharmacy after consulting with a pharmacist? Is it possible to do therapeutic massage at home? How to straighten a bulging navel so that the hernia that is causing it to protrude will “resolve”?
Massage is best left to professionals. In a few sessions, an experienced doctor will correct the hernia, and the baby’s internal organs will no longer protrude through the abdominal wall so much. After this, parents will be able to carry out all the necessary manipulations independently:
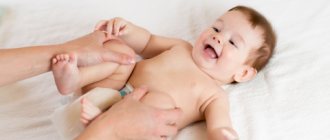
- Stroking circular movements strictly clockwise.
- Counter strokes. The left hand is passed along the right side of the abdomen (in the upward direction), the right hand simultaneously performs a “mirror” movement.
- Stroking the oblique muscles. One hand is placed directly on the navel, and the other one performs light massaging movements in the area around it.
A tummy massage can only be given to a baby if he is at least 2 weeks old. His umbilical wound should be completely healed and not cause any concern. If during the massage the baby begins to cry, you should stop the session immediately.
There are other methods of therapy. So, according to Komarovsky, in order to cure a hernia, it is not at all necessary to resort to wearing a bandage. To achieve results it is enough:
- harden your child all year round;
- do a tummy massage;
- regularly do exercises and therapeutic exercises with your baby;
- include more fiber and grains in your diet to promote regular bowel movements.
Benefits of massage
Massage procedures undoubtedly have a healing effect. With the help of stroking and pinching you can achieve the following positive results:
- Strengthen your abdominal muscles.
- Normalize intestinal function by improving peristalsis.
- Relieve muscle spasms throughout the body.
- Stimulate blood circulation.
- Normalize the sleep of a restless baby.
- Reduce the number of colic attacks.
- Strengthen the baby, increase overall immunity.
- Establish emotional contact between parents and baby.
On a note! The main goal of massage for umbilical hernia in newborns is to prevent pinching and further development of the disease. If non-surgical methods do not help, the bulge grows and cannot be reduced, you cannot refuse the help of a surgeon.
How to cure an umbilical hernia in newborns: video lesson on massage and gymnastics with an infant
Young mothers are ready to sound the alarm at the first signs of illness in their newborn. In some cases, such concern is completely justified, but if the baby has a protruding umbilical hernia, worry is unnecessary. According to medical research, the disease occurs in 1/5 of children born at term; among premature babies, the percentage of umbilical hernias increases to 1/3. The symptoms most clearly manifest themselves when the newborn cries for a long time. Despite the frightening appearance of a protruding umbilical ring, there is nothing terrible about the disease: the course of treatment may take several weeks, but the result in all cases is positive, but only if the child’s parents promptly seek help from the attending physician.
A doctor diagnoses an umbilical hernia, but there is nothing terrible about this disease - if you follow medical instructions, removing the frightening symptom is quite simple
Preparation
Preparatory procedures need to be given special attention. Start manipulations after following the following recommendations:
- Wash your hands, remove long nails, lubricate your brushes with cream.
- Ventilate the room if it is hot, or warm it to 25°C.
- Lay an oilcloth on a table, hard bed or sofa, with a medium-soft blanket on top.
- Place massage oil or rich cream next to the table.
The product will have to be added to the baby’s hands and body several times, so it’s not worth removing them. - Calm the baby if he cries. Walk around the room with him, talk and kiss him to improve his emotional mood.
- Hold the baby upright to help the gases pass.
- Before starting the massage, warm your hands and baby's tummy with a flannel diaper ironed with a hot iron.
- Strip your newborn naked.
- Place your baby on the massage table, straighten the belly button if possible, and secure it with a bandage.
- Warm up the baby's body with stroking and rubbing movements using your palms.
- Place some oil on your hands. The procedure can begin.
On a note! To massage newborns, use hypoallergenic cosmetics. This is baby cream, Vaseline, olive oil. Store-bought oils, even the well-known ones “Eared Nannies”, “Our Mother” and others), contain fragrances and fragrances that are unsafe for sensitive skin. Use them after six months.
Preparing for a massage procedure
You can start massage treatment after consulting a pediatrician. The baby's body is very vulnerable, and careless movements can aggravate the situation. It is advisable to entrust the first session to a pediatric specialist and learn all the intricacies.
The following rules must be followed:
- Massage for newborns should be carried out 30 minutes before feeding, several times a day, at least 2 times;
- it is possible that 45 minutes after eating, if the child is awake, you cannot specially wake him up for the procedure;
- the room temperature should be 25-26°C;
- you need to ventilate the room in advance;
- hands must be clean, without sharp nails, before the procedure they are lubricated with baby cream, olive or petroleum jelly (flavored oils and creams are prohibited for use up to 6 months);
- the baby must be undressed and have a heated flannel diaper on hand;
- hands should also be warm;
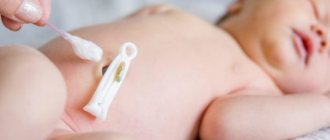
- The procedure begins with the fact that the protrusion above the navel should be carefully adjusted and sealed with a special hernia plaster.
If a child cries, he must first be calmed down and carried in a diaper in his arms.
Preparation for the procedure also includes actions in the following order:
- Place it on the tummy for a few minutes, while lightly stroking the back.
- Installation in a “column” on the legs - this way the gases will pass away faster.
- Roll the baby from side to side several times and do 5-6 movements of useful gymnastics for a hernia: bicycle exercise, raising the legs, pressing them to the tummy.
The duration of the preparatory stage is 3-4 minutes. Next, proceed directly to massage for umbilical hernia for newborns.
Massage techniques
Massage for umbilical hernia in newborns can be done at home. It's not difficult at all. You can take a couple of lessons from a professional or learn the technique of massaging your tummy with an umbilical hernia on your own.
Infants should not knead the body with force; movements should be light and gentle. The range of massage techniques and the duration of the procedure depend on the age of the baby.
The following types of movements are suitable for newborns up to 1–2 months:
- Stroking. In the first weeks after birth, it is enough to stroke the baby’s tummy with your palm without pressing. Move clockwise around the navel.
- Counter stroking. Stroke your belly with both hands, moving in opposite directions above and below your navel.
When the umbilical wound is completely healed, add a few more massage techniques to this set of movements:
- Vibrating movements. This is a tingling sensation in the abdominal muscles around the navel and sides.
- Pressure. Place three fingers on your tummy above your navel and apply pressure. Hold your hands like this for 1-3 seconds, then release. Gently press the entire body around the navel. Before this procedure, the hernia must be reduced and covered with a plaster.
After 4 months, expand the range of techniques with the following massage methods:
- Stroking the oblique muscles. Move in a circle from the sides or from the hips to the umbilical wound. Repeat at least 7 times.
- Trituration. Stroke the tummy with little effort with your fingertips, moving in a spiral from the sides to the central part.
- Stroking the umbilical ring. The skin is stroked with your fingertips.
- Tingling. Grab the skin with your fingers near the navel and move in a circle.
- Reduction of the hernia. Apply direct pressure to the bulge with your index finger.
- Connecting the edges of the navel. First, the hernia needs to be repaired, then grab the skin around the navel and close it. Hold the position for several seconds.
Repeat massage techniques during the newborn period 3-5 times, after 3-4 months do 7-10 repetitions. Kneading is useful and correctly combined with gymnastics and physical education for infants.
Important! Massage for a hernia and restorative procedures should not be done immediately after meals or on an empty stomach. Feed your child 30–40 minutes before starting therapy. After the massage, eating immediately is also not recommended; wait 30 minutes.
We also advise you to watch these short videos, which clearly show how to massage a hernia:
Are you afraid to massage your baby yourself?
- I'm a little afraid, but I can handle the instructions 54%, 22 votes
22 votes 54%22 votes - 54% of all votes
- Yes, scary 27%, 11 votes
11 votes 27%
11 votes - 27% of all votes
- No, everything is easy and simple 20%, 8 votes
8 votes 20%
8 votes - 20% of all votes
Total votes: 41
28.02.2019
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
Actions after massage
When the session is over, the baby is relaxed and very warmed up. First of all, you should put it on to prevent hypothermia.
If the child is dozing, let him rest and sleep, and if he is awake, let him play with toys in a lying position.
Forbidden:
- wipe with a damp diaper and wash the baby;
- lift vertically and force you to do exercises after the massage;
- water and feed the baby earlier than 20-30 minutes.
After a massage, children are in a good mood, they are satisfied with close communication with their parents and are happy to simply relax or play on their own.
Preventive exercises. Gymnastics
Special preventive exercises help reduce the risk of an umbilical hernia in a healthy baby:
- laying on the stomach;
- bending the legs while lying on the stomach;
- pulling the knees towards the stomach;
- spreading the bent legs to the sides;
- bike. You need to spin imaginary pedals for 10–15 seconds;
- imitation of running, walking. Move your baby's legs carefully. It must lie on a hard surface;
- pulling up by the handles. Lay the baby on his back, hold his hands in your palms and lightly pull him towards you. There is no need to sit down the baby; he can only lift himself off the table a couple of centimeters;
- swimming. Start free lessons with a six-month-old child in the bath; with a one-year-old you can go to joint classes under the supervision of a trainer in the pool.
A set of preventive exercises is aimed at strengthening the abdominal muscles, developing strength and endurance. Teach your child to sports from an early age, then he will grow up healthy.
Gymnastics is useful for children with diagnosed umbilical hernia. Do physical exercise in the morning or throughout the day. Gymnastics before bedtime is not recommended; active games can cause insomnia in a child.
Include the following exercises in your physical education lesson:
- We teach a child to crawl. Place the baby on his tummy. Place your palm under the heels, let the baby rest against it and try to push off. You can help him bend his knees.
- Rifles. Turn the baby from the stomach to the side, then to the back.
- Squats. Hold the baby by the arms and help him sit down. The exercise develops different muscle groups: in the legs, back and abdomen.
- Tilts. Do it closer to a year. Place the baby on the floor, hold him by outstretched arms and tilt him forward and backward.
- Airplane. An effective exercise for training the abdominal muscles. Take the baby in your hands, grab it by the chest and lift it up in a horizontal position. The baby will instinctively stretch his legs and tense his abdominal muscles.
- Exercises with your baby on a fitball. Place your baby's tummy on a sports ball and roll it from side to side. The baby himself will tell you how long to continue the exercise. Usually babies really like this task, they calm down and are lulled to sleep.
Massage for children's illnesses
Home Medical encyclopedia Encyclopedia of massage Infant massage
FIRST YEAR OF LIFE
For various diseases of children in the first year of life, massage is one of the most important components of complex treatment. Massage in combination with gymnastics gives a good effect in the treatment of children with diseases of the central nervous system, when the functions of movement and tissue trophism are impaired.
When performing therapeutic massage and gymnastics for children, the movements of the methodologist should be softer and more careful than when performing the same techniques on adults. For example, patting should be done with the back of a half-bent finger, first with one finger, and then with two or more. The massage therapist’s hand should move only in the wrist joint, and not in the elbow, so that only the weight of the hand, and not the forearm, acts on the child’s body.
When performing a baby massage, the methodologist should not use Vaseline or powders, which contribute to contamination of the baby’s skin. But when massaging an emaciated child with dry skin that is sensitive to the slightest touch, the massage therapist’s hands should be lubricated with sterile Vaseline. The use of Vaseline is discontinued after the child's skin reaches its normal state.
You cannot perform a massage if the child is overexcited or capricious, as his nervousness will lead to hypertonicity of the flexor muscles and inhibition of reflexes. First of all, you should find out and eliminate the cause of the child’s bad mood (hunger, disruption of the routine, fear at the sight of strangers) and only after that begin the procedure, during which you need to talk to him affectionately, creating a positive emotional tone.
Before and after the massage, the child should be wrapped in a diaper, because in young children the heat-regulating function of the skin is not yet sufficiently developed.
CONGENITAL MUSCULAR TORTICOLLISSE
With muscular torticollis, the child's head is constantly tilted towards the affected muscle. With severe torticollis, asymmetry of the face, skull or shoulder girdle is often observed (on the affected side the scapula and collarbone are located higher). The causes of this disease are underdevelopment of the sternocleidomastoid muscles, with the help of which a person performs various head movements, or a birth injury of the cervical spine. For this type of disease, treatment should begin at 2-3 months of age, using:
- treatment by position;
- therapeutic massage and gymnastics.
Treatment by position. It is important that the baby’s torso on the crib is positioned symmetrically, directly in relation to the head. The child should lie on a semi-rigid mattress, with blanket bags or “rolls” placed from the baby’s armpits to the knees. The baby should be placed on its side more often. If the child sleeps on the side of the torticollis, then a high pillow is placed under his head, but if he lies on the healthy side, then the pillow is not used at all. It is recommended to frequently shift the baby and approach his crib not from one, but from different sides. In this case, light, toys, communication with an adult should be on the side of the affected muscle.
You can give the baby a correct position in the crib using special placements: a rubber ring wrapped in fabric (placed under the back of the head), as well as soft bags with sand (placed on the bed on both sides of the head or on the side of the torticollis above the shoulder girdle). It should be borne in mind that if the child often spits up, the use of styling is excluded.
You should hold the baby in your arms or on the affected side with your back to you, while supporting the head with your hand, lifting it to the healthy side. Or pick him up, turn him back to you, use your cheek to point the baby’s head towards the painful side and slightly tilt him towards the healthy side. Another way: press the baby with your chest, while the baby’s shoulders should be at the same level as the adult’s shoulders; turn the baby's head to the painful side, fixing this position with your cheek.
Therapeutic massage and gymnastics. Laying out and turning from the back to the stomach are performed, as a rule, on the healthy side, but they can also be performed on the torticollis side.
Rib cage. Relaxing techniques (stroking, rubbing) are carried out on the sore side, first in the upper part of the chest, and then in the lower.
Sternocleidomastoid muscle. The child's head should be tilted towards the torticollis during the massage. Only relaxing techniques can be used on the affected muscle: gentle stroking (from the mastoid process to the collarbone), rubbing (done gently with the pad of one finger), vibration (along the muscle).
Back. Stroking, rubbing on the healthy side. On the sore side, stroking, vibration, gentle stretching along the shoulder girdle and rubbing, pinching, puncturing, and tapping in the area of the shoulder blade are performed.
Approximate complex of massage and gymnastics (child’s age from 2 to 3 months)
Perform 3-4 times during the day for 5-10 minutes.
1. I. p. - lying on your back. General stroking of arms and legs. Breast massage. Stroking and vibration massage of the neck muscles on the torticollis side, Massage of the cheek muscles on the healthy side: stroking, rubbing, kneading., Cor-
rigging gymnastic exercises in turns through the diseased and healthy side. Stroking massage of the sternocleidomastoid muscle on both sides. Laying on the stomach.
2. I. p. - lying on your stomach. General stroking back massage. Reflex crawling. Stroking massage of the back and neck. Reflex extension of the back in the position on the right and left side.
3. I. p. - lying on your back. Stroking abdominal massage. Repeat the techniques of special neck massage. Stroking massage and reflex exercises for the feet.
4. At the end of the complex, a stroking massage of the arms and legs is performed.
UMBILICAL HERNIA
An umbilical hernia is a consequence of a defect in the anterior abdominal wall caused by weakness of the umbilical ring. According to statistics, umbilical hernia is common in infants, especially premature ones. It can occur as a result of severe coughing, constipation, or prolonged crying. Diseases such as rickets and malnutrition, which reduce muscle tone, also create favorable conditions for the formation of an umbilical hernia. Externally, an umbilical hernia appears as a round or oval protrusion in the area of the umbilical ring, which is easily retracted into the abdominal cavity. Often, along with a hernia, there is a divergence of the rectus abdominis muscles due to weakness of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall.
In the future, with the correct development of the child, normalization of intestinal activity, and sufficient motor activity, self-healing of the umbilical hernia may occur. However, it is extremely useful to perform special exercises that help strengthen the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall and do a tonic abdominal massage.
Methods of massage and therapeutic exercises
From the first days of life, the baby should be placed on his stomach for a few minutes before each feeding. In this position, he raises his head, actively moves his arms and legs, and strains his back and abdominal muscles.
Therapeutic massage can begin 2-3 weeks after the umbilical wound has healed. It should be carried out in combination with a general massage. All therapeutic exercises should be performed only after the hernia has been reduced and secured with a bandage (adhesive plaster). If it is not possible to reduce the hernia, then during the procedure it is necessary to press it with one hand, pressing it with your fingers, and with the other hand perform massage movements.
Massage techniques for umbilical hernia: circular stroking of the abdomen in a clockwise direction; counter stroking; stroking the oblique muscles; rubbing the abdomen (done from one month of age); tingling around the navel. All massage techniques aimed at increasing the tone of the abdominal wall muscles should alternate with soothing circular stroking. For children aged 4-5 months, “hovering” on their back is recommended; sitting down with support by straightened and outstretched arms; sitting down with support from bent arms; independent turns from back to stomach. Older children are recommended to sit with support from the rings, by one hand, without support; tense arching of the spine; raising straight legs; bending and straightening the body; “Pick up a toy from a chair” exercise.
On the recommendation of a doctor, you can perform acupressure: using the pads of straightened fingers, quickly and abruptly press on the points around the navel, which causes muscle tension and reduction of the hernia.
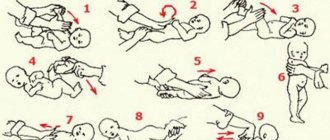
An approximate complex of therapeutic massage and gymnastics for umbilical hernia for children under 4 months of age
First, you should reflexively hold the child’s body (horizontally) in a position lying on its side. The exercise should be performed for a few seconds on the right and left sides alternately.
Then you need to turn the child from a semi-vertical position to a horizontal one. The exercise should be performed on the lap of an adult or on a table previously prepared for massage (see chapter “Hygienic requirements”). At the same time, tilting the child’s body back, you need to make sure that the baby’s head does not fall back.
Next, you should reflexively hold the child’s body suspended (horizontally) in a supine position - “swimmer’s pose.”
Then turn the baby from back to stomach with the help of an adult.
Next is reflex crawling on your stomach.
Finally, laying out on the ball in a supine position.
FLAT FOOT
Deformation of the foot, expressed in straightening the longitudinal arch and fixing it in an abducted position, is called flat feet (Fig. 305 a, b).
| Figure 305. Foot prints: a - the foot of a healthy person, b - the foot of a patient with flat feet. |
To determine flat feet, it is necessary to have a clear understanding of the structure of the foot (Fig. 306).
The foot consists of a large number of bones that form two arches: anteroposterior and lateral. The anteroposterior (longitudinal) arch of the foot, contracted by the tendons and muscles that lift the inner side of the foot, performs primarily a “spring” function, reducing the shaking of the body during movement and gives confidence and softness to the gait. The lateral arch (shaded in the figure) rises upward and inward. It performs primarily a supporting function, which, in combination with the function of the anteroposterior arch, determines the usefulness of the entire foot.
| Figure 306. |
The foot is held in a certain position thanks to the muscles located on the dorsal and plantar surfaces and ligaments. The muscles of the rear of the foot are much weaker than the muscles of the sole, which take part in holding the arches of the foot and largely provide its spring properties. Normal arch height is maintained both actively and passively. Bones and ligaments resist the movement of one or another joint of the foot beyond the permissible amplitude and thereby act as a passive force that maintains the physiological position of the foot. The main role in maintaining the position of the foot and its function belongs to the muscles. By contracting and lengthening, they change the shape of the foot.
A child's foot is shorter and wider than an adult's, narrowed in the heel area, and the toes diverge radially. In children under 3 years of age, the foot is flat, its arch is lowered, so when walking the child quickly gets tired. With normal development, over time the foot acquires the correct shape. But sometimes, as a result of muscle weakening caused by paralysis, paresis, injuries, serious illnesses, or a significant increase in the load on the muscles and ligaments of the lower extremities, the arches of the feet become flattened. In a healthy person, when there is a load on the foot, the internal arch straightens slightly, but with the cessation of pressure, its curvature quickly returns to normal. With flat feet, the original curvature of the internal arch is not completely restored.
Flat feet are especially common in children, as a result of which the supporting function of the legs sharply decreases and the position of the pelvis and spine is disrupted. This, in turn, leads to postural defects, can cause spinal deformation and weaken the activity of the entire musculoskeletal system.
Flat feet can be congenital or acquired. Signs of congenital flat feet are a flat sole and a foot slightly turned outward. Such a child does not stand correctly and quickly gets tired when walking.
Flat feet can be:
- paralytic, developing as a result of paralysis or paresis of the muscles of the lower leg, foot (cerebral palsy, poliomyelitis, etc.);
- traumatic as a consequence of injury to the bones or muscles of the foot;
- static, observed with obesity, weakness of the muscles of the lower extremities, impaired blood supply to the lower extremities due to anemia or other reasons, wearing wide or, conversely, narrow shoes, chronic diseases that weaken the body, frequent headaches (hence fatigue and deterioration in school performance) .
Flat feet manifest themselves in different ways: some do not even notice it, others complain of pain in the foot, lower leg, ankle, and knee joints. But severe pain does not always correspond to a severe form of the disease.
Physical education and sports in combination with exposure to natural factors (sun, air, water) are simple, affordable and reliable means of preventing and treating flat feet. In addition, great importance is attached to shoes: in the absence of a disease, they should always correspond to the size of the foot, and if present, have an instep support - a specially shaped insole.
For preventive purposes, you can teach your child various games with elements of correction, which in an interesting way will help strengthen the child’s skill of correct posture. We offer two options for such games:
Hanging tags. The children run away. The driver runs after them, trying to tarnish someone. You cannot stain someone who sits on their toes, straightens their back, bends their elbows, clasps their fingers, extending their index fingers upward.
Pull tags. The children run away. You can “save yourself” from the driver by standing on your toes and raising your hands up. The one who is stained becomes the driver.
CONGENITAL CLUBFOOT
Congenital clubfoot is a contracture of the joints of the foot, as a result of which the relationship of the bones is disrupted and gross changes occur in the muscles. The main signs of clubfoot are supination of the foot - inward rotation of the sole with raising the inner edge of the foot and lowering the outer one, adduction of the foot in the forefoot, plantar flexion, and significant limitation of mobility in the ankle joint. Clubfoot is most often bilateral. According to statistics, this defect is most often observed in boys.
When a child begins to walk, leaning on the damaged foot, its deformation intensifies, and the shape and function of the entire leg are disrupted. This worsens posture and gait. Only at an early age, when the child’s muscles and ligaments are pliable and elastic, is there a high probability of bringing the foot into the correct position. For this purpose, a whole range of measures is used, which includes, in addition to orthopedic treatment, massage and therapeutic exercises.
Methods of massage and therapeutic exercises for congenital clubfoot
1. Special massage and corrective exercises should be performed against the background of restorative massage and gymnastics appropriate to the age and development of the child. For example, to relax the internal and posterior muscle groups of the lower leg, where increased tone is noted, you need to use stroking, shaking the muscles, and stretching with vibration. And to strengthen the stretched and weakened anterior and outer groups of muscles of the lower leg, you should use more energetic techniques: rubbing, kneading, tapping.
2. All exercises should be carried out in combination with massage, performed without pressure so that the child does not feel pain. Special therapeutic exercises after thermal procedures have a good effect.
3. The complex of massage and gymnastics should include the following techniques:
- rotational movements of the foot outward (along the longitudinal axis), which should be carried out very carefully, gradually lowering the inner and raising the outer edge of the foot;
- to eliminate the adduction of the forefoot, you should fix the child’s foot in the ankle joint with one hand, and with the other hand gently make straightening movements, gradually moving the forefoot outward;
- to stretch the heel tendon and eliminate plantar flexion of the foot, the baby should be placed on his stomach, bend his leg at the knee joint, holding the shin with one hand, and gently press the child’s foot with the palm of the other, bending it dorsally. From and. p. - lying on the back: with one hand, press the child’s shin to the surface of the body, fixing it in the ankle area, with the other, grab the foot so that the palm rests on the sole, and carefully bend the foot to the back with simultaneous pressure on its outer edge (effectively a combination of flexion of the foot with simultaneous acupressure at the transition of the dorsum of the foot to the lower leg).
CONGENITAL HIP DISPLACEMENT, HIP DYSPLASIA
The main symptom of congenital hip dislocation (hip dysplasia) is limited passive abduction of the hips. The presence of the disease in a child is checked as follows:
1. Passive abduction of the hip joints to the sides. You should put the baby on his back, bend his legs at the hip and knee joints at a right angle and gently spread his hips to the sides. If a joint is affected, abduction is limited to the side of the affected joint. You can also determine the restriction of movement in the position of the child on his stomach when bending his legs, as when crawling.
2. Assessing the symmetry of the subgluteal folds and folds on the hips. You need to put the baby on his stomach, straighten his legs and carefully examine the symmetry of the folds: asymmetry of the folds on the hips and buttocks is a common sign of damage to the hip joint.
If you suspect the presence of a disease, you should immediately contact an orthopedist.
Treatment by position. An orthopedic doctor applies a splint, and parents, in turn, must strictly follow his recommendations. If there is no need to use splints, then wide swaddling should be used, which is performed as follows: two diapers should be folded several times and placed between the child’s legs, bent at the hip and knee joints and set aside at 60-80 degrees. In this position, the baby’s legs need to be secured with a third diaper or panties.
You should carry the baby in your arms, supporting him with one hand behind his back and the other under his buttocks. In this case, the child should, with his widely spaced legs, hug the adult’s torso. You should not carry a child “astride” on an adult’s side, since in this position the child’s torso is located asymmetrically).
Therapeutic massage and gymnastics. In case of congenital dislocation of the hip and hip dysplasia, massage is performed only with the permission of an orthopedic doctor. This especially applies to massage complexes, which include exercises such as reflex “walking”, “dancing”, and squatting. When treating a child using orthopedic splints, massage and exercises should be carried out to the extent permitted by the placement.
To relax the adductor muscles of the thighs, you can do acupressure with simultaneous abduction of the leg: use the pad of the index or middle finger to gently press in the area of the hip joint, then move the baby’s bent leg outward, combining this movement with light shaking. You can use a vibration massage of the inner thighs: rocking the pelvis of a child lying on a support, suspended.
Exercises in warm water are useful: supporting the baby under the chest and stomach, you should bring him to the wall of the bathtub, achieving bending of the legs. While swimming, reflex “walking” and “dancing” are also possible (in water, the axial load on the hip joint is less). When the child is swimming on his stomach, you can perform a strengthening massage of the gluteal muscles, affecting the points located in the middle of the subgluteal folds.
An approximate complex of massage and gymnastics for children aged 2 weeks to 3 months
Therapeutic gymnastics techniques and foot massage must be repeated 10-15 times with each swaddling.
1. I. p. - lying on your back. A general stroking massage of the arms, legs, and abdomen should be performed.
2. I. p. - lying on your stomach. It is necessary to lay the child on his stomach with his legs apart and massage the posterior-outer surfaces of the legs: stroking, rubbing, then alternately moving the baby’s bent legs to the sides (as when crawling) with the pelvis fixed.
This should be followed by stroking the back and lumbar region. Massage the lumbar region (stroking and rubbing), buttocks (stroking, rubbing, stimulating techniques - pinching, tapping with fingers), the hip joint area (circular stroking, rubbing) and the back-outer surface of the legs. This should be followed by abduction of the bent legs to the sides (as when crawling). And finally - “soaring”.
3. I. p. - lying on your back. The front-outer surface of the legs should be massaged: stroking, rubbing in combination with techniques for relaxing the adductor muscles of the thigh, bending the child’s legs at the knee and hip joints and soft plastic spreading of the hips. At the same time, you should always remember that when spreading your hips, you should not allow sudden movements, so as not to cause pain during the reflex contraction of the adductor muscles of the thigh and the child’s negative reaction to the procedure.
This should be followed by inward rotation of the hip: with one hand you should fix the hip joint, and with the palm of the other hand gently clasp the child’s knee and, lightly pressing on it, gradually rotate the femur along its axis inward (this exercise achieves gentle pressure of the femoral head on the articular (acetabular) ) depression). Then a foot massage: rubbing, kneading.
Then you should perform reflex exercises for the feet. To train the supporting function of the feet, it is recommended to perform exercises with the child lying on his stomach and back using a ball, while support for the feet is created by the hand or the ball. The procedure ends with a chest massage.
DISEASES AND DAMAGES OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
Disorders of the functions of the central nervous system are the most common pathology of early childhood. In order to promptly detect deviations in the development of a child’s mental and motor skills, you need to constantly carefully monitor him.
3-4 months. Place the completely undressed baby on his stomach. A healthy baby is able to hold his head for several minutes and freely turn it to the sides. In doing so, he should rest on his forearms extended forward. The chest is slightly raised above the table surface. The stomach and pelvis are pressed tightly to the table. Hips slightly apart, shins raised. The body is straight. Then you need to straighten the child’s legs and bring them together, then check whether the gluteal and popliteal folds are symmetrical. Also at this age, the child should be able to freely turn his head in both directions. Flexion of the knee joint should occur easily without lifting the pelvis from the table surface. If the position of the torso and head is asymmetrical, you should immediately contact a pediatrician or neurologist.
6-7 months. A healthy child lying on his stomach rests on his outstretched arms, the hand is well open. The chest is raised above the table surface. The stomach and pelvis are pressed against the table. The legs are spread, the knees are bent, the shins are easily raised. The head turns freely in all directions. Visually, the spine occupies a middle position, deviating neither to the right nor to the left. Lying on his back, he plays with his arms and legs, while his movements are purposeful and coordinated. The baby is trying to independently turn from back to stomach.
9-10 months. The baby begins to crawl on all fours back and forth, can transfer his weight from arms to legs, and sit up independently. When he sits, his back should be straight. The child tries to stand, holding onto support, and step with his feet. It is necessary to ensure that in a standing position, his feet are parallel to each other and the entire surface of the sole is in contact with the surface of the support.
An important stage in the development of the nervous system is the first 2-3 years of a child’s life. At this time, motor skills and the foundations of mental activity are most intensively formed. In most children with diseases of the central or peripheral nervous system, the functions of movement and tissue trophism are impaired. Massage irritates peripheral receptors, influencing the central nervous system through them. Therefore, massage and gymnastics as a factor of irritation are extremely necessary in the treatment of diseases of this kind. Gymnastics and massage are used in combination with orthopedic measures, physiotherapeutic procedures, and drug therapy.
Methods of massage and gymnastics
| Figure 307. |
When choosing exercises, you need to take into account the age and capabilities of the child.
Strengthening body muscles. All techniques of classical massage are used in combination with acupressure (stimulating method).
The massage begins with laying on the stomach. This should be followed by turns to the side with reflex extension of the spine.
Next - the “swimmer” pose, reflex crawling, extension of the back while “swimming” on the stomach (Fig. 307).
Then “flight” on the stomach (Fig. 308).
Next, you need to lay out on the ball in a position on your stomach with your feet supporting you (Fig. 309).
| Figure 308. |
Then - raising the legs hanging from the table using stimulating acupressure techniques (Fig. 310).
This should be followed by bending from a standing position and tense bending of the spine (Fig. 311).
At the end of the complex - “take a toy” (see Chapter 4 “Gymnastic exercises and massage for children from 9 to 12 months, exercise “Bridge”).
| Figure 309. |
With asymmetry of muscle tone of the trunk and limbs. Against the background of general strengthening, breathing exercises, as well as exercises and massage techniques that stimulate the gradual (age-related) development of psychomotor skills and the emotional sphere, special massage techniques, therapeutic exercises, and positional treatment should be used.
1. Relaxation of the flexors of the affected side: neck muscles, pectoralis major, trapezius, latissimus dorsi, iliopsoas, gluteal, adductor muscles of the thighs, calf muscles. Massage techniques such as stroking, light rubbing, vibration, felting, and acupressure (relaxing method) should be used.
| Figure 310. |
2. Strengthening massage of the extensor muscles of the back (classical techniques and acupressure - tonic method), which is performed more intensively on the healthy side.
3. Special exercises combined with relaxing massage techniques: vibration of the affected muscles of the torso and legs, as well as rocking the pelvis in different directions is accompanied by stretching of the muscles. The child lies on his back with his feet facing the massage therapist. In conclusion, you need to place your bent leg at the knee (left or right, depending on the affected area) over the other straight leg and pull slightly, trying to correct the oblique position of the pelvis.
| Figure 311. |
| print version | This information is not a guide to self-treatment. A doctor's consultation is required. |
Contraindications
Gymnastics and massage for umbilical hernia are allowed if the baby is healthy, in a good mood, and the baby reacts positively to touching the belly. Any manipulation of the navel and home methods of treating protrusion should be prohibited in the following situations:
- The newborn's umbilical wound has not healed.
- Blood and mucus are released from the navel, the wound becomes wet and smells bad. If you have such symptoms of inflammation or pathologies, consult a doctor.
- The baby has a fever and signs of a cold.
- The gases do not pass for more than a day, the stomach is swollen, and the baby suffers from severe colic.
- Blood and ichor are released from the anus.
- The stomach is asymmetrical.
- During the massage, the stomach muscles actively contract.
- The child is weakened, pale, lethargic, apathetic.
- A round spot, bruise, and swelling formed around the navel.
- There is a rash and hives on the skin.
Before starting or continuing therapy, you need to wait until the skin has completely recovered. If the rash is caused by the massage oil you are using, rub with talcum powder or a dry palm.
- The hernia is inflamed, swollen, and pinched.
- The child has infectious diseases of any etiology.
- The baby reacts inadequately to touching and kneading the body: cries, twists. This scenario is considered the norm during the first procedures. After 2-3 days, if there are no other health problems, the baby will get used to the massage.
Be sure to watch the video of Dr. Komarovsky’s TV show about the myths associated with umbilical hernia in newborns:
Effective muscle massaging techniques
When performing the procedure, parents should use a combination of the following movements:
- Stroking. This is where an effective procedure begins, and the massage also ends with strokes. They are performed with light movements of the palms from the navel to the lymph nodes.
- Kneading. Do it with the middle, index and ring fingers, in progressive circular movements to improve lymph flow and relieve swelling. You can massage all parts of the body in this way.
- Vibrations. They are performed by frequent but light tapping with your fingers; you should not make too deep, penetrating blows.
- Trituration. Helps warm up muscles and normalize tissue nutrition. Perform rubbing clockwise without applying strong pressure.
When using these movements, parents must adhere to a certain technique.
Step-by-step execution technique
After warming up, which lasts 3 minutes, begin the massage.
- Movement around the navel clockwise.
- Grasp the oblique muscles with your palms and move from them to the navel.
- The palms above and below the navel move towards each other.
- Pinching the skin around the umbilical area in a circle.
- Rubbing the lateral muscles with the fingertips, gradually moving towards the center.
- Spiral rubbing along the oblique muscles.
- Point pressure with 1-2 fingers on the stomach.
- Light pressing of the hernia if it is bulging. You can't put in extra effort. Perform 20 indentations.
If during the massage the child begins to cry and twitch heavily, the procedure cannot be continued.
General rules
- The first few times you need to practice under the supervision of a physical therapy instructor;
- Regardless of the patient’s age, before training you need to check whether the protrusion is reduced;
- Before the start of the lesson, it is recommended to perform a special light massage of the anterior abdominal wall;
- It is recommended that patients train in a brace to reduce the risk of pinching;
- All gymnastic elements are performed smoothly, slowly, without significant muscle effort;
- The duration of classes is increased gradually;
- During muscle activity, it is advisable to keep your palm in the navel area;
- If pain and discomfort appear in the area of the umbilical ring, the training must be stopped.
Contraindications
It should be remembered that physical activity is contraindicated if:
- Acute infectious and inflammatory processes;
- Severe disorders of the cardiovascular or respiratory system;
- Any chronic diseases of internal organs in the acute stage;
- High risk of strangulation of hernial protrusion;
- Pain in the abdominal area;
- Pregnancy in the II and III trimesters.
Important!
Exercises on the abdominal muscles in some cases lead to strangulation of the hernia, so they are contraindicated for this disease.
For newborns
The following complex is performed:
- Place three fingers of your right hand on the baby's navel so that the middle finger is located inside the umbilical ring.
- The other two fingers are side by side on the outside, without gaps.
- Perform circular movements with light pressure 20 times in each direction.
- Using the edge of your palm, move along the umbilical ring in a clockwise direction 30 times. With both palms, make simultaneous longitudinal movements along the navel, back and forth about 10 times.
This procedure must be performed at least twice a day. Do it shortly before feeding your baby, and your hands should work through a diaper or T-shirt so as not to injure the baby’s skin and avoid infection. Before you begin, prepare your hands: trim your nails, warm your palms so they are not cold.
You will find on our website a lot of information about massage for umbilical hernia in newborns: videos, articles, reference materials and more.
Operation
Sometimes elimination of pathology is only possible through surgery. In our clinic, umbilical hernia surgery in children is performed using gentle and safe methods.
The surgeon prescribes surgical intervention in the following cases:
- the umbilical ring is 2 cm in diameter or more;
- the hernia is strangulated and must be removed immediately;
- the child in whom the pathology is detected is more than one year old, and the disease is constantly progressing;
- the child is 4-5 years old, but treatment of the hernia did not produce results.
If the protrusion is small, the operation is quick, about 20 minutes. Here an incision is made above the navel, then the umbilical ring is tightened. You can use laparoscopy instead of this method. This method of surgical intervention usually has no complications, and there are no scars after it.
If the protrusion is large enough, hernioplasty is used. In this case, the formation is first reduced, and then a special synthetic mesh (like a patch) is installed on the hernial orifice. Subsequently, the mesh fuses with the tissues of the body and prevents the formation of a new formation.