Doctors call an allergy to cold a “pseudo-allergy” because it develops differently than most allergic reactions. Allergy requires contact with the allergen - its contact with the skin, mucous membranes or in the digestive system.
With cold urticaria, there is no contact with the allergen, but the body’s reaction resembles an allergic one: redness of the affected areas, swelling, disruption of the respiratory system. Why and who develops an allergy to cold, what are its symptoms? How to distinguish it from a cold? And how to protect a child and an adult? We answer questions about the body's individual reaction to cold.
Causes of allergies to cold
This allergy can appear completely unexpectedly, but for the most part it is a manifestation of malfunctions that have appeared in the body. So, allergies can be caused not only by weakened immunity, but also by the following reasons:
- Sedentary and passive lifestyle. Thus, modern children are not accustomed to active games on the street. Passive relaxation at home playing computer games or television programs can manifest itself in a purely negative way. The body's defense systems weaken and it becomes unable to cope even with ordinary cold.
- The presence of herpes viruses, hepatitis, mycoplasma in the body. Viruses and infections always strike mercilessly throughout all systems of the body. They may be in a frozen state, but despite this they easily exert their negative influence.
- Presence of chronic diseases. Diseases and disorders such as tonsillitis, arthritis, pyelonephritis can cause not only an unhealthy reaction - allergies, but also a number of other dangerous ailments.
- High sensitivity to cold. This type of disorder is not directly related to allergies, but causes similar discomfort. The child may suffer from severe pain in the hands, parts of the face, the tips of the fingers turn white, as do the lips. In this case, special examinations are necessary to help eliminate serious disturbances in the functioning of blood vessels.
Who is to blame and what to do?
It is very rare to accurately determine the cause that caused the development of cold allergies. Usually its symptoms appear completely unexpectedly for the patient and his relatives. But it has been noted that the risk of developing an allergy to cold is higher in those who have already encountered other types of hypersensitivity.
The high-risk group for developing cold allergies includes children who are often and long-term ill, patients with endocrine, vascular and skin diseases, and disorders of the digestive system. An allergic reaction can be triggered by past infections, for example, infectious mononucleosis, taking certain medications, insect bites, and even treatment of other types of allergic diseases.
Whatever factors serve as the basis for the development of cold allergy, it is very important not to miss its onset and consult a doctor as early as possible to confirm the alleged diagnosis and begin treatment.
This is especially important if we are talking about a child who already has some other allergic disease, because... If left untreated, even mild forms of cold allergies can lead to severe complications over time - from bronchial asthma to anaphylactic shock.
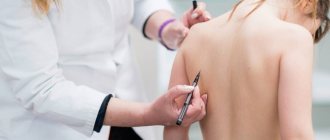
You can also check for cold allergies at home. To do this, you need to put a small piece of ice on your wrist or elbow for 5-10 minutes, and then evaluate the condition of the skin around the test site. The appearance of characteristic rashes - hives, itchy or painful red spots - indicates that the test was positive.
How to recognize the disease?
The symptoms of cold allergies are pronounced and begin to manifest themselves as soon as the child gets outside in the cold. The presence of an allergy is indicated by:
- Excessively red cheeks;
- Profuse lacrimation;
- Runny nose;
- The appearance of a rash and small blisters on the cheeks;
- Scratching on the face.
These symptoms directly demonstrate that the child has an allergic reaction to the cold. However, if the redness does not disappear from the cheeks quickly enough, then it makes sense to check the child for allergies caused by other factors.
Read also: Tracheitis in children
What to do at the first signs of a cold allergy?
First of all, it should be said that it is quite difficult to fight cold allergies, and, probably, the most important reason for this is the inability to eliminate the cause, the allergen - cold in our geographical latitudes. It is a mistake to believe that you can gradually get used to it. It is quite possible that after such attempts at “hardening” allergic reactions will occur more often and become even more severe.
- If the fact of cold allergy is proven, you can take the antihistamine recommended by the doctor in a dosage appropriate for age and other indications. However, it is wrong to believe that by taking a few tablets you can get rid of the disease - treatment for this type of allergy can be quite lengthy. If an allergic reaction to cold appears constantly, it is necessary to find out whether it is associated with any other disease. It is very important.
- Before going out into the cold, apply a special cream to exposed areas of the body, face, and balm or lipstick to the lips.
- Dress appropriately for the weather - hat, hood, scarf, mittens, mittens, etc.
- Forget about hardening and especially winter swimming: such attempts can lead to unpredictable allergic reactions.
- If possible, limit your time outside. When ventilating the room, do not forget to leave there and return when the air temperature warms up to a comfortable level.
If every walk in the cold turns into real torture for you or your child, then perhaps you are suffering from an allergic reaction to the cold. In order to establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to go to the clinic as soon as possible for a consultation with an allergist. This will allow you to start treatment in a timely manner and prevent the development of emergency conditions.
Cold allergy is an allergic reaction that occurs when exposed to low temperatures.
It is important to note that a cold allergy can develop both from the first minute of being in the cold, and after some time, and it can also be caused by eating cold foods!
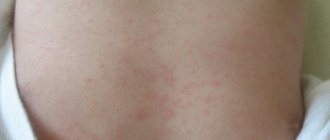
Most often, cold allergies appear a few minutes after exposure to low temperatures. It can manifest itself in the form of rashes on the face, lips, hands and other parts of the body that are in direct contact with the external environment. As a rule, the appearance of rashes is preceded by skin itching and a feeling of pain from the effects of cold. The rashes are quite dense, of different sizes and shapes, and can be in the form of blisters, red or whitish spots. Sometimes, with a generalized reaction, the spots can merge and spread throughout the body, increasing the affected area and causing swelling of the surrounding tissues. If the reaction spreads to the entire body, the itching can be very severe, the temperature may rise, sudden weakness, headache, shortness of breath, and tachycardia may occur. Usually the stains last for several hours and then disappear without a trace. This type of reaction can appear gradually and increase over time, or it can be repeated constantly in the same form.
When can you suspect a cold allergy?
When exposed to cold air, they turn red, and sometimes all areas of the body exposed to the cold swell. The rash is dense, pink or whitish, accompanied by itching, and after a few hours the symptoms disappear without the use of medications.
Symptoms of cold allergy in a child:
- Some time after being exposed to the cold, the cheeks not only turn red (which is an absolutely normal reaction), but also a rash appears, similar in appearance to a nettle burn. The child begins to itch, trying to reach his cheeks with his hands. The rash may also appear upon entering a warm room, spreading to the arms, and in very young children, to the inner surface of the thighs, legs, and knees.
- The eyes become watery and/or swelling appears around the eyes and lips, cracks, “jams” in the corners of the mouth, peeling of the lips and cracking, and all this even with minor temperature changes.
- Sometimes a cold allergy can manifest itself as a common cold: a dry cough at night, wheezing when breathing, a stuffy nose - and all this against the background of reddened cheeks.
Cold allergies can worsen and occur against the background of other diseases and be just a mask for them. This often happens with a lack of vitamins and microelements, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, vegetative-vascular dystonia, etc.
Some patients note a general tendency to allergic reactions or their manifestations in childhood. Sometimes a rare form occurs - hereditary cold allergy, the treatment of which does not differ from the usual treatment. However, it is often accompanied by a burning sensation rather than itching and is more of a reaction of the body to the wind than to the cold.
If there is another allergic disease, for example atopic dermatitis, food allergies, allergic rhinitis, then cold allergies will be more severe. Often, increased sensitivity to cold begins after suffering from acute respiratory viral infections or other infectious diseases.
Allergy treatment
Cold allergies are not as harmless as they seem. If symptoms are not eliminated in a timely manner, conjunctivitis (due to excessive lacrimation) and streptoderma (due to constant scratching on the skin) may occur. Therefore, treatment must be carried out in a timely manner and under the strict supervision of a doctor.
The peculiarity of this type of allergy is that it can suddenly disappear as it appeared, or, on the contrary, it can worsen its impact, manifesting itself not only in winter, but also in the middle of the year. Therefore, fighting allergies is necessary.
In most cases, the doctor prescribes antihistamine therapy and an individual walking schedule. This schedule implies that children with high sensitivity to cold are contraindicated to go outside at -10 and -15 degrees.
In warmer temperatures, short walks are recommended. The skin is treated with a protective cream. It would be a good idea to take a course of vitamins to improve the functions of the immune system.
Cold allergy or cold urticaria
Allergist, Head of the Department of Allergology and Occupational Pathology Dudareva N.I.
Cold allergy or cold urticaria (Latin “Urtica” - nettle) is an allergic reaction on exposed parts of the body in the form of hives-like rashes or red spots caused by cold (cold air or water).
Although it is called an allergy, in reality this response of the body has nothing to do with a true allergic reaction. Cold, dampness, frost are physical factors, and not a substance that causes sensitization - hypersensitivity. But in this article, we will not replace generally accepted definitions, so we will still call this reaction to cold a cold allergy.
Cold allergies manifest themselves literally within a few minutes after exposure to low temperatures in the form of rashes on open areas of the skin: on the face, hands, and often on the lips after drinking cold drinks. The rash is pink or whitish in color, dense, accompanied by itching, can last for several hours, and then disappear without a trace.
There are also other forms of cold allergies that occur in the presence of other diseases - dysfunction of the thyroid gland, lupus erythematosus, and are much more severe. Sometimes a rare form occurs - hereditary. It is accompanied by a burning sensation and is more the body's reaction to the wind than to the cold.
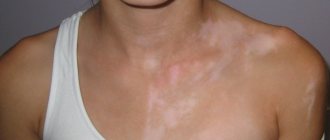
But even the most seemingly harmless form of cold allergy is not as safe as we think. It causes severe itching and discomfort, and your health worsens: headaches appear and blood pressure drops. And with general hypothermia of the body, more severe manifestations may appear - the so-called Quincke's edema. (Manifestation of Quincke's edema is an enlargement of the face or part of it, or a limb, but the color of the skin does not change.)
Cold allergy test
Therefore, it is very important for both the doctor and the patient to determine the nature of the allergic reaction in time. For this, along with complex studies using special equipment, there are quite simple methods. You can check whether you have a cold allergy at home: place a piece of ice on the crook of your elbow for 10-15 minutes, and if hives appear, then we can assume that you are predisposed to a cold allergy.
But if in doubt, you should consult a doctor; allergic diseases require laboratory blood tests.
Symptoms of cold allergy
So, how to recognize it, because cold allergies skillfully “disguise” as dermatitis, colds, acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections.
As soon as you stepped out into the cold, your head immediately began to hurt. The facial and neck muscles contract, pressing pain begins in the back of the head and forehead, and a feeling of nausea appears from the intensifying headache. It's time to go into a warm room: 10-15 minutes are usually enough to say goodbye to a headache attack. This symptom can be provoked not only by sub-zero air temperatures, but also, for example, by ice-cold drinks or a cold bed.
Reddish rashes, peeling and itching on the skin of the hands and face, sometimes under the knee and on the inner thighs.
In adults, it all starts with cold allergies in the hands. At first, the skin of the hands simply itches, then becomes dry, rough, covered with cracks and even rashes such as hives. In the skin form of cold allergy in a child, the favorite place for rashes is the face. The cheeks, chin, and nasolabial area turn red. Then a burning sensation will appear, the baby will begin to rub these places, and a rash very similar to herpes is guaranteed. Those who love thin tights in winter suffer from delicate, cold-sensitive skin under the knees and on the inner thighs.
Following urticaria, swelling of the face, legs, and arms appears.
Unexplained long-term runny nose, nasal congestion, itching in the nasal passages, sore throat and even conjunctivitis with lacrimation and itching of the mucous membranes of the eyes.
Breathing in the cold becomes difficult and difficult; narrowing of the bronchi often causes shortness of breath.
And there are also signs of cold allergies such as feeling tired and mood swings.
Cold allergies can worsen and occur against the background of other diseases and be just their mask, for example, with a lack of vitamins (avitaminosis) and microelements, dysfunction of the thyroid gland, vegetative-vascular dystonia, etc.
If there is another allergic disease, for example atopic dermatitis, food allergies, allergic rhinitis, then cold allergies will be more severe. Often, cold allergies begin after suffering from acute respiratory viral infections or other infectious diseases.
Causes of cold allergies
Experts are sure: cold allergy is not an independent disease, but only a symptom that accompanies some kind of physical disease. The body, weakened by a long and latent course of the disease, gives such a response to cold, so the true reasons for the body’s non-standard reaction to cold have not yet been established. There are suggestions that the development of allergies to cold is associated with the production of special cryoglobulin proteins in the body, which are actually the “culprits” for the activation of histamine, which causes allergic reactions. And the main trigger for this is cold. Various predisposing factors help this trigger mechanism work: decreased immunity, infectious, colds and parasitic diseases, for example, chronic throat disease, untreated teeth, inflammatory processes in the gynecological area in women.
A separate point is problems with the gastrointestinal tract: upon examination, it turns out that a person has chronic gastritis or cholecystitis, an ulcer... In principle, quite a few chronic ailments can provoke cold urticaria.
Cold allergies in children can also be a continuation of food allergies.
Therefore, all the attention is not on getting rid of symptoms, but on treating the underlying disease. The remaining measures can be considered temporary; they do not solve the problem, they only slightly alleviate the condition.
Treatment of cold allergies
The treatment method for cold allergies is similar to the treatment for true allergies. First of all, it is necessary to avoid contact with the provoking factor, in this case - cold. Winter allergy sufferers need to dress in clothes made from natural fabrics and not be exposed to cold. The degree of sensitivity is individual. For some, allergic reactions occur at an air temperature of minus 24-28°C, for others - minus 8-10°C, for some - after washing with cold water. If hypothermia cannot be avoided, take a warm shower or bath.
Medicines - antihistamines "Suprastin", "Tavegil", "Claritin". It must be borne in mind that some of them have a hypnotic effect and should not be used when performing work that requires concentration and quick reaction, for example, driving car. For bronchospasms, bronchodilators are used. In severe cases, doctors prescribe plasmapheresis, which clears the blood of cryoglobulins, glucocorticosteroids, and some immunosuppressants.
Most often, cold allergies appear in people who are not hardened and have foci of chronic infection (sore teeth, sinusitis, tonsillitis, bronchitis, cholecystitis, pyelonephritis, etc.). Therefore, it is necessary to pay special attention to their treatment. Liver and intestinal dysfunctions and dysbacteriosis predispose to allergies, including cold allergies.
What does a cold allergy look like?
Features of prevention
The prevention plan is not complicated. It is enough for parents to protect their child from contact with the cold and take the necessary measures in time if the allergy makes itself known again.
If you have sensitive skin, cover exposed areas with a scarf or jacket with a hood. It is also advisable to switch the child to a healthy diet, but this does not mean at all that it is necessary to deprive the child of sweets and starchy foods. It is necessary to expand the child’s menu by adding more raw vegetables, fish, and fruits.
Winter allergies - what is it?
Cold allergy is a disorder that is usually classified as a special group of so-called pseudoallergic reactions. It differs from other types of allergies, in particular hay fever and food allergies, in that the immune system reacts not to some irritant substance that has entered the body, but to low air temperature.
Under the influence of cold, the cells of the immune system located in the skin and mucous membranes release large amounts of histamine into the blood, a substance that is responsible for the development of all the main allergic symptoms - redness and swelling of the skin, itching, burning, etc. But as soon as the cold wears off, the release of histamine from the cells stops, and after that all signs of the allergy may disappear even without treatment.
A cold allergic reaction can occur not only when going out into the frosty air in winter, but also from contact with chilled drinks, frozen foods, or even after swimming in not too warm water.
Depending on exactly how and when cold allergies develop, it is customary to distinguish several types of this disease:
- hereditary or congenital - diagnosed already in the first year of life;
- acquired - can appear for the first time at any age;
- localized - symptoms appear in only one place,
- common - allergic rash over a large area.
It can have an immediate type reaction - when symptoms appear within a few minutes after contact with cold, or a delayed type reaction - symptoms begin to bother 2-3 hours after exposure to cold.