A fairly large percentage of infants suffer from jaundice from the first days of life. This condition manifests itself against the background of increased bilirubin in the blood of the newborn. If it is not treated, then in the future the advanced state of the disease can have a detrimental effect on the baby’s nervous system.
Of course, no parents want to stuff their baby with pills. And it's not necessary. After all, jaundice can be cured through phototherapy. A phototherapeutic irradiator for the treatment of neonatal jaundice can do this.
How this device works, how long you need to lie under it and what the phototherapy method is, you will learn from this article.
Diagnosis of jaundice in newborns (differential diagnosis of jaundice in newborns)
jaundice of newborns newborn
bilirubin anamnesis
Severity of jaundice in newborns according to the Cramer scale
brain
Severity of jaundice in newborns according to the Cramer scale
| Degree | Visible signs |
| First degree | Yellowness is observed only on the baby’s face and neck. |
| Second degree | Jaundice affects the area of the face, neck and upper body (up to the navel ). |
| Third degree | Not only the face and torso are painted yellow, but also the upper thighs (to the knee ). |
| Fourth degree | Jaundice affects all parts of the child's body, with the exception of the palms and soles. There is a threat of bilirubin encephalopathy. |
| Fifth degree | Total jaundice, in which the baby’s entire body is stained, including the palms and soles. |
Bilirubin for neonatal jaundice
Indicators of bilirubin in the blood of a newborn with physiological jaundice
| Hours\days after birth | Indicators |
| First 24 hours after birth | 119 micromoles per liter, skin color unchanged. |
| 48 hours after birth | 153 micromoles per liter, the baby’s skin color remains the same. |
| 72 hours after birth | 187 micromoles per liter, slight yellowness appears. |
| 4 – 5 days after birth | 200 micromoles per liter, jaundice is most pronounced. |
| On days 6 – 7 | The concentration of bilirubin begins to fall, and the jaundice subsides. |
| 9 – 10 day | Bilirubin in the blood returns to normal, the skin acquires a natural color. |
blood transfusions
Severity of jaundice based on the amount of bilirubin in the blood
| Severity | Bilirubin concentration |
| First degree | Up to 100 micromoles per liter |
| Second degree | up to 150 micromoles per liter |
| Third degree | Up to 200 – 205 micromoles per liter |
| Fourth degree | 300 or more micromoles per liter |
| Fifth degree | 400 or more micromoles per liter |
liver of premature babies
Tests for neonatal jaundice
blood test urine test
| Type of analysis | What does it show? |
| General blood analysis |
|
| Blood chemistry |
|
| Coagulogram | deficiency of fibrinogen and other coagulation factors - occurs due to a lack of vitamin K, which, in turn, is synthesized in the liver. |
| Analysis of urine | Results depend on the type of jaundice:
|
Urine and feces in neonatal jaundice
Characteristics of urine and feces in various types of jaundice
| Sign | Hemolytic jaundice | Parenchymal jaundice | Obstructive jaundice |
| Urine | Dark orange in color, no bilirubin in urine | Dark, the color of strong tea, bilirubin is present in the urine. | Dark, foamy urine, the color of beer. |
| Feces | Dark color | Light | Completely bleached |
How to treat jaundice in newborns
How is jaundice transmitted in newborns?
If your newborn baby's skin and/or whites of the eyes turn yellowish on the second or third day, then you are dealing with a fairly common phenomenon called neonatal jaundice.
What causes jaundice?
The immediate cause of jaundice in a newborn is an increased level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a substance formed when red blood cells - red blood cells - break down. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which is involved in saturating tissues and organs with oxygen. When a baby is born, he begins to receive oxygen not from the mother, but directly from the air when breathing. The baby’s body no longer needs special, embryonic hemoglobin, and the “extra” red blood cells containing it begin to break down, releasing bilirubin, which has a yellow or orange color.
The liver is in charge of processing and removing bilirubin from the body. If it is sufficiently developed in a newborn, bilirubin is excreted from the child’s body with meconium (newborn feces) and urine. But often, even in healthy children, in the first days of life, immaturity of the liver enzyme systems is observed - in this case, bilirubin is not excreted from the body, but is carried by the blood throughout the body. It is this substance that colors the tissues: skin and mucous membranes yellow. As a result, we observe what is commonly called newborn jaundice.
How to get rid of jaundice?
First of all, you need to figure out, with the help of doctors, what type of jaundice you are dealing with. In most cases (60-70% of newborns, more often in weak and premature infants), so-called physiological jaundice is observed. This is not a disease and, as a rule, there is no need to treat it. The best cure for physiological jaundice is early and frequent breastfeeding. If the baby receives breast milk, physiological jaundice usually goes away on its own within 2-3 weeks. In case of physiological jaundice, it is recommended that bottle-fed children be supplemented with water and rosehip decoction.
Artificially born, weak and premature babies, as a rule, undergo phototherapy sessions in the maternity hospital - irradiation with a special lamp for jaundice. Under the influence of light, “unnecessary” bilirubin breaks down into non-toxic derivatives, which are excreted from the body in feces and urine.
If jaundice does not go away for more than 3 weeks, this is a reason to wonder why. Long-term changes in the color of the skin and mucous membranes may indicate the presence of pathological jaundice. Also a cause for concern are:
- child's drowsiness, sluggish sucking;
- greenish skin tone;
- discolored or, conversely, too dark color of stool and urine;
- inconsistency with the normal levels of bilirubin, hemoglobin, erythrocytes, and reticulocytes in the blood.
Pathological jaundice in newborns requires immediate treatment, which will be prescribed by a doctor in accordance with the cause of the disease. Treatment of such jaundice at home is out of the question. Depending on the causes, there are several types of pathological jaundice of newborns:
- Hemolytic. Occurs when mother and fetus are incompatible in terms of blood type and (or) Rh factor, leading to massive destruction of red blood cells in the child’s blood.
- Conjugation. Disruption of bilirubin processing processes caused by hereditary diseases.
- Hepatic. Caused by liver damage - infectious or toxic (for example, hepatitis).
- Mechanical. Caused by a mechanical disruption of the outflow of bile due to anatomical features or cysts of the bile ducts.
Untreated, prolonged jaundice can lead to bilirubin encephalopathy, or kernicterus, which develops toxic damage to bilirubin in the gray matter of the brain. This leads to drowsiness, lethargy, changes in reflexes, and in extreme cases, paralysis, deafness, and mental retardation.
Side effects
Light therapy for neonatal jaundice is safe. However, babies who were lying under artificial ultraviolet light may experience overheating, or, conversely, hypothermia. The baby's skin may acquire a bronze tint. There is a possibility of dryness, redness of the baby's skin, intestinal upset with a greenish tint to the stool, drowsiness, and dehydration.
Many of the above phenomena can be avoided by frequent breastfeeding.
If there is not enough mother's milk, then you should supplement the baby with water or a weak rosehip decoction. Its diuretic properties will help quickly remove toxins from the child’s body, plus it will strengthen the baby’s immunity.
Home treatments
Conjugation jaundice
Since jaundice can be treated at home during its normal course, gentle methods of therapy are used using herbs and infusions, which significantly speed up the healing process. It is also necessary to adjust the daily routine of both the baby and the young mother.
Light therapy
Bilirubin is sensitive to ultraviolet light, so sun exposure is one of the best ways to cure jaundice.
Medical institutions use special equipment to conduct treatment sessions throughout the entire therapy. Babies born in summer can be taken outside for a short time to sunbathe. You should not go out into direct sunlight; it is better to use diffused light with an exposure duration of no more than 10-15 minutes.
Diet of a young mother
There is no better cure for jaundice than breast milk. It contains all the useful and nutritious substances necessary for the baby's health. But if the mother’s diet is improper, the newborn also receives harmful components that can aggravate the course of the disease. Need to exclude:
- smoked meats;
- spicy foods;
- foods high in fat;
- marinades;
- semi-finished products;
- allergens;
- foods that promote excessive formation and accumulation of gases in the intestines.
Particular attention should be paid to drinking - a young mother needs to drink at least two liters of water per day
Folk remedies
If jaundice is detected in a newborn, treatment at home should be comprehensive. To do this, they not only take medications, but also use various lotions, baths, and compresses.
- Magnesia. At any pharmacy you can purchase a solution of magnesium sulfate, which is sold in standard ampoules. This tool is considered an excellent alternative to electrophoresis. Clean gauze is moistened in the solution and applied to the baby’s projection of the liver area for 15-20 minutes. The procedure should be carried out after feeding, which will help speed up the process of removing bilirubin from the body.
- Rose hip. The action of the berries is aimed at normalizing digestive function and removing toxic substances from the body. It is easy to prepare a rosehip decoction: 0.5 liters of water will require 100 g of berries, which need to be poured with boiling water and boiled for 10 minutes. The product is recommended for both mother and baby. The baby should be given a teaspoon of decoction after each feeding.
- Glucose. For jaundice in newborns, treatment must necessarily include replenishing glucose reserves in the body. Before you start giving a 5-10% solution to your baby on your own, you need to consult a doctor who will explain all the intricacies of this stage of therapy.
- Peppermint. Mint decoction can be given only if the baby tolerates it normally. You need to make sure that there are no rashes on the skin and no colic after taking the product. For a glass of boiling water you need to take 5 g of dry mint. Infuse the product in a thermos for two hours. The strained tea should be given a teaspoon twice a day after meals.
Baths based on decoctions of chamomile, calendula, and golden flower help speed up the process of removing bilirubin from the body. The only condition for bathing the baby is a healed umbilical cord. 200 g of any of the listed herbs are boiled in four liters of water for 30 minutes, then left under the lid for another half hour. The finished broth is filtered and the baby is bathed in it. The duration of water procedures is 15 minutes. After bathing, the baby should be dried and wrapped warmly.
All of the above remedies have proven themselves in the treatment of jaundice, but, as is known, self-medication is dangerous, especially for newborns. In any case, a visit to the doctor is mandatory, and you can start home therapy only after the doctor approves the plan.
Light therapy at home
It is possible to cure jaundice at home using an ultraviolet lamp. You can find a similar device on the Internet, in medical equipment stores, where you can buy or rent it if you wish.
Connecting the device is not difficult - just read the instructions and plug it into a power outlet. However, be careful about the irradiation process itself. The distance between the device and the baby should not be less than 50 cm.
The baby's eyes and genitals (especially for boys) should be closed and protected from ultraviolet radiation.
The baby needs to be constantly monitored, turned over every 2 hours, and body temperature measured every hour. Get your blood tested regularly to monitor your bilirubin levels and consult your doctor.
If, when treated with ultraviolet light at home, the child’s skin does not turn pale, but rather becomes deep yellow, immediately contact your pediatrician.
Ordinary sunbathing can easily help cope with neonatal jaundice of moderate severity. This is also a kind of phototherapy, only of natural origin. Walk your baby outside more, but avoid direct sunlight. Being under the scorching sun for a long time can cause the baby to overheat and get burns.
If you are sunbathing at home, you can undress your baby, but beware of hypothermia.
This method of home phototherapy works more slowly, but it is no less effective, plus it does not require strict adherence to any rules. However, everything depends on the severity of the disease, which only a doctor can diagnose and prescribe the correct treatment.
Indications for phototherapy
How long does it take for jaundice in newborns to go away and how long does it last?
In fact, phototherapy, as phototherapy is also called, is recognized by leading experts in the field of pediatrics and neontology as the safest and most effective method of combating the manifestations of infantile jaundice. It has been proven that ultraviolet waves have the ability to accelerate the dissolution of bilirubin molecules in tissues. It is converted to a simple isomer, which is excreted from tissues naturally.
Main indications for phototherapy:
- in newborns, mild or moderate yellowness of the skin was detected;
- a situation of Rh conflict between the organisms of the mother and her child has been established;
- suspicion of established blood diseases in a newborn - for example, hemolytic anemia;
- the need for complex treatment of hyperbilirubinemia - a rapid increase in toxic substances.
On an individual basis, light therapy can be recommended for a newborn if he is born prematurely - morphofunctionally immature, or when examining the skin, extensive subcutaneous hematomas are observed. Less commonly, phototherapy is performed at the stage of preparing a child for surgery or during the rehabilitation period after organ transplantation.
How and for how long should you lie under the lamp?
Phototherapy is carried out in a prepared box equipped with a special photo lamp with blue ultraviolet rays. The newborn is undressed and placed in the incubator. A thick bandage is put on his eyes to protect the retina. The newborn's groin is also covered, since exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the genitals is not desirable. A diaper or any thick diaper folded in several layers is suitable for this task.
UV therapy for jaundice is carried out for at least 2 hours with the baby periodically turning over.
The child should lie under the blue lamp for at least 2 hours. If the levels of bilirubin in the blood are too high, then the babies lie under ultraviolet radiation until the bilirubin completely disappears. You can take a short break while feeding your baby.
While the baby lies under the lamp during phototherapy, it must be periodically turned from side to side, from back to tummy and vice versa, so that the ultraviolet radiation evenly reaches all parts of the baby’s body.
A newborn exposed to a blue ultraviolet lamp must be breastfed frequently, as the mother's milk tends to weaken. This will speed up the work of the intestines and increase the frequency of bowel movements, which will quickly remove broken bilirubin from the baby’s body. Even if the baby is sleeping, it is worth waking him up to breastfeed.
When a child lies under ultraviolet radiation, his body intensively loses water, which can lead to overheating and dehydration. Therefore, liquids in the baby’s body should be 20% more than the daily norm. Foremilk, provided frequent breastfeeding, compensates for this loss.
A newborn exposed to ultraviolet light during phototherapy should be closely monitored by a health care professional. If the toddler's condition worsens, blood tests should be performed periodically. This will show how much bilirubin remains in the baby’s body and what is the intensity of its decomposition.
Indications for light therapy
There are several cases when the use of this technique during the treatment of jaundice is required:
- pronounced yellowness on the skin of a newborn;
- yellowed eyeballs;
- the rich yellow color of the fluids secreted by the baby’s body.
Premature babies with low birth weight who require urgent resuscitation procedures may need a lamp with ultraviolet rays.
Newborns with multiple hematomas, hemorrhages, deep anemia, body temperature less than 35 C, and who have a low Apgar score may lie under ultraviolet light.
The predisposition of the fetus to an increase in bilirubin after birth, revealed during pregnancy, and Rh conflict with the mother can become a reason for the development of neonatal jaundice and the use of an ultraviolet lamp.
Since phototherapy affects the entire body of the child, it is not prescribed for mild forms of jaundice.
You should also not self-medicate; without the advice of specialists, the baby can be harmed.
But when the level of indirect bilirubin is critical, the procedure is almost irreplaceable. It is especially effective when combined with taking certain medications and breastfeeding. If you follow all the instructions, you will be able to avoid adverse reactions.
Treatment of jaundice in newborns
Treatment of jaundice in a newborn does not involve the use of special high-tech complex interventions. It is advisable to begin treatment when bilirubin levels exceed acceptable limits and the child’s condition suffers.
The nervous system of a full-term newborn suffers when the bilirubin level is more than 345 µmol/l, 230–260 in a premature infant, and 160–225 µmol/l in a very premature infant.
Left to chance, treatment of neonatal jaundice leads to disastrous results.
Treatment of jaundice with glucose
How to give glucose to a newborn with jaundice? To treat newborns with jaundice, glucose solutions are used intravenously along with insulin and ascorbic acid. These funds:
- improve the absorption of drugs;
- normalize the permeability of the vascular wall;
- prevent the development of edema.
If the child cannot drink, then the medicine is administered through a tube.
Being a source of energy, participating in all metabolic processes, glucose for jaundice in newborns should be used only as prescribed by a doctor. Its thoughtless use leads to diabetes mellitus
Particular caution should be taken when prescribing these drugs if the mother of the newborn suffers from a carbohydrate metabolism disorder.
In what dosage, how to give and with what medications is it better to combine glucose for jaundice in newborns:
- The child should gradually drink 100 ml of 5 percent glucose in small increments per day. We remember that this is a medicine for newborns for jaundice, and not sweet water. It helps the liver cope with the intoxication caused by bilirubin.
- If a child, weakened, cannot suck from a bottle, glucose should be drawn into a syringe with a capacity of 2 ml and a few drops of the solution should be injected into the cheek. This is a long process. You cannot pour in a stream of solution, otherwise the newborn will choke.
In inpatient conditions, intravenous administration of drug solutions is used to treat jaundice in newborns, followed by stimulation of urine excretion from the body with diuretics. This is called forced diuresis in neonatal jaundice.
Glucose for newborns with jaundice is combined with phenobarbital, which improves the breakdown of bilirubin. The average therapeutic dose is 2 mg/kg per day for a week. There is a method for using loading doses of phenobarbital: 10 mg/kg on day 1, then 4 mg/kg. The danger of this method: high dosages block the respiratory center, causing respiratory arrest.
Other areas of therapy
Intravenous drip is used in newborns with jaundice to restore electrolyte levels:
Enterosorbents are used to treat jaundice in newborns:
These are auxiliary agents that do not directly affect bilirubin, but have detoxifying properties.
If there are no abnormalities in the development of the bile ducts, then for the treatment of postpartum jaundice in newborns the following are prescribed:
Ursofalk suspension is convenient to take, prescribed 10–15 mg/kg per day. If the effect is insufficient, the dose is increased to 25–35 mg/kg per day. For long-term use for neonatal jaundice, the maintenance dosage is 5 mg/kg.
For infantile jaundice, newborns are prescribed treatment and a special feeding regimen is established, taking into account the fact that jaundice is a symptom of a severe disorder. Therefore, the use of fat-soluble vitamins is mandatory:
- D3–20,000 IM once a month or 5,000 orally daily;
- A - 20,000 IM once a month or 5,000 orally daily;
- E - 5 mg/kg IM or 20 orally once every 2 weeks;
- K - 1 mg/kg 1 time.
Pancreatic enzymes are periodically prescribed to newborns for replacement purposes for jaundice:
In case of prolonged course, Viferon is used rectally, 1 suppository for a week, then every other day for a month. Goal: stimulate your own immunity, suppress the harmful effects of viruses on a weakened body.
If the causative agents of cytomegalovirus and herpes are identified, drugs are used that do not have a toxic effect on hematopoiesis in the child’s body:
When mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, and chlamydia are detected, the following is prescribed:
The use of drugs according to the scheme under the guise of Folic acid, Essentiale, Heptral, LIV 52 to reduce the side effects of the prescribed treatment.
Contraindications and restrictions
Phototherapy is prescribed to newborns in the following situations:
- When the physiological form of jaundice has developed - with high bilirubin levels and an hourly increase of more than 5 µmol/l in full-term babies and more than 4 µmol/l in infants born prematurely.
- If during pregnancy an increased risk of hyperbilirubinemia was detected in the baby.
- When a child was born morphofunctionally immature.
- If the baby has extensive hematomas and hemorrhages.
- When there is a risk of developing hemolytic anemia (its hereditary form).
- If the baby’s blood type is incompatible with the mother’s, as well as in case of Rh conflict.
- During rehabilitation or preparation of a child for surgery.
The bilirubin level at which phototherapy is prescribed to an infant with physiological jaundice depends on the baby’s weight:
Phototherapy is not performed if:
- The child has a high level of bound bilirubin fraction, which does not decrease.
- The baby was diagnosed with liver problems.
- The baby was diagnosed with obstructive jaundice.
Despite the fact that phototherapy is one of the safest ways to remove bilirubin from the body of a small patient, the procedure has contraindications. Light therapy is prohibited for children with:
- functional liver disorders;
- complications caused by jaundice;
- significant deviations of bilirubin levels from the norm.
Phototherapy should be carried out under the strict supervision of medical professionals, so that if the baby’s condition worsens, immediate assistance measures are taken. But not all newborns are allowed ultraviolet treatment; there are some contraindications to the procedure:
- the baby has any abnormalities in liver function;
- if there is a malfunction in the biliary tract (obstructive jaundice);
- if the baby is diagnosed with severe anemia;
- for sepsis;
- if the baby’s skin and mucous membranes are prone to increased bleeding;
- with high levels of bound bilirubin.
In these cases, the newborn will require medication treatment, which is aimed at eliminating the disease that caused the high bilirubin level.
Sometimes during the process of phototherapy, a newborn experiences side effects that can be completely safe for the baby’s health and do not require drug intervention:
- decreased child activity. The baby spends most of his time sleeping;
- the skin acquires a bronze tint;
- diarrhea may occur;
- The baby's skin begins to peel off.
A phototherapeutic irradiator is used to treat neonatal jaundice in hospitals. The doctor decides to use this method individually, based on the test results and the general condition of the baby. The main indications for the use of a UV irradiator are:
- Pronounced signs of jaundice.
- Early date of birth.
- Insufficient body weight.
- Iron deficiency in the blood.
- Weak appetite and low activity.
- Reduced body temperature.
Phototherapeutic exposure is a safe method of treatment, so there are practically no categorical contraindications
But there are a number of clinical situations when the procedure is prescribed with caution due to the high likelihood of side effects. The main conditions under which it is prohibited to use a photo lamp are:
- Eye pathologies. In this case, prolonged exposure to UV radiation on a newborn leads to the development of complications and a decrease in visual acuity. Therefore, the procedure is performed only with protective tight glasses.
- Skin diseases. The epidermis, sensitive to ultraviolet rays, may become inflamed during the procedure. Therefore, if absolutely necessary, it is prescribed only for a short time.
- Neurological disorders. Ultraviolet radiation has a stimulating effect, so for many diseases of the central nervous system, irradiation is not recommended.
- Hormonal disorder. Phototherapy causes excessive production of a number of hormones. In case of endocrine disruption, it is prohibited.
- Tuberculosis or lung diseases. There is a high risk of developing serious complications.
Phototherapy is not prescribed by a pediatrician for acute conditions, hyperthermia, tumor processes and a tendency to bleeding. Otherwise, the procedure becomes a trigger for a number of complications or serious deterioration of the condition.
- high level of free bilirubin,
- liver dysfunction,
- obstructive jaundice is a malfunction of the biliary tract.
Description and principle of operation of the lamp for jaundice
What is a lamp for jaundice
In 32-86% of newborns in the first week of life, mainly on the second or third day, so-called physiological jaundice is noted, which is manifested externally by jaundice of the skin and sclera of the eyes.
Visual determination of Hb level.
The phenomenon in itself is not abnormal and occurs due to a reduced level of liver enzymes and, as a consequence, an insufficient rate of breakdown of indirect bilirubin in the liver, formed during the decomposition of dying red blood cells and hemoglobin. The most common causes are:
- prematurity and/or low birth weight of the child;
- endocrine disorders in the mother, especially diabetes mellitus and thyroid disease;
- Rh conflict between the blood of mother and child;
- gestosis during pregnancy.
For the full development of a child’s enzyme system, it takes from one and a half to three months. In the initial period of development, therapy is aimed at combating hyperbilirubinemia. It is indirect bilirubin that poses the greatest danger to a newborn due to its histotoxicity - the ability to adversely affect metabolic processes in tissues, including the brain.
There are 25 known forms of neonatal jaundice, and only the rarest of them require drug or surgical treatment. In 95% of cases, this condition is compensated by phototherapy with lamps emitting a light spectrum close to ultraviolet.
How it works
Under the influence of lamps emitting light with a wavelength of 400-500 nm, photoisomerization of indirect bilirubin molecules occurs in the skin, transforming it into a water-soluble form. The resulting direct bilirubin is not dangerous and is easily excreted by the body's excretory systems through urine, feces and, to some extent, sweat.
Newborn in an incubator under a lamp.
The therapeutic effect is manifested:
- laboratory - a decrease in the level of bilirubin in the blood already on the second day of phototherapy and complete normalization on days 5-6;
- visually - a decrease in yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera of the eyes on the third or fourth day of treatment.
For your information. Dark green coloration of a newborn's stool during phototherapy is a normal phenomenon that occurs due to the excretion of direct bilirubin and does not pose any danger. Can be taken into account as an additional indicator of the effectiveness of lamp treatment.
It was experimentally determined that the highest degree of photoisomerization is achieved when irradiated with light in the blue spectrum and a narrow wavelength range of 450-460 nm. The use of ultraviolet lamps is not so effective for newborns, since their operating range lies in the range from 100 to 400 nanometers, which is dangerous for the fragile body of infants.
Varieties
Depending on the design, there are lamps:
- overhead light - installed on a portable tripod or in a stationary panel connected to the incubator. The main disadvantage is the requirements for the protection of the genitals and organs of vision in the case of using light sources close to the aggressive ultraviolet range;
Fluorescent lamp on a tripod.
- bottom light - lamps located at the bottom of the incubator with a transparent bottom, or under a hammock with translucent fabric. Less demanding on eye protection, provided you monitor the child’s posture or use safe LED lamps;
LED panel at the bottom of the incubator.
- wrapping - fabric with a fiber optic cable located on the inner surface of the blanket or bedspread. The development of American scientists is considered safe and convenient, since the light rays are directed inward and do not enter the eyes, and the small volume of the folded blanket allows you to take it with you and use it wherever there is a power source.
Fiber optic blanket.
As an alternative to lamps in countries with warm climates, sunlight passed through a special filter fabric is used. This material cuts off the ultraviolet and infrared range, allowing only the blue spectrum of visible light to pass through. The child is placed under a canopy made of filter fabric, and remains undressed under it throughout the day. Studies have shown that the therapeutic effect of filtered sunlight is equal to, and in some groups even exceeds, that of phototherapy with electric lamps. The only drawback of the method is the need to monitor the baby’s temperature, and when the body heats up to 38 °C, place it in the shade until the thermometer readings normalize.
The design differences of photolamps from jaundice for the comfort of the newborn and the result of treatment are not of fundamental importance, since different types of lighting elements can be used in the same installations. Some types of lamps have a limited useful life. This means that the efficiency of an externally working device decreases over time. New devices are equipped with special meters and lamps. The condition and efficiency of a lamp without a meter is determined by a photometer.
Jaundice of newborns: causes, whether treatment is needed
LED or LED devices
The most economical and safe light sources. It is the LEDs that are mounted in cuvuses with a transparent bottom. Since these lamps practically do not heat up, they can be placed at any convenient distance from the baby’s body, and the intensity of the blue spectrum with a wavelength of 420-470 nm and a power of 500 μW/cm2 at a distance of 800 mm from the body eliminates the harmful effects of high- and low-wave radiation. The peculiarity of LED devices is that their light is less efficient, but at the same time relatively safe for the eyesight and skin of a newborn. Another positive difference between LEDs is their service life, which is 20,000–50,000 hours of operation. LED lamps are a complete replacement for halogen and fluorescent devices.
Patient under LED device.
Halogen lamps
Improved incandescent lamps with a tungsten filament located in a bulb containing iodine or bromine vapor. Light filters are used to cut off unnecessary waves of radiation, but halogen lamps operate in the range of 380-600 nm, and their light output reaches 22 Lm/W, which places special demands on the protection of the organs of vision and groin area from light burns. In addition, the heating temperature of the flask of 300 °C requires placing the device at a distance from the patient to avoid hyperthermia, which reduces the concentration of the light flux. The operating life of halogen devices is a maximum of 4000 hours. The uneven distribution of the useful spectrum and increased requirements for monitoring possible hyperthermia and overdose of UV radiation make the use of halogen lamps in devices for the treatment of hyperbilirubinemia impractical.
Halogen lamp.
Fluorescent photo lamps
They are most often used as bactericidal, since an electric discharge in mercury vapor is capable of producing a wide range of light waves, starting from the green visible spectrum with a length of 520 nm up to aggressive low-wave ultraviolet class B. Gas discharge devices with turquoise - 490 nm and blue are suitable for the treatment of jaundice light - 420-460 nm. In terms of energy consumption, they are not inferior to LEDs with the same light output power, and the working life reaches up to 70 thousand hours. Low heat transfer does not lead to hyperthermia and allows fluorescent flasks to be installed in devices without special radiators and forced cooling. Some disadvantages:
- the presence of poisonous mercury inside the fragile flask;
- frequent breakdowns of starting devices;
- burnout of light-forming photocells and photofilters in the flask with a change in the operating range to the ultraviolet side.
All this requires attention to operating conditions, maintenance and protection of the child’s eyes and groin area from burns. In this respect, fluorescent lamps are inferior to LED lamps.
Fluorescent lamp.
Hybrid
Combination of upper and lower light lamps, when LED lamps are installed in the bottom of the incubator, and halogen or fluorescent lamps are installed on top at an adjustable height. In some cases, combinations of low light with a photo-optical blanket are used. Combined systems are used when it is necessary to achieve maximum effect in a short time, but the application requires special skills from the operating personnel.
Combination of fluorescent and LED systems.
How to choose the right lamp
The stationary conditions of neonatal centers allow the use of any types of devices and their combinations, since all indicators and the condition of the baby are monitored by professional doctors. In cases where the attending physician allows phototherapy at home, the conditions for choosing a device for the treatment of neonatal jaundice are:
- Safety.
- Mobility.
- Ease of use.
Two types of lamps fit these criteria:
- portable incubators with bottom light or tripods with LED elements. They do not harm the organs of vision, practically do not lead to UV overdose or hyperthermia. As a rule, they are equipped with an electronic control system with a programmable operating mode and a counter showing the remaining useful life. At the same time, they are relatively accessible and economical;
- photo blankets and photo bedspreads. They have all the advantages of LED lamps, but at the same time do not cause concern for a newborn; when folded, they fit into a small case. The main and only drawback is the high price and small assortment on the medical equipment market.
Given a short course of treatment, it is not advisable to purchase such equipment, so most parents limit themselves to the services of companies that provide rental devices.
Portable incubator.
Indications and contraindications for use
The final decision on the advisability of using a conservative method of treating neonatal jaundice is made by a neonatologist or local pediatrician. Prescription of phototherapy is possible based on examination data, laboratory tests and maternal medical history, including during pregnancy. Most often, phototherapy is indicated in the following cases:
- physiological jaundice of newborns with the level of indirect bilirubin in full-term infants - above 70 µmol/l, in premature infants - 60 µmol/l.
- mild hemolytic disease of newborns, when the level of indirect bilirubin in the blood serum does not exceed 60 µmol/l;
- maternal history of diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathologies, severe gestosis, anemia during pregnancy;
- physiological immaturity of a premature newborn;
- preparation or rehabilitation before/after surgical interventions;
- the presence of subcutaneous and parenchymal hemorrhages in the child.
Absolute contraindications for phototherapy include:
- cholestasis due to obstruction of the bile ducts;
- “bronze baby” syndrome - increased photosensitivity of the skin, when phototherapy leads to a grayish-brown discoloration of the skin, urine and discoloration of feces;
- inflammatory processes in liver tissues;
- critical level of bilirubin, which poses a danger to the child’s life due to damage to the central nervous system: for full-term infants 342 µmol/l;
- for premature infants 270 µmol/l;
- for very premature infants from 170 µmol/l.
If there are contraindications and in cases of ineffective phototherapy, when there is no time for conservative therapy, drug treatment is used, and in some cases surgery is indicated.
Appearance of a icteric newborn.
Instructions for use
Fluorescent lamps
- The newborn's clothes are removed, leaving a diaper, special safety glasses are put on with a fixation under the chin to prevent involuntary slipping, and they are placed in an incubator.
- The device is turned on and installed at a distance of 400-600 mm from the child’s body.
- The timer is set to 30 minutes. up to 8 hours, depending on the instructions of the neonatologist.
- The session is interrupted for feeding and diaper changing. If redness of the skin is detected and the child is very restless, the doctor should be notified.
Safety glasses with double fixation.
Halogen lamps
Due to the wide spectrum of radiation, including the ultraviolet range and heating the bulb up to 300 °C, halogen lamps are used with the most careful approach to safety precautions, including:
- mandatory use of eye and genital area protection;
- placing the lamp no closer than 800 mm from the child;
- monitoring body temperature and identifying hyperemic areas of the skin.
For treatment with halogen devices, it is recommended that the child be in a hospital.
Combined systems
When using combinations of fluorescent and LED light sources, treatment tactics correspond to the standard ones for a specific type of device. If the combined system means therapy with a photo blanket with a fiber-optic surface, then the method of its use implies:
- exclusion of protective devices;
- daily cycle of therapy with breaks for hygiene procedures;
- the possibility of feeding without removing the newborn from the overalls or blanket.
Feeding position in fiberoptic blanket.
LED lamps
- The child is undressed completely or down to the diaper. A cap or glasses are placed over the eyes to improve the quality of sleep.
- The patient is placed under the device, in an incubator or hammock, face up.
- Using the control panel, the operating mode and session time specified by the treating pediatrician are set.
Duration of treatment
It is prohibited to independently determine the required course of treatment and the duration of periods of phototherapy. During home treatment, the local pediatrician is required to examine the patient and monitor the progress of therapy throughout the course. Parents or nannies follow all doctor's orders. During the normal course of phototherapy, the jaundice of the skin disappears completely within 7-8 days. The onset of symptoms on the first day or persistent jaundice for more than 14 days is a deviation from the norm and a reason to transfer the patient to the hospital for additional examination and outpatient treatment.
Adverse reactions when using lamps
Prolonged exposure to the blue spectrum of light, even with full compliance with safety precautions, is sometimes accompanied by:
- skin hyperemia, sometimes burns;
- dryness and peeling of the epidermis;
- hyperthermia;
- stool disorder;
- increased anxiety, sleep disturbance.
In order to prevent disturbances in water balance, the child is given water or 0.9% NaCl from a spoon, and in severe cases, infusion therapy with a 3% glucose solution is carried out.
How quickly does bilirubin decrease?
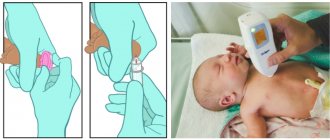
To independently determine the level of bilirubin in the baby’s skin, there are transcutaneous bilirubinometers.
The final formation of the liver enzyme system of a newborn occurs by 1.5-3.5 months of life. Complications and relapses are possible throughout the entire period. Treatment is considered effective if the level of indirect bilirubin in the patient’s blood decreases by 19-21 µmol/day.
Phototherapy as a method of treating jaundice
Yellowing of the face in the first month of a baby’s life is far from the norm, as many people think. If the jaundice is severe and the bilirubin level is significantly higher than normal, treatment cannot be avoided. There are different methods: taking medications for the liver, sorbents that remove toxins, transfusion of blood components. However, the simplest and most effective way to combat jaundice is phototherapy.
Phototherapy belongs to the category of physiotherapeutic procedures. It is based on the healing properties of UV rays, simulating sunlight with a certain wavelength (in the range of 400-550 nm).
Ultraviolet light, coming into contact with the baby’s skin, neutralizes bilirubin by converting it into an isomer, after which it is easily excreted from the body along with feces and urine. A special photo lamp is used for treatment. The most effective is considered to be a combination of 4 ultraviolet and 2 daylight lamps.
Important! High bilirubin causes intoxication of the body. Infants with jaundice often have no appetite, do not gain weight well, and sleep a lot
If the concentration of bilirubin is not reduced in a timely manner, this can lead to damage to the brain and nervous system (bilirubin encephalopathy).
Phototherapy is based on the effect of ultraviolet lamps on the skin of patients. Such light waves convert the dangerous form of bilirubin into its isomers, which are excreted from the child’s body in feces and urine. The procedure reduces the quantitative indicators of the substance in the blood and prevents the development of a number of complications. The effectiveness of the manipulation is explained by the following points:
- as a result of the oxidation of indirect bilirubin under the influence of UV rays, the formation of biliverdin, mono- and dipyroles occurs, which dissolve in water and are excreted in urine and feces;
- configurational changes occur in the molecules of the indirect fraction of bilirubin, and isomers that are harmless to the body are formed, which again easily dissolve in water;
- Structural changes occur in bilirubin molecules, resulting in the formation of lumirubin. The latter is eliminated from the baby’s body within a few hours.
Experts have found that the phototherapy procedure for neonatal jaundice will produce the maximum effect if the area and intensity of irradiation are as large as possible. Doctors recommend increasing the radiation power to 30 μW/cm2/nm, and also installing the lamps in such a way that ultraviolet radiation hits all parts of the child’s body at the same time.
There are special blankets for phototherapy
Phototherapy for newborns - what is it?
After a child is born, his body adapts to completely different environmental conditions and undergoes many changes. One of the adaptation mechanisms is physiological jaundice of newborns. In the intrauterine life of a child, his blood contains much more red blood cells than an adult.
This is due to the fact that it receives oxygen by transporting it from the maternal blood through the umbilical cord, and for sufficient saturation it requires a large amount of hemoglobin, which is part of the red blood cells, because it is hemoglobin that carries oxygen to organs and tissues.
After the birth of a child, his body no longer needs such a large number of red blood cells, they are destroyed, releasing fetal hemoglobin, which in turn is destroyed and releases bilirubin, and a large amount of free bilirubin turns the mucous membranes and skin yellow.
Physiological jaundice usually appears on days 3–4 of life and goes away on its own after 2–3 weeks.
Bilirubin is a toxic substance. The body tries to remove it by binding it to the protein albumin.
But if there is significantly more bilirubin than albumin, it affects the nervous system, causing “kernicterus.”
In addition to physiological jaundice, there are pathological forms: conjugative hereditary jaundice, hemolytic disease of newborns, infectious-toxic hepatic jaundice.
One of the most effective methods of reducing bilirubin toxicity is light therapy, or phototherapy.
Phototherapy is one of the physiotherapy procedures based on the therapeutic effects of the ultraviolet spectrum of sunlight with a wavelength of 400–550 nm.
Under the influence of a light wave of the required range, bilirubin is converted into an isomer, which the newborn’s body is able to excrete with physiological waste, which reduces the level of bilirubin in the blood and protects the body from its toxic effects.
Technique of the procedure
A completely undressed child is placed in an incubator, his eyes are covered with special glasses to protect him from ultraviolet radiation, and the boys’ genitals are covered with light-proof fabric. A thick, light-proof gauze dressing is often used.
Ultraviolet lamps are installed at a distance of about 50 cm from the child. Moreover, the combination of four ultraviolet lamps with two fluorescent lamps turned out to be more effective, but the therapeutic effect comes only from the ultraviolet source.
During the procedure, the maximum break can last from two to four hours in a row. In cases of a pronounced increase in bilirubin, light therapy is carried out in a continuous course.
The course lasts on average 96 hours.
Every hour the baby is in the incubator, it is necessary to change the position of his body - on his back, on his stomach, on his side, and measure his body temperature every 2 hours to avoid overheating.
It is worth knowing that during phototherapy, the daily volume of fluid required for a child should exceed the physiological need by 10–20%.
It is necessary to take the baby’s blood for biochemical analysis daily (and if there is a threat of encephalopathy, every 6 hours); this is the only method that serves as a criterion for the effectiveness of the treatment.
Indications for phototherapy
Indications for phototherapy in newborns are:
- the risk of developing hyperbilirubinemia in a child identified during pregnancy;
- morphofunctional immaturity of the child;
- the presence of extensive hemorrhages and hematomas;
- newborns requiring resuscitation;
- identified high risk of developing a hereditary form of hemolytic anemia;
- physiological jaundice of newborns;
- hemolytic disease of newborns with blood group incompatibility - as the main method of treatment;
- hemolytic disease of newborns with Rh conflict - as an additional method of treatment after blood transfusion to prevent a re-rise in bilirubin levels;
- preparation for replacement blood transfusion and rehabilitation after surgery;
- an increase in bilirubin of more than 5 µmol/l per hour for full-term infants and more than 4 µmol/l per hour for premature infants.
Indications for newborns in the first week of life depending on weight and bilirubin level (*):
- body weight less than 1.5 kg, bilirubin level from 85 to 140 µmol/l;
- body weight up to 2 kg, bilirubin level from 140 to 200 µmol/l;
- body weight up to 2.5 kg, bilirubin level from 190 to 240 µmol/l;
- body weight more than 2.5 kg, bilirubin level – 255–295 µmol/l.
Types of devices
Depending on the size, photo lamps for the treatment of jaundice can be:
- Stationary. They are used in the maternity hospital immediately after birth. Such emitters are installed on stands above incubators; the height can be adjusted. They work with short breaks for feeding and changing.
- Mobile. These lamps are used to treat jaundice at home. They look like a plastic incubator, in the lower part of which there are emitters. That is, light is scattered not from above, but from below. The baby is located in a hammock above the lamp, and the impact occurs only on the back. Therefore, no additional eye protection is required. The lamp heats the hammock fabric to a comfortable temperature. At the same time, the material transmits the required amount of light.
- Photo blankets have recently appeared. They scatter light using photo-optical radiation from halogen or UV elements that are located on the fabric material. To use them, the baby is wrapped in a blanket that is connected to a power source.