A little about chickenpox
Chickenpox (varicella) is a viral disease transmitted from a sick person by airborne droplets. It has distinctive features, which greatly facilitates diagnosis. Chickenpox is characterized by the appearance of skin rashes that go through several stages in their development, after which the disease gradually subsides.
Chickenpox is predominantly a childhood disease, since 90% of those who have been ill are children under 14 years of age. But adults can also get chickenpox if they avoided it in childhood.
Properties of the chickenpox virus
Varicella Zoster is a virus that, when it enters the human body, provokes the development of chickenpox. It belongs to the group of herpes viruses, due to which it has a certain property. This pathogen no longer leaves the body into which it entered, being located in the nerve ganglia. Moreover, he may not remind of himself for a long time. But if this virus is reactivated (with decreased immunity, stress and exhaustion), then it causes another disease - shingles.
The virus cannot exist in our environment, so it dies quickly. But it is known that you can become infected with it due to its spread.
When a person suffers chickenpox, a strong immunity is formed in his body, which lasts for life. This is why it is very unlikely that you will get chickenpox again.
How can you get chickenpox?
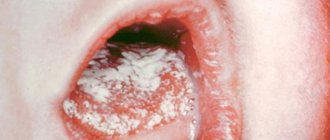
Chickenpox, or chickenpox, is a highly contagious infectious disease caused by the Varicella Zoster virus. The disease is characterized by the appearance of an itchy rash. On average, 250-500 papules appear throughout the body, and in severe cases even in the mouth, eyes, anus and genitals.
Because 90% of chickenpox cases occur in children, it is often called a childhood disease. Although adults who did not have chickenpox in childhood can also get sick.
Olga Aleksandrovna Chvertka, a pediatrician at the ON Clinic Poltava [/anchor], talks about possible routes of infection with chickenpox:
“It is quite easy to become infected with chickenpox, and it almost always results from close contact with a sick person. The virus can spread through saliva, sneezing and coughing, and through contact with fluid from blisters. Most often, children under 12 years of age who are actively in contact with peers in kindergarten and school get sick.”
The incubation period can last from 10 to 21 days. In this case, the carrier becomes infectious to the environment several days before the rash appears.
Features of the newborn's body
In babies, the body has many characteristics, since it is still actively developing and adapting to new conditions. Chickenpox in newborns is a rare occurrence. Why?
The child’s own immune system is still weak. But all the necessary antibodies that will cope with pathogens of a variety of diseases come to him through mother's milk. It is known that milk has such a protective function for the first six months, and at approximately 6 months the baby’s body begins to independently fight microbes.
When can a baby get chickenpox?
Chickenpox in infants is still possible. But this requires the presence of the following factors:
- The baby was born with a very weak immune system (for example, he has congenital immunodeficiency).
- Lack of breastfeeding, early introduction of formula.
- Mom did not have chickenpox.
- A pregnant woman suffered from chickenpox while carrying a baby, or she fell ill during childbirth.
Chickenpox in infants has its own characteristics, because their immune system is not yet perfect. Various complications or other diseases may occur against the background of the main one. Therefore, it is necessary to protect the baby as much as possible, and in case of infection, consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all instructions.
How is chickenpox spread?
Children and adults can get chickenpox, but the disease is more common in unvaccinated children. Chickenpox is highly contagious. Infection occurs through direct contact with a sick person, especially if there was contact with liquid from the chickenpox papules (blisters) of the patient. Chickenpox is also spread through droplets of fluid that are released into the air when you cough or sneeze. A person with chickenpox becomes contagious to others one to two days before the rash appears, and remains so until the last blisters on the skin have dried. Family members who have not had chickenpox may need to stay away from the child during this stage of the disease. Anyone who takes oral steroids long-term or is immunocompromised (for example, due to chemotherapy), pregnant women or children under three months of age should see a doctor if they have been in contact with someone with chickenpox, as they are very are likely to develop the disease, they may need preventive treatment to prevent the disease from developing.
Children with chickenpox should not go to nursery, kindergarten or school until the last blister on the skin has dried. Parents are required to notify the school or kindergarten if their child has chickenpox, because there may be other children in the group or class who will need to be vaccinated or undergo preventive treatment.
Pregnancy and chickenpox
Adults do not tolerate chickenpox as easily as younger children. But doctors are especially afraid for pregnant women who have not yet had time to get sick. This disease can have a negative impact on the fetus (if the woman herself becomes ill for the first time), so blood tests for pregnant women must include an analysis for antibodies to the varicella zoster virus.
Depending on the stage of pregnancy, the virus affects the health of the fetus in different ways. In the first trimester, the damage will be very serious (the narnar system, eyes, skin suffers), and the risk of death is high. The disease in the second trimester of pregnancy can lead to various malformations of the baby. In the third trimester, the degree of exposure to the fetus decreases, but there may also be consequences.
There is such a thing as “congenital chickenpox in newborns.” It occurs in a quarter of cases after the expectant mother gets chickenpox, and the fatality rate is approximately 20%. With congenital chickenpox, children experience developmental disorders; many children develop various neurological disorders. If the virus has been detected in the body of a newborn, then timely prescribed antiviral treatment will produce results.
How does the disease progress?
There are 4 periods of the disease: incubation period, prodrome period, clinical manifestations, recovery. It is possible to determine that it is chickenpox only during the period of clinical manifestations, which is accompanied by specific skin rashes.
In children under one year of age, the incubation period is shorter - about 7 days pass from the moment of infection to the appearance of the rash. At this time, the baby may experience a rise in temperature to 38 degrees, lethargy, decreased appetite, and bad mood. In general, the symptoms resemble those of a viral disease.
Skin rash
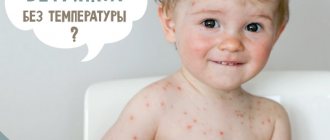
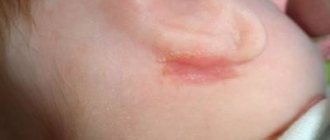
It is thanks to skin manifestations that chickenpox is diagnosed without unnecessary difficulties. The rash goes through several stages in its development: spot, papule, vesicle, crust.
- First, a red spot appears on the skin, which indicates the reaction of the immune system to the virus in the body.
- During the inflammatory process, a tubercle (papule) is formed.
- Then, intercellular (serous) fluid is released, causing the top layer of skin to separate from the underlying layers and form a vesicle with clear fluid (vesicle). When scratching the vesicles, the virus enters the skin, which provokes the appearance of new elements of the rash.
- When the vesicles dry out, a crust forms in their place. If it is torn off while combing, scars may remain in this place.
The skin rash is accompanied by severe itching, but everything possible must be done to prevent the baby from scratching the rash.
How to treat chickenpox in a child?
Since chickenpox is caused by a virus, it is useless to treat the disease with antibiotics. The doctor may prescribe antibacterial drugs in cases where the course of chickenpox is complicated by the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
There is no specific treatment against this infection, but necessary measures aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition must be taken. If a child gets chickenpox, the parents' task will be to minimize unpleasant symptoms and alleviate the baby's condition. To do this, at home, you must fulfill the basic conditions necessary for a speedy recovery:
- Observance of strict bed rest;
- Frequent change of underwear and bed linen;
- Increased drinking regimen to reduce intoxication;
- Light dairy-vegetable diet.
At the first unfavorable symptoms, you should call a doctor at home, who will give the necessary advice on care and prescribe medications to alleviate the child’s condition. The most important point of treatment during the active phase is the elimination of severe itching. When a rash appears, the skin itches and itches, and parents need to ensure that the baby does not scratch the itchy areas. This will help avoid the addition of a secondary bacterial infection.
- Blisters on the body should be treated several times a day with antiseptic solutions (green or colorless Castellani liquid). This will help prevent the infection from spreading further throughout the body and reduce the number of rashes. This treatment helps dry out the blisters and form a crust, speeding up recovery.
- To eliminate itching, the doctor may prescribe antihistamines (Suprastin, Diazolin, Diphenhydramine). These drugs effectively eliminate itching and have a mild calming and sedative effect, which will help cope with sleep disorders. The attending physician will select the required dose and dosage regimen.
- If a child has a high temperature, the doctor will prescribe antipyretics (Paracetamol, Nurofen, Efferalgan). It is not advisable to give aspirin to children under 10 years of age.
Drinking plenty of fluids (lemon tea, compotes, juices, green and herbal tea) will help you recover quickly; the liquid will remove toxins from the body. During illness, the child loses his appetite, but it is necessary to maintain his strength. A dairy-vegetable diet will help with this, providing the body with the necessary vitamins and nutrients.
Severe forms of chickenpox affecting internal organs are treated in a hospital. Complex therapy necessarily includes antiherpetic drugs (Zovirx, Acyclovir); immunoglobulin and interferon are used to treat the condition.
Chickenpox treatment
Chickenpox in children under 1 year of age is treated in almost the same way as in the older population. Treatment is prescribed depending on the severity of the disease:
- Antiviral therapy is carried out in a hospital setting for severe chickenpox.
- In turn, mild and moderate-severe degrees can be easily cured at home.
If the high temperature persists for a long time, it can be brought down with the help of antipyretics (for example, before bedtime). But you should remember that antibodies to the chickenpox virus are produced precisely at elevated temperatures, so there is no need to lower it all the time. In any case, it is necessary to treat the child as prescribed by the doctor, and also ask what is best to do in this or that case. For example, some pediatricians prescribe antihistamines instead of antipyretics.
In the event that a child develops complications (widespread rashes on the mucous membranes, bacterial infection, inflammatory processes in internal organs), he will be sent to a hospital, where he will be under the close supervision of doctors and receive appropriate treatment.
Chickenpox in an infant requires adherence to a home regimen. It is necessary to ensure that the baby does not become dehydrated. You can give him water, tea or compote to drink. In this case, skin care plays a big role.
How to care for your baby's skin?
It is difficult to explain to a child under one year old that it is impossible to scratch the elements of the rash. He will still try to get rid of the itching in this way, and this will lead to the spread of the virus and the formation of new rashes. Therefore, parents need to ensure that these actions are kept to a minimum. Your baby can wear gloves that will soften the impact on the skin. To prevent the itching from increasing, you need to regularly ventilate the room, monitor the temperature in it, and also make sure that the child is not hot (sweat irritates the skin, which increases the discomfort).
To make it easier to track what stage a baby’s chickenpox is at, you can use brilliant green. It does not speed up recovery, but it helps to visually identify new rashes and also relieves itching a little.
You don't have to completely give up bathing. The main thing is not to rub the skin after this, so as not to disrupt the integrity of the vesicles with serous fluid. You also need to remember to regularly change bed linen and clothes.
Chickenpox in infants
It must be remembered that any child over the age of six months can get chickenpox. In most cases, the course of the disease in infants is quite complex: such young children do not tolerate symptoms well, cannot complain and cannot take advice. As a result, they need more careful care and constant attention from the mother.
Chickenpox in newborns is characterized by the same symptoms, but in young children, chickenpox, which occurs in a particularly complex form, can cause serious harm to the body, affecting the development of internal organs. Treatment of chickenpox in infants should be carried out under the strict supervision of a qualified pediatrician.
You should try to ensure that the child does not tear off the scabs from drying out rashes, because This will only make it more itchy and increase the risk of re-infection. The child's hands need to be washed more often, since the causative virus may be present on the skin and under the nails. Nails should be cut short. It is recommended that your baby wear cotton gloves at night.
Prevention of chickenpox in children
If there are older children in the family, then it is unlikely that it will be possible to protect the baby from chickenpox. In this case, you can try to limit their contact, and also carry out wet cleaning and ventilate the room more often. Knowing that one of your relatives or friends is sick, it is better to refuse meetings for the period of their illness.
There is the possibility of prevention with a vaccine, but it is carried out as prescribed by a doctor. For example, it is recommended to vaccinate women who are planning a pregnancy but have not yet had chickenpox. And pregnant women who become ill while carrying a child are given immunoglobulin to reduce the impact of the virus on the fetus.
The most important thing is to be attentive to the baby’s health, consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow his recommendations. In this case, you can avoid unpleasant consequences.