Increased uterine tone at different stages of pregnancy
Pregnant women experience major adaptive changes in anatomy, physiology and the functioning of internal organs, which determine the normal course of pregnancy and successful childbirth.
The uterus, which has three layers: outer serous, inner epithelial, intermediate muscular - myometrium, undergoes radical changes. The middle layer is quite elastic, which allows it to stretch and contract during childbirth and return to its previous state after childbirth. However, against the background of the development of certain factors, contractile activity of the uterus may appear earlier than expected.
Various symptoms appear in the form of heaviness or nagging pain in the lower abdomen; in such cases, uterine hypertonicity is often diagnosed. Such a diagnosis is not a reason to panic, but this condition should not be considered the norm, so you need to make an appointment with a gynecologist as soon as possible.
Causes and symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia
There are forms of hyperplasia:
- glandular – the glandular tissue of the mucous membrane thickens;
- glandular-cystic - benign cysts are formed;
- focal - glandular and fibrous polyps appear;
- atypical (adenomatous) – altered cells appear, which is dangerous due to degeneration into an oncological form (adenocarcinoma).
The main causes of the disease are hormonal imbalances. There is a likelihood of encountering signs of endometrial hyperplasia during puberty and at the beginning of menopause, when hormonal changes occur in the female body. A number of related problems increase the risk of pathology:
- inflammation in the genitourinary system;
- abortions, gynecological operations on the uterus;
- heredity;
- excess weight;
- endocrine diseases;
- diseases of the poppy and appendages - fibroids, polycystic ovary syndrome;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- hormonal therapy.
It is difficult to determine pathology only from patient complaints. Many gynecological diseases manifest themselves in a similar way. The main symptoms of endometrial hyperplasia include:
- irregular, frequent (more than 21 days), prolonged menstruation, with spotting between them;
- cramping pain in the abdomen;
- spotting during menopause.
The disease can be asymptomatic, especially during menopause.
Uterine tone during pregnancy - symptoms
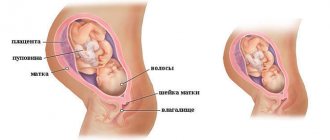
The uterus is located in the pelvis between the rectum and bladder. The fallopian tubes are located symmetrically on both sides of the uterus, thanks to which the fertilized egg is transported. The uterus consists of three parts: the fundus, the body, and the cervix. The organ wall is formed by three types of tissue: perimeter, myometrium, endometrium.
At the moment of bearing a child, the uterus has the ability to increase 10 times, its muscles stretch, and its walls thicken. The main role in increasing the tone of the uterus is played by the myometrium, represented by a layer of smooth muscle. Throughout pregnancy, the myometrium remains relatively motionless, providing a suitable environment for the developing baby. In the short term, rhythmic and prolonged contractions of the muscle layer and expansion of the cervical region combine and physiological labor occurs.
If contractile activity of the uterus appears long before childbirth, in the first or second trimester, then the doctor often diagnoses uterine hypertonicity. Of course, such a phenomenon is not in all cases considered as a pathological process. But, if hypertonicity is observed all the time, this phenomenon can lead to critical consequences. The present symptoms of increased uterine tone during pregnancy can cause spontaneous abortion in the 1st trimester, and in the 2nd-3rd trimester lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus (hypoxia).
It is worth noting that the clinical manifestation of tone does not differ in characteristic signs; usually the expectant mother complains of discomfort and soreness in the lower abdomen, similar to menstrual pain.
The pain syndrome in most cases is not of a pronounced type, but can radiate to the lower back.
In the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, the symptoms of increased uterine tone do not differ much from the first, but upon palpation you can notice that the abdomen has become denser. In rare cases, a woman observes a spotting reddish-brown discharge from the vagina. If such a symptom develops, you should consult a doctor as an emergency.
It is also worth describing the symptoms of uterine hypertonicity during late pregnancy, in the 3rd trimester. At the end of the 38th week, tone has a completely different meaning and is considered as a manifestation of training contractions. This tone has the scientific name of a Braxton-Higgs contraction. Braxton Hicks contractions are designed to strengthen the muscles of the uterus in preparation for subsequent labor. Contractions usually last about 30-45 seconds. However, in the eighth and ninth months of pregnancy they can even occur every 20-30 minutes. Braxton Hicks contractions are called “predictive contractions” and have an average duration of no more than two minutes.
In some women, hypertonicity is asymptomatic and is diagnosed during ultrasound examination.
How is the condition of the uterus assessed?
If in the first trimester of pregnancy the condition of the uterus is assessed during a bimanual examination, then from about the fourth month, to assess the progression of pregnancy and the condition of the uterus, the obstetrician-gynecologist uses four external obstetric examination techniques (Leopold's techniques):
- During the first external obstetric examination, the doctor places the palms of both hands on the uppermost part of the uterus (fundus), and the UMR is determined, the correspondence of this indicator to the gestational age and the part of the fetus located in the fundus of the uterus.
- During the second external obstetric examination, the doctor moves both hands from the bottom of the uterus down to the level of the navel and places them on the lateral surfaces of the uterus, after which he alternately palpates parts of the fetus with his right and left hands. When the fetus is positioned longitudinally, the back is palpated on one side and small parts of the fetus (arms and legs) on the other. The back is palpated in the form of a uniform area, small parts - in the form of small protrusions that can change their position. The second technique allows you to determine the tone of the uterus and its excitability (contraction of the uterus in response to palpation), as well as the position of the fetus. In the first position, the fetal back is turned to the left, in the second - to the right.
- At the third appointment, the obstetrician-gynecologist determines the presenting part of the fetus - this is the part of the fetus that faces the entrance to the pelvis and is the first to pass through the birth canal (usually the fetal head). The doctor stands on the right, facing the pregnant woman. With one hand (usually the right) palpation is carried out slightly above the symphysis pubis, so that the thumb is on one side, and the other four are on the other side of the lower part of the uterus. The head is palpated in the form of a dense round part with clear contours, the pelvic end is felt in the form of a voluminous softish part that does not have a round shape. When the fetus is in a transverse or oblique position, the presenting part is not determined.
- At the fourth appointment, palpation (feeling) of the uterus is carried out with both hands, while the doctor stands facing the pregnant woman’s feet. The palms of both hands are placed on the lower segment of the uterus on the right and left, with outstretched fingers carefully palpating the height of its standing and the presenting part of the fetus. This technique allows you to determine the location of the presenting part of the fetus relative to the entrance to the mother’s pelvis (the presenting part is above the entrance to the small pelvis, pressed against the entrance, descended into the pelvic cavity). If the head is present, the obstetrician determines its size, the density of its bones and its gradual descent into the pelvis during childbirth.
All techniques are carried out very carefully and carefully, since sudden movements can cause reflex tension in the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall and increase the tone of the uterus.
During an external obstetric examination, the doctor assesses the tone of the uterine muscles. Normally, the wall of the uterus should be soft; when the tone of the uterus increases, the wall of the uterus becomes hard. Increased tone (hypertonicity) of the uterus is one of the signs of a threatened miscarriage; it can occur at any stage, and the woman usually feels pain in the lower abdomen and lower back. The pain can be minor, nagging or very severe. The severity of the pain symptom depends on the threshold of pain sensitivity, duration and intensity of uterine hypertonicity. If the increased tone of the uterus occurs for a short time, then the pain or feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen is most often insignificant. With prolonged hypertonicity of the uterine muscles, the pain symptom is usually more pronounced.
Advertising
Reasons for increased uterine tone during pregnancy
The causes of uterine tone during pregnancy are varied, for example, changes in hormonal levels, in which there is a deficiency of progesterone or an increase in the concentration of testosterone. A disease or pathological process, somatic disorders and even stress can also be a provoking factor.
An increase in the contractile activity of the reproductive organ may be observed for the following reasons:
- Lack of progesterone
- Intense physical activity
- Stress
- Oncological diseases
- Hormonal disorders
- Acute infections
- Activation of chronic processes
- Alcohol abuse, smoking
- Genetic disorders in the fetus
- Micronutrient deficiency
- Large fetus, several fetuses in the uterus
- Large volume of amniotic fluid
- Increased blood clotting
The most important role of progesterone is to prepare the uterus for embryo implantation. Thanks to this, the mucous membrane thickens and expands, its blood supply becomes more intense, and nutrients accumulate. Progesterone also allows the uterus to gradually grow and limits its contractility, which allows pregnancy to proceed physiologically. But a reduced level of progesterone disrupts the natural course of pregnancy and can cause uterine hypertonicity.
Other factors:
- Psychological problems
- Long trips
- Flying an airplane
- Overweight
- Age over 35 years
- Violation of fetal position
- Intestinal motility disorder
- History of miscarriages
Separately, doctors note a diet that negatively affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, which often becomes the cause of hypertension. Doctors recommend excluding the following foods:
- Legumes, cabbage: provoke gas formation.
- Blue cheese: contains mushrooms that are dangerous for expectant mothers.
- Coffee: intensively removes fluid from the body, which can cause hypertension.
- Raw eggs: are a potential source of salmonellosis and cause disruption of the digestive tract.
Many experts argue that tone is very dangerous, and not as harmless as it seems. In fact, such a condition is not always dangerous; contractile activity may be present normally.
But with such clinical manifestations, you should consult a gynecologist to determine possible deviations, as well as decide on tactics to combat them. If you do not pay attention to hypertonicity and do not take timely measures, the long-awaited pregnancy may end in miscarriage or severe fetal hypoxia.
The tone of the uterus during pregnancy in the earliest stages almost always requires appropriate intervention. Because in the first trimester there is the greatest risk of sudden miscarriage. If moderate hypertonicity is present, the woman is recommended to take antispasmodics. In cases where increased tone is caused by hormonal disorders, products containing progestin are prescribed.
Increased uterine tone in the second trimester of pregnancy in most cases is part of the natural process of preparing the body for labor, but it can also be a sign of pathology.
If clinical signs of hypertonicity develop, you should inform your doctor. As a treatment, it is possible to prescribe B vitamins and special sets of exercises.
Norm indicators of cervical length during Cervicometry.
In our clinic in Pyatigorsk “Ultrasound 4D”, cervicometry is carried out by highly qualified specialists who master the research methodology at a high level. Specially trained employees will quickly and efficiently perform the cervicometry procedure, which will immediately identify abnormalities, if any, and make a final diagnosis.
The normal length of the cervix depends on what stage of pregnancy the patient is at:
- At 20 weeks of pregnancy the norm is 40 mm
- At 34 weeks – 34 mm
These indicators are considered the norm, but deviations from it are possible; a length of over 25 mm is considered normal. Such indicators are not considered a violation and do not indicate the presence of pathology in the body. For more accurate determinations, you need to resort to ultrasound and measurement of the cervix using cervicometry.
If the readings are lower, there is a risk of miscarriage. In such situations, measures are taken to prevent premature birth, and after stabilization of the condition, ultrasound cervicometry is performed every 2 weeks.
Diagnosis of hypertension and related diseases
There are several methods for diagnostic confirmation of the presence of hypertonicity. Ultrasound examination is considered the simplest and most accessible. Ultrasound allows you to assess the condition of the uterine muscles, determines possible pathological processes and directly indicates ongoing hypertonicity.
Another, more modern method of determining tone is tonusometry. The essence of the diagnostic method is that sensors are placed on the woman’s stomach, which send a signal to a special device that visualizes the presence of tone.
If hypertension is confirmed, the doctor prescribes a number of additional studies:
- General clinical analysis of blood and urine
- Determination of hormone levels in the blood
- Diagnostics of blood clotting
- Research for STDs
Uterine tone in the 3rd trimester
Uterine tone in the third trimester is difficult to distinguish from preparatory contractions. Therefore, when a typical clinical picture of tone develops, cardiotocography is prescribed. This is monitoring the fetal heart rate along with simultaneous recording of contractions of the reproductive organ. The examination is carried out as part of intensive prenatal care and allows us to identify early changes that threaten the life of the fetus.
The study is initially conducted as a stress test. It involves recording fetal heart function and uterine contractions for 30 minutes. The test can be extended up to 60 minutes.
How to relieve uterine tone, what to do if it increases
What to do and how to properly remove excess uterine tone during pregnancy? If the problem is of an unexpressed nature, you can try to relieve it without resorting to taking medications. If symptoms develop, light physical activity such as walking or swimming is recommended. You can also do the following exercise: tilt your head as low as possible, relax, take a few deep breaths and exhales. All this can be done only after consulting a gynecologist.
Doctors also recommend attending classes for pregnant women. Experts will show you what exercises can be used to reduce tone and how to help the body prepare for further childbirth. Even a slight tone does not cancel a visit to the gynecologist.
Signs of precancerous pathologies of the cervix
Cervical dysplasia, adenomatosis, and erythroplakia usually appear blurred. This is another reason why regular visits to the doctor are necessary, because the woman herself cannot see what is inside her and identify a dangerous disease in time. Common symptoms of precancerous cervical diseases are:
- atypia according to the results of oncocytology analysis;
- a change in the nature of the discharge, it may become too abundant and acquire an unpleasant odor;
- streaks of blood appear in the discharge, intermenstrual bleeding may occur;
- pain occurs during sexual intercourse;
- The nature of menstruation may change.
Treatment of benign and precancerous diseases of the cervix is not difficult, but it is important to identify them in time in order to neutralize the threat. If you have unusual symptoms related to gynecology, contact the Dr.AkNer clinic, they will definitely provide you with the help you need.